Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 6: Frequency Reuse Concepts: A. Fixed Channel Assignment
Uploaded by
Smitesh MukaneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 6: Frequency Reuse Concepts: A. Fixed Channel Assignment
Uploaded by
Smitesh MukaneCopyright:
Available Formats
EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communications (082)
Dr. Wajih A. Abu-Al-Saud
Lecture6:FrequencyReuseConcepts
ChannelAssignmentStrategies
Channelassignmentaffectstheperformanceofthesystem,especiallywhenitcomestohandoffs.There
areseveralchannelassignmentstrategies.Wewilldiscusstwobasictypes:
A. Fixed Channel Assignment
In this channel assignment, channels are preallocated to different cells meaning that each cell is
assignedaspecific numberofchannelsandthefrequenciesofthesechannelsareset.Suchachannel
assignmenthasthefollowingaspects:
1. Any call attempts in a cell after all channels of that cell become occupied gets BLOCKED
(meaningthatthecallergetsasignalindicatingthatallchannelsareoccupied),
2. Verysimpleandrequiresleastamountofprocessing,
3. AvariationofthismethodistheBorrowingStrategy:
a. Cellsinthisstrategyareallowedtoborrowchannelsfromadjacentcellsiftheirchannels
arefullyoccupiedwhileadjacentcellshavefreechannels,
b. MSC(MobileSwitchingCenter)monitorstheprocessandgivespermissiontoborrowing
celltoborrowchannelsputtinginmind(i)donatingcellisnotaffectedbytheborrowing
process,(ii)nointerferencewilloccurbymovingthechannelfromonecelltoanother.
B. Dynamic Channel Assignment
Inthischannelassignment,channelsareNOTpreallocatedtoanycellsmeaningthatanychannelcanbe
allocated to any desired cell during the operation of the system. Such a channel assignment has the
followingaspects:
1. MSCmonitorsallcellsandallchannels,
2. Eachtimeacallrequestismade,servingBSrequestsachannelfromtheMSC,
3. MSCrunsanalgorithmthattakesintoaccount:
a. Possibilityoffutureblockingincells
b. Frequencybeingusedforchannel
c. Thereusedistanceofthechannel
4. MSCassignsachannelonlyifitisnotusedandifitwillnotcausecochannelinterferencewith
anycellinrange,
5. Thisalgorithmprovideshighercapacity(lessblocking),
6. Itrequireshugecomputationalpower,
7. MSCcollectsrealtimedataofchanneloccupancy,trafficdistribution,andradiosignalstrengths
indicators(RSSI).
EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communications (082)
Dr. Wajih A. Abu-Al-Saud
Lecture6:FrequencyReuseConcepts
HandoffStrategies
Handoff(H.O.)istheprocessoftransferringanactivecallfromonecelltoanotherasthemobileunit
movesfromthefirstcelltotheothercellwithoutdisconnectingthecall.Theamountofreceivedpower
by the mobile phone or the amount of received power by the tower or both are usually used to
determinewhitheraH.O.isnecessaryornot.Thefollowingpointsareputintomind:
Most systems give higher priority to H.O. over call initiation (it is more annoying to have an
activecalldisconnectedthantohaveanewcallblocked),
Handoffsmustbecompletedsuccessfullyasmuchaspossibleasinfrequently(asfewtimes)as
possibleandmustbeunnoticeabletotheuser(theusershouldnotfeeltheH.O)
Tomeettheserequirements,twopowerlevelsaredefined:
Minimumacceptablesignaltomaintainthecall PMinimum to maintain call :thisistheminimumpower
receivedbythemobilephoneortowerthatallowsthecalltocontinue.Oncethesignaldrops
below this level, it becomes impossible to maintain the active call because the signal is too
weak(noiselevelbecomeshighrelativetosignallevel).Thisisafundamentalpowerlevelthat
isusuallyintherangeof100dBmto90dBm(0.0000000001mWto0.000000001mW).
HandoffThreshold PThreshold :thispowerlimitisusuallyselectedtobefewdBs(5dBto10dB)
abovetheminimumacceptablesignaltomainthecalllevel.
Themargin = PThreshold PMinimum to maintain call shouldnotbetoolargeortoosmall.Ifitis:
o Too large, unnecessary handoffs will occur because the handoff threshold is high and
willbereachedveryoftenevenwhilethemobilephoneisstilldeepinsidetheserving
cell.Unnecessaryhandoffsputalotofstrain(alotofwork)ontheMSCandsystemand
reducenetworkcapacitybecauseoftheneedoffreechannelsinothercells,
o Toosmall,callsmaygetdroppedbeforeasuccessfulhandofftakesplacebecausenot
enoughtimeisavailableforthehandoffwherethesignalpowerwilldropveryquickly
fromthehandoffthresholdtotheminimumpowertomaintainacall.
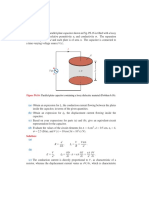
Thefollowingtwofiguresshowtwohandoffsituations.Inthefirstcase,asuccessfulhandofftakesplace
where the mobile phone is switched from one tower to another while in the second case, the signal
power drops to the minimum value needed for maintating a call and the call is dropped without a
handoff.
EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communications (082)
Dr. Wajih A. Abu-Al-Saud
Lecture6:FrequencyReuseConcepts
Power received
by Mobile Phone
Handoff Threshold
Minimum power to
maintain call
Handoff
Occurred Here
Successful Handoff
Power received
by Mobile Phone
Handoff Threshold
Minimum power to
maintain call
Handoff did not occur,
Call was dropped
Unsuccessful Handoff
3
EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communications (082)
Dr. Wajih A. Abu-Al-Saud
Lecture6:FrequencyReuseConcepts
Whenstudyinghandoffs,weneedtoobservethefollowingpoints:
Duringhighdemandtimes(whenmostchannelsareoccupied),excessivedelayinhandoffmay
occur because of high computational load on the MSC, which may cause signal power of calls
needingahandofftoreachlevelofminimumpowertomaintainacall.
MSC has to ensure that any drop in signal power is not due to signal fluctuations (it has to
monitor the signal over relatively long periods of time). So, MSC monitors signal power to
determineifthemobileunitismovingaway,stationary,ormovingcloser.
Speedofmobileunitdeterminestimeneededforhandoff:
o Forslowdropinpower,slowhandoffsispossible,
o Forfastdropinsignal power,fasthandoffisrequiredtoinsure thesignalpowerdoes
notreachtheminimumpowertomaintainacall.
You might also like
- Decrease Call BlockingDocument5 pagesDecrease Call BlockingTim KabiNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document24 pagesClass 3md sakhwat hossainNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Handoffs, Droped Calls and Cell Splitting: Ece/Liet C410 CMC Notes Sudheer Asst Prof ECE DeptDocument13 pagesUnit-V Handoffs, Droped Calls and Cell Splitting: Ece/Liet C410 CMC Notes Sudheer Asst Prof ECE DeptJeevan Sai MaddiNo ratings yet
- EEG473 Mobile Communications Module 2: Week # (5) : The Cellular Concept - System Design FundamentalsDocument21 pagesEEG473 Mobile Communications Module 2: Week # (5) : The Cellular Concept - System Design FundamentalsAnoop K. MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit V Handoffs & Dropped CallsDocument25 pagesUnit V Handoffs & Dropped Callsramanaidu1100% (3)
- Cellular Concept and System Design Fundamentals (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesCellular Concept and System Design Fundamentals (Chapter 3)WALEEDNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV HandoffsDocument9 pagesUNIT IV HandoffsMohammed WaqarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Mobile Networks: 1.cellular Wireless NetworkDocument45 pagesUnit 1 Mobile Networks: 1.cellular Wireless Networkdgk84_idNo ratings yet
- CHP2Part2Cellular ConceptDocument5 pagesCHP2Part2Cellular Conceptabdul wakeelNo ratings yet
- Unit One Wireless Communication: 1 Cellular SystemsDocument7 pagesUnit One Wireless Communication: 1 Cellular Systemsمجيد علاء خضيرNo ratings yet
- Various Handover Management Techniques in GSM Cellular SystemDocument4 pagesVarious Handover Management Techniques in GSM Cellular SystembinjibrilNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Basic Electronics Notes 2021Document32 pagesModule 5 Basic Electronics Notes 2021Sharanabasaveshwara H BNo ratings yet
- WC Assignment 3 RahmatDocument10 pagesWC Assignment 3 RahmatRahmatullah MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Channel Assignment Strategies - Handoff StrategiesDocument7 pagesChannel Assignment Strategies - Handoff StrategiesJean ReneNo ratings yet
- Channel Assignment StrategiesDocument15 pagesChannel Assignment StrategiesShahidan KirkukyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Assignment 1Document5 pagesMobile Computing Assignment 1Hey BroNo ratings yet
- Cellular Telephone NetworksDocument15 pagesCellular Telephone NetworksPragya100% (1)
- Draw The General View of Telecommunication and Explain The Function of The Each Unit?Document22 pagesDraw The General View of Telecommunication and Explain The Function of The Each Unit?Jeevan Sai MaddiNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: - Aarushi Srivastava IT-4 BbdniitDocument22 pagesAcknowledgement: - Aarushi Srivastava IT-4 BbdniitVarun LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Unit-Vii 1.why Hand Off Is Necessary ?: Cellular and Mobile Communications Questions & AnswersDocument12 pagesUnit-Vii 1.why Hand Off Is Necessary ?: Cellular and Mobile Communications Questions & AnswersShaik Maqsood HussainNo ratings yet
- Wireless CommunicationDocument15 pagesWireless CommunicationShahzebKhurshidNo ratings yet
- Cellular SystemDocument20 pagesCellular SystemAMINA SHEMAHONGENo ratings yet
- Ps1 MobileDocument6 pagesPs1 Mobilechikku090700No ratings yet
- Fundamental of HandoverDocument7 pagesFundamental of Handoverrajeshtripathi2004No ratings yet
- WC QBDocument23 pagesWC QBsandeep kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Operation of Cellular SystemsDocument12 pagesOperation of Cellular SystemsYerramilli SvramanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cellular FundamentalsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Cellular FundamentalsMilinda MendisNo ratings yet
- Ec8652 QBDocument15 pagesEc8652 QBTECH FROM ASHNo ratings yet
- Gaurav WCDocument24 pagesGaurav WCGaurav MishraNo ratings yet
- Cellular and Mobile Communication Question and AnswerDocument18 pagesCellular and Mobile Communication Question and Answerakvdmp100% (2)
- Rohini 36253873921Document5 pagesRohini 36253873921www.ayush000000No ratings yet
- Operation of Cellular SystemsDocument12 pagesOperation of Cellular SystemsNupur DewanganNo ratings yet
- CMC UNIT-1 Part-1Document24 pagesCMC UNIT-1 Part-1Dambu RNo ratings yet
- Lec5channel Assignment StrategiesDocument14 pagesLec5channel Assignment StrategiesSipan HazimNo ratings yet
- SR - No Topic Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8: Celluler Network Technology GSMDocument36 pagesSR - No Topic Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8: Celluler Network Technology GSMMahavir JadavNo ratings yet
- Handoff in Mobile Cellular CommunicationsDocument14 pagesHandoff in Mobile Cellular CommunicationsNitin SahuNo ratings yet
- Handoff StrategiesDocument35 pagesHandoff StrategiesAshima Aggarwal0% (2)
- Cellular Networks and InterfaceDocument62 pagesCellular Networks and InterfaceMd Alamin HossainNo ratings yet
- CHapter 2 - Cellular Wireless NetworksDocument82 pagesCHapter 2 - Cellular Wireless NetworksdhanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Practical No:-5: Aim: Study of Cellular Network Architecture. DefinitionDocument7 pagesPractical No:-5: Aim: Study of Cellular Network Architecture. DefinitionMsd Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- 19CBS1003 - Mobile Computing - TheoryDocument8 pages19CBS1003 - Mobile Computing - TheoryYala yoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 33celular Concepts (ECEg5307)Document128 pagesChapter 3 - 33celular Concepts (ECEg5307)nesredinshussen36No ratings yet
- ECS 445 Mobile Communications The CellulDocument16 pagesECS 445 Mobile Communications The CellulRAJAMANI BANDINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document71 pagesChapter 3Natnel TsehayeNo ratings yet
- CMC Unit 1 NotesDocument19 pagesCMC Unit 1 Notesdharani kodatiNo ratings yet
- 611 PDFDocument23 pages611 PDFNilNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument36 pagesModule 1 NotesKunwar Partap SinghNo ratings yet
- Cellular Mobile Communication Systems (EE-463) : Dr. Waleed Tariq SethiDocument66 pagesCellular Mobile Communication Systems (EE-463) : Dr. Waleed Tariq SethiAmnualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cellular 1Document131 pagesChapter 2 Cellular 1Selam TadeleNo ratings yet
- Cellular Access TechnologyDocument11 pagesCellular Access TechnologyKhandai SeenananNo ratings yet
- Handoff in Cellular Systems: Submitted By: Sireesha Vempati. Venkata Uppuluri. Vijaya PetlaDocument6 pagesHandoff in Cellular Systems: Submitted By: Sireesha Vempati. Venkata Uppuluri. Vijaya Petlaanc62No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Stalling)Document5 pagesChapter 10 (Stalling)Marufa Kamal LabonnoNo ratings yet
- Cellular and Mobile Communication: Handoff Strategies Prioritizing Handoff Practical Handoff ConsiderationsDocument20 pagesCellular and Mobile Communication: Handoff Strategies Prioritizing Handoff Practical Handoff ConsiderationsThiruGovindNo ratings yet
- Cellular & Mobile Communication NotesDocument22 pagesCellular & Mobile Communication NotesVamsi Krishna100% (6)
- Unit 5 CMCDocument8 pagesUnit 5 CMCTejasri ChokkapuNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document9 pagesModule 1Eric LucasNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Radio Resource Management in Multi-Tier Cellular Wireless NetworksFrom EverandRadio Resource Management in Multi-Tier Cellular Wireless NetworksNo ratings yet
- CQI Basics PDFDocument8 pagesCQI Basics PDFWale OgunniranNo ratings yet
- Tell Us About LTE Frame Structure?Document3 pagesTell Us About LTE Frame Structure?Smitesh MukaneNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM) : Li-Hsing Yen Assistant Prof. Dept. of CSIE, Chung Hua UnivDocument22 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM) : Li-Hsing Yen Assistant Prof. Dept. of CSIE, Chung Hua UnivVipul GargNo ratings yet
- Channel Assignment Strategies For Cellular Phone SystemsDocument26 pagesChannel Assignment Strategies For Cellular Phone SystemsSmitesh MukaneNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument35 pagesGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationNaveen PandeyNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Physical and Logical Channels Physical ChannelDocument22 pages4.4 Physical and Logical Channels Physical ChannelSmitesh MukaneNo ratings yet
- Tell Us About LTEDocument3 pagesTell Us About LTESmitesh MukaneNo ratings yet
- Aeolos-H 50kW BrochureDocument3 pagesAeolos-H 50kW BrochureFhjuefg DfrewrghtrNo ratings yet
- Distributed By:: Electronics Parts and KitsDocument8 pagesDistributed By:: Electronics Parts and KitsGonzalo RiveraNo ratings yet
- IBM TS7610 PortecTIER Deduplication Appliance Overview - TSD03107USENDocument2 pagesIBM TS7610 PortecTIER Deduplication Appliance Overview - TSD03107USENRaymund CatiisNo ratings yet
- Motorola Confidential Restricted: Product Technology APCDocument32 pagesMotorola Confidential Restricted: Product Technology APCCiro SneiderNo ratings yet
- Build An Arduino-LabVIEW Analog Voltmeter - ProjectsDocument7 pagesBuild An Arduino-LabVIEW Analog Voltmeter - ProjectsMelinia HdyNo ratings yet
- Chapter05 Systems 2020-03-04Document28 pagesChapter05 Systems 2020-03-04Ali GMNo ratings yet
- Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDS) : ProgrammingDocument10 pagesComplex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDS) : Programminganshu4u06No ratings yet
- DB750X UserManualDocument46 pagesDB750X UserManualBob GageNo ratings yet
- Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) : GeneralDocument47 pagesGas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) : Generalমোঃ মহসিনNo ratings yet
- As 2402.1.1-2005 Traction Batteries - Lead-Acid Vented Cells - RequirementsDocument7 pagesAs 2402.1.1-2005 Traction Batteries - Lead-Acid Vented Cells - RequirementsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Question Paper JEDocument11 pagesQuestion Paper JECSE SWRNo ratings yet
- Sepeaker Aktif POLYTRON PAS 67 - 68Document3 pagesSepeaker Aktif POLYTRON PAS 67 - 68Waton Rinekso0% (1)
- Die To Die Connectivity: Walter KatzDocument11 pagesDie To Die Connectivity: Walter KatzJouNo ratings yet
- 94 Isuzu Trooper Valve Cover RepairDocument5 pages94 Isuzu Trooper Valve Cover Repairturbopimp2000No ratings yet
- Complete EDM Handbook - 10Document8 pagesComplete EDM Handbook - 10peroz_ak47No ratings yet
- TYRE PRESSURE MONITORING USING ZIGBEE - Final NEWDocument39 pagesTYRE PRESSURE MONITORING USING ZIGBEE - Final NEWgauravkumar bhandariNo ratings yet
- Intake System: Parts LocationDocument7 pagesIntake System: Parts LocationMenzie Peter RefolNo ratings yet
- 6 16Document2 pages6 16Indira KarimovaNo ratings yet
- Heathkit CR-1Document2 pagesHeathkit CR-1SamRNo ratings yet
- ST3254.X ST3214.x Datasheet3Document1 pageST3254.X ST3214.x Datasheet3Alejandro HernandezNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Color Television Chassis: Cp-520Document85 pagesService Manual: Color Television Chassis: Cp-520Aivar SooneNo ratings yet
- High Voltage and Ustable States of MatterDocument21 pagesHigh Voltage and Ustable States of MatterSyedTamkanatMunirNo ratings yet
- Bridgewater HallDocument4 pagesBridgewater HallHuzaifa J AhmedabadwalaNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument6 pagesAnalytical ChemistryRodney Salazar0% (1)
- 3092 RC Stunt CarDocument2 pages3092 RC Stunt CarCooperNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of A Welding Transformer: IJRRAS 18Document10 pagesFinite Element Analysis of A Welding Transformer: IJRRAS 18Akash VermaNo ratings yet
- Intro To FPGA Design Using MATLAB and Simulink PublishedDocument31 pagesIntro To FPGA Design Using MATLAB and Simulink PublishedelectrocarbonNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3310.001.11s Taught by William Frensley (Frensley)Document6 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3310.001.11s Taught by William Frensley (Frensley)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- E Jac ManualDocument10 pagesE Jac ManualJhon Elier Arango TrillosNo ratings yet
- Iia Module Iii PDFDocument13 pagesIia Module Iii PDFgayathri vishnuNo ratings yet