Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Valves: "Hose Bibb"
Uploaded by
queeneequeeneeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Valves: "Hose Bibb"
Uploaded by
queeneequeeneeCopyright:
Available Formats
Valves
Function of Valves: Control of the
Water System
1.
2.
3.
4.
Start or Shut Down a System
Regulate Pressure
Check Backflow
Control the Direction of
water
Rules Regarding Location of Valves
-
Locate and distribute valves
in such a manner that they
can isolate a certain section
of the network in case of
system breakdown (before
each branch)
Locate valves where they are
not
too
visible
while
remaining
accessible
to
users
Type of Valves
1. Gate Valve a.k.a. Pull-away
Valve
- Use mainly to completely
close or completely open
the water line (does not
control flow of water)
- Best suited to the main
supply an pump lines
wherein
operation
is
infrequent
2. Globe Valve
- Controls the flow of water
with a movable spindle
- Can
reduce
water
pressure
- Only one side of the valve
is inlet
3. Check Valve
- Main
function
is
to
prevent the reversal of
flow (backflow) in the line
A line of valve that allows
fluid to flow in the
direction
but
closes
automatically to prevent
flow in the opposite
direction
4. Angle Valve
- Operates in the same
manner as Globe Valve
(disc and seat design)
- Used to make a 90 turn
in a line
- Reduces number of joints
Types of Faucets/Bibbs
1. Compression Cock
- Operates
by
the
compression of
a soft
packing upon a metal
sheet
2. Key Cock
- Operates with a round
tapering plug ground to
fit a metal sheet
Hose Bibb
- Has grooves fit for hose
3. Ball Faucet
- Constructed with a ball
connected to the handle
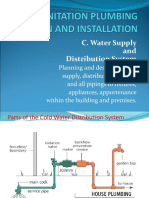
Parts of
System
Cold
Water
Distribution
1. Service Pipe
- Pipe from the street
water or other source of
water supply to the
building served
2. Water Meter
- Device used to measure
in liters or gallons the
amount of water that
passes through the water
service
3. Horizontal Supply Main
The
principal
water
distribution pipe running
from the water meter
from which the various
branches and risers to
the fixtures
4. Riser
- A water supply pipe
extending vertically to
one full storey or more to
convey water into pipe
branches or plumbing
fixtures
5. Fixture Branch
- The water supply pipe
between
the
fixture
supply pipe and the
water distributing pipe
6. Controls and Valves
- Used
for
control,
isolation, and repair of
the water distribution
system
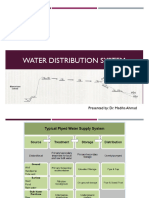
Types of a Cold Water Distribution
System
1. Upfeed System
- Direct Upfeed
- water is provided by
the
city
water
companies
using
normal pressure from
public water main
- Air
Pressure
System
(Pneumatic)
when
pressure
supplied by the city
water supplied is not
strong enough
- Compressed
air
is
used to raise and push
water into the system.
2. Downfeed (Overheadfeed) or
Gravity System
water is purified into a
large tank on top of the
building and is distributed
to the fixtures by means
of gravity
Upfeed System
Advantages
1. Eliminates extra cost of pumps
and tanks
Disadvantages
1. Pressure from water main is
inadequate
to
supply
tall
buildings
2. Water
Supply
is
affected
between peak load hour
Air Pressure System
Advantages
1. With compact pumping unit
2. Sanitary due to air tight water
chamber
3. Economic
(smaller
pipe
diameter)
4. Less initial construction and
maintenance cost
5. Oxygen in the compressed air
serves as purifying agent
6. Adaptable air pressure
7. Air pressure serves zones of
about 10 storeys interval
Disadvantages
1. Water supply is affected by loss
of pressure inside the tank in
case of power interruption
Overheadfeed System
Advantages
1. Water is not affected by peak
load hour
2. Not
affected
by
power
interruption
3. Time needed to replace broken
parts does not affect water
supply
Disadvantages
1. Water
is
subject
to
contamination
2. High maintenance cost
3. Occupies valuable space
4. Requires stronger foundation
and other structure to carry
additional load of tank and
water
Fire Protection System
Types of Fire Protection System
1. Dry Standpipe System
- No longer utilized in new
buildings
How it works: A standpipe is
connected to the exterior of
the building
- The standpipe is a pipe
installed in buildings not as
part of the water supply or
waste disposal system but
primarily used as water
conveyance in case of fire
2. Wet Standpipe System
- How it works: A piping
network (Line is directly
connected to the main
waterline) connected to all
levels of the building (at
least 1 standpipe on each
level)
3. Wet Standpipe System with
Siamese Connection
- How it works: A piping
network (line is directly
connected to the main
waterline) connected to all
levels of the building (at
least 1 standpipe on each
level);
additionally
a
Siamese
connected
is
located outside the building
for additional water supply
(connects to fire truck hose)
You might also like
- Cold Water Supply in BuildingDocument21 pagesCold Water Supply in BuildingDanz Alanna100% (2)
- Water Distribution SystemDocument8 pagesWater Distribution SystemYel AbrilloNo ratings yet
- Sara 5103Document95 pagesSara 5103Shah PrachiNo ratings yet
- JPT RMP C1Document24 pagesJPT RMP C1HaRriet De Guzman Villanueva100% (1)
- 2023 2 - Water Supply Equipment - JGDGrullaDocument22 pages2023 2 - Water Supply Equipment - JGDGrullaDarlene Jane DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Design HandoutsDocument136 pagesPlumbing Design HandoutsVenus Jasmin Falceso Leyble100% (10)
- Plumbing System For Water Refilling StationsDocument38 pagesPlumbing System For Water Refilling StationsPrincess BarredoNo ratings yet
- Plumbing For ArchitectureDocument102 pagesPlumbing For ArchitectureMd. Abdul QuayumNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power - (ME353) - Lec10Document35 pagesFluid Power - (ME353) - Lec10Mohamed MaherNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution: Cross Connection Control Water ConservationDocument10 pagesWater Distribution: Cross Connection Control Water ConservationOwolabi RuthNo ratings yet
- ValvesDocument4 pagesValvesKevinNavidadNo ratings yet
- Building Services Unit 1Document8 pagesBuilding Services Unit 1Payal Yadav100% (1)
- Unit-5 Group 5Document45 pagesUnit-5 Group 5pmovie194No ratings yet
- C1. Water SupplyDocument34 pagesC1. Water Supplyhermano balbon67% (3)
- Operation and Maintenance of HVAC Water SystemDocument8 pagesOperation and Maintenance of HVAC Water SystemHenry SuarezNo ratings yet
- Building Services 1 (BAP 213) : Assignment 1Document8 pagesBuilding Services 1 (BAP 213) : Assignment 1puja Dhamija100% (1)
- Building UtilitiesDocument41 pagesBuilding UtilitiesJara Mi SerinoNo ratings yet
- Design of Fire Protection System 1 Dr. Abdullah Olimat First Semester 2015/2016 Subject 6: PumpsDocument66 pagesDesign of Fire Protection System 1 Dr. Abdullah Olimat First Semester 2015/2016 Subject 6: Pumpsahmad adnanNo ratings yet
- Water Supply System - Minal PalveDocument51 pagesWater Supply System - Minal PalveminalNo ratings yet
- Zamora Bsce3b Cea132 Assignment-2Document9 pagesZamora Bsce3b Cea132 Assignment-2Mrdy CaiNo ratings yet
- Plumbing BookDocument111 pagesPlumbing BookKhit MakaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Distribution SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Distribution SystemBeerappa RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Theory Application and Sizing of Air ValvesDocument9 pagesTheory Application and Sizing of Air ValveskcplemmonsNo ratings yet
- L1 U 1.1 Distribution System IntroductionDocument27 pagesL1 U 1.1 Distribution System IntroductionSumit Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Module 01 Definition of Terms ArTY 1Document14 pagesModule 01 Definition of Terms ArTY 1JOSE RAFAEL COLUMNANo ratings yet
- Building Services and Workshop TechnologyDocument21 pagesBuilding Services and Workshop Technologytiffa BosiboriNo ratings yet
- Elements of PlumbingDocument70 pagesElements of Plumbinglad odie0% (1)
- Gravity - Flow Water Systems Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 DefinitionDocument5 pagesGravity - Flow Water Systems Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Definitionraju acharyaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Hydraulic CircuitsDocument43 pagesIndustrial Hydraulic CircuitsFidel Garcia GarciaNo ratings yet
- 4 TH Unit ValvesDocument43 pages4 TH Unit ValvesBahaa EmadNo ratings yet
- ABA 2207 BUILDING SERVICES AND WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY Batch 01Document25 pagesABA 2207 BUILDING SERVICES AND WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY Batch 01Sheryl CaneteNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Systems Guide: Water Supply, Sanitary Drainage & ComponentsDocument59 pagesPlumbing Systems Guide: Water Supply, Sanitary Drainage & ComponentsLanz Sumagaysay100% (1)
- 2 - ValvesDocument7 pages2 - ValvesDumindu Chandana PunchihewaNo ratings yet
- Closed Return Loop SystemsDocument31 pagesClosed Return Loop Systemsrecep1No ratings yet
- PLB ElementsDocument50 pagesPLB Elementslouie21No ratings yet
- Theory, Applications and Sizing of Air ValvesDocument11 pagesTheory, Applications and Sizing of Air Valvesretrospect1000No ratings yet
- Efficient Water Distribution SystemsDocument32 pagesEfficient Water Distribution SystemsLeo ThomasNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 Water Distribution System16!02!24Document27 pagesLec-3 Water Distribution System16!02!24muhammadurafm.aliNo ratings yet
- Building water supply systemsDocument3 pagesBuilding water supply systemsMariya DolceNo ratings yet
- Chapter7-Plumbing system-WS&SEDocument30 pagesChapter7-Plumbing system-WS&SERwagatare civilcontractorsNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Design and Distribution SystemsDocument26 pagesWater Supply Design and Distribution SystemsAlchea Aldeguer100% (1)
- امداد مدن بالمياهDocument8 pagesامداد مدن بالمياهAmr Abdelraouf MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Robotics Unit2 SlidesDocument104 pagesRobotics Unit2 SlidesJanarthanan BalakrishnasamyNo ratings yet
- Parts and Working of Fluid Power SystemsDocument14 pagesParts and Working of Fluid Power SystemsnidhidarklordNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution - BetterBricksDocument11 pagesWater Distribution - BetterBricksdimchienNo ratings yet
- Gravity - Flow Water Systems Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 DefinitionDocument4 pagesGravity - Flow Water Systems Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Definitionraju acharyaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Reviewer Chapters 1-3Document14 pagesPlumbing Reviewer Chapters 1-3Karl Alexander CaraanNo ratings yet
- Air Valve 460Document6 pagesAir Valve 460amrezzatNo ratings yet
- Water Supply in High Rise BuildingsDocument8 pagesWater Supply in High Rise BuildingsVaishnavi Parmar100% (1)
- PLUMBING Training - UpdatedDocument104 pagesPLUMBING Training - Updatedmohamed shariefNo ratings yet
- Domestic Cold Water SupplyDocument68 pagesDomestic Cold Water SupplyMark Hade Jayson100% (1)
- 07 Hydronic Systems App 1Document12 pages07 Hydronic Systems App 1scarpredator5No ratings yet
- Water Supply System OverviewDocument36 pagesWater Supply System OverviewDharmesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Water Supply in A BuildingDocument10 pagesWater Supply in A Buildingmcs united100% (1)
- Flow Control-Wps OfficeDocument11 pagesFlow Control-Wps Officechigoziemba9No ratings yet
- Summary TECNO WHOLE UNIT 2Document10 pagesSummary TECNO WHOLE UNIT 2EmiliamakedaNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Theory: Sugar Land Fire Department Driver/Operator-Pumper Academy Spring 2003Document70 pagesFire Pump Theory: Sugar Land Fire Department Driver/Operator-Pumper Academy Spring 2003Jose AndradeNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document47 pagesChapter 14Johnclaude ChamandiNo ratings yet
- Bosch Inline Piezo Injector Delivery PlanDocument9 pagesBosch Inline Piezo Injector Delivery PlandieseldvNo ratings yet
- Engine Oil ViscosityDocument1 pageEngine Oil ViscosityJainendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Salaulim Dam and Botanical GardenDocument1 pageSalaulim Dam and Botanical GardenCornella PardedeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics LabDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics LabRonald Muñez BadicNo ratings yet
- Vorticity and CirculationDocument18 pagesVorticity and CirculationShweta NagpalNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Reliability: Resolving Vibration Problems in A Crude Booster PumpDocument5 pagesMaintenance and Reliability: Resolving Vibration Problems in A Crude Booster Pump김형진No ratings yet
- Rota Meter Flow-MeasurementDocument18 pagesRota Meter Flow-MeasurementMudit BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tube HX Paper I J MetDocument11 pagesCoiled Tube HX Paper I J Metsitti salehaNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Spec MD6250Document12 pagesLubricant Spec MD6250reza rizkitaNo ratings yet
- Review of Changes in OSD Computation Methods Between MSMA EditionsDocument15 pagesReview of Changes in OSD Computation Methods Between MSMA EditionsGan Chin PhangNo ratings yet
- 349DL Electrical Circuit Kenr7799kenr7799-04 - SisDocument12 pages349DL Electrical Circuit Kenr7799kenr7799-04 - SisZAIN0% (1)
- Chapter 12 - Water DistributionDocument51 pagesChapter 12 - Water Distributionsalt2009No ratings yet
- 19 - Heavy Crude Oil ProcessingDocument22 pages19 - Heavy Crude Oil ProcessingSHREENo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SystemsDocument49 pagesHydraulic Systemsajuklm88No ratings yet
- Me 2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Unit-I PART-A (2 Marks)Document14 pagesMe 2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Unit-I PART-A (2 Marks)vsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Calculate pneumatic or hydraulic cylinder forceDocument2 pagesCalculate pneumatic or hydraulic cylinder forceD KANCUTZNo ratings yet
- Bore Water 12 Pump System - Assesment ReportDocument6 pagesBore Water 12 Pump System - Assesment ReportKrishna JashaNo ratings yet
- Tiefenbach Directional Control Valves for Safe Hydraulic Circuit SwitchingDocument4 pagesTiefenbach Directional Control Valves for Safe Hydraulic Circuit SwitchingCarlos Bruno MatosNo ratings yet
- MECH 430 Assignment 4 F2018Document9 pagesMECH 430 Assignment 4 F2018Апцгдк Ьфш БгднчллNo ratings yet
- What is Sanitation and its ImportanceDocument12 pagesWhat is Sanitation and its Importancesumanpunia100% (9)
- Fluid Flow Ideal Fluid Bernoulli'S PrincipleDocument19 pagesFluid Flow Ideal Fluid Bernoulli'S PrincipleTài NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Fluid StaticsDocument16 pagesWeek 3 Fluid StaticsJoquem PamesaNo ratings yet
- LUBRICANTS: CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIESDocument25 pagesLUBRICANTS: CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIESSiontan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Mixer Ejector NozzleDocument28 pagesDesign and Analysis of Mixer Ejector NozzleRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- KSB VALVE With HS CodeDocument2 pagesKSB VALVE With HS Codezakaria masud sonyNo ratings yet
- Reynolds NumberDocument12 pagesReynolds NumberChris Thel MayNo ratings yet
- Developments of A Flow Visualization Borescope and A Two-Phase Flow Probe For Aeroengine Transmission GearsDocument13 pagesDevelopments of A Flow Visualization Borescope and A Two-Phase Flow Probe For Aeroengine Transmission GearsNguyễn Đức HuyNo ratings yet
- Polymer Flooding Introduction PDFDocument307 pagesPolymer Flooding Introduction PDFDaniela NietoNo ratings yet
- VacuumDocument7 pagesVacuumMassimilianø Erricø100% (1)