Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Signs & Symptoms Lesions Are
Uploaded by
Alodia Ejorango CabigaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clinical Signs & Symptoms Lesions Are
Uploaded by
Alodia Ejorango CabigaoCopyright:
Available Formats
P4- ORAL PATHOLOGY
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
-
Epithelial malignancy
Squamous cell differentiation
Flattened polyhedral, round, ovoid
epithelial cells
Intracellular/ extracellular keratinization
Intercellular bridges
_____________________________________________
MALIGNANCY
Tumor:
-
New growth, mass
Malignant/ benign
Not Normal in the area
Cancer:
-
Unknown etiology
With predisposing factors
Benign Tumor:
Clinical signs & symptoms; Lesions are:
-
Fixed, sessile/ pedunculated
Slow growing
Asymptomatic
May become malignant
_____________________________________________
CARCINOMA VS. SARCOMA
-
Different locations
Different features
2.
-
EMBRYONAL REST THEORY
Cells are left forms growth
Remnant sometimes become malignant
DURING GROWTH
3. HUMORAL THEORY
- 4 Humors:
1) Blood
2) Phlegm
3) Yellow bile
4) Black bile
- Balanced = healthy
4. CANCER CELL THEORY
- Improved: Embryonal Rest theory
- Cancer cells:
o Renew & sustain organs & tissues
- Anti cancer therapies
o Shrink tumors
o But if it doesnt kill the cancer stem
cell tumor will grow back
5. POST FETAL THEORY
- Remnants of epithelial or CT develop to
new growth
- Alterations between epithelial & CT
- AFTER GROWTH
6. HEREDITY
- Genes to develop malignancy
7. CO-CARCINOGENESIS THEORY
Initiation Phase
-
Initiating agent that cause neoplastic
formation
Instantaneous effect (will just appear)
Irreversible changes
CARCINOMA
Promotion Phase
Epidermoid
Epithelial in origin
SARCOMA
-
Mesodermal
Mesenchymal in origin
_____________________________________________
THEORIES OF MALIGNANCY
1. VIRCHOW CHRONIC IRRITATION
THEORY
- Continuous/ constant irritation to normal
tissue
- Ex:
o Ill fitting denture
o Cheek biting
Non specific agents (Ex. Chronic irritants)
Action is prolonged
Effect is reversible
_____________________________________________
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
1. CHEMICAL AGENTS
- Strong acids
- Ex: Asbestos can cause injury to the cell
change in morphology or mutation can
result in malignancy
o Chemist; Factory workers
2. TOBACCO
- Time-dose relationship meaning:
CUMULATIVE
- Smoke, smokeless, reverse-smoking
- Mix it with other agents
o Betel nut, lime (acids)
Poor hygiene, poor nutrition, poor
immunity Lower chance to fight
3. PHYSICAL AGENTS
- Sunlight: UV
- Know carcinogen:
o BCCA: deeper
o SCCA: superficial
- Cumulative sunlight exposure
- Radiation alters cells
4. ALCOHOL
- Absinthe, ethanol
- Ethanol & tobacco
o Risk: Head & neck 100-fold
- Alcohol-containing mouthwash although
not really proven
5. AGE
- Risk increases with age. Why?
o Immune system compromised
6. NUTRITIONAL STATUS
- Increase risk if you lack Vit. A, D & E
- Fe deficiency:
o Plummer-Vinson Syndrome
o Affects middle aged women
o Painful red tongue
o Mucosal atrophy &dysphagia
7. PREVIOUS RADIATION & CHRONIC
IRRITATION
- Mechanical trauma
- Ex: Ill fitting dentures
8.
-
BACTERIA/ VIRUSES/ FUNGI
Increase risk if untreated
Immunocompromised patient
TreponemaPallidum
EBV, HSV, HPV, cytomegalovirus
Candida albicans
_____________________________________________
5S IN ORAL MALIGNANCY
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Smoking
Spicy food
Spirits
Syphilis/ Sunlight
Sepsis
_____________________________________________
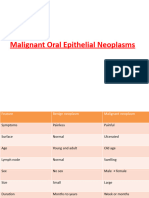
CLINICAL FEATURES
LIPS
-
25-30%
50-70 yrs old; M > F
Lower lip > Upper lip? Exposure to
sunlight
Vermillion, chronic non healing ulcers or
exophytic growths
Metastasis Local
submental&submandibular
Tx: Excise (Pre-op:
tanggalinnayungngipin)
TONGUE
-
25-40%
6th, 7th& 8th decade; M > F
45% post lateral border
25% post 1/3 or base of tongue
o Late detection. Why? Asymptomatic.
Rare dorsum or on tip of tongue
Asymptomatic
Indurated, non healing ulcer
Exophytic or endophytic pattern
Leukoplakia/ erythroplakia
FLOOR OF THE MOUTH
-
15-20% (2nd most common)
Older male smoker & drinkers
Painless, indurated, non healing ulcer
White or red patch
Cells infiltrate soft tissues causing
immobility of tongue (Invasion of tumor
cells)
Metastasis Submandibular lymph
nodes (Multiple organ metastasis)
BUCCAL MUCOSA & GINGIVA
-
10%, associated with smokeless tobacco
7th decade, Men
White patch, ulcer, exophytic lesion
Verrucous CA Broad based, wart like,
slow growing
Well differentiated, rare metastasis
Good prognosis
PALATE
-
10& Soft > hard palate
Older men
Soft: Faucial tissues (tonsils); 10-20%
Hard: Rare SCCA, common adeno CA
Asymptomatic red/ white plaques, ulcer,
keratotic masses
Metastasis cervical nodes
Commonly encountered in countries like
India. WHY?
o Spices & smokeless tobacco
_____________________________________________
NEOPLASMS
1. SCCA IN SITU
- Does not go beyond the basement
membrane; Does not invade
2. INVASIVE SCCA
- Breaks in the BM & spreads
3. SPINDLE CELL CA
- Similar to smooth cells showing a change
in morphology
6. PAPILLARY SCCA
7. MUCOEPIDERMOID SCCA
- Duct like structures
- Tx: Maxillectomy (Fabricate: Obturator)
4.
-
BASALOID SCCA
Base of tongue;
Basaloid pattern of tumor cells
Squamous cell differentiation
o (Islands)
8. NASOPHARYNGEAL SCCA
- Replicating
5.
-
VERRUCOUS SCCA
Very well differentiated
More hyperplastic than neoplastic
Invasive nature with broad, pushing
margins
o Like fingers = HARD TO REMOVE;
remove the block (whole)
_____________________________________________
EARLY SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Painless lump/ mass
Sore throat that does not heal for weeks
Progressive change in color
Fast growing
Chronic/ progressive thickening of lips/
membrane
6. Unexplained bleeding/ discharge
7. Difficulty in opening the mouth
- Especially saNaso SCCA kasilumalakina
tumor
8. Sudden appearance of swelling of the
neck
9. Dysphagia, hoarseness, cough
10. Unexplained numbness of lips
What to do when not sure?
o Check history
o Eradicate DD
o BIOPSY
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
HISTOLOGIC FEATURES
CLASSIFICATION
More undifferentiated, more malignant
1. Grade 1
- 75-100% well differentiated
2. Grade 2
- 50-75%
3. Grade 3
- 25-50%
4. Grade 4
- 0-25% (More malignant) Poorly
differentiated: Highly aggressive
_____________________________________________
TREATMENT
1.
2.
3.
-
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Keratinizing SCCA
Non-keratinizing SCCA
Moderately/ well differentiated
Keratin pearls
Inflammatory cells: Lymphocytes,
Plasma, Macrophage
6. Spindle shaped cells
(#5 & 6: Chronic in nature;
pag may Neutrophils = Acute)
_____________________________________________
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Radiation
Effective on less differentiated cells
40-70 Gy lymphomas
60-70 SCCA
Side effects:
o Pain
o Xerostomia
o Loss of taste
o Dysguesia
*Last: Palliative treatment
_____________________________________________
SIDE EFFECTS OF RADIOTHERAPY
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Mucosal ulcers
Pain
Dysguesia/ hypoguesia
Dermatitis
Candidiasis
Erythema
Alopecia (low)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
_____________________________________________
1. Ulcers (Non healing)
2. Clinical TB, syphilis, deep fungal
infections (oral infections)
3. Palate: Midline granuloma& necrotizing
sialometaplasia
4. Chronic trauma from factitial injuries may
also mimic SCCA
PROGNOSIS
-
Dependent on histologic subtype (grade)
& clinical extent (stage)
Age, gender, general health, immune
system
If SCCA metastasize: 5 years survival
rate is cut in half (25-50% 20%)
Secondary primary lesion 10% (1-2 years
after) Recurrence in another location
EX: less than 2cm tumor with no node & no
metastasis
_____________________________________________
STAGES
_____________________________________________
CLASSIFICATION
T (Tumor)
1.
2.
3.
4.
T1:<2cm
T2: 2-4cm
T3:>4cm
T4: Invades in adjacent area (Metastasis)
N (Node)
1.
2.
3.
4.
N0: None
N1:Ipsilateral (same side)
N2:Contralateral/ bilateral
N3: Fixed
M (Metastasis)
1. M0: None
2. M1: Distant M
1. Stage 1
- T1N0M0
2. Stage 2
- T2N0M0
3.
-
Stage 3
T1N1M0
T2N1M0
T3N0M0
T3N1M0
4.
-
Stage 4
T1N2M0
T1N3M0
T2N2M0
T2N3M0
T3N2M0
T3N3M0
T4N0M0
You might also like
- Oncology NursingDocument15 pagesOncology NursingArdrina Sappari100% (1)
- IMC College of Nursing Midwifery and Health Aide Students Report on Skin CancerDocument5 pagesIMC College of Nursing Midwifery and Health Aide Students Report on Skin CancerJeLai Lozano AbeciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing OncologyDocument208 pagesNursing OncologyfelxhuNo ratings yet
- Nursing OncologyDocument131 pagesNursing Oncologyapi-3818438100% (5)
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectrahulrohitnairNo ratings yet
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectsaralaNo ratings yet
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectShiva SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cancer NursingDocument93 pagesCancer Nursingnursereview100% (2)
- Study of Cancer: By: Zara Hayat Khan Xi-BDocument15 pagesStudy of Cancer: By: Zara Hayat Khan Xi-BLakki MalikNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cancer: A Study of Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Cancer: A Study of Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAfroz Alam Ki VinesNo ratings yet
- CH15 Patho D&R AgamDocument11 pagesCH15 Patho D&R AgamBio CheNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberration: Disturbance in Cellular FunctioningDocument78 pagesCellular Aberration: Disturbance in Cellular FunctioningAnne-Igi De Leon BermudezNo ratings yet
- Infancy & Childhood DiseasesDocument48 pagesInfancy & Childhood DiseasesDr. Janarthanan V100% (1)
- CASE STUDY #4 Integumentary System (Basal Cell Carcinoma)Document5 pagesCASE STUDY #4 Integumentary System (Basal Cell Carcinoma)Lerma PagcaliwanganNo ratings yet
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectIshaan AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Slide 15 Diseases of Salivary Glands IIDocument64 pagesSlide 15 Diseases of Salivary Glands IIJustDen09100% (1)
- Biology Project on Cancer Causes, Types and TreatmentDocument18 pagesBiology Project on Cancer Causes, Types and TreatmentAkash DixitNo ratings yet
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDipikaNo ratings yet
- Study of Cancer)Document17 pagesStudy of Cancer)rautshreyash22No ratings yet
- Cancer NursingDocument100 pagesCancer NursingGabriel Roco100% (1)
- Achondroplasia Ach: OMIM 2010Document56 pagesAchondroplasia Ach: OMIM 2010Sevil GasanovaNo ratings yet
- Case #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3Document10 pagesCase #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3api-536664543No ratings yet
- Understanding Ameloblastoma: A True Neoplasm of Enamel Organ TissueDocument51 pagesUnderstanding Ameloblastoma: A True Neoplasm of Enamel Organ TissueDrRobin SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology I ReviewDocument373 pagesOral Pathology I ReviewAlex ChangNo ratings yet
- Skin CancersDocument283 pagesSkin CancershaniNo ratings yet
- 1.understanding Cancer PPT LectureDocument184 pages1.understanding Cancer PPT LectureCherry Lou GuanzingNo ratings yet
- Mar Gregorios Memorial Central Public School: Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesMar Gregorios Memorial Central Public School: Biology Investigatory ProjectPavithra PNo ratings yet
- Lecture, 9Document38 pagesLecture, 9محمد ربيعيNo ratings yet
- Copy Oncology 1Document57 pagesCopy Oncology 1Brielle ShoppNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant Tumor of The Oral CavityDocument82 pagesBenign and Malignant Tumor of The Oral CavitymelNo ratings yet
- Paps SmearDocument51 pagesPaps SmearCatherine MerillenoNo ratings yet
- Oncology NursingDocument7 pagesOncology NursingBlitz KriegNo ratings yet
- Cancer NotesDocument9 pagesCancer NotesEmily CarlsonNo ratings yet
- Genpath NeoplasiaDocument35 pagesGenpath Neoplasiajulo_05No ratings yet
- What Is CancerDocument7 pagesWhat Is CancerDarlyn AmplayoNo ratings yet
- 1 Tmu - JD - 039Document4 pages1 Tmu - JD - 039Hasan BlackNo ratings yet
- 1 Tmu - JD - 039 PDFDocument4 pages1 Tmu - JD - 039 PDFKristina SabuNo ratings yet
- Metabolic and Deposition Disorders: Protein Energy Malnutrition, Amyloidosis, Porphyria, and Langerhans Cell HistiocytosisDocument55 pagesMetabolic and Deposition Disorders: Protein Energy Malnutrition, Amyloidosis, Porphyria, and Langerhans Cell HistiocytosisMAHMUDNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tumours - SreejaDocument184 pagesEpithelial Tumours - SreejaaakiNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Manjari Reshikesh Iv Bds Part Ii Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument51 pagesSubmitted by Manjari Reshikesh Iv Bds Part Ii Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgerykishoreNo ratings yet
- Cancer 2Document8 pagesCancer 2Faraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Malignant Tumor: 1. Basal Cell CarcinomaDocument3 pagesMalignant Tumor: 1. Basal Cell CarcinomaERIKA MARIZ DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With CancerDocument57 pagesCare of Patients With CancerAyessa Yvonne PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Sotos Syndrome / Cerebral Gigantism /: Clinical SynopsisDocument2 pagesSotos Syndrome / Cerebral Gigantism /: Clinical SynopsisAreef MuarifNo ratings yet
- History TakingDocument4 pagesHistory TakingDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Cancer IntroDocument29 pagesCancer Intromara5140No ratings yet
- Care of The Clients With Cancer: Prof. Hashim N. Alawi Jr. RN, MANDocument78 pagesCare of The Clients With Cancer: Prof. Hashim N. Alawi Jr. RN, MANjisooNo ratings yet
- 8 Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodDocument23 pages8 Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodBalaji DNo ratings yet
- Microbio 12Document5 pagesMicrobio 12Chicken AdoboNo ratings yet
- Hpe Final 110529Document98 pagesHpe Final 110529deeps.u.97No ratings yet
- Study of Cancer Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesStudy of Cancer Investigatory ProjectPankaj gola GolaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal PathologyDocument14 pagesGastrointestinal PathologyRahul ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Age Spots (Lentigines), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAge Spots (Lentigines), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandFanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Williams Syndrome, (Happy Elf Syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandWilliams Syndrome, (Happy Elf Syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Sebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unraveling Cancer: Progress and Future Directions in Cancer ResearchFrom EverandUnraveling Cancer: Progress and Future Directions in Cancer ResearchNo ratings yet
- Leukoplakia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLeukoplakia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ash Wednesday FINALDocument29 pagesAsh Wednesday FINALAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- The Trung Sisters: Vietnam's First Female Leaders Who Fought Chinese RuleDocument1 pageThe Trung Sisters: Vietnam's First Female Leaders Who Fought Chinese RuleAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Negative Impacts Caused by HumansDocument5 pagesNegative Impacts Caused by HumansAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Fiber Reinforced Composites As Fixed Space MaintainerDocument2 pagesFiber Reinforced Composites As Fixed Space MaintainerAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Snatiago V Sec of Public WorksDocument5 pagesHeirs of Snatiago V Sec of Public WorksAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Fiber Reinforced Composites As Fixed Space MaintainerDocument2 pagesFiber Reinforced Composites As Fixed Space MaintainerAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Fishery CodeDocument38 pagesFishery CodeAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Wanted WorkersDocument2 pagesWanted WorkersAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stone DiseaseDocument6 pagesKidney Stone DiseaseAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Atong Paglaum, Inc. Vs Commission On ElectionsDocument55 pagesAtong Paglaum, Inc. Vs Commission On ElectionsVERA FilesNo ratings yet
- Leveriza vs. Iyap 1Document8 pagesLeveriza vs. Iyap 1Alodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Iron vs. Steel Authority 2Document8 pagesIron vs. Steel Authority 2Alodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Gonzales Vs CADocument55 pagesGonzales Vs CAAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Tatad v. Garcia OriginalDocument35 pagesTatad v. Garcia OriginalRizza TagleNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Snatiago V Sec of Public WorksDocument5 pagesHeirs of Snatiago V Sec of Public WorksAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Eastern Shipping Lines Vs POEADocument6 pagesEastern Shipping Lines Vs POEASharon Padaoan RuedasNo ratings yet
- Gatchalian Vs CirDocument8 pagesGatchalian Vs CirElizabeth ReedNo ratings yet
- Bluebarco V TantuicoDocument9 pagesBluebarco V TantuicoAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- RA 10142 Financial Rehabilitation and Insolvency ActDocument25 pagesRA 10142 Financial Rehabilitation and Insolvency ActCharles DumasiNo ratings yet
- Class Officers: PRESIDENT: Marianne ClaireDocument4 pagesClass Officers: PRESIDENT: Marianne ClaireAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- General Oral Health CareDocument16 pagesGeneral Oral Health CareAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- SalesDocument10 pagesSalesJodivie MalnegroNo ratings yet
- Fishery CodeDocument38 pagesFishery CodeAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Salad MakingDocument2 pagesSalad MakingAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Two-Word Verb MeaningsDocument2 pagesTwo-Word Verb MeaningsAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Ledesma Vs MclachlinDocument3 pagesLedesma Vs MclachlinAlodia Ejorango CabigaoNo ratings yet
- The Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic On US Medical Students in Their Clinical YearsDocument3 pagesThe Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic On US Medical Students in Their Clinical YearsOmarNo ratings yet
- Physical Disabilities, Health Impairments, and ADHDDocument10 pagesPhysical Disabilities, Health Impairments, and ADHDZeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 1992 - 2007 KPDS İlgisiz Cümle SorularıDocument24 pages1992 - 2007 KPDS İlgisiz Cümle SorularıBilgin AkbabaNo ratings yet
- English: Third 2Document16 pagesEnglish: Third 2Andoy BarcebalNo ratings yet
- Biochemical ID of Salmonella and ShigellaDocument46 pagesBiochemical ID of Salmonella and ShigellaNurfadillamansyurNo ratings yet
- Feminist Perspectives On Values in Science - IntemannDocument15 pagesFeminist Perspectives On Values in Science - Intemannpanos stebNo ratings yet
- Radiation Therapy Template for Gynecological CancerDocument12 pagesRadiation Therapy Template for Gynecological CancerarifpharmjuNo ratings yet
- Benefits of a Low-Protein Diet for Kidney HealthDocument1 pageBenefits of a Low-Protein Diet for Kidney HealthLovely FinuliarNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument112 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYC100% (2)
- Myrin P ForteDocument3 pagesMyrin P ForteJohn Zedric Villanueva ArciagaNo ratings yet
- 3M Disposable Respirator 1860, 1860S, N95: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pages3M Disposable Respirator 1860, 1860S, N95: Technical Data SheetRoshidul AlomNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University College of Nursing Fundamentals of Nursing Practice Activity 4Document7 pagesCentral Mindanao University College of Nursing Fundamentals of Nursing Practice Activity 4Junaiza Adrayan MariNo ratings yet
- S Enz Farret2022 Article AntiseizureDrugsAndMovementDisDocument19 pagesS Enz Farret2022 Article AntiseizureDrugsAndMovementDisTajul TajNo ratings yet
- Cci Midterm Practice ExamDocument36 pagesCci Midterm Practice ExamMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Left Bundle Branch Block - UpToDateDocument25 pagesLeft Bundle Branch Block - UpToDateKrull TTTeamNo ratings yet
- Demyelinating DisordersDocument29 pagesDemyelinating Disordersbpt2100% (1)
- Ocular manifestation in COVID-19 patient: A case report of episcleritisDocument3 pagesOcular manifestation in COVID-19 patient: A case report of episcleritisHocie Trinanda SardiNo ratings yet
- 2021 Book Artificial Intelligence in OphthalmoDocument280 pages2021 Book Artificial Intelligence in OphthalmoSamir Ghouali100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Planleozel fulgeNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonographic Anatomy of Reproductive Female LeDocument13 pagesUltrasonographic Anatomy of Reproductive Female LeLaily IlmiNo ratings yet
- PF Pathfath EquipoDocument6 pagesPF Pathfath EquipoWilliams Alejandro Choroco VillegasNo ratings yet
- Health Care Delivery SystemDocument37 pagesHealth Care Delivery SystemMARICEL BAUTISTA MARAYAG100% (1)
- Health Consequences of Adverse Childhood Experiences: A Systematic ReviewDocument9 pagesHealth Consequences of Adverse Childhood Experiences: A Systematic ReviewCocia Podina Ioana RoxanaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Family and Nursing AssessmentDocument9 pagesConcept of Family and Nursing AssessmentJunry PilapilNo ratings yet
- Medical Diseases in The Surgical PatientsDocument33 pagesMedical Diseases in The Surgical PatientsGiovanni HenryNo ratings yet
- Vascular Access Type, Inflammatory Markers, and Mortality in Incident Hemodialysis PatientsDocument18 pagesVascular Access Type, Inflammatory Markers, and Mortality in Incident Hemodialysis PatientsYulius DonyNo ratings yet
- Scripta Ethnologica 1669-0990: IssnDocument40 pagesScripta Ethnologica 1669-0990: IssnJaime CoatzinNo ratings yet
- Concept Map PT 1Document1 pageConcept Map PT 1api-657741346No ratings yet
- Timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP 0.25% and 0.5%: Comparative Product InformationDocument5 pagesTimolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP 0.25% and 0.5%: Comparative Product InformationNur Utami PakayaNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Health Care in IndiaDocument17 pagesHistorical Development of Health Care in IndiaNikkash ÁrchiNo ratings yet