Professional Documents
Culture Documents
60744
Uploaded by
akppk1384Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
60744
Uploaded by
akppk1384Copyright:
Available Formats
INNOVATION IMPACT
Quick Facts
NREL analysts have developed a variety
of modeling tools for the electrical grid,
including ReEDS, which looks at the
build-out of generation and transmission
systems, and FESTIV, which examines the
impacts of variability from wind and solar
energy sources.
.....................................................................
Building on the groundbreaking Western
Wind and Solar Integration Study
(WWSIS), NREL analysts created simulations for a more in-depth WWSIS-2.
NREL found that the increased cycling
of a fossil-fueled plant to accommodate
high levels of wind and solar generation
increases operating costs by 2%5%.
However, from a system perspective, the
fossil fuel costs that are avoided by using
solar and wind power are far greater than
the increased cycling costs.
.....................................................................
WWSIS-2 also found that the negative
impact of cycling on overall plant emissions is relatively small, and that the
increase in plant emissions from cycling
to accommodate variable renewable
sources is more than offset by the overall
reduction in carbon dioxide and other
pollutants.
.....................................................................
ReEDS provided the underpinning for
the Renewable Electricity Futures Study,
and in conjunction with production cost
modeling, demonstrated that renewable
energy generation from technologies that
are commercially available today, combined with a more flexible electric system,
is more than adequate to supply 80% of
U.S. electricity by 2050.
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
15013 Denver West Parkway, Golden, CO 80401
303-275-3000 www.nrel.gov
NREL is a national laboratory of the U.S.
Department of Energy, Office of Energy
Efficiency and Renewable Energy, operated
by the Alliance for Sustainable Energy, LLC.
Analysis
NREL Energy Models Examine the Potential
for Wind and Solar Grid Integration
As renewable energy generating sources, such as wind turbines and solar power
systems, reach high levels of penetration in parts of the United States, the National
Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) is helping the utility industry to peer into the
future. Using software modeling tools that the lab developed, NREL is examining the
future operation of the electrical grid as renewable energy continues to grow.
NRELs Regional Energy Deployment System (ReEDS) model, for example, primarily
addresses issues for integrating renewable electric technologies, especially wind and
solar resources. At a finer timescale, NRELs Flexible Energy Scheduling Tool for Integration of Variable Generation (FESTIV) simulates the behavior of the electric power
system, helping researchers understand the impacts of variability and uncertainty
on operating reserves requirements. For many integration studies, NREL also runs
a production cost model. All these tools help the utility industry to understand the
potential impacts of increased renewable power generation.
NREL has employed these tools to support key regional studies, including the
Western Wind and Solar Integration Study, Phase 2 (WWSIS-2), which analyzed
the impact of cycling conventional power plants to accommodate more renewable
energy generation on the western grid. NREL analysts, using the PLEXOS commercial
modeling tool, found that although cycling has an impact on costs and emissions,
those impacts are small compared to fuel savings and displaced emissions. Also, the
on-going Eastern Renewable Generation Integration Study (ERGIS) is analyzing operations of the eastern grid at an unprecedented resolution to understand how operational changes can be used to more efficiently manage the variability and uncertainty
of wind and solar resources.
Using ReEDS, the lab also led the Renewable Electricity Futures Study, which found
that renewable electricity generation from technologies that are commercially available today, combined with a more flexible electric system, is more than adequate
to supply 80% of total U.S. electricity generation by 2050. NREL also used ReEDS for
the SunShot Vision Study, which provides an in-depth assessment of the potential for
solar technologies. In addition, NREL studies have quantified the positive impact of
other generation, storage, and demand-response technologies.
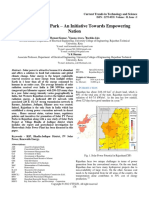
NRELs ERGIS study is modeling the U.S.
portion of the Eastern Interconnection,
shown here, at unprecedented
resolution. The pie charts on this map
show the percentage of wind, solar, and
other generation sources for each grid
operator under a scenario in which the
U.S. portion of the interconnection
reaches 30% renewable energy by
2025. The size of the pie charts
indicates the amount of power
generation for each grid operator.
Illustration by Jenny Melius and Aaron
Townsend, NREL
NREL/FS-6A42-60744 November 2013
NREL prints on paper that contains recycled content.
For more NREL innovations, visit www.nrel.gov/innovation/
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Rei1 PDFDocument300 pagesRei1 PDFakppk1384No ratings yet
- Arc Flash - ResideDocument54 pagesArc Flash - Residewaldo_astudilloNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production: Fundamentals and Cas Study Summaries eDocument21 pagesHydrogen Production: Fundamentals and Cas Study Summaries eakppk1384No ratings yet
- Scada ReviewDocument57 pagesScada ReviewastonjonesNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument164 pagesSolar EnergykapenziaNo ratings yet
- Eth 2903 02Document132 pagesEth 2903 02akppk1384No ratings yet
- 63540Document17 pages63540akppk1384No ratings yet
- Land - Use RequirementsDocument47 pagesLand - Use RequirementsgaddipatimalliNo ratings yet
- Concentrating Solar Power: Solar Energy Technologies ProgramDocument2 pagesConcentrating Solar Power: Solar Energy Technologies ProgramMoiz SubhanNo ratings yet
- Technical Potential of Solar Energy To Address Energy Poverty and Avoid GHG Emissions in AfricaDocument1 pageTechnical Potential of Solar Energy To Address Energy Poverty and Avoid GHG Emissions in Africaakppk1384No ratings yet
- Fermentation: Bench-Scale To Pilot-Scale Capabilities For The Conversion of Biomass To Sugars, Fuels, and ChemicalsDocument1 pageFermentation: Bench-Scale To Pilot-Scale Capabilities For The Conversion of Biomass To Sugars, Fuels, and ChemicalsComan GigiNo ratings yet
- 47676Document29 pages47676akppk1384No ratings yet
- High Solids Enzymatic Hydrolysis Reactors: New Capability To Produce More Highly Concentrated Sugars StreamsDocument1 pageHigh Solids Enzymatic Hydrolysis Reactors: New Capability To Produce More Highly Concentrated Sugars StreamsComan GigiNo ratings yet
- Wartsila SP B IMC FerriesDocument4 pagesWartsila SP B IMC Ferriesakppk1384No ratings yet
- تحميل الاشتراطات الفنية لتركيب مشروعات الخلايا الشمسيةDocument9 pagesتحميل الاشتراطات الفنية لتركيب مشروعات الخلايا الشمسيةakppk1384No ratings yet
- Asab GBDocument67 pagesAsab GBakppk1384No ratings yet
- C Ife: MEP Coordination in Building and Industrial ProjectsDocument51 pagesC Ife: MEP Coordination in Building and Industrial Projectsfifthslip100% (1)
- EPA Well Design Ground Water Monitoring WwelldctDocument224 pagesEPA Well Design Ground Water Monitoring Wwelldctintoyou2007No ratings yet
- 111 - 1. 40 50 MVA 13233 KV Power TFDocument32 pages111 - 1. 40 50 MVA 13233 KV Power TFakppk1384No ratings yet
- WP Arc Flash Basics Testing UpdateDocument6 pagesWP Arc Flash Basics Testing Updateakppk1384No ratings yet
- WWCC Arc Flash Mitigation AtlantaDocument47 pagesWWCC Arc Flash Mitigation Atlantaakppk1384100% (1)
- 110KV Substation SpecDocument63 pages110KV Substation Specdeepthik27No ratings yet
- WWCC Arc Flash Mitigation AtlantaDocument47 pagesWWCC Arc Flash Mitigation Atlantaakppk1384100% (1)
- General Technical Specifications Electrical PDFDocument205 pagesGeneral Technical Specifications Electrical PDFAnonymous cXOu9TDVlNo ratings yet
- 32Document4 pages32Shahrukh SaleemNo ratings yet
- 12-886 Arc Flash Analysis 4Document33 pages12-886 Arc Flash Analysis 4akppk1384No ratings yet
- 10 Soft StartersDocument40 pages10 Soft Startersvinay nagvanshiNo ratings yet
- 03 - Calculating Arc Flash Energy For Systems Upto 250VDocument18 pages03 - Calculating Arc Flash Energy For Systems Upto 250Vakppk1384No ratings yet
- 02 - NEX 17.5 Panel CatalogueDocument40 pages02 - NEX 17.5 Panel Catalogueakppk1384No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Buku Energi Outlook 2022 Versi Bhs InggrisDocument132 pagesBuku Energi Outlook 2022 Versi Bhs InggrisHaryo Pandu WinotoNo ratings yet
- Energy 4Document100 pagesEnergy 4Roman TilahunNo ratings yet
- FLECCS DE-FOA-0002220 Final PDFDocument57 pagesFLECCS DE-FOA-0002220 Final PDFvggupta2No ratings yet
- Email Gillespie Home Advisor Referrals Solar PanelsDocument30 pagesEmail Gillespie Home Advisor Referrals Solar PanelsNeil GillespieNo ratings yet
- Sunforce 50232 30 Watt Folding Solar Panel Owner's ManualDocument6 pagesSunforce 50232 30 Watt Folding Solar Panel Owner's Manual21st-Century-Goods.comNo ratings yet
- 1600PowerShade E ADocument6 pages1600PowerShade E AmaysamgholampourNo ratings yet
- Hydro Regulations PoliciesDocument310 pagesHydro Regulations Policiesनिपुण कुमारNo ratings yet
- 900 21 010 US Sustainability Report 2021Document61 pages900 21 010 US Sustainability Report 2021visutsiNo ratings yet
- Hanoi Pedagogical University 2 (Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội 2) Hanoi Pedagogical University 2 (Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội 2)Document103 pagesHanoi Pedagogical University 2 (Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội 2) Hanoi Pedagogical University 2 (Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội 2)luceiNo ratings yet
- Biofuels in Gas TurbinesDocument3 pagesBiofuels in Gas TurbinesturkfatalNo ratings yet
- Trade & Investment 02-03-2010Document110 pagesTrade & Investment 02-03-2010Trade_Investment100% (1)
- Micro WInd TurbineDocument7 pagesMicro WInd Turbinesakale007No ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A PI-MPPT Based Buck-Boost ConverterDocument6 pagesDesign and Implementation of A PI-MPPT Based Buck-Boost ConverterWesley de PaulaNo ratings yet
- Following Is The Updated List of Suppliers/EPC Contractors Under IDCOL Solar Irrigation ProgramDocument3 pagesFollowing Is The Updated List of Suppliers/EPC Contractors Under IDCOL Solar Irrigation ProgramtanvirNo ratings yet
- Shichun Yang Xinhua Liu Shen Li Cheng Zhang: Advanced Battery Management System For Electric VehiclesDocument318 pagesShichun Yang Xinhua Liu Shen Li Cheng Zhang: Advanced Battery Management System For Electric VehiclesDennis FielNo ratings yet
- Algoritm PV-WindDocument29 pagesAlgoritm PV-WindIonașcu IonNo ratings yet
- Petitioner Philippine Geothermal Production Company, Inc. (PGPCI) v. Commissioner of Internal RevenueDocument2 pagesPetitioner Philippine Geothermal Production Company, Inc. (PGPCI) v. Commissioner of Internal RevenueMirabel VidalNo ratings yet
- Renewable RevolutionDocument52 pagesRenewable RevolutionDaisyNo ratings yet
- Global Gas Outlook 2020 Gecf 2050Document136 pagesGlobal Gas Outlook 2020 Gecf 2050Ruben PerezNo ratings yet
- Hanwha 2013 Dealer ConferenceDocument23 pagesHanwha 2013 Dealer ConferenceKenpachi ZarakiNo ratings yet
- 8587ctts 330v 2i 1178 182Document5 pages8587ctts 330v 2i 1178 182Haresh RaisinghaniNo ratings yet
- Ebin - Pub - Surge in Solar Powered Homes Experience in Off Grid Rural Bangladesh 1nbsped 9781464803758 9781464803741Document171 pagesEbin - Pub - Surge in Solar Powered Homes Experience in Off Grid Rural Bangladesh 1nbsped 9781464803758 9781464803741MeemNo ratings yet
- Net Zero Energy Building Movement in IndDocument4 pagesNet Zero Energy Building Movement in IndsriguruNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy SourceDocument13 pagesAlternative Energy SourcecolladonicoledesireeNo ratings yet
- ISCC Presentation - GHG 25 Aug 2021 Rvuno SentDocument20 pagesISCC Presentation - GHG 25 Aug 2021 Rvuno SentsaredohertyNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation - Definition, Benefits and IssuesDocument12 pagesDistributed Generation - Definition, Benefits and Issuesapi-3697505100% (1)
- Sembcorp Group-Brochure-2019Document22 pagesSembcorp Group-Brochure-2019TaraFKhairaNo ratings yet
- Climate CatastropheDocument2 pagesClimate CatastropheFarooq KhanNo ratings yet
- News Brazil Biomass Export Wood ChipsDocument18 pagesNews Brazil Biomass Export Wood Chipsmar4478100% (2)