Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rigid Frame Structural Analysis and Design
Uploaded by
Fatima KhalidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rigid Frame Structural Analysis and Design
Uploaded by
Fatima KhalidCopyright:
Available Formats
APPLIED ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES:
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS
Rigid Frames
ARCH 631
composed of linear elements
member geometry fixed at joints
DR. ANNE NICHOLS
FALL 2013
no relative rotation
lecture
seven
statically indeterminate
see
rigid frames:
analysis & design
Rigid Frames 1
Lecture 7
Applied Architectural Structures
ARCH 631
shear
axial forces
bending moments
http:// nisee.berkeley.edu/godden
F2009abn
Rigid Frames 2
Lecture 7
Rigid Frames
Rigid Frames
rigidity
end
constraints
smaller
horizontal
members
larger
vertical
members
behavior
Rigid Frames 3
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 4
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames
Rigid Frames
resists lateral
loadings
shape depends on
stiffness of beams
and columns
90 maintained
moments get redistributed
deflections are smaller
effective column lengths are shorter
Rigid Frames 5
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frame Analysis
F2008abn
need support reactions
free body diagram each member
end reactions are equal and opposite on
next member
turn member
like beam
draw V & M
shear
axial force
bending
V & M diagrams
plot on outside
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
Rigid Frame Analysis
members see
Rigid Frames 7
Lecture 7
Rigid Frames 6
Lecture 7
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 8
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Analysis Methods
Rigid Frame Analysis
FBD & M
opposite end
reactions at joints
computer-based
matrix analysis or finite element analysis
equilibrium
support conditions
joint locations
relative stiffness of members
output
M+
deflections
member forces
http://eng.midasuser.com
Rigid Frames 9
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 10
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
Analysis Methods
Analysis Methods
RAM
approximate methods
F2008abn
presume where inflection points occur in
deformed shape
these points have zero moment
portal method
hinge is placed at the center of each girder
hinge is placed at the center of each column
shear at interior columns
is twice that of exterior
columns
Rigid Frames 11
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 12
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2009abn
Rigid Frames
Sidesway
member sizes do affect behavior
location of inflection points critical
translation with vertical load
Rigid Frames 13
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 14
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
Support Settlements
Multistory Frame Analysis
moments induced
cantilever method (approximate)
F2008abn
point of inflection at midspan of each beam
point of inflection at midheight
of each column
axial force in each column
proportional to the horizontal
distance of that column from the
centroid of all columns in the story
centroids are average locations
Rigid Frames 15
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 16
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2009abn
Multistory Frame Analysis
Rigid Frame Design - Types
cantilever method
(approximate)
Rigid Frames 17
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 18
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
Rigid Frame Design
Rigid Frame Design
materials
forms
steel
monolithic
concrete
laminated
wood
F2008abn
small
large
forms
small
Riola Parish Church, Alto Alvar
www.greatbuildings.com
single story, gabled frame, portal, hinged...
large - multistory
http:// nisee.berkeley.edu/godden
Rigid Frames 19
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2009abn
Rigid Frames 20
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frame Design
Rigid Frame Design
staggered truss
connections
rigidity
clear stories
steel
concrete
http:// nisee.berkeley.edu/godden
Rigid Frames 21
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 22
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
Rigid Frame Design
Rigid Frame Design
considerations
load combinations
need frame?
minimize moment (affects member size)
increasing stiffness
F2008abn
worst case for largest moments...
wind direction can increase moments
redistributes moments
limits deflections
joint rigidity
support types
Rigid Frames 23
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 24
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Combined Stresses & Design
Combined Stresses
axial + bending
beam-columns have moments at end
often due to eccentric load
P Mc
A I
M Pe
f max
design
f max Fcr
Rigid Frames 25
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 26
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Biaxial Bending
Eccentric Loading
when there is moment in two directions
find e such that the minimum stress = 0
f min
f cr
F .S .
P Pe c
0
A
I
M 1 P e1
M 2 P e2
P M y M z
f max 1 2
A
I
I
area defined by e from centroid is the kern
biaxial bending
y
B
b
e1
e2
z
+
x
M 2 P e2
Rigid Frames 27
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 28
Lecture 7
P
z
result
M 1 P e1
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Stress Limit Conditions
Stress Limit Conditions
ASD interaction formula
f a fb
1.0
Fa Fb
in reality, as the column flexes,
the moment increases
fa
Fa
P- effect
with biaxial bending
f a f bx f by
1.0
Fa Fbx Fby
Rigid Frames 29
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
fb
Fb
F2008abn
f a f b ( Magnification factor )
1.0
Fa
Fb
Rigid Frames 30
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
Design for Combined Stress
Tools Multiframe4D
satisfy
in computer lab
F2008abn
strength
stability
pick
section
Rigid Frames 31
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 32
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
Tools Multiframe4D
Tools Multiframe4D
frame window
to run analysis choose
Analyze menu
define frame members
Linear
or pre-defined frame
plot
select points, assign supports
select members,
assign section
load window
select point or member,
add point or distributed
loads
Rigid Frames 33
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
choose options
results
choose
options
F2008abn
Rigid Frames 34
Lecture 7
Architectural Structures III
ARCH 631
F2008abn
You might also like
- Structural Analysis II Notes Rev1Document106 pagesStructural Analysis II Notes Rev1Chris Jansen Van Rensburg100% (1)
- British Problem 5 PDFDocument5 pagesBritish Problem 5 PDFelixnzNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Clear Water Reservoir-3961Document15 pagesDesign and Analysis of Clear Water Reservoir-3961rrpenolio0% (1)
- Steady Flow in Pipes: BTB 323/ Cse 352 Hydraulics Edwin K. Kanda, PHDDocument19 pagesSteady Flow in Pipes: BTB 323/ Cse 352 Hydraulics Edwin K. Kanda, PHDErick WanduNo ratings yet
- Ref Books ListDocument2 pagesRef Books ListShubhankar KhareNo ratings yet
- Retainingwall 140712100253 Phpapp02 PDFDocument67 pagesRetainingwall 140712100253 Phpapp02 PDFDr-Hany HashishNo ratings yet
- CE8011 Design of Prestressed Concrete Structure - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument185 pagesCE8011 Design of Prestressed Concrete Structure - by WWW - Learnengineering.inSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Deflections in Thin PlatesDocument29 pagesDeflections in Thin PlatesPrashant KoteNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Design of Beams-Part 2Document41 pagesTopic 3 Design of Beams-Part 2Amirul Ashraf100% (1)
- Ce2404-Prestressed Concrete StructuresDocument1 pageCe2404-Prestressed Concrete StructuresDhivya RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis of Unbraced Portal Frames of Steel Structures in PDFDocument99 pagesPlastic Analysis of Unbraced Portal Frames of Steel Structures in PDFbiniamNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures 2017 PDFDocument45 pagesShell Structures 2017 PDFBilal Al-MuhtasebNo ratings yet
- Gantry Girder DesignDocument45 pagesGantry Girder DesignmonaliNo ratings yet
- Design of ColumnsDocument26 pagesDesign of ColumnsMandar NadgaundiNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing Design PDFDocument2 pagesCombined Footing Design PDFRenee100% (1)
- Design of Concrete & Masonry Structures: Dr. Ye Lu Lecture #7-2 (Week 7)Document20 pagesDesign of Concrete & Masonry Structures: Dr. Ye Lu Lecture #7-2 (Week 7)tien2506onlineNo ratings yet
- Domes, ShellsDocument20 pagesDomes, ShellsTenzin Phenz100% (1)
- Far Western University Civil Engineering CourseDocument5 pagesFar Western University Civil Engineering Coursedinesh100% (1)
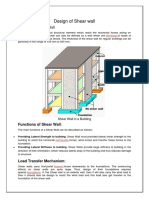
- Design of Shear Walls in BuildingsDocument3 pagesDesign of Shear Walls in BuildingsCHARINo ratings yet
- RCC Design TipsDocument9 pagesRCC Design Tipssatoni12No ratings yet
- Engineering Calculation Sheet Consulting EngineersDocument21 pagesEngineering Calculation Sheet Consulting EngineersParthiban Arivazhagan100% (1)
- Moment Distribution Method ExplainedDocument37 pagesMoment Distribution Method ExplainedSuleiman Yusuf JibrilNo ratings yet
- Lect2 - 1 11 2011 PDFDocument62 pagesLect2 - 1 11 2011 PDFgendadeyu552625100% (1)
- Prepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum FekheraldinDocument55 pagesPrepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum Fekheraldinhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- DDA 3164 BEAM Shear Deflection and CrackDocument20 pagesDDA 3164 BEAM Shear Deflection and CrackZayyan RomjonNo ratings yet
- Spread footing design for temporary bridgeDocument3 pagesSpread footing design for temporary bridgeFeras TemimiNo ratings yet
- Lever Rule For Computation of Live Load Distribution Factors in CONSPANDocument3 pagesLever Rule For Computation of Live Load Distribution Factors in CONSPANMuhammad Arslan100% (3)
- ACI Beam LedgeDocument7 pagesACI Beam LedgeMahmoud ShakerNo ratings yet
- Eccentric LoadDocument6 pagesEccentric LoadAtish Kumar100% (3)
- University of Mindanao College of Engineering EducationDocument42 pagesUniversity of Mindanao College of Engineering EducationLi LiNo ratings yet
- 10 FT Restrained Wall Design of CMU Wall: See Analysis BelowDocument1 page10 FT Restrained Wall Design of CMU Wall: See Analysis Belowmeetvinayak2007No ratings yet
- Designing compression piles according to Eurocode 7Document12 pagesDesigning compression piles according to Eurocode 7Aniket DNo ratings yet
- Masonry Design ExamplesDocument13 pagesMasonry Design ExamplesRoger FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Designing of Reinforce Concrete Deck Slab Bridge With Aashto (LRFD) Design SpecificationDocument54 pagesDesigning of Reinforce Concrete Deck Slab Bridge With Aashto (LRFD) Design SpecificationTharach JanesuapasaereeNo ratings yet
- Flexural Analysis of Singly Reinforced Beams-ExampleDocument2 pagesFlexural Analysis of Singly Reinforced Beams-ExampleFahad Areeb100% (1)
- Design of Composite ColumnsDocument7 pagesDesign of Composite Columnsabozaid19No ratings yet
- Notes On Design of RCC ElementsDocument3 pagesNotes On Design of RCC ElementsrangarajanNo ratings yet
- Example1 1-StraightsupportedDocument7 pagesExample1 1-StraightsupportedOmar BayouNo ratings yet
- LRFD Design of Full Height Abutment on Spread FootingDocument71 pagesLRFD Design of Full Height Abutment on Spread FootingJustinNo ratings yet
- Beam to beam design with landingsDocument10 pagesBeam to beam design with landingsUmesh ChamaraNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationDocument44 pagesPile FoundationKasim MalekNo ratings yet
- Design Recommendations For Steel Deck Floor SlabsDocument32 pagesDesign Recommendations For Steel Deck Floor Slabswayzane100% (1)
- Retainning WallDocument14 pagesRetainning Wallahamedtouhid899No ratings yet
- Ductile Beam Design PDFDocument72 pagesDuctile Beam Design PDFanirban nayekNo ratings yet
- Design of Timber Columns and Beam-ColumnsDocument41 pagesDesign of Timber Columns and Beam-ColumnsElvisLeeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Manual-6Document35 pagesEngineering Manual-6cengizNo ratings yet
- MnDOT LRFD 12-20-10Document898 pagesMnDOT LRFD 12-20-10Dan GatzNo ratings yet
- Basement Concrete WallDocument14 pagesBasement Concrete WallHabibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Calculation Note of Coulmn 162Document18 pagesCalculation Note of Coulmn 162Der3'am Al m7armehNo ratings yet
- Sample Portal AnalysisDocument63 pagesSample Portal Analysisacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Design Considerations for Prestressed ConcreteDocument23 pagesDesign Considerations for Prestressed ConcreteglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Timber dome structures for salt storageDocument6 pagesTimber dome structures for salt storageLidhia Fairuz HarlyNo ratings yet
- Structural engineering design problem set analysisDocument7 pagesStructural engineering design problem set analysisfegenbushNo ratings yet
- Slender Column Design and Two-way Slab AnalysisDocument83 pagesSlender Column Design and Two-way Slab Analysisshakirhamid6687100% (1)
- Case 1: Middle Span Carry Minimum LoadDocument10 pagesCase 1: Middle Span Carry Minimum Loadsam_cm100% (1)
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Concrete-Filled Double-Skin Steel Tubular Columns: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandConcrete-Filled Double-Skin Steel Tubular Columns: Behavior and DesignNo ratings yet
- Development of SurfacesDocument15 pagesDevelopment of SurfacesFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Document 408-425 summaryDocument18 pagesDocument 408-425 summaryFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Cki 03 PDFDocument163 pagesCki 03 PDFFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Mohr Circle1 PDFDocument5 pagesMohr Circle1 PDFFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- SAP2000 PresentationDocument63 pagesSAP2000 PresentationFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection Frame Problem Solutions PDFDocument8 pagesSlope Deflection Frame Problem Solutions PDFFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Strong Form and Weak FormDocument2 pagesStrong Form and Weak FormFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- IMPLICATION OF UNBONDEDNESSDocument13 pagesIMPLICATION OF UNBONDEDNESSFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Infills in OpenseesDocument11 pagesInfills in OpenseesFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Example Ccmpa 2009Document6 pagesExample Ccmpa 2009Fatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Final Gantt ChartDocument2 pagesFinal Gantt ChartFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Final Gantt ChartDocument2 pagesFinal Gantt ChartFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- 2003 CUREE ExcerptDocument24 pages2003 CUREE ExcerptFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Mech Anl 14.0 L02-Adv-PlasticityDocument28 pagesMech Anl 14.0 L02-Adv-PlasticityFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Vibrations: Free Response of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsDocument8 pagesVibrations: Free Response of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsCharlie TejNo ratings yet
- Applicatn For IspDocument1 pageApplicatn For IspFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Application For Entry PassDocument1 pageApplication For Entry PassFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-4: Creating & Editing Logs in BoreholesDocument1 pageLesson 1-4: Creating & Editing Logs in BoreholesFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Application For Entry PassDocument1 pageApplication For Entry PassFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- SAP General InformationDocument25 pagesSAP General InformationFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Shape Functions 5-Noded QuadDocument2 pagesShape Functions 5-Noded QuadFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Shape Functions 5-Noded QuadDocument2 pagesShape Functions 5-Noded QuadFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- CE 437/537 Retaining Wall Design ExampleDocument8 pagesCE 437/537 Retaining Wall Design ExampleJefferson Nobleza67% (3)
- Stiffness MatrixDocument12 pagesStiffness MatrixFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTUREDocument4 pagesARCHITECTUREFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Beam Analysis Using Stiffness MethodDocument148 pagesBeam Analysis Using Stiffness MethodArif WaitsNo ratings yet
- SAP2000 PresentationDocument63 pagesSAP2000 PresentationFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Synoptic Description of EarthquakesDocument2 pagesSynoptic Description of EarthquakesFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Measurement UnitsDocument4 pagesMeasurement UnitsFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- 692 Pressure SensorDocument5 pages692 Pressure SensorSyed Waheed Ul HasanNo ratings yet
- E 447 PDFDocument13 pagesE 447 PDFIsm el100% (1)
- Define Soil Stabilization?: UN IT - 5 ST Abi Liz Atio NDocument5 pagesDefine Soil Stabilization?: UN IT - 5 ST Abi Liz Atio Nhimabindugvsd71No ratings yet
- Jockey Pump 96517052 - CR - 520 - AFGJAEHQQEDocument8 pagesJockey Pump 96517052 - CR - 520 - AFGJAEHQQEShafa AlmaliyaNo ratings yet
- Helmet Color Code For Construction SitesDocument38 pagesHelmet Color Code For Construction SitesChandrasekhar ChintadaNo ratings yet
- Problem 8.3: u p f L 2D Δ = P pV p D 4 u = Δ = Δ &Document14 pagesProblem 8.3: u p f L 2D Δ = P pV p D 4 u = Δ = Δ &Siva PrasadNo ratings yet
- 00 Hvac CalcDocument52 pages00 Hvac CalcjosebolisNo ratings yet
- Reference Data - Metric Conversion ChartDocument20 pagesReference Data - Metric Conversion ChartmshedidNo ratings yet
- 6-With-Cover-Page-V2 221009 101917esen 221009 102139Document19 pages6-With-Cover-Page-V2 221009 101917esen 221009 102139ajskfdhasknNo ratings yet
- Transmission Conductors SouthwireDocument5 pagesTransmission Conductors SouthwireGunji Venkata Srinivasa BabuNo ratings yet
- Crystal GrowthDocument6 pagesCrystal GrowthArunmaalaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Protection Evaluation of Some Organic Coatings in Water Transmission LinesDocument2 pagesCorrosion Protection Evaluation of Some Organic Coatings in Water Transmission LinesGabo TellezNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Wire RopesDocument95 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Wire Ropesengrsyoti100% (1)
- API Storage Tank Job SpecificationDocument15 pagesAPI Storage Tank Job Specificationhuynhthanhtamga1981No ratings yet
- MDSReport 942254230Document183 pagesMDSReport 942254230javier ortizNo ratings yet
- Juntas EnchaquetadasDocument1 pageJuntas EnchaquetadasPablo PasqualiniNo ratings yet
- Knauf Insulation Solutions Guide en UkDocument136 pagesKnauf Insulation Solutions Guide en UkFANo ratings yet
- Conplast F292Document4 pagesConplast F292Mohammed AdilNo ratings yet
- PDPS Earth Fault L2 Rev Oct 20 PDFDocument167 pagesPDPS Earth Fault L2 Rev Oct 20 PDFMatthew WongNo ratings yet
- Com Brochure Luxacote - EN EUDocument12 pagesCom Brochure Luxacote - EN EUAli HasanNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection ProductsDocument56 pagesFire Protection ProductsHector Dario Tobon BenjumeaNo ratings yet
- STRESS AND STRAIN DEFINITIONS AND CALCULATIONSDocument2 pagesSTRESS AND STRAIN DEFINITIONS AND CALCULATIONSCalvin Jude GoveiaNo ratings yet
- Deflection and Stresses of Tapered BeamDocument56 pagesDeflection and Stresses of Tapered BeamRanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Aashto T 119Document6 pagesAashto T 119Regen BasiñoNo ratings yet
- Abu Dhabi Investment Council BuildingDocument7 pagesAbu Dhabi Investment Council BuildingJinaliDoshiNo ratings yet
- Webforge Access WebDocument32 pagesWebforge Access WebWajeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Solution To Problem 323 Torsion - Strength of Materials ReviewDocument1 pageSolution To Problem 323 Torsion - Strength of Materials ReviewMark ObcianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 FoundationDocument53 pagesChapter-3 Foundationkader ArefeNo ratings yet
- Physics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8Document9 pagesPhysics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8dhureyaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BEAMDocument25 pagesChapter 1 BEAMDawit TesfayNo ratings yet