Professional Documents
Culture Documents
09 Mo1517
Uploaded by
TombongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
09 Mo1517
Uploaded by
TombongCopyright:
Available Formats
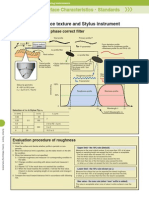
TECHNICAL DATA
EXCERPT FROM JIS B 0601
(1994)
AND JIS B 0031
(1994)
SURFACE ROUGHNESS
Categories of surface roughness
Definitions and indications for surface roughness parameters(for industrial products)
are specified.
They are arithmetical mean roughness(Ra)
, maximum height(Ry), ten-point mean roughness(Rz), mean
spacing of profile irregularities(Sm)
, mean spacing of local peaks of theprofile(S)and profile bearing length
ratio
(tp)
. Surface roughness is given as the arithmetical mean value for a randomly sampled area.
Mean center line roughness(Ra 75)
is defined in the annexes of JIS B 0031 and JIS B 0601.
Typical ways for obtaining surface roughness
Arithmetical mean roughness (Ra)
f() d
Ra
A section of standard length is sampled from the mean line on
the roughness chart. The mean line is laid on a Cartesian
coordinate system where in the mean line runs in the direction
of the x-axis and magnification is the y-axis. The value
obtained with the formula on the right is expressed in
micrometer(Om)when y=f()
.
Ra= R
R
R
Maximum peak (Ry)
Rv
Ry
Rp
A section of standard length is sampled from the mean line on
the roughness chart. The distance between the peaks and
valleys of the sampled line is measured in the y direction.
The value is expressed in micrometerr(Om).
Note: To obtain Ry, sample only the standard length. The part,
where peaks and valleys are wide enough to be interpreted
as scratches, should be avoided.
Ry=Rp+Rv
Ten-point mean roughness (Rz)
Rz=
Yp 5
Yp 4
Y V5
Y V4
Y V2
Y V3
Yp 3
Yp 2
Y V1
A section of standard length is sampled from the mean line on
the roughness chart. The distance between the peaks and
valleys of the sampled line is measured in the y direction.
Then, the average peak is obtained among 5 tallest peaks
(Yp)
, as is the average valley between 5 lowest valleys(Yv).
The sum of these two values is expressed in micrometerr(Om).
Yp 1
Yp 1 +Yp 2 +Yp 3 +Yp 4 +Yp 5 + Yv 1 +Yv 2 +Yv 3 +Yv 4 +Yv 5
5
Yp1 Yp2 Yp3 Yp4
Yp5: Tallest 5 peaks within sample
Yv1 Yv2 Yv3 Yv4
Yv5: Lowest 5 peaks within sample
Reference:Relationship between arithmetical mean roughness(Ra)and conventional symbols
Arithmetical mean roughness
Ra
Preferred number series
Cut-off value
(mm)
c
0.012
0.025
0.05
0.1
0.2
a
a
a
a
a
0.08
0.4
0.8
1.6
a
a
a
0.8
3.2
6.3
a
a
12.5
25
a
a
50
100
a
a
0.25
2.5
Max. height
Ry
Indication of surface
texture on drawings
0.012 ~ 0.2
Ten-point mean
roughness
Rz
Preferred number series
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.4
0.8
s
s
s
s
s
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.4
0.8
z
z
z
z
z
0.4
~ 1.6
1.6 s
3.2 s
6.3 s
1.6 z
3.2 z
6.3 z
3.2
~ 6.3
12.5 s
25 s
12.5 z
25 z
12.5
~ 25
50
100
50
~ 100
200
400
s
s
50
100
z
z
s
s
200
400
z
z
GThe interdependence for 3 classes is not strictly enforced.
GThe evaluation lengths of Ra: Ry and Rz:Five times the cut-off value and standard length respectively.
Standard length
of RyC Rz
R
(mm)
Triangular
indication
0.08
0.25
0.8
2.5
8
-
TECHNICAL DATA
TECHNICAL DRAWINGS-METHOD OF INDICATING SURFACE TEXTURE ON DRAWING
EXCERPT FROM
JIS Z B0031
(1994)
Positions of respective indicating symbols relative to indicating symbol of surface
Each grain surface position is indicated as shown in Drawing 7 This includes surface roughness,
cutoff value or reference length, processing method, symbol of direction of lay, surface waviness, etc.
Drawing7 Entry position of each indication
a:Value of Ra
b:Processing method
a
e
c
d
b
f
cV
g
c:Cutoff valueCvaluation length
:Reference lengthCvaluation length
cV
d:Symbol of direction of lay
f:Parameter other than Ra(With tp, parameter/cutoff level)
g:Surface waviness(according to JIS B 0610)
Note: Items other than a and f are added as necessary.
Reference: The location of lay of e in Drawing7 is given as the finish allowance in ISO 1302.
Symbol
Meaning
I Examples Indicating
Surface Texture on Drawing
Figure
Indicating symbol of surface
Parallel to the projected surface
on which the direction of lay of
the cutting blade is indicated.
(ex)Shaped surface
Direction of lay of cutting blade
Indicating symbol of surface
requiring removal press
Direction of lay of cutting blade
Indicating symbol of surface
on which no removal process is permitted
(ex)Shaped surface
(when viewed from the side),
machined or cylindrical
ground surface.
Direction of lay of cutting blade
Examples indicating
the upper limits of Ra
Intersection of two diagonal
lines on the projected surface
on which the direction of lay of
the cutting blade is indicated.
(ex)Honing finished surface
Multidirectional intersection or non-directional
point on the projected surface on which the
direction of lay of the cutting blade is indicated.
(a)
(b)
(c)
25
6.3
25
25
6.3
25
Direction of lay of cutting blade
Examples indicating direction of lay
(ex)Rapping finished surface,
super finished surface, face
milled or end milled surface
in surfacing feed direction
Concentric circles roughly
centered on the same on the
surface on which the direction
of lay of the cutting blade is
indicated.
Examples indicating the upper
limit and lower limit of Ra
(a)
(b)
6.3
1.6
(ex)Facing surface
Radiating shape roughly
centered on the same point on
the surface on which the
direction of lay of the cutting
blade is indicated.
6.3
1.6
Examples indicating processing method
(b)
(a)
Front milled
3.2
M
3.2
You might also like
- Jis B 0601 1994Document1 pageJis B 0601 1994amsubra8874No ratings yet
- Surface Roughness (JIS B 0601-2001)Document3 pagesSurface Roughness (JIS B 0601-2001)Prashantha Raju100% (3)
- Surface RoughnessDocument3 pagesSurface RoughnessRahul BetgeriNo ratings yet
- Surface FinishDocument38 pagesSurface FinishSunilNo ratings yet
- Amew101 Surface RoughnessDocument6 pagesAmew101 Surface Roughnessmoney_d_ochukoNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument6 pagesSurface RoughnessIltefatNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness - Geometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Document24 pagesSurface Roughness - Geometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Kishor kumar Bhatia100% (27)
- Surface TextureDocument20 pagesSurface TextureROHAN DESAINo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Guide for Engineering ComponentsDocument23 pagesSurface Roughness Guide for Engineering Componentslw124No ratings yet
- Criteria of Surface RoughnessDocument13 pagesCriteria of Surface RoughnessMadan JoshiNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Significance and SymboDocument18 pagesSurface Roughness Significance and SymboStefan NikolićNo ratings yet
- 2001 Engin Mechanicsanddynamicsofgeneralmillingcutters - PartIhelicalendmills IJMTDocument18 pages2001 Engin Mechanicsanddynamicsofgeneralmillingcutters - PartIhelicalendmills IJMTHamdan MacoNo ratings yet
- Surface Finish NotesDocument8 pagesSurface Finish NotesSuhailshah1234No ratings yet
- Cutting Force Modeling and Simulation of Tee Slot MillingDocument6 pagesCutting Force Modeling and Simulation of Tee Slot MillingJing YinNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Single Point Turning ToolsDocument9 pagesGeometry of Single Point Turning Tools21UME003 TUSHAR DEBNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument1 pageSurface Roughnessapi-3848892100% (2)
- Surface RoughnessDocument9 pagesSurface RoughnessKarthick DuraiNo ratings yet
- 22 - Kyocera Technical Information 2010-2011 (ENG)Document42 pages22 - Kyocera Technical Information 2010-2011 (ENG)HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument10 pagesSurface RoughnessBa TollohNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument8 pagesSurface RoughnessMahmoud S NasereddinNo ratings yet
- Surface Finish Guide for Engineering DrawingsDocument163 pagesSurface Finish Guide for Engineering DrawingsGilbert ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Vimp Theory of Metal Cutting 2Document100 pagesVimp Theory of Metal Cutting 2Harsh PawarNo ratings yet
- Single Point Cutting ToolDocument26 pagesSingle Point Cutting ToolBalabadra MaheshNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument20 pages11 - Chapter 2 PDFalmedin_hecimov8494No ratings yet
- Cutting Tool Geometry SystemsDocument26 pagesCutting Tool Geometry SystemsspectrogknNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness: StructureDocument10 pagesSurface Roughness: Structuremohamed1khalifa-2No ratings yet
- Group: Thurs (C) Hadeel Ali Al Jundi 0100558 Rand Saleh Shorouq Tarawenah Ola Khader Wafa ' HindiDocument13 pagesGroup: Thurs (C) Hadeel Ali Al Jundi 0100558 Rand Saleh Shorouq Tarawenah Ola Khader Wafa ' HindiNisreen ArabiyatNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Cutting Force Analysis in End MillingDocument11 pagesThree Dimensional Cutting Force Analysis in End Millingamsubra8874No ratings yet
- 1984 Surf Roughness PGDocument8 pages1984 Surf Roughness PGMaey AkimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document22 pagesChapter 5Shubham BhasinNo ratings yet
- Explanation of Surface RoughnessDocument8 pagesExplanation of Surface RoughnessN.Palaniappan100% (6)
- 1984 Surf Roughness PGDocument8 pages1984 Surf Roughness PGSajjan SNo ratings yet
- PDP- Understanding Surface Finish RequirementsDocument22 pagesPDP- Understanding Surface Finish RequirementsBollu SatyanarayanaNo ratings yet
- Surface Quality and Machining Symbols GuideDocument28 pagesSurface Quality and Machining Symbols GuideSudhir DwivediNo ratings yet
- Roughness ParametersDocument13 pagesRoughness ParametersAnoop KizhakathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Kaedah Penunjuk Bentuk Permukaan Ukuran Had Terima Fit Simbol Bentuk PermukaanDocument21 pagesChapter 4 Kaedah Penunjuk Bentuk Permukaan Ukuran Had Terima Fit Simbol Bentuk PermukaanhaziqismailNo ratings yet
- 1984 Surf Roughness PGDocument8 pages1984 Surf Roughness PGHussn YazdanNo ratings yet
- 3D Roughness ParametersDocument11 pages3D Roughness ParametersKarthi SundarNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Experimental Setup For The Proposed MLR-IPSRR SystemDocument5 pagesFigure 1. Experimental Setup For The Proposed MLR-IPSRR Systemasitzone4uNo ratings yet
- Empi105 Practical P&iDocument28 pagesEmpi105 Practical P&igupta rahulNo ratings yet
- Din 1302 SupplementDocument2 pagesDin 1302 SupplementRodrigo García Cruz100% (1)
- Manual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsFrom EverandManual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- The Volatility Surface: A Practitioner's GuideFrom EverandThe Volatility Surface: A Practitioner's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Combinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsFrom EverandCombinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Six-Figure Tables of Trigonometric Functions: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandSix-Figure Tables of Trigonometric Functions: Mathematical Tables SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Surfaces: A Practical Guide for Mechanical EngineersFrom EverandGeometry of Surfaces: A Practical Guide for Mechanical EngineersNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsFrom EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNo ratings yet
- Corrosion AllowanceDocument35 pagesCorrosion AllowanceReni Mutiara Sari50% (2)
- COM - Doosan TX Series Servo Drive Operation Manual (Rev B01) - 131204Document92 pagesCOM - Doosan TX Series Servo Drive Operation Manual (Rev B01) - 131204Tombong100% (1)
- Bolt MaterialDocument817 pagesBolt MaterialTombongNo ratings yet
- 17-4 PH Data BulletinDocument20 pages17-4 PH Data Bulletinekidazu19848816No ratings yet
- Measuring Taper With BallDocument5 pagesMeasuring Taper With BallTombongNo ratings yet
- O RingDocument89 pagesO RingNikolat84No ratings yet
- 13 Technical InformationDocument28 pages13 Technical InformationTombongNo ratings yet
- Mss sp-75 2004 PDFDocument9 pagesMss sp-75 2004 PDFNesrine MhedhbiNo ratings yet
- 0id ParameterDocument450 pages0id ParameterGustavo Adrián TorrettaNo ratings yet
- Laser Engraver K40ManualDocument25 pagesLaser Engraver K40ManualLiber666No ratings yet
- 5 ProgrammingDocument24 pages5 ProgrammingRaymond LO OtucopiNo ratings yet
- High Performance Turning CenterDocument24 pagesHigh Performance Turning CenterTombongNo ratings yet
- Tesr 4.catalog 2012 Final Wo Tables-030612-WEBDocument83 pagesTesr 4.catalog 2012 Final Wo Tables-030612-WEBTombong100% (1)
- Best TutorialDocument106 pagesBest TutorialTombongNo ratings yet
- Casinghardware Saga Trade Product RDocument37 pagesCasinghardware Saga Trade Product RTombongNo ratings yet
- Aisi SpecificationsDocument104 pagesAisi Specificationsnatrajiitm100% (1)
- Heavy Duty Vertical Machining Center VX750M/960MDocument6 pagesHeavy Duty Vertical Machining Center VX750M/960MTombong100% (1)
- Huanyang InverterDocument1 pageHuanyang InverterTombongNo ratings yet
- SM-78Ages and AveragesDocument14 pagesSM-78Ages and Averagespavan kumar kvsNo ratings yet
- Mean Median ModeDocument29 pagesMean Median ModeJc LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Testing of Fiber Reinforced ConcreteDocument254 pagesTesting of Fiber Reinforced ConcreteGurbirNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentEthan HuntNo ratings yet
- Glenn D Israel Sampling PDFDocument9 pagesGlenn D Israel Sampling PDFRischy SyhaputraaNo ratings yet
- One Sample t TestDocument26 pagesOne Sample t TestMax SantosNo ratings yet
- Measures of Relative SkewnessDocument32 pagesMeasures of Relative SkewnessKarl VillegasNo ratings yet
- Zscores HANDOUT PDFDocument56 pagesZscores HANDOUT PDFikhwanghazaliNo ratings yet
- CH No. 3: Measure of LocationDocument4 pagesCH No. 3: Measure of LocationSania IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating CreatingDocument4 pagesTable of Specification: Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creatingjake chuaNo ratings yet
- Percentiles & Normal Distr (2-3) BiostatisticsDocument12 pagesPercentiles & Normal Distr (2-3) BiostatisticsBlackstarNo ratings yet
- Discrete Data AnalysisDocument36 pagesDiscrete Data AnalysisDenise CheungNo ratings yet
- 2.9 Kiwi BirdsDocument3 pages2.9 Kiwi BirdsAidan GallenNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory FormulasDocument2 pagesQueuing Theory Formulasghkb4pxptxNo ratings yet
- Exponential SmoothingDocument7 pagesExponential SmoothingJerry FtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Two Sample InferencesDocument82 pagesChapter 10 Two Sample Inferencesscribdrules0101No ratings yet
- Quarter I - Week 5Document5 pagesQuarter I - Week 5Lowie D GacetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - ABM12 Group 2 - 1Document32 pagesChapter 1 - ABM12 Group 2 - 1Shann 2No ratings yet
- Statistics 2Document3 pagesStatistics 2Fadi Al-BzourNo ratings yet
- Bcom Prof Acc 2023 24Document88 pagesBcom Prof Acc 2023 24sree dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineering: Tutorials ForDocument18 pagesIndustrial Engineering: Tutorials ForYahya Abdelhameed AamerNo ratings yet
- Statistics-TryItAnswers HyLxP71Document109 pagesStatistics-TryItAnswers HyLxP71Starlynn McDanielNo ratings yet
- Confidence Interval EstimationDocument39 pagesConfidence Interval EstimationSamantha WeinertNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Fast Fashion Purchase Intentions Among Indonesian Gen-ZDocument12 pagesFactors Influencing Fast Fashion Purchase Intentions Among Indonesian Gen-ZSyrus Dwyane RamosNo ratings yet
- BBFH 103 NotesDocument38 pagesBBFH 103 NotesGivemore NyamutukwaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 QTDocument3 pagesAssignment-1 QTkumarshravan66712No ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation of LearningDocument22 pagesAssessment and Evaluation of LearningChristopher Celis100% (1)
- Investigating Data PDFDocument44 pagesInvestigating Data PDFOlivia Ngo100% (1)
- Palamuru University Statistics SyllabusDocument34 pagesPalamuru University Statistics SyllabusAmtech MubeenNo ratings yet













































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)