Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TW - Assignment No. 1 - Simple Stress and Strain
Uploaded by
Sameer ShaikhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TW - Assignment No. 1 - Simple Stress and Strain
Uploaded by
Sameer ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
Term Work
S.E. MECH (A & B)
Term Work Assignment No. 1
1. The internal resistance which the body offers to meet the load or external load is called
a. Stress
b. Strain
c. Pressure
d. None of above
2. The ratio of lateral strain to linear strain is known as
a. Modulus of Elasticity
b. Modulus of rigidity
c. Poissons ratio
d. Elastic limit.
3. __________strain is the deformation of the bar per unit length in the direction of the force
a. Volumetric
b. Shear
c. Lateral
d. Linear
4. Thermal stress is given by
a.
b.
c.
d.
5. The elongation product in a rod (by its own weight) of length (L) and diameter (d) rigidly
fixed at the upper end and hanging is equal to
a.
b.
c.
d.
6. When Bulk modulus and Youngs modulus are same, then Poissons ratio will be
a. 1/2
b. 2/3
c. 1/3
d. 4/3
7. Bulk modulus is ratio of
a. Longitudinal stress / longitudinal strain
b. Shear stress / shear strain
c. Direct stress / volumetric strain
d. Lateral strain / linear strain
8. Hooks law holds good upto
a. Proportional limit
c. Elastic limit
b. Yield point
d. Plastic limit
9. When a bar is subjected to change in temperature and its deformation is prevented which of
the following stress is induced
a. Thermal Stress
b. Shear stress
c. Tensile stress
d. Compressive stress
10. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
a. Stress is directly proportional to strain within elastic limit.
b. The stress is force per unit area.
c. Hooks law holds good upto breaking stress.
d. The ratio of liner stress to linear strain is called Youngs modulus
Prof. Sameer Shaikh (VVPIET, Solapur)
Term Work
S.E. MECH (A & B)
1. Define Youngs modulus and modulus of rigidity. Derive relation between Youngs
modulus E and modulus of rigidity C in terms of Poissons ratio.
2. The following data relate to a bar subjected to a tensile test :
a. Diameter of bar, d = 30 mm
b. Tensile load, P = 54 kN
c. Gauge length, L = 300 mm
d. Extension of the bar, l = 0.112 mm
e. Change in diameter, d = 0.00366 mm
Calculate: i) Poissons ratio. ii) The values of E, K and G.
3. What is bulk modulus? Derive and expression for Youngs modulus in terms of bulk
modulus and Poissons ratio. OR Derive the relation between bulk modulus and Youngs
modulus.
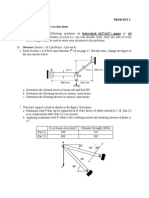
4. A bar of circular cross section, 70 mm diameter is supported and loaded as shown in figure.
Find the displacements of B and C. Take E = 200 GPa.
B
5 kN
500 mm
2 kN
1000 mm
200 mm
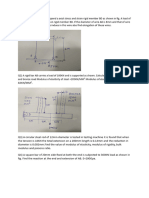
5. A steel rod AB of diameter 30 mm and length 680 mm is held between two supports at
ends A and B. Temperature of the rod is raised uniformly from 26 0C to 64 0C. Assuming
the rod to be stress free at 26 0C, find
a. Thermal stress and thermal strain, if the support do not yield.
b. Thermal stress and thermal strain, if one support yield by 0.2 mm.
Take E = 210 GPa, and = 12.5 x 10-6 / 0C
Also find the axial force in support in case b.
6. A mild steel plate is 4 mm in thickness. A square hole of size 30 mm x 30 mm is to be
punched in this plate. The ultimate shearing stress for the material is 354 MPa. Determine
the force required to punch the hole.
7. What do you mean by thermal stress and strain? State required expressions?
Prof. Sameer Shaikh (VVPIET, Solapur)
You might also like
- Strength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainFrom EverandStrength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- FMEM MCQsDocument162 pagesFMEM MCQsjawaliyaabhishek1312No ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument54 pagesStrength of MaterialsShimuye GetachewNo ratings yet
- DR. BABASAHEB AMBEDKAR TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MID SEMESTER EXAMDocument2 pagesDR. BABASAHEB AMBEDKAR TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MID SEMESTER EXAMdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- University of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesDocument11 pagesUniversity of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesTroy SundoNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Strength of Materials Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocument11 pagesMCQ in Strength of Materials Part 1 ECE Board Examlance galorportNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structure QuestionsDocument45 pagesTheory of Structure Questionsanamika shrivastavNo ratings yet
- Simple StrainDocument36 pagesSimple StrainMartina CelsoNo ratings yet
- Telegram-Solid Mechanics Civil 2nd YearDocument244 pagesTelegram-Solid Mechanics Civil 2nd YearinvestorNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering (Paper-I) Objective QuestionsDocument18 pagesCivil Engineering (Paper-I) Objective QuestionsvishnupsudhakaranNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: 50 Multiple Choice Questions For SSC JE EXAM-2020Document14 pagesStrength of Materials: 50 Multiple Choice Questions For SSC JE EXAM-2020Yogendra Kumar100% (2)
- Mos 07062012Document2 pagesMos 07062012Bhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Questions and Answers Objective Type111111Document36 pagesStrength of Materials Questions and Answers Objective Type111111Bipul Prince BarmanNo ratings yet
- Forces & Moments, Stress, Strain, Displacement, Support Reaction, EtcDocument12 pagesForces & Moments, Stress, Strain, Displacement, Support Reaction, EtccerebralnomadNo ratings yet
- Me2003d Solid Mechanics - 16-11Document164 pagesMe2003d Solid Mechanics - 16-11Vidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument833 pagesStrength of MaterialsSuvendu ParidaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Material in Mechanics of Deformable Bodies (CE BSC 232b)Document15 pagesInstructional Material in Mechanics of Deformable Bodies (CE BSC 232b)Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Mechanical Engineering 2007 Paper IIDocument14 pagesIES OBJ Mechanical Engineering 2007 Paper IIGopal KrishanNo ratings yet
- TestDocument51 pagesTestAdriane Gabrielle BautistaNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and Strain Relationship: Stress and Strain in Two Dimensions, Principal Stresses, Stress Transformation, Mohr's CircleDocument67 pagesSimple Stress and Strain Relationship: Stress and Strain in Two Dimensions, Principal Stresses, Stress Transformation, Mohr's CircleMushini NagabhushanNo ratings yet
- Ce6306 Strength of MaterialsDocument21 pagesCe6306 Strength of Materialsmithunarjun10108No ratings yet
- Deformable BodiesDocument4 pagesDeformable BodiesChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- SSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For CIVIL 5Document18 pagesSSC Junior Engineer Question Papers For CIVIL 5Agnibesh Dasgupta0% (1)
- Chapter 1 - STRESS AND STRAIN PDFDocument34 pagesChapter 1 - STRESS AND STRAIN PDFnurul eryn100% (1)
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Document3 pagesEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials MCQsDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials MCQsddeepak123No ratings yet
- Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pagesEs 13 Prob Set 1Julian de LaraNo ratings yet
- 63309Document13 pages63309amdevaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Hooke's Law, Poisson's Ratio, Axial DeformationDocument29 pagesMechanics of Materials Hooke's Law, Poisson's Ratio, Axial DeformationDiradiva DitaNo ratings yet
- Mos QBDocument15 pagesMos QBKarnalPreethNo ratings yet
- Som WordDocument130 pagesSom Wordmadicharla nikhilNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials MCQDocument10 pagesStrength of Materials MCQgowthami sirana baluNo ratings yet
- Mechanics (Finals)Document6 pagesMechanics (Finals)Sherwin ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- A. Poisson's Ratio: Strength of MaterialsDocument31 pagesA. Poisson's Ratio: Strength of MaterialsAmpolNo ratings yet
- Module 1 StressDocument20 pagesModule 1 StressKylla Shane DuntonNo ratings yet
- 45662597562obj CivilEngineering 2006paper IDocument18 pages45662597562obj CivilEngineering 2006paper I94738183No ratings yet
- STRENGTH OF MATERIALS DOCUMENT ANALYSISDocument24 pagesSTRENGTH OF MATERIALS DOCUMENT ANALYSISsarul_murugan2483No ratings yet
- Stress and Strain RenewDocument65 pagesStress and Strain Renewshafarizy100% (1)
- Som Book 2019 - Final BookDocument70 pagesSom Book 2019 - Final BookSubhash NaiduNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument60 pagesStress and StrainMuhammad Shafie100% (1)
- Strength of Materials QuestionsDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials QuestionsLawrrence LozanoNo ratings yet
- Assigment 3Document8 pagesAssigment 3Zoheb ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Shearing DeformationDocument21 pagesShearing DeformationRyan Joseph Rabino100% (1)
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper IDocument18 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2006 Paper ISudharsananPRSNo ratings yet
- CCB 241 - Assignment 1 - Due On 21 Feb. 2023Document7 pagesCCB 241 - Assignment 1 - Due On 21 Feb. 2023aaschlysebakisoNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Mid Exam Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials Mid Exam Questions and Answerssrihari_bhadabhagniNo ratings yet
- Extended All SOM MCQs - pdf-1-5000Document5,000 pagesExtended All SOM MCQs - pdf-1-5000202D099 Amit D GuruleNo ratings yet
- LE1 Problem Set PDFDocument14 pagesLE1 Problem Set PDFJunhong BapNo ratings yet
- Manual Mechanics of Deformable Bodies 3Document48 pagesManual Mechanics of Deformable Bodies 3Miyamura IzumiNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument6 pagesStrength of MaterialsSheryll de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument60 pagesStrength of MaterialsRam AcNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material (Stress and Strain)Document31 pagesStrength of Material (Stress and Strain)Mg SicsicNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Simple Stresses and StrainsDocument6 pagesUnit - I Simple Stresses and StrainsNavin SinghNo ratings yet
- Structural MembersDocument14 pagesStructural MemberscataiceNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2. Bending TestDocument5 pagesExperiment 2. Bending TestLana AlakhrasNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2007 Paper IDocument15 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2007 Paper Iravi maharajNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- V. V. P. Institute of Engineering & Technology, SolapurDocument3 pagesV. V. P. Institute of Engineering & Technology, SolapurSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 02Document24 pages02Sameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Details of Competitive ExamsDocument18 pagesDetails of Competitive ExamsSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- M.E. Mechanical Design - SyllabusDocument36 pagesM.E. Mechanical Design - SyllabusSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Annex-III-pg Rules Revised Dbatu 2013Document11 pagesAnnex-III-pg Rules Revised Dbatu 2013Sameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- USB StickDocument3 pagesUSB StickSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic Features: 2.1 Simple MathDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Basic Features: 2.1 Simple MathSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Assignment 1 - Scalar OperationsDocument2 pagesMATLAB Assignment 1 - Scalar OperationsSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Iso Shaft Support-ModelDocument1 pageIso Shaft Support-ModelSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Cross Head Model1Document1 pageCross Head Model1Sameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 6: CNC TechnologyDocument23 pagesChapter No. 6: CNC TechnologySameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Assignments 2013 14Document6 pagesAssignments 2013 14Sameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Cross Head Model1Document1 pageCross Head Model1Sameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 29 ModelDocument1 page29 ModelSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity PrecastDocument38 pagesPile Capacity Precastbasum matNo ratings yet
- Transition From One-Way To Two-Way Shear PDFDocument14 pagesTransition From One-Way To Two-Way Shear PDFAdhi MukminNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Composite Drive Shaft Using Ansys AcpDocument8 pagesAn Analysis of Composite Drive Shaft Using Ansys AcpTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Soil Young's ModulusDocument4 pagesSoil Young's ModulusHK KhooNo ratings yet
- Vibroreplacement PDFDocument9 pagesVibroreplacement PDFthadikkaranNo ratings yet
- Engineering Seismology Ch 1Document60 pagesEngineering Seismology Ch 1prashmceNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Deep Foundations, Including Liquefaction-Induced DowndragDocument30 pagesSeismic Design of Deep Foundations, Including Liquefaction-Induced DowndragM IslamNo ratings yet
- CyclicFoundationDesign_Prague_Masin_2023Document32 pagesCyclicFoundationDesign_Prague_Masin_2023Peteris SkelsNo ratings yet
- Combined Shear and TensionDocument16 pagesCombined Shear and TensionDAN MARK OPONDANo ratings yet
- Study On Analysis of Flexible Pavement Using Finite Element Based Software Tool IJERTV4IS090865Document5 pagesStudy On Analysis of Flexible Pavement Using Finite Element Based Software Tool IJERTV4IS090865pravin surveNo ratings yet
- Cracked Slab Analysis Compared to Published ExampleDocument8 pagesCracked Slab Analysis Compared to Published ExampleGemechuNo ratings yet
- UNITEC-Geotechnical Engineering B 6045 2013 s2Document9 pagesUNITEC-Geotechnical Engineering B 6045 2013 s2donNo ratings yet
- 11 Slope Stability PDFDocument20 pages11 Slope Stability PDFMohamed MuayidNo ratings yet
- Stiffness Analysis of Parallel Leaf-Spring Flexures: RZ Direction Can Be Approximated Based On CDocument4 pagesStiffness Analysis of Parallel Leaf-Spring Flexures: RZ Direction Can Be Approximated Based On CmdrehmerNo ratings yet
- TCC42 Post Tensioned Analysis & DesignDocument17 pagesTCC42 Post Tensioned Analysis & Designhala_azhariNo ratings yet
- Effect of Ambient Vibration On Solid Rocket Motor Grain and Propellant/liner Bonding InterfaceDocument7 pagesEffect of Ambient Vibration On Solid Rocket Motor Grain and Propellant/liner Bonding InterfaceZehra KabasakalNo ratings yet
- Rail-Structure Interaction-Midas-Analysis PDFDocument17 pagesRail-Structure Interaction-Midas-Analysis PDFabdullahNo ratings yet
- 02 - STRUCTURE - 01 - European Fitness For Service Network (FITNET) Fatigue Module DevelopmentDocument10 pages02 - STRUCTURE - 01 - European Fitness For Service Network (FITNET) Fatigue Module DevelopmentnotsofarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Behavior of Concrete-Filled Aluminum Tubular Stub Columns Under Axial Compression, 2019 (Fa-Cheng Wang) PDFDocument10 pagesAnalytical Behavior of Concrete-Filled Aluminum Tubular Stub Columns Under Axial Compression, 2019 (Fa-Cheng Wang) PDFPhan Đào Hoàng HiệpNo ratings yet
- Understanding Viscosity: Newton's Law of ViscosityDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Viscosity: Newton's Law of ViscosityMufeesNo ratings yet
- Stress Paths Effects On Multistage Triaxial TestDocument10 pagesStress Paths Effects On Multistage Triaxial TestCandra NishfaNo ratings yet
- Pressuremeter TestDocument9 pagesPressuremeter TestASAMENEWNo ratings yet
- DBMT SHV01 PDFDocument56 pagesDBMT SHV01 PDFRitxar DfNo ratings yet
- ENGR 340 - Foundations 3 - Ashlock - SchaeferDocument36 pagesENGR 340 - Foundations 3 - Ashlock - SchaeferSnaz_nedainNo ratings yet
- 27 - Romana Slope Mass RatingDocument45 pages27 - Romana Slope Mass RatingChocolatos PanasNo ratings yet
- Steel Design QDocument3 pagesSteel Design QDave JarangueNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress & Material Properties & Testing: Soil Mechanics & Foundation EnggDocument25 pagesSimple Stress & Material Properties & Testing: Soil Mechanics & Foundation EnggConceptual GATE & ESENo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Mekanika Tanah Direct Shear Test UIDocument11 pagesLaporan Praktikum Mekanika Tanah Direct Shear Test UIsipilPI12No ratings yet
- Common Mistakes in Fatigue AnalysisDocument14 pagesCommon Mistakes in Fatigue AnalysismuhannedNo ratings yet