Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 Equipment
Uploaded by
ngtchungCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8 Equipment
Uploaded by
ngtchungCopyright:
Available Formats
COURSE
FACILITIES LAYOUT TRAINING
EQUIPMENT
FACILITIES LAYOUT TRAINING COURSE
EQUIPMENT MAIN TOPICS
Skids and Packages
Rotating equipment (Turbines, compressors, pumps)
Static equipment (Vessels, heat exchangers, tanks, etc)
Valves, flowmeters
Cranes
Portable/temporary equipment
Tools / sampling areas / maintenance withdrawal areas
Access / clearances
FACILITIES LAYOUT TRAINING COURSE
SKIDS & PACKAGES - GENERAL
Skids & Packages covers both rotating and static equipment
NORSOK R-001, Mechanical equipment use it informative but
be critical
SKIDS & PACKAGES GENERAL
PACKAGE INTERFACES - PIPING
Piping interfaces, some options to think about:
Open drain
Closed drain
LP Flare system
HP Flare system
Closed loop cooling medium system
Fuel gas system
Instrument air system
Hydraulic Power System
Firewater
4
SKIDS & PACKAGES GENERAL
PACKAGE INTERFACES - PIPING
SKIDS & PACKAGES GENERAL
PACKAGE INTERFACES NOZZLE LOADS
For secondary / utility connection interfaces as guideline:
NORSOK R-001, sec. 5.1 gives the following requirement, which
may be adopted (based on old M. W. Kellogg guideline):
Allowable nozzle loads only required when very sensitive rotating
equipment and when connected lines are subject to stress analysis
SKIDS & PACKAGES GENERAL
PACKAGE INTERFACES POWER & CONTROL
Interface junction boxes shall be provided at skid edge, as appropriate. The following
need separate junction boxes:
Control system (IS signals)
Control system (non-IS)
ESD system (IS)
ESD system (non-IS)
Data transmission (if applicable), modulating, pulse and frequency
LV normal Power (230 V, 400 V)
LV emergency power (including UPS power, if applicable)
Skids/units containing electric motors and/or heaters will need to be equipped with
a Local Push Button Control Station.
7
SKIDS & PACKAGES GENERAL
PACKAGE INTERFACES JUNCTION BOXES
The control and ESD signals must be further sub-divided into
separate junction boxes:
Analogue signals
Thermocouple and RTD signals
Digital inputs (switch signals for electronic equipment)
Digital outputs: Solenoid valves, lamps, relays, actuators, etc.
FACILITIES LAYOUT TRAINING COURSE
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
Gas turbines
API Gas Compressors
API Pumps
Also need for RPM control of major electric driven compressors
and packages addressed:
VFD (HV frequency control)
Permanent Magnet motors with variable speed
VSD (Variable hydrodynamic gear, Voith Vorecon or equal)
FACILITIES LAYOUT TRAINING COURSE
MAJOR EQUIPMENT - NEED FOR RPM CONTROL
HV frequency control (VFD) has no impact in the process area,
but the control unit in electrical equipment room is massive
Controller: Ca. 2 m3/MW ca. 1 ton/MW
PM Motor controller. Size and weight as the HV frequency control
but no gearbox required on the compressor or pump unit.
Hydrodynamic gear (Voith) has about same size as normal
mechanical gear is slightly larger - but require large oil unit and
large oil coolers)
HV VFD
Voith Vorecon
10
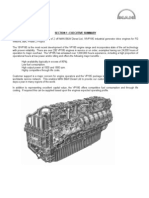
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS TURBINES
Gas turbines to API 616 (as appropriate)
Options / selections:
Steam
injection
Industrial
Single fuel
(gas or
diesel?)
Single shaft
Type?
Fuel?
Shafts?
Dual fuel (gas
and diesel)
Twin shaft
Water
injection
Yes
Dry (DLE)
Specify
Gas Turbine
AeroDerivative /
Modular
Low NOX?
(< 25 ppm)
No,
conventional
11
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS TURBINES
Gas turbines are always in acoustic enclosures
Electric / VFD
Hydraulic
Air or gas
Separate on
turbine
3-point
supported
Yes
Yes
Specified
AntiIcing?
Starter ?
Oil system
Skid
WHRU
No
Un Specified
Common with
driven
equipment
Directly on
Deck
No
12
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS TURBINES
Siemens SGT 200 (Ruston/ EGT Tornado) in acoustic enclosure
Typical from API 616
13
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS TURBINES MICRO TURBINES
Only for power generation.
Can be an option for emergency/UPS power generation
Or for remote unmanned installations w/o cable connection
Name
Sizes
Capstone
30 kW, 65 kW
Turbec
100 kW
Calnetix
100 kW, 125 kW
Capstone C30
Calnetix 125 kW
14
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
GAS TURBINE PACKAGES
Industrial gas turbines and driven equipment to have one
common lube oil system (preferably in machine frame)
Aero-derivative turbines must have their own lube oil system
(part of machine frame); driven equipment require external lube
oil console.
Turbine skid preferably on 3-point AVM support
Turbines in unclassified area:
Fuel gas supply: One flange per machine allowed in unclassified area
Combustion air & ventilation inlet air preferably from below cellar deck
(separate air intakes), but acceptable from above turbine when far
from classified area. Taken upwind if possible.
Turbines in classified area:
As above, but no requirements on fuel gas supply.
15
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
GAS TURBINE PACKAGES
Turbine exhaust in unclassified area as far from classified area as
possible
Mechanical handling equipment inside acoustic enclosure to be
part of turbine suppliers scope
Parts usually taken out of the side of the enclosure
16
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
GAS TURBINE PACKAGES
Example of mechanical handling facilities at gas
turbine (TWAD Dolly)
17
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
GAS TURBINE PACKAGES
Suitable lay-down areas provided close to the gas turbine for
components dismantled during maintenance.
Such components include sections of acoustic enclosure, casings,
ducting, covers, sections of exhaust diffuser, etc.
Floor must be rated to the maximum maintenance weights
Safe access to air filter (may be several levels on large turbine)
Permanent steps and platforms to be provided for easy and safe
access to turbine enclosure
18
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
GAS TURBINE PACKAGES
Turbine air intakes. Almost as low as possible for the two main
compressor turbines. Could have been lower.
Air intake for the smaller turbo generator on the side is not in
accordance with the book.
19
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
GAS TURBINE PACKAGES
Exhaust
Air intake
Turbo
compressors
After
coolers,
scrubbers,
gas chill.
How air intakes should not be
20
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API GAS COMPRESSORS - SELECTION
OPTIONS - ESPECIALLY
FOR CENTRIFUGAL
COMPRESSORS
API
COMPRESSORS
API 616 / ISO
10631 Gas
turbines
Positive
displacement types
Dynamic types
API 614 / ISO
10438
Lubrication &
shaft sealing
Rotary
compressors
Reciprocating
compressors
screw compressors
API 11P / ISO
13631,
Packaged
Reciprocating
Minor skid/container
mounted units "portable"
API 618 / ISO
13707
Reciprocating
API 619 / ISO
10441-1
Rotary
Major machines.
Permanent installed
machines
API 617 / ISO
10439
compressors
API 681
Liquid Ring
vacuum
pumps &
compressors
Centrifugal &
axial
compressors
Integral
geared
compressors
API 670
Machinery
Protection
Systems
Expander
compressors
(Special Not real API 617)
Dry
type
Oil
flooded
Motor
compressors
(sealless,
magnetic
bearings)
MAN Turbo HOFIM
Siemens Eco
GE ICL (Integrated Compressor Line)
API 671 / ISO
10441 Special
purpose
couplings
API 677
General
purpose
Gears
API 613 / ISO
13691
Special
purpose
Gears
21
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS COMPRESSORS - SELECTION
Source:
Shell DEP
22
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS COMPRESSORS MAIN REFERENCES
API 617, Centrifugal Compressors / Turbo expanders
API 618, Reciprocating Compressors
API 619, Rotary (screw) Compressors
API RP 686 Machinery Installation and Installation Design
And Shell DEPs in relation to the above
23
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS COMPRESSORS EXAMPLE. API 617 CENTRIFUGAL
Note the 3
point AVM
support
Centrifugal compressor (HP Compressor), a 7.6 MW electric driven
fixed speed compressor with 7 stages. Skid weight 78 tons,
compressor approx. 8 tons
This compressor operates at about 14000 RPM, and a turbo-gear is
included between the electric motor and the compressor.
24
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS COMPRESSORS
HP compressor on BE p/f.
LP / IP compressor on BE
p/f. Tandem compressor. (4
nozzles)
25
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
GAS COMPRESSORS BARREL TYPE CENTRIFUGAL
Usually centrifugal compressors for offshore application are barrel
type (rather than split casing).
Compressor barrel
Compressor bundle
26
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS ANTI-SURGE LOOP
Centrifugal compressors are equipped with anti-surge loop
27
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS MAIN SYSTEMS
Lube oil system (sometimes a separate skid for larger machines)
Dry gas seal system most often separate skid
Often also a nitrogen generator is required for seal system
Dry gas seal system
for centrifugal
compressor
28
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS NOZZLE LOADS / ORIENTATION
BP wishes nozzles downwards but often this is not possible
Compressor nozzles are either:
ANSI flanges (RF/RTJ as per the piping spec)
Integral type
Hub type (Graylok, G-Lok, Techlok or equal)
Nozzle loads are given in API 617, Annex 2E. It refers to NEMA
SM 23.
29
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS NOZZLE LOADS / ORIENTATION
NOZZLE LOADS:
Nozzle loads API 586/API 617 require minimum 1.85 x NEMA
SM 23
It is strongly recommended to limit the nozzle loads, although
piping designers often ask for 4 x SM 23 or 6 x SM 23.
In some Maersk projects we agreed on 3 x SM 23 nozzle loads
(NORSOK R-001: 4 x NEMA SM 23. No good idea.......)
Large design nozzle loads require heavy/stiff skid frames and
heavy holding down bolting and machinery alignment is a
problem.
30
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS NOZZLE LOADS
Highest stress in flex legs
Relative rotation of compressor
axis
Highest risk for misalignment of
compressor is resultant moment
around vertical axis
FEA calculation results of a SCT-SV
compressor with flex legs
31
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS INTEGRAL MOTOR COMPRESSORS
These compressors are not to API 617
No gearbox, no lube oil system, no seal system,
Magnetic bearings, PM variable speed motor
GE Oil & Gas, ICL model
MAN Turbo, HOFIM &
MOPICO
32
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
Reference documents:
API 586, Machinery Installation and Installation Design
NORSOK L-002, Piping System layout, design and structural analysis
Shell DEP, BP standard
33
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
Located on one of the highest decks.
Suction drum on lower level, with compressor inlet piping sloping
down towards the suction drum
Anti-surge lines with slope and anti-surge valve on highest point
Preferably 3-point supported to deck
Access at sides of skid: 2 3 meter free space (minimum)
When more compressor casings on same skid, typically electric
motor/turbine must be removed before the compressor 2 bundle
can be taken out.
34
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
It must be possible to take out motor, gear, or complete
compressor (mechanical handling), but typically not the skid
Bundle removal maintenance area (about 1,5 times length of
compressor barrel)
35
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
Compressor mechanical handling gantry crane is a possibility.
Access by platform crane also possibility (prefered). Removable
hatches if located below main deck.
Bundle stored/transported in nitrogen filled container / canister
(typically vertical transport / storage)
36
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
If separate lube oil skid, it can be shared with other compressor
skids, but it must be located in the vicinity
Seal gas unit either directly on the compressor skid or as separate
skid located nearby (MOTS-06 require on-skid seal gas unit)
Start-up inlet strainer must be installed in inlet piping as near to
the compressor as possible
Inlet piping, Minimum 3 5 dia straight run (measured on
compressor flange nominal diameter)
Non-slam check valve(s) on compressor discharge piping after
branch for anti-surge loop.
Note flow direction on
start-up strainer
37
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
Compressor discharge line routed to cooler with no pockets
Limit volume of gas between discharge nozzle, anti-surge valve
and discharge check valve(s)
Instruments in relation to anti-surge loop located with tapping
points as near to the compressor as possible.
Horizontal run of inlet piping preferably parallel with the
compressor shaft
38
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
Compressor piping arrangement described in next slide
39
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
CENTRIFUGAL GAS COMPRESSORS
P&ID example from the notes:
Compressor inlet piping sloping back towards suction drum
Min 10 dia pipe run before flow orifice (FIT), 5 dia after
Inlet side, PV (inlet throtling) minimum distance from compressor
suction nozzle. PV to have mechanical minimum stop.
Suction strainer, minimum distance from compressor suction
Two non-slam check valves located as near to compressor
discharge as possible (required if upstream suction drum cannot
sustain the SOP (settle-out-pressure) for a larger volume of
discharge piping). Ref. NORSOK P-100
2 check valves in series will reduce design backflow rate (10% of
nominal ID of largest check valve). Ref. API 521, 4.3.4.4.
40
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 618 RECIPROCATING GAS COMPRESSORS
Should preferably not be used offshore due to vibrations
Ariel recip
Nuevo Pignone recip
41
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 619 SCREW COMPRESSORS
On some offshore installations used as LP gas compressors
In Europe also used as compressors in zero flare systems
Further: Booster compressors for gas turbine fuel gas
Two main types: Oil flooded & dry type
The oil flooded type has many auxiliaries, oil tank, oil
pump, oil cooler, etc.
42
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 619 SCREW COMPRESSORS
Dry screw
compressors
with timing
gear.
MAN Turbo
Oil flooded screw
compressor.
Kobelco
43
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 619 SCREW COMPRESSORS
Oil system for oil flooded
screw compressor
figure from API 619
44
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 619 SCREW COMPRESSORS
Allowable nozzle loads:
API 619, Annex C (tables over loads)
45
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API PUMPS - SELECTION
API PUMPS
Positive
displacement
Pumps
Rotary
pumps
Plunger/piston
pumps
API 674 / ISO
13710,
Reciprocating
Larger high pressure
duplex, triplex,
quantoplex pumps
Dynamic pumps
API 675,
Controlled
Volume
Smaller, chemical
injection/
dosing pumps. Exact
dosing. Might be
a.diaphragm pump
head.
API 676/
Rotary
Gear-, lobe-,
twin/tripple screwProgressing cavity pump (excentric
worm)
Centrifugal
Pumps
API 610 / ISO
13709,
Centrifugal Pumps
All types of centrifugal
pumps, typical with mech.
seal - see separate API 610
overview
API 685,
Sealless
Centrifugal Pumps
Magnet-coupled /
Canned typer
API 682 / ISO
21049,
Shaft sealing systems
Shell DEP 31.29.02.11 gives recommendations in
text regarding selection between the types
46
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API PUMPS - SELECTION
From Campbell course material
47
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - SELECTION
48
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS SELECTION / CLASSIFICATION
Source:
API 610
49
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API PUMPS - SELECTION
Source:
Ramboll ITA
50
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
PUMPS POWER REQUIREMENT
Ptheory Q.H . .g
Power, Ptheory is in W,
For water:
Ptheory = 0,028.Q. P
flow Q is in m3/sec,
[Q] = m3/hour,
height (height difference) H is in meter
WG,
[P] = bar (differential
pressure over the pump)
density of the liquid in kg/m3,
gravity constant, g, is in m/sec2.
Actual power requirement: Assume hydraulic efficiency of 50 %,
for special designed pumps, multistage WI pumps, etc., assume
efficiency of 60 65 %
51
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
PUMPS NPSH NET POSITIVE SUCTION HEAD
NPSHA: NPSH available
NPSHR: NPSH required (the pumps minimum required NPSH)
NPSHA > NPSHR
Ha:
The absolute pressure at the liquid surface in the suction tank [meter
liquid column] , in an open tank this number is the atmospheric pressure
in meter WG, in a closed multiphase separator operating at vapour
pressure, Ha is zero
Hb:
Height difference in meter liquid column, from the liquid surface in the
tank to the pump inlet (can be negative it is positive for pumps under
the tank and it is negative for pumps above the tank)
Hf:
Friction loss in the suction line
Hvp:
Vapour pressure of the liquid at pumping temperature(*)
Hv:
Velocity height on the suction side (meter liquid)
(*) A 3-phase separator operates at the vapour pressure in the separator.
Tank and pump definition of the terms
for calculating NPSHA
NPSHA = Ha + Hb Hf - Hvp - Hv
52
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
PUMPS NPSH NET POSITIVE SUCTION HEAD
NPSHR is for many industrial pumps
in the range of 2,0 and 2,5 meter but
may with increased flow reach 8 to
10 meters or even more.
POSITIVE NPSH!
To the right: HA is positive
(pump below liquid level), to
the left HA is negative
(pump over the liquid level)
however, NPSHA is still
positive, otherwise the
pumping will not work
The above also indicates that the
calculated NPSHA shall always be
positive, and preferably larger than
+2.5 m.
Otherwise the layout (location of pump
in relation to the tank/vessel) most
probably will need to be changed until
the calculated NPSHA becomes
positive.
53
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
PUMPS NPSH NET POSITIVE SUCTION HEAD
P
Ha
g
HVP
P
VP
g
V2
HV
2 g
P PVP
V2
( NPSH ) A
Hb
F
.g
2.g
54
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
PUMPS NPSH NET POSITIVE SUCTION HEAD
NPSHR for study/estimation purposes (source: Brennan):
n(Q)0.5 / (NPSHR)3/4 = C,
where
Speed, RPM
Capacity, GPM
Constant between 7000 and 10000
55
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
PUMPS NPSH NET POSITIVE SUCTION HEAD
NPSHR for study/estimation purposes (Source: Brennan)
C = 9000
For large required NPSHR, booster pump may be required
56
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - TYPES
57
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - TYPES
58
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - TYPES
59
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - TYPES
60
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - TYPES
61
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - TYPES
62
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS - TYPES
Vertical pumps are prefered
where low NPSHA
63
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS EXAMPLES OH6 PUMP
Sundyne LMV vertical
high speed with
integral gear. (OH6
pump)
Sundyne selection chart
64
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS EXAMPLES OH2 PUMP
SPX OH2 single stage centrifugal pump
65
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS EXAMPLES BB5 PUMP
Also for these large pumps,
3-point AVM installation is
recommended
Sulzer HPcp injection pump skid. Due to large
nozzle loads on the pump, the skid frame needs
to be very strong and heavy to avoid distortions
and deformations. Note the electric motor, gear
and the pump itself to the right
66
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS EXAMPLES BB5 PUMP
67
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS EXAMPLES BB5 PUMP
Sulzer HPcp with
twistlock allowing fast
change out of cartridge
68
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS EXAMPLES BB5 PUMP
The cartridge being drawn out of a Weir AHBP multistage pump.
The frame with beams and legs is erected only for drawing out the
cartridge and inserting a new one. Sulzers system is similar.
69
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 610 PUMPS EXAMPLES BB5 PUMP
Stripped WI pump skid showing the withdrawal area and
withdrawal support structure in place
70
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 674 RECIPROCATING PUMPS
Mainly used for
NGL Injection pumping
Power frame
end
Pipeline pressure testing
Well service purposes
Liquid end
David Brown triplex PD pump, 27
m3/hour, 690 barg. (API 674 equal
execution) power frame type
71
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 675 CONTROLLED VOLUME PUMPS
Mainly used for
Chemical dosing / injection
1 Lewa dosing pumps. Each
pump head on a common drive
has a crank with adjustable
stroke. See adjustment handles
on top of the pumps.
Low flow, high
pressure, accurate
Milton Roy chemical injection pump
72
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 675 CONTROLLED VOLUME PUMPS
Methanol injection
skid with 3 pumps
Danfoss axial piston pump
73
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
API 676 PUMPS MULTIPHASE TWIN SCREW
Bornemann twin screw multiphase pump
74
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
SEAWATER LIFT PUMPS & RISER PIPES
Electric
submersible
pumps
Riser pipes. Each
typically 3 m long
It is required with sufficient
head room above the pump
caison, to allow the riser
pipes and pump(s) to be
drawn up
75
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
SEAWATER LIFT PUMPS & RISER PIPES
76
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
SEAWATER LIFT PUMPS & RISER PIPES
Lift pump with the riser pipe
sections test assemblied in the
workshop (Sulzer Pumps)
77
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
FIRE PUMPS
Angle gear and long
shaft submersible
pump
Diesel hydraulic or diesel electric
driven submersible pump
78
TURBINES, COMPRESSORS & PUMPS
FIRE PUMPS
Framo diesel-hydraulic unit with
booster pump in engine
container
Framo diesel-electric unit
without booster pump
79
MAINTENANCE WITHDRAWAL AREAS
SUBMERGED PUMPS
On cellar deck, sufficient head room (4 meter ca)
Traverse crane located above pump riser pipes
Space for laydown of riser pipes (4m x 3 m) ca
Space for laydown of pump itself (1 m x 4 m) ca.
Deck designed for the loads
80
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PUMPS - GENERALLY
Consider 3-point AVM mounting for pumps > 200 kW
Ensure sufficient NPSH at all conditions
Typically low speed pumps = low NPSHR
Suction line one size larger than the suction nozzle, no pockets
Excentric reducer at the suction, flat top of reducer
Preferable 5 - 10 x Dia straight run suction pipe
81
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PUMPS SUCTION LINE SLOPE (API RP 686)
If suction source higher than pump, slope towards pump
If suction source lower than pump, slope towards source
82
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PUMPS NPSH EVALUATION
MOTS-06
Volatile liquids: Min margin between NPSH(A/R): 2 m liquid
Non flamable liquids: Min margin NPSH(A/R): 1 m liquid
Evaluate NPSHA from layout:
Evaluate NPSHR from Brannan curves, earlier slide this section)
83
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PUMPS PUMP DISCHARGE
Must be provided with check valve to avoid backflow
For pumps > 180 kW consider non-slam check valve
Valves in pump discharge located as close to the pump as
possible
84
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PUMPS NOZZLE LOADS
Centrifugal pumps: API 610, table 5
Metering pumps: API 675 has no nozzle load requirements
85
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PUMPS INSTALLATION/ACCESS
All pumps: Easy access to mechanical seal for service
Smaller pumps: Piping must allow easy removal of complete pump
Mechanical handling for removing complete pump, gear and motor
as individual items (not the skid)
86
FACILITIES LAYOUT TRAINING COURSE
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
Fixed static equipment
Pressure vessels (separators, drums, etc)
Pig launcher / receivers
Heat exchangers (main types + S&T TEMA types)
Atmospheric tanks
Offshore pedestal cranes
Wellhead control panel
Life boats, MOB boat life rafts, other life saving appliances
Portable equipment
Containers, skips, temporary service equipment, etc.
87
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Pressure vessels (separators, drums, columns)
Pressure design to PD 5500, EN 13445 or ASME VIII
CE-marking to PED (where applicable, i.e. EU/EEA)
88
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT - VESSELS
Vessels are typically
Skirt supported or
Saddle supported
Minimum distance
between weld and
nozzle
89
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT - VESSELS
Large vessels (diameter > 1500 mm), must have manway for
inspection
Min. 24 manhole
Manway with davit
manway must be easy
accessible
Nozzle standouts at least so
bolting is
possible. Extra
long stand-out
when vessel is
insulated
Name plate for
pressure vessel
90
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT - VESSELS
All pressure vessels are designed for allowable nozzle loads
Design loads (example).
EXTERNAL FORCES AND MOMENTS ON NOZZLES
For pressure vessels, tanks, pig launchers/recivers and shell & tube exchangers.
Global forces (N)
Global moments (Nm)
Pipe
PIPE
Longitud.
C ircum
Axial
Resultant
Longitud.
C ircum
Torsional
Sch.
SIZE
Fl
Fc
Fa
Fr
Ml
Mc
Mt
Resultant
Mr
150# & 300#
1962
1472
1962
2452
255
196
294
322
b-value
2943
2207
2943
3678
574
441
662
724
0,50
3924
2943
3924
4904
1020
784
1176
1286
5886
4415
5886
7357
2295
1764
2646
2894
7848
5886
7848
9809
4080
3136
4704
5146
10
9810
7358
9810
12261
6375
4900
7350
8040
12
11772
8829
11772
14713
9180
7056
10584
11578
14
13734
10301
13734
17165
12495
9604
14406
15758
16
15696
11772
15696
19618
16320
12544
18816
20582
18
17658
13244
17658
22070
20655
15876
23814
26050
20
19620
14715
19620
24522
25500
19600
29400
32160
24
23544
17658
23544
29426
36720
28224
42336
46310
91
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PRESSURE VESSELS
Separators and vessels otherwise with large liquid hydrocarbon
inventories. Locate on lower decks (as low as possible).
Flare drum, closed drain drum. Locate on cellar deck or sub-cellar
deck (air gap)
Check valves installed directly on block valves if possible
To reduce risk of overstressing vessel nozzles, pipe size should be
equal to or less than vessel nozzle
Nozzle
stand-out
92
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PRESSURE VESSELS
Manway davits so oriented that cover opens away from ladders /
stairs and instrument access
Working platform on top of vessel (operation of valves, etc.)
All instruments, stand pipes etc. Located on one side of vessel.
Unobstructed access of 3 m from one side, other side normal for
walkway (1 m) or escape way (1.2 m)
No equipment installed over pressure vessels unless there is a
tight deck in between
93
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PRESSURE VESSELS VERTICAL VESSELS
Previous slide also applies here
More manways may be required along height
Can access to manways be from deck or is access platforms
required?
Possibility to take loose ladder into vessel for inspection purposes?
Needs for access to trays inside vessel?
Need for fixed ladder inside vessel?
94
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Pig Launcher / receivers
Pressure design to PD 5500, EN 13445
or ASME VIII
CE-marking to PED (EU/EEA only)
Receiver - horizontal
Launcher - vertical
95
LAYOUT OF FACILITY - SPECIFIC AREAS
PIG TRAPS GENERAL DESIGN RULES
Designed as pressure vessel
Equipped with quick opening device (Scholz or equal)
Equipped with pressure-interlock to ensure against opening a
pressurised trap
Pressure indicator located so it is visible for the operator
Face outwards away from:
HC equipment
Laydown / Handling areas & travel routes
96
LAYOUT OF FACILITY - SPECIFIC AREAS
SPACE REQUIREMENTS PIG LAUNCHER / RECEIVERS
Recommendation from Shell DEP
97
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PIG TRAPS DIMENSIONS
98
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PIG TRAPS - ARRANGEMENT
Min 0.76 m headroom above deck (drainage, inspection)
Pig traps opening face to outbound
Horizontal traps sloped towards the trap closure
Retention tray directly underneath the end closure
Storage area for pigs
Cradle for inserting pigs in horizontal launcher
Mechanical handling facilities (crane, etc.)
99
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
PIG TRAPS - ARRANGEMENT
Wet Gas Receiver Crude Oil Receiver
Gas Slug catcher
Test separator
100
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Hydro cyclone
Pressure design to PD 5500, EN 13445 or ASME VIII
CE-marking to PED (where applicable, i.e. EU/EEA)
Contains liners / dummies
Ca. 1000 g acc.
101
MAINTENANCE WITHDRAWAL AREAS
HYDRO CYCLONE
Free space required in front to
change liners.
A liner is almost as long as the
hydro cyclone (1 meter ca.)
102
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Heat exchangers Plate heat exchanger
103
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Shell & Tube heat exchangers
Pressure design to PD 5500, EN
13445 or ASME VIII.
CE-marked to PED (EU/EEA)
Thermal design: TEMA R
104
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
TEMA TYPES OF S&T HEAT EXCHANGERS
An exchanger
may for
example be
type AES
105
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
TEMA TYPES OF S&T HEAT EXCHANGERS
106
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Shell & Tube heat exchangers
Stacked S&T heat exchangers
Vertical exchangers shell with
expansion joint.
107
MAINTENANCE WITHDRAWAL AREAS
HEAT EXCHANGERS
Complete plate pack need to be taken out at a
time.
Look at the actual
type to see if
withdrawal area is to
the left or right
108
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
PCHE Printed Circuit Heat Exchangers (Heatric)
PCHE on BE platform
109
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT AIR COOLERS
Air coolers (for process cooling, API 661 / ISO 13706)
Two horizontal types:
Forced draft (as shown, fan under)
Induced draft (fan over)
Left: Vertical air cooler (non-API)
for example for engine cooling
110
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT AIR COOLERS
Air coolers (for process cooling, API 661 / ISO 13706)
111
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Box shaped & vertical atmospheric tank:
Design: Eurocode 3 (EN 1993-4-2)
Design loads: Eurocode 1 (EN 1991-4)
Other options:
a) Crane pedestal as
diesel storage tank
b) Space between main
deck beams as
potable water tank
API 620 and 650 are
not applicable as
they are for large,
vertical storage
tanks as seen
onshore in refineries
& storage plants
112
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
Horizontal atmospheric tank:
EN 12285-2, Workshop fabricated steel tanks. Horizontal
cylindrical single skin and double skin tanks for the aboveground
storage of flammable and non-flammable water polluting liquids.
CE Marking to CPD/CPR
Standard has tables of standard
designs: Length, diameter and
shell thickness, i.e. no
calculations are required
113
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
STORAGE TANKS
Keep storage tanks for water, diesel etc. in unclassified (service /
utility) area - prefered
Storage tanks for methanol and process chemicals in classified
(process) area
Potable water tank may be embedded in deck structure
Diesel tank may be embedded in deck structure or crane pedestal
Otherwise, most recommendations for pressure vessels applies
114
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
ATMOSPHERIC TANK EXPANSION TANK
Tank is open in
the top!
115
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
BREAK-OUT SPOOLS
Break-out spools are required where equipment may need to be
taken out for maintenance / inspection when not sufficient pipe
flexibility
Often designed as an angle or as a U-spool
116
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
VALVES - ORIENTATION
Check valves horizontal with hinge vertical
Or vertical with flow upwards
If different specify to vendor when ordering valve
117
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
VALVES - ORIENTATION
Larger (12 and bigger), with stem horizontal
118
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
VALVES - ORIENTATION
Smaller gate valves installed horizontally: Tilt 45if possible
119
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
VALVES - ORIENTATION
Plug valves, standard is horizontal orientation with gear or handle
on top
If installed differently specify to vendor when ordering valve
120
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
VALVES - ORIENTATION
Actuated ball valves installed horizontally
If installed differently specify to vendor when ordering valve
121
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
VALVES - ORIENTATION
Valve wheel has a diameter up to 700 mm
Gear can be turned 180around the shaft/stem
122
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
FLOWMETER STRAIGHT PIPE LENGTH
Usually 10 x straight dia (NB) piperun upstream flowmeter
Usually 5 x straight dia (NB) piperun downstream flowmeter
But may vary and for fiscal / custody transfer often stronger
requirements
123
SPECIFIC LAYOUT REQUIREMENTS FOR EQUIPMENT
ORIFICE METER STRAIGHT PIPE LENGTH
124
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
OFFSHORE PEDESTAL CRANES
API 2C, Specification for Offshore Pedestal Mounted Cranes
EN 13852-1, Offshore Cranes, General Purpose Offshore Cranes
Wire luffing with whip
hoist
Telescopic ram type
Ram luffing
Right:
Knockle
boom type
125
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
WELLHEAD CONTROL PANEL
126
FIXED STATIC EQUIPMENT
LIFE BOATS, LIFE RAFTS, MOB BOAT
127
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
Rented power generation units (temporary)
Hook-up support containers (workshop, storage, etc)
Painting container (epoxy work container)
Scaffold containers / skips
Rigger container
Transport containers (20 feet standard) equipment, spares,
consumables
Food Containers (10 feet, 14 feet)
Compactor for accommodation paper waste
Food waste skips
128
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
Waste skips / production area
Helifuel tanks (tote tanks)
Chemical tanks (tote tanks)
Nitrogen bottle racks
Personnel basket / "Billy Pugh
MOB Boat / FRB
Nitrogen spread (initial start-up purge/leak test + start up after
major shutdowns), i.e. liquid nitrogen, pumps, evaporators, etc.
Well service equipment sets (wireline, coiled tubing)
129
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
Offshore containers are
PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
certified to DNV 2-7.1
20 ft closed
offshore container
40 ft cargo basket
Tote tanks
10 ft half height
basket (open)
Waste compactor
Waste skip
130
MAJOR STATIC AND PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
PORTABLE EQUIPMENT
Nitrogen spread
Aggreko 20 ft
temporary diesel gen
Nitrogen
bottle rack
Typical coiled tubing set
also contains control
container, tanks, pumps,
etc.
Coiled tubing reel & goose
neck
131
MAINTENANCE WITHDRAWAL AREAS
TOOLS
Cosasco corrosion fittings retrieval tool
Well service, VR tool (Cylinder, 15 x 110 from well center line)
In addition: Access for production sampling (cylinders)
132
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
GENERAL
ISO 14122-2, Permanent means of access to machinery, Part 2:
Working platforms and Walkways
Guidelines from NORSOK S-002, Table B.1, Vertical and Horizontal
Clearances and distances.
Guidelines from NORSOK L-002, Table 1
ASTM F1166, Standard Practice for Human Engineering.
See next slides
133
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
GENERAL
134
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
GENERAL
135
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
ACCESS TO INSTRUMENTS/VALVES
136
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
VALVES - INSTALLATION
137
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
ROG ITA Offshore Facility Layout
VALVES - INSTALLATION
138
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
VALVES - INSTALLATION
ROG ITA Offshore Facility Layout (ref. ASTM F1166)
Operation from one
side only
139
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
VALVES INSTALLATION RISER ESDV
Statoil require riser ESDVs to be in
horizontal lines.
Top entry riser ESDV to be placed
horizontally
140
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
MAJOR EQUIPMENT DISTANCE BETWEEN
Minimum distance between major equipment (gas turbines,
centrifugal compressors, major pumps) is mainly given by the
requirement to be able to transport the largest component away.
Mechanical handling study will verify if it is possible.
For the conceptual layout, consider largest part (electric motor,
gearbox, power turbine of a gas turbine).
Depending on the actual machine size, it will typically result in a
minimum spacing of 2 3 meter (with free transport way)
141
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
HOW NOT TO DO
142
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
HOW NOT TO DO
143
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
HOW NOT TO DO
144
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
HOW NOT TO DO
145
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
HOW NOT TO DO
146
ACCESS / CLEARANCE REQUIREMENTS
HOW NOT TO DO
147
THANK YOU
148
You might also like
- Claas Celtis Diagnostic ManualDocument887 pagesClaas Celtis Diagnostic ManualMichal PolakNo ratings yet
- Komatsu d61px 15e0 Parts BookDocument20 pagesKomatsu d61px 15e0 Parts Bookpatricia100% (35)
- Turbo ExpanderDocument105 pagesTurbo Expandermartinandrei100% (11)
- End-Suction Fire Pumpset Diesel Engine Driven: LBSD SeriesDocument6 pagesEnd-Suction Fire Pumpset Diesel Engine Driven: LBSD SeriesMuhammad MustafaNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas ProcessingDocument104 pagesNatural Gas ProcessingSrinivas BobbyNo ratings yet
- CE Marking On FPSO - Rev1Document38 pagesCE Marking On FPSO - Rev1Felix Diaz100% (1)
- tp6255 Generator Sets Service Manual PDFDocument116 pagestp6255 Generator Sets Service Manual PDFAnonymous M0OEZEKoGi100% (1)
- Copeland General Product Guide 2019 PDFDocument318 pagesCopeland General Product Guide 2019 PDFMohamad FazliNo ratings yet
- Atkins Human Factor Oil and GasDocument12 pagesAtkins Human Factor Oil and GasEyoma EtimNo ratings yet
- NORSOK L-002 Edition 3, July 2009 PDFDocument36 pagesNORSOK L-002 Edition 3, July 2009 PDFKarthick VenkatswamyNo ratings yet
- Y2 PumpsDocument70 pagesY2 Pumpsfacebookshop100% (1)
- Unit 3 Module 3Document6 pagesUnit 3 Module 3ngtchungNo ratings yet
- 5 Offshore Work OperationsDocument6 pages5 Offshore Work OperationsngtchungNo ratings yet
- Project Standards and Specifications Piping Insulation Design Rev01Document10 pagesProject Standards and Specifications Piping Insulation Design Rev01hiyeonNo ratings yet
- ICE Civil Engineering ProceedingsDocument52 pagesICE Civil Engineering ProceedingsYasela100% (1)
- Process Piping Design & Construction As Per ASME B 31.3 PDFDocument12 pagesProcess Piping Design & Construction As Per ASME B 31.3 PDFDRASTINo ratings yet
- Stative VerbsDocument3 pagesStative Verbsngtchung0% (1)
- PneumaticsDocument193 pagesPneumaticsvarungoldy100% (6)
- Paxman SpecsDocument9 pagesPaxman Specsbastech100% (2)
- Compressor and Sealing SystemDocument40 pagesCompressor and Sealing Systemprabhjotbhangal67% (3)
- Packing ProcedureDocument67 pagesPacking ProcedurengtchungNo ratings yet
- Engineering Reference DocumentDocument50 pagesEngineering Reference DocumentjeddijNo ratings yet
- Rootcause of Piping FailurDocument14 pagesRootcause of Piping FailurDanan WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Under Insulation Problems and Solutions PDFDocument29 pagesCorrosion Under Insulation Problems and Solutions PDFniqutomo100% (1)
- HAZARDOUS AREA CLASSIFICATION - UpdatedDocument132 pagesHAZARDOUS AREA CLASSIFICATION - Updatedabdelrahman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Certificate Course On Piping EnggDocument453 pagesCertificate Course On Piping EnggVignesh DheenakumarNo ratings yet
- Valves and InstrumentsDocument296 pagesValves and InstrumentsRommel Heredia TejadaNo ratings yet
- 1-Piping Manual-Pdms12Document413 pages1-Piping Manual-Pdms12MOHSEN2005IBNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design Engineer Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanical Design Engineer Interview QuestionssuseevNo ratings yet
- Turbo Machines Lab: Centrifugal and Reciprocating CompressorsDocument38 pagesTurbo Machines Lab: Centrifugal and Reciprocating CompressorsUpendra SravanNo ratings yet
- API Rp-571 - GuideDocument33 pagesAPI Rp-571 - Guidengtchung100% (1)
- Gas Turbine FundamentalsDocument30 pagesGas Turbine Fundamentalsnaga_raj_19No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction GeneralDocument45 pages1 Introduction GeneralngtchungNo ratings yet
- PSV FarrisDocument20 pagesPSV FarrisIkhsan Arif100% (1)
- Zulser PumpsDocument56 pagesZulser PumpsManuel CarreñoNo ratings yet
- TR Diss 6736 PDFDocument166 pagesTR Diss 6736 PDFmohammed ramzi CHAHBINo ratings yet
- Flexible Pipe Technology For Deepwater and Gas Riser SystemsDocument22 pagesFlexible Pipe Technology For Deepwater and Gas Riser SystemssiswoutNo ratings yet
- PG Diploma in Piping Design and Autocad Training CourseDocument4 pagesPG Diploma in Piping Design and Autocad Training CourseWin LinnNo ratings yet
- SIHI HandbookDocument391 pagesSIHI HandbookFuchsbau100% (4)
- Checklist Inspeccion de TaladrosDocument4 pagesChecklist Inspeccion de TaladrosAdolfo AnguloNo ratings yet
- Material For HEDocument36 pagesMaterial For HEMohd Idris MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.module 2Document6 pagesUnit 3.module 2ngtchung100% (1)
- Heater Inspection PlanDocument2 pagesHeater Inspection Plancamasa2011No ratings yet
- PMP50 Using This ManualDocument5 pagesPMP50 Using This Manualsalic2013No ratings yet
- Ethanol Production PidDocument18 pagesEthanol Production PidCyduck GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Pump Sealing Systems Scott 060712 PDFDocument50 pagesPump Sealing Systems Scott 060712 PDFmishraenggNo ratings yet
- Donalson GDX BrochureDocument4 pagesDonalson GDX Brochuretoon_naNo ratings yet
- Caliper Presentation Pig LauncherDocument34 pagesCaliper Presentation Pig LauncherMix VichaitanapatNo ratings yet
- Valve Interlock - Smith Flow COntrolDocument40 pagesValve Interlock - Smith Flow COntrolteacg100% (3)
- Statoil Technology LNG PDFDocument15 pagesStatoil Technology LNG PDFmctimlimNo ratings yet
- Baltimore Gas & Electric Co. v. NRDC, 462 U.S. 87 (1983)Document24 pagesBaltimore Gas & Electric Co. v. NRDC, 462 U.S. 87 (1983)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument27 pagesSteam Turbinecram1960100% (1)
- Powell Valve HandbookDocument29 pagesPowell Valve Handbookddoyle1351100% (11)
- DEW Equivalent Products TableDocument1 pageDEW Equivalent Products TableednsmnNo ratings yet
- 7 Safety SystemsDocument61 pages7 Safety SystemsngtchungNo ratings yet
- Cp01195den 0117.Document124 pagesCp01195den 0117.Shijumon KpNo ratings yet
- HydrocrackerDocument18 pagesHydrocrackerBhavin RanaNo ratings yet
- Mokveld Brochure Angle Choke ValveDocument16 pagesMokveld Brochure Angle Choke ValvekglorstadNo ratings yet
- 12 - OLGA UGM Curtin PresentationDocument40 pages12 - OLGA UGM Curtin PresentationGui Do Esp100% (1)
- Valves PresDocument287 pagesValves PresEnas Al-khawaldehNo ratings yet
- Valtek Noise Control PDFDocument32 pagesValtek Noise Control PDFSandeep Kumar Krishnaraj100% (1)
- Parker Industrial Hose Catalog 4800Document258 pagesParker Industrial Hose Catalog 4800MROstop.comNo ratings yet
- To Rerate or Not To RerateDocument6 pagesTo Rerate or Not To ReratekblaxtonNo ratings yet
- 01-SAMSS-017 PDF Download - Auxiliary Piping For Mechanical EquipmentDocument4 pages01-SAMSS-017 PDF Download - Auxiliary Piping For Mechanical EquipmentZahidRafiqueNo ratings yet
- Specification For Firewater Pump Package S 721v2020 08Document90 pagesSpecification For Firewater Pump Package S 721v2020 08Serge RINAUDONo ratings yet
- DNV-OS-J102 (Draft October 2004) Design and Manufacturing of Wind Turbine Blades (Offshore)Document54 pagesDNV-OS-J102 (Draft October 2004) Design and Manufacturing of Wind Turbine Blades (Offshore)mpk8588No ratings yet
- Eriks Sealing Elements Precision O-Ring Technical Manual PDFDocument221 pagesEriks Sealing Elements Precision O-Ring Technical Manual PDFCarlos Eduardo Flores TorresNo ratings yet
- Technical Design Guide PDFDocument28 pagesTechnical Design Guide PDFPrabhu MohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document113 pagesChapter 1Charlene KronstedtNo ratings yet
- Pre Insulated Piping Sytem HDPEDocument15 pagesPre Insulated Piping Sytem HDPEVincent SablanNo ratings yet
- Seamless Stainless Tubes For Hydraulic and Instrumentation SystemsDocument10 pagesSeamless Stainless Tubes For Hydraulic and Instrumentation Systemsfezzeh kabiri kenariNo ratings yet
- Centaur 40 Gas Turbine Compressor SetDocument2 pagesCentaur 40 Gas Turbine Compressor SetRommy RomanzaNo ratings yet
- 0Document170 pages0Patricia J ÁngelesNo ratings yet
- Solar Turbines Taurus 65 Data SheetDocument2 pagesSolar Turbines Taurus 65 Data SheetLuis SanguinettiNo ratings yet
- Ruud UMPC Series ManualDocument8 pagesRuud UMPC Series ManualisothermNo ratings yet
- Centaur 40: Gas Turbine Generator SetDocument2 pagesCentaur 40: Gas Turbine Generator Setaemis2010No ratings yet
- Repaired But Still Remain Defect Not Yet RepairDocument4 pagesRepaired But Still Remain Defect Not Yet RepairngtchungNo ratings yet
- PTSC M&C: Resources DepartmentDocument2 pagesPTSC M&C: Resources DepartmentngtchungNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument7 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationngtchungNo ratings yet
- Love TestDocument4 pagesLove TestngtchungNo ratings yet
- Visa Application Form To Enter-JapanDocument1 pageVisa Application Form To Enter-JapanngtchungNo ratings yet
- 3-List of Main EquipmentDocument2 pages3-List of Main EquipmentngtchungNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing in Advanced Nondestructive Materials InspectionDocument155 pagesSignal Processing in Advanced Nondestructive Materials InspectionngtchungNo ratings yet
- New Doc 106Document1 pageNew Doc 106ngtchungNo ratings yet
- Recognition of Welding Defects in Radiographic Images by Using Support Vector Machine ClassifierDocument7 pagesRecognition of Welding Defects in Radiographic Images by Using Support Vector Machine ClassifierngtchungNo ratings yet
- Mang Hoat Dong Ban ThanDocument6 pagesMang Hoat Dong Ban ThanngtchungNo ratings yet
- Manual Tecnico Motor TDIDocument146 pagesManual Tecnico Motor TDIMoysess OliverNo ratings yet
- Quiz No.1 For 30 March 2020Document5 pagesQuiz No.1 For 30 March 2020Justin CaliguiaNo ratings yet
- Lister Petter GensetsDocument2 pagesLister Petter Gensetsmoaazabubakr100% (1)
- D7 at PDFDocument4 pagesD7 at PDFStathis MoumousisNo ratings yet
- Greddy SBD ManualDocument22 pagesGreddy SBD ManualKenneth ChanNo ratings yet
- RL4 VerticalDocument72 pagesRL4 VerticalEffendiCibuburNo ratings yet
- Missions of BPCLDocument12 pagesMissions of BPCLImaad TungekarNo ratings yet
- Kota Super Thermal Power Station: Presented byDocument21 pagesKota Super Thermal Power Station: Presented byajayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry: Nagpur UniversityDocument25 pagesEngineering Chemistry: Nagpur UniversityTHE MANAGEMENT CONSORTIUM (TMC) ‘All for knowledge, and knowledge for all’No ratings yet
- Fuel PUMP Overhauling Class IVDocument8 pagesFuel PUMP Overhauling Class IVRutvikNo ratings yet
- AvK DIG 156Document1 pageAvK DIG 156Galih Trisna NugrahaNo ratings yet
- RINNER Motor 57 SeriesDocument2 pagesRINNER Motor 57 Serieschar_lynNo ratings yet
- Camless Engine PresentationDocument20 pagesCamless Engine PresentationRavi Bhadani80% (10)
- F & M Act 1967 and Regulations For Steam Boilers PDFDocument19 pagesF & M Act 1967 and Regulations For Steam Boilers PDFأمير حارثNo ratings yet
- 4.1.4,5,6 Properties of Gaseous FuelsDocument5 pages4.1.4,5,6 Properties of Gaseous FuelsOkky Kusumo Indradi100% (1)
- How Can We Raise Butanes Production From Our FCC UnitDocument2 pagesHow Can We Raise Butanes Production From Our FCC UnitBIBLIOTECA TECNICA 3J100% (1)
- Exam in Engine Management 1Document3 pagesExam in Engine Management 1Jhezel Mae Alfaro Aquino100% (1)
- Common Rail Direct Injection EngineDocument13 pagesCommon Rail Direct Injection Enginenikhil sengarNo ratings yet
- Honda General Purpose Engine GX35TDocument76 pagesHonda General Purpose Engine GX35TJuan Pueblo AgachadoNo ratings yet