Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ic2401 Digital Control System Syllabus
Uploaded by
Sharmila83Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ic2401 Digital Control System Syllabus
Uploaded by
Sharmila83Copyright:
Available Formats
IC2401 DIGITAL CONTROL SYSTEM
LTPC
3003
AIM
To provide sound knowledge on the principles of discrete data control system
OBJECTIVES
i. To study the importance of sample data control system.
ii. To give adequate knowledge about signal processing in digital control.
iii. To study the importance of modeling of discrete systems and stability analysis of discrete
data system.
iv. To study the importance of state space representation for discrete data system.
v. To introduce the design concept for digital controllers.
UNIT I
COMPUTER CONTROLLED SYSTEM
6
Configuration of the basic digital control scheme general sampled data system variables signal
classifications why use digital control system Advantages disadvantages examples of
discrete data and digital control systems.
UNIT II
SIGNAL PROCESSING IN DIGITAL CONTROL
9
Sampling process Frequency domain analysis ideal samples Shanons sampling theorem
generation and solution of process linear difference equations data reconstruction process
frequency domain characteristics.
UNIT III
DISCRETE SYSTEM MODELLING
Determination of the Z transform mapping between s and Z domains - Z transform of system
equations open loop Hybrid sampled Data Control Systems open loop discrete Input Data
Control System closed loop sampled data control system modified Z transform method
response between sampling instants stability on the Z - plane and jurys stability test steady
state error analysis for stable systems.
UNIT IV
STATE VARIABLE ANALYSIS OF DIGITAL CONTROL SYSTEMS
State descriptions of digital processors conversion of state variable models to transfer functions
conversion of transfer functions to canonical state variable models first comparison form
second companion form Jordon Canonical form state description of sampled continuous time
plants solution of state difference equations closed form solution state transition matrix
Caley Hamilton Technique concept of controllability and absorbability loss of controllability
and absorbability due to sampling.
UNIT V
DESIGN OF DIGITAL CONTROL
12
Digital PI, PD and PID Controller Position and velocity forms state regulator design design
of state observers dead beat control by state feed back and dead beat observers.
TOTAL : 45 PERIODS
TEXT BOOKS
1. C.M. Houpis, G.B. Lamount, Digital Control Systems-Theory, Hardware, Software,
International Student Edition, McGraw Hill Book Co., 1985.
2. M.Gopal, Digital Control and State Variables Methods, Tata McGraw HILL, 2nd Edition, 2003.
REFERENCES
1. B.C. Kuo, Digital control systems, Second Edition, Oxford University press, 1992.
2. P.B. Deshpande and R.H. Ash, Computer Process Control, ISA Publication, USA, 1995.
You might also like
- Caterpillar Service ManualDocument242 pagesCaterpillar Service Manualsmudger197390% (52)
- Discrete-Data Control Systems: Benjamin C. KuoDocument1 pageDiscrete-Data Control Systems: Benjamin C. KuoSandra GilbertNo ratings yet
- EE2253 NotesDocument124 pagesEE2253 NotesSiva Kathikeyan100% (1)
- Be Instrumentation Control Syllabus CourseDocument43 pagesBe Instrumentation Control Syllabus CourseVikas KharavalikarNo ratings yet
- Eee.60-62Document3 pagesEee.60-62skrtamilNo ratings yet
- Viscoelastic Modeling of Flexible Pavement With Abaqus PDFDocument143 pagesViscoelastic Modeling of Flexible Pavement With Abaqus PDFcabrel TokamNo ratings yet
- IM KR180A E 4thDocument80 pagesIM KR180A E 4thbatizap batizapNo ratings yet
- Komatsu PC200LC-6Document12 pagesKomatsu PC200LC-6Collin Corp100% (2)
- EI6801 CCP SyllabusDocument1 pageEI6801 CCP SyllabusKotteeswaran Rangasamy RNo ratings yet
- Ec 1304 Control SystemsDocument2 pagesEc 1304 Control SystemsMohamed Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Ec 8391 Cs Auqp Merged 8.5.19Document31 pagesEc 8391 Cs Auqp Merged 8.5.19sivaNo ratings yet
- Cont Sys SyllabusDocument1 pageCont Sys Syllabuskavithakumar87No ratings yet
- EEE 354 Nasiruddin Course PlanDocument6 pagesEEE 354 Nasiruddin Course PlanAitzaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Ec6405control System Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesEc6405control System Engineering SyllabusmaheshboobalanNo ratings yet
- Control System EngineeringDocument2 pagesControl System EngineeringVASANTHKUMAR M SNo ratings yet
- EC6405 Control System EngineeringDocument1 pageEC6405 Control System EngineeringSaravanan PazapughalNo ratings yet
- Digital Control Systems: Unit - I Sampling and ReconstructionDocument4 pagesDigital Control Systems: Unit - I Sampling and Reconstructionvamkrishna33% (3)
- EE462 Design of Digital Control Systems PDFDocument2 pagesEE462 Design of Digital Control Systems PDFArya RahulNo ratings yet
- EE462 Design of Digital Control SystemsDocument2 pagesEE462 Design of Digital Control SystemsArya RahulNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics Optical Instrumentation Cdma MBSD Process Control Lab ProjectDocument8 pagesIndustrial Electronics Optical Instrumentation Cdma MBSD Process Control Lab ProjectKarthik NairNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 07 08 Eee 4-2 DcsDocument1 pageSyllabus 07 08 Eee 4-2 DcsPadhu KesaboyanaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Control Systems ECE R13Document2 pagesSyllabus Control Systems ECE R13tansnvarmaNo ratings yet
- JNTUK M.tech R13 I&CS SyllabusDocument15 pagesJNTUK M.tech R13 I&CS Syllabuschakri474No ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Lesson Plan: TH NDDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Lesson Plan: TH NDshadiqengineer0% (1)
- Ap923 Digital Control EngineeringDocument2 pagesAp923 Digital Control EngineeringRuban RubanpNo ratings yet
- Control Systems r13 MtechDocument24 pagesControl Systems r13 MtechSal ExcelNo ratings yet
- Regulations - 2009: Affiliated Institutions Anna University, ChennaiDocument10 pagesRegulations - 2009: Affiliated Institutions Anna University, Chennaisri_vas00074013No ratings yet
- Ramgarh Engineering College: 6 Semester, Electrical Engineering Advanced Control Systems (EE603)Document1 pageRamgarh Engineering College: 6 Semester, Electrical Engineering Advanced Control Systems (EE603)Arunabha DattaNo ratings yet
- Control System EngineeringDocument2 pagesControl System EngineeringGokulNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation EngineeringDocument34 pagesInstrumentation Engineeringvaithy1990No ratings yet
- BE Instrumentation Syllabus 2011 Pune UniversityDocument34 pagesBE Instrumentation Syllabus 2011 Pune Universityksahil2410No ratings yet
- E2 Linear Control Systems SyllabusDocument2 pagesE2 Linear Control Systems SyllabussasikalaNo ratings yet
- Inbound1209687539 PDFDocument7 pagesInbound1209687539 PDFAbhishek ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate M E Instrumentation and ControlDocument8 pagesPostgraduate M E Instrumentation and Controljricardo019763535No ratings yet
- Control and InstrumentationDocument31 pagesControl and InstrumentationSiva MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Control Systems EngineeringDocument2 pagesControl Systems EngineeringSaurabhBisht67% (3)
- EE163 Digital Control SystemsDocument1 pageEE163 Digital Control Systemsarunkumar SNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics SyllabysDocument1 pageMechatronics SyllabyskothandanNo ratings yet
- Telemetry & Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument10 pagesTelemetry & Wireless Sensor NetworkSwapan DasNo ratings yet
- Ramgarh Engineering College: Advanced Control Systems (EE603)Document15 pagesRamgarh Engineering College: Advanced Control Systems (EE603)Arunabha DattaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control (ME1401)Document2 pagesAutomatic Control (ME1401)Mehroos AliNo ratings yet
- EIE410 Digital Control SystemDocument3 pagesEIE410 Digital Control SystemgurusaravanaNo ratings yet
- EECP 3375-Digital Control SystemsDocument1 pageEECP 3375-Digital Control SystemsPandimadevi GanesanNo ratings yet
- EEE 6th Sem SyllabusDocument6 pagesEEE 6th Sem SyllabusRajesh0% (1)
- Digital Control Sys SyllabusDocument3 pagesDigital Control Sys SyllabusAndre Silva0% (1)
- CSD Syllabus COsDocument2 pagesCSD Syllabus COsBharath PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- M.E. SyllabusDocument13 pagesM.E. Syllabusகோகுல்நாத் ஸ்ரீ கிNo ratings yet
- Control System EngineeringDocument3 pagesControl System Engineeringnisarg0% (1)
- Template FullDocument6 pagesTemplate Full21-055 KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Process Control LessonDocument1 pageProcess Control LessonAnonymous JDXbBDBNo ratings yet
- EmbeddedDocument9 pagesEmbeddedNanc Joy100% (1)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University II Year B.Tech. ECE. Il-Sem T P 0 C Control SystemsDocument1 pageJawaharlal Nehru Technological University II Year B.Tech. ECE. Il-Sem T P 0 C Control SystemsappuamreddyNo ratings yet
- CS Syllabus JntukDocument2 pagesCS Syllabus JntukEEE CRRNo ratings yet
- Modern Control TheoryDocument137 pagesModern Control TheorypragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Computer Control of Process - KSDocument77 pagesComputer Control of Process - KSSaravana ElectricNo ratings yet
- EE2253 - Control SystemsDocument124 pagesEE2253 - Control SystemsrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - EE3405 - 2-2021ADocument1 pageSyllabus - EE3405 - 2-2021Acoulibaly y pascalNo ratings yet
- Digital Control SystemsDocument1 pageDigital Control SystemsAnonymous HyOfbJ6No ratings yet
- Jntuk B.tech 4-2 r13 EeeDocument33 pagesJntuk B.tech 4-2 r13 EeeKanisetty JanardanNo ratings yet
- 401 M.E. Applied ElectronicsDocument10 pages401 M.E. Applied Electronicsd_vijay666No ratings yet
- Digital Control Systems Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Control Systems Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Time Control System Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandDiscrete-Time Control System Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Dynamic-System Simulation: Model Replication and Monte Carlo StudiesFrom EverandAdvanced Dynamic-System Simulation: Model Replication and Monte Carlo StudiesNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Instrumentation QBDocument24 pagesPower Plant Instrumentation QBSharmila83No ratings yet
- Syllabus AP5008 PATTERN RECOGNITIONDocument1 pageSyllabus AP5008 PATTERN RECOGNITIONSharmila83No ratings yet
- Be3251 Beee - Cse SyllabusDocument1 pageBe3251 Beee - Cse SyllabusSharmila83No ratings yet
- EI8092 THERMAL POWER PLANT SyllabusDocument1 pageEI8092 THERMAL POWER PLANT SyllabusSharmila83No ratings yet
- Computing Stable Equilibrium Stances of A Legged Robot in Frictional EnvironmentsDocument40 pagesComputing Stable Equilibrium Stances of A Legged Robot in Frictional EnvironmentsSharmila83No ratings yet
- RObotics and Automation Question Bank AnDocument19 pagesRObotics and Automation Question Bank AnSharmila83No ratings yet
- Unit1 Part2Document29 pagesUnit1 Part2Sharmila83No ratings yet
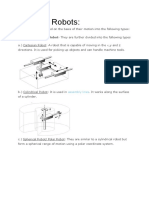
- Types of RobotsDocument7 pagesTypes of RobotsSharmila83No ratings yet
- Robotics Notes 1Document19 pagesRobotics Notes 1Dammalapati HarshavardhanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Manipulators, Actuators and End Effectors: Prepared by Asst. Prof - Dept. of ICEDocument66 pagesUnit - 3 Manipulators, Actuators and End Effectors: Prepared by Asst. Prof - Dept. of ICESharmila83No ratings yet
- A Notebook On Instrumentation SystemsDocument108 pagesA Notebook On Instrumentation SystemsSharmila83No ratings yet
- Sharmi ECE a-D-Circuits Lab ManualDocument74 pagesSharmi ECE a-D-Circuits Lab ManualSharmila83No ratings yet
- II SyllabysDocument1 pageII SyllabysAbii BaluuNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Basic ConceptsDocument73 pagesUnit1 - Basic ConceptsSharmila83No ratings yet
- Evolution of MicroprocessorsDocument10 pagesEvolution of MicroprocessorsSharmila83No ratings yet
- II SyllabysDocument1 pageII SyllabysAbii BaluuNo ratings yet
- A.V.C College of Engineering, Mannampandal M.E - Applied ElectronicsDocument3 pagesA.V.C College of Engineering, Mannampandal M.E - Applied ElectronicsAnonymous IkB7TZjNo ratings yet
- Ge6252 Beee April May 2015 Rejinpaul QP PDFDocument2 pagesGe6252 Beee April May 2015 Rejinpaul QP PDFSharmila83No ratings yet
- A.V.C College of Engineering: Mannampandal, Mayiladuthurai. Department of Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDocument5 pagesA.V.C College of Engineering: Mannampandal, Mayiladuthurai. Department of Instrumentation and Control EngineeringSharmila83No ratings yet
- Ee6502 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument2 pagesEe6502 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersgokulchandruNo ratings yet
- Structural MembersDocument37 pagesStructural Membersmario gadianoNo ratings yet
- Iso 5294 1989Document9 pagesIso 5294 1989a.mursadinNo ratings yet
- 802 OM 4-InspDocument12 pages802 OM 4-InspGabriel vieiraNo ratings yet
- SET-1: Answer To The Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesSET-1: Answer To The Interview QuestionsÆshok IncreĐible KingNo ratings yet
- GPU Programming in MATLABDocument6 pagesGPU Programming in MATLABkhaardNo ratings yet
- Scania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFDocument2 pagesScania Jenerator DC1372A - 438-487kW PDFMehmet ErenNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of The Performances of Four Photovoltaic-Thermal Solar Air CollectorsDocument21 pagesComparative Study of The Performances of Four Photovoltaic-Thermal Solar Air CollectorsMarco MGNo ratings yet
- 2015f - CPCS 202 - Quiz 2 - SolutionDocument3 pages2015f - CPCS 202 - Quiz 2 - SolutionOsama MaherNo ratings yet
- Carbon Regeneration KilnsDocument3 pagesCarbon Regeneration KilnsLuis LabradorNo ratings yet
- Joraform JK Series Operating PrinciplesDocument6 pagesJoraform JK Series Operating Principlesapi-236782993No ratings yet
- Instrument and Control Designer Rev01Document5 pagesInstrument and Control Designer Rev01masilamaniNo ratings yet
- Emacs CookbooksDocument102 pagesEmacs CookbooksDavid IrelandNo ratings yet
- CPP Exceptions Handling PDFDocument4 pagesCPP Exceptions Handling PDFRakib Uddin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- H Molecule. The First Problem They Considered Was The Determination of The Change inDocument2 pagesH Molecule. The First Problem They Considered Was The Determination of The Change inDesita KamilaNo ratings yet
- Aircon Maintenance Singapore NdurwDocument5 pagesAircon Maintenance Singapore Ndurwchinfrench0No ratings yet
- Mastering Bitcoin PDFDocument282 pagesMastering Bitcoin PDFdoanminhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Vapor Power Cycles - CompleteDocument97 pagesChapter 1 Vapor Power Cycles - CompleteAdnan NimachwalaNo ratings yet
- KSB KWP: Non-Clogging Centrifugal PumpsDocument12 pagesKSB KWP: Non-Clogging Centrifugal PumpsalfredNo ratings yet
- As BuiltDocument12 pagesAs BuiltAnurag PandeyNo ratings yet
- ATM SecurityDocument87 pagesATM SecurityHristo Dokov100% (1)
- Falcon DEMCO Fire Alarm Bell (Weatherproof Type)Document1 pageFalcon DEMCO Fire Alarm Bell (Weatherproof Type)LaMinn PaingNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Ce Law Ethics Contracts Midterm - 103742Document13 pagesAssignment 2 Ce Law Ethics Contracts Midterm - 103742Myka SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1Z0 053 PDFDocument36 pages1Z0 053 PDFOscarRamirezNo ratings yet
- Company ProfileDocument6 pagesCompany ProfileFaidzil ChabibNo ratings yet
- Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm Based Design of StructuresDocument1 pageGrasshopper Optimization Algorithm Based Design of Structuresinvisible25No ratings yet
- Raymond Scott - Cindy ElectroniumDocument2 pagesRaymond Scott - Cindy ElectroniumJen HillNo ratings yet