Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Welding QC 18 - NDT
Uploaded by
Exsan OthmanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Welding QC 18 - NDT
Uploaded by
Exsan OthmanCopyright:
Available Formats
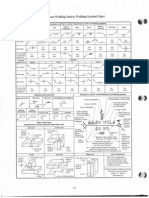
TWI
voot
THE WELDTNG I}{STITIJTE
S EC T IO N1 8
TWI
wot
THE wp1p1p6 nrsTITuTE-
NON DESTRUCTIVE
TESTTNG
Ultrasonic inspection
Colhode - ray
IUDE
Tronsmittd pu tse
Rellected pu tse
f ine /diyonce
scole
Sen siliYily
control
pulse
Type of operatlon:
Manualor mechanised
Rellec(edputse
Probe Gre ose
Work
oelecl
Equlpment:
Main unit containingpulsegenerator,
displayoscilloscope,
probe(chosento
suitwork).
Modeof operation:
A pulseof electricar
energy.isfed to the probein whicha piezo-erectric
crystal
convertsit to mechanicalvibrationsat an ultrasonicfrequency. ne vinratiim.
are transmitted(via a rayerof greaseto excrudethe air) throughthe work: if
they encountera defectsomeare reflectedbackto the probe,wherethey
regeneratean electricalsignal. A cathoderay tubetraceis startedwhenthe
originalsignalis sent,dispraysthe reflecteddlfect signar,and from it time,
indicatingdistancefrom probe,and ampritude,
indicating
defectsize,can be
calculated.
Materials:
Most metal,exceptthosewithcoarseor varyinggrainstructure
WELDING TECHNOLOGY
lssue 0191
1.1
T\)t/I
wor
THE \4I-DING NSTm_rfE
Overall advantages:
lmmediatepresentationof results
n:ed to move personnelout
lo
uan De Dafterypowered
Depth locationsof defects.
Overall limitations:
Trained and skiiledoperatorrequired
No pictorialrecord
Safety
Moderatecare neededas for other electronic
equipment.
to.z
WELDINGTECHN'LOGY
Issueolgl
i
T\4/I
wot
TE
WELDING U{STI|IJ-TE
Magneticparticleinspection
Currenl
t'lognelic t ietd
Type of operation:
Manuajor mechanised.
Equipment:
Powersupply
Contactsor coil
Ultra-violetla.rnp(optional)
Portableor fixedinstallation.
Mode of operation:
The work is magnetised
eitherby passinga currentthroughit, or through
a coil
surroundingit' Defectson or nearthe
surface
disrupt
the
magnetic
fierd
(unlessthey are para'el to
4 T;Sn;ti; p".ti"f" nriO suspensionis apptied
whichconcentrates
aroundit]
tre oetecis.-rn! ""riii! vrewecr
eitherdirecty or
by.-ultra-violet
lightsusinga dye whichfluoresces;
tfrat
is,
emitsvisibleliqht
(.nrsmustbe donewhere
normal
tishtins
is il;ili.'
be demagnetisedif required.
;iJ;'i;,i";, ;"H,;",
Materials:
Magnetic materialsonlv
Ferriticsteels
Some nickel ajlovs
WELDING TECHNOLOGY
Issue Ol gl
't9.3
II
T\^/I
wot
I,ELDING NSTrnJTE
Overalladvantages:
Directindicationof defectlocation
Initialinspection
by unskilled
labour(goor no_qo)
Someindicationof sub_surface
defecisOrt of il-ui,sensitivity
Not criticallydependenton surfacecondition.
Overalllimitations:
Io.use for non-magneticmaterials
uerectdetectioncriticarvdependenton arignment
Sub-surfaceflawsrequirespecialprocedures. acrossmagneticfield
Safety:
Moderatecare neededin handringerectric
equipment
and flammabre
fluids.
18.4
WELDING TECHNOLOGY
lssue O191
. :
TWI
Wg
T}|E !!T LDI Nc lr.'sTn-Lrf:
G a m m ar a d i o g r a p h y
Handle
Shulter
Shierding
P h al o gr a p h i c
I t g h l c o s s el l e
'-*!ource
So u r c en o l l e n V.in
0ock shteldtng
Xr
rQltoh
Type of operation:
Static
Development
maybe mechanrsed
Equipment:
Radioactiveisotopein storagecontalner
Hemotehandlinggear
Lightproof cassette
Photographic
development
facilities
uarKroomand illuminatorfor asses.sment
Mode of operation:
Gamma-rays, similarto X-rays, but
of shorterwaveleng,th
are emitted
continuouslyfrom the isotope:it cannot
o",rn i;n"J ofr, so that when not in
use it is kept in a heavy storage container
whiin J-"oro" radiation. They pass
nrough the work to be inspected. parts
of the work presentingless
gamma-rays, such as cavitiesof
inclusions,
-"
:.?:l'"]i"" i9
ajlow increased
exposure
of the firm' The firm is oevetopedl0
ro'i'ini.*n.ss
,uoiograph
with cavities
or inclusionsindicatedbv darker images.
s".tion
increases
(such as
weld) appear as les_sdense rmaqes.
Materials:
Most weldablemetalsmay be inspected_
WELDING TECHNOLOGY
Issue 0191
T\vI
70cr
THE W.ELDING NSTrn,TTE
X-radiographs
rleot ed colhode
Anade
tfork
Phologrophic
t rocualed
X-my
lube
X - rn".
Lighr- tighl
cosJe//e
rposure
View
Type of operation:
Staticor transportable.
Equipment:
X-ray tube
Standand controlqear
Ught-proof casset6
Photographic
development
facilities
uarK roomand illumination
for assessment.
Modeof operation:
X-rays are emittedfrom the
yf-" Td. eay throrlOhthe work to be inspected.
presentingtessobstruction
to Xlrays, sucn as cavitiesor
l^:P,:i!. alrow
,york
Incrusrons,
increasedexposureof the firm. 'r" dr r.
oevetofeJto rurm
a radiographwith cavities incrusions
i"oi*i"o
oy
ourr"'
images.
section
-orwetd
thicknessincreases(suchas
under-beaJi.oJ"o as ressdenseimaoes.
Materials:
Mostweldablemetalsmay be inspected.
19.6
WELDINGTECHNOLOGY
lssueOlgI
rI
T\VI
WZT$
THE \IELDINC INSTit-L-ta
Overall advantages:
AccuTatepictorialpresentation
of results
Radiographsmay be kept as a pernnanent
record
Not confined to welds
O v e r a l lI i m i t a t i o n s :
Personnelmust be clearof area duringexposure
Cracksparallelro film amy not show up
F m expenstve.
gog
INTERNATIONAL
RADIATIONWARNINGSYMBOL
Safety:
Cumulativeradiationrisk to personnelrequires
stringenrprecaLjtions.
WELDING TECHNOLOGY
Issue O19l
IE'.1
.I
T\)t/I
THE WELDING L\STMJTE
EXAMPLE OF IMAGE OUAUW INDTCATORS
Step-hole type
B S3 9 7 1
9FEI5
Wire t ype
18.8
Duplex t vDe
WELDING TECHNOLOGY
Is.sueO19l
:
T\MI
wot
rTHE ILDING
TNSTmI|E
Dye penetrantdetection
t:.t-2:?r,y,!r rbiii,,,u,o,,
pouderdevetoper
and exomine
utio-'ii'orct
Type of operation;
Manuajor mechanised
Equipment:
Min:
Max:
Aerosolscontaining
dye, developeretc.
Tanks_ worxhanJlini gear (in ir"
"ou" uttra_violet
tamp).
Modeof operation:
A specialdye is appriedto the surfaceof the
articreto be tested. An intervalof
1-10 min arrowsit to soak.into.any
"urru"" o"r".i"i The surfaceis then freed
from surplusdye and the dye in the crack
r*""Ll'Oy "rtn"r,
(a)
applyinga whitepowderdeveloperintowhicn
the dye is absorbed
producinga colourcontrastindication.
or
(b)
i'uminatingwith ultra-vioret
rightunderwhichthe dye fluoresces;
that
is, emitsvisibtelight. Thismust be donerrnur"
noi,nilidt,.;;"-.
subdued.
WELDINGTECHNOLOGY
lssueO19l
.to o
rI
TWI
wos
TiG WELDINC INSTm_rt:
M at e r i al s :
O v e r a l la d v a n t a g e s :
Low cost
Directindicationof defectlocation
Initialexaminationby unskilledlabour(go
or no go)
Overall limitations:
Surfacedefectsonly detected
Uetectscannotreadilybe^rewelded
due to entrappeddye. Roughwelds
producespuriousindications.
Further reading:
Non-destructive
testjnq
GenerajDynamics
ConvairDiv
ban urego
usA (1s67)
Safety:
Low flash pointdye and properrant
gases.
1S.10
WELDING TECHNOLOGY
Issue 0191
TWI
Wg
T}G WELDING [\STMT-E
OUESTIONS
NON-DESTRUCTIVE
TESTING
01
Q2
Q3
04
Q5
Name four (4) NDT methods
State the two typesof rays used
in radiograpnyand a limitationof
What processuses mechanical
vibrationsto detect defects?
Name a limitationof Mpl.
what is the mainrimitation
of usingthe 'dye'methodof inspection?
QSlE
You might also like
- PETRONAS Employee Medical Top-Up PlanDocument2 pagesPETRONAS Employee Medical Top-Up PlanExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- A-Health Advance - Application Form With InstructionsDocument14 pagesA-Health Advance - Application Form With InstructionsExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- TUBE INSPECTION SOLUTIONS: SELECTION GUIDEDocument28 pagesTUBE INSPECTION SOLUTIONS: SELECTION GUIDEAkhileshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Your Future PDFDocument605 pagesEngineering Your Future PDFExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- RFET Technique Detects Local and Gradual DefectsDocument4 pagesRFET Technique Detects Local and Gradual DefectsExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Astm C 871Document5 pagesAstm C 871Exsan Othman100% (2)
- Farris Valve ManualDocument11 pagesFarris Valve ManualsumsolcaggNo ratings yet
- April 2015. Any New Application Form Must Reach Us Before The Stipulated DateDocument1 pageApril 2015. Any New Application Form Must Reach Us Before The Stipulated DateExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Farris Series 2600Document96 pagesFarris Series 2600johngoff100% (1)
- Senarai Nama Arkitek BerdaftarDocument150 pagesSenarai Nama Arkitek BerdaftarCgu Bola Tampar83% (6)
- P91 T91 Engl PDFDocument3 pagesP91 T91 Engl PDFparmodrtkNo ratings yet
- SSI Guideline V3 PDFDocument34 pagesSSI Guideline V3 PDFSyed Mohd FirdausNo ratings yet
- Astm C 692 PDFDocument7 pagesAstm C 692 PDFExsan Othman100% (1)
- MetrodeHandbook - ZavarivanjeDocument416 pagesMetrodeHandbook - ZavarivanjetonicmiraNo ratings yet
- AWS Specifications For Filler MaterialDocument9 pagesAWS Specifications For Filler MaterialExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- AWS Weld Symbol ChartDocument1 pageAWS Weld Symbol ChartExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- EPA RMP OSHA PSM State Law SummaryDocument1 pageEPA RMP OSHA PSM State Law SummaryExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Asmt C 795Document4 pagesAsmt C 795Exsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument181 pagesMaterialsExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Calculation Minimum Required Thickness For Straight Pipe 8inch Leak May10Document6 pagesCalculation Minimum Required Thickness For Straight Pipe 8inch Leak May10Exsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Design Tool AnalysisDocument2 pagesNozzle Design Tool AnalysisArt G. EnziNo ratings yet
- Calculation Minimum Required Thickness For Bending Pipe r2Document11 pagesCalculation Minimum Required Thickness For Bending Pipe r2Exsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Pipeline DataDocument4 pagesPipeline DataExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- 300 - F&D Head Design Tool Ver E4.01Document1 page300 - F&D Head Design Tool Ver E4.01Honey TiwariNo ratings yet
- Material CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesMaterial CharacteristicsExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Piping CalDocument13 pagesPiping CalglazetmNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design SpreadsheetDocument1 pageMechanical Design SpreadsheetHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hemispherical Head Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDDocument1 pageHemispherical Head Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- FM End-Sem Question Paper - 2021Document1 pageFM End-Sem Question Paper - 2021Anshu MeenaNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument8 pagesDoppler EffectJemimah MpofuNo ratings yet
- rinhs science 9 4th activity 2 projectile motion word puzzleDocument2 pagesrinhs science 9 4th activity 2 projectile motion word puzzleRyan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium and Industrial Applications PDFDocument5 pagesChemical Equilibrium and Industrial Applications PDFRida MariamNo ratings yet
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Ad 0299980Document68 pagesAd 0299980alexNo ratings yet
- Physics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Document29 pagesPhysics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Jo Ey Goh75% (4)
- Significant Figures, Scientific Notation and Metric PrefixesDocument3 pagesSignificant Figures, Scientific Notation and Metric PrefixesmphoNo ratings yet
- Bet Article PDFDocument23 pagesBet Article PDFGabriel de SáNo ratings yet
- Appendix For GlassDocument2 pagesAppendix For GlassGian ClimacoNo ratings yet
- Radio Propagation and Network PlanningDocument46 pagesRadio Propagation and Network Planningمحمد فاضلNo ratings yet
- Enrtl-Rk Rate Based Dipa ModelDocument34 pagesEnrtl-Rk Rate Based Dipa ModelsamandondonNo ratings yet
- Liserre Lecture 8Document23 pagesLiserre Lecture 8jack_cliftNo ratings yet
- In Each of Problems 1 Through 8 Solve The Given Differential EquationDocument21 pagesIn Each of Problems 1 Through 8 Solve The Given Differential EquationJonathan HuNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection and Dosimetry Assessment 2Document2 pagesRadiation Protection and Dosimetry Assessment 2George ChahniNo ratings yet
- 2 - Ec3 1 8Document5 pages2 - Ec3 1 8dmardetkNo ratings yet
- 18mat11 PDFDocument3 pages18mat11 PDFRavi TilaganjiNo ratings yet
- Final Project ReportDocument20 pagesFinal Project ReportNimisha Srivastava0% (1)
- Experiment No: Objective: ApparatusDocument3 pagesExperiment No: Objective: ApparatusAfzaal FiazNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Solution To Microwave Engineering Pozar 4th Ed. Example 1.5Document5 pagesMATLAB Solution To Microwave Engineering Pozar 4th Ed. Example 1.5John Bofarull GuixNo ratings yet
- General Relativity: Proff. Valeria Ferrari, Leonardo GualtieriDocument327 pagesGeneral Relativity: Proff. Valeria Ferrari, Leonardo GualtieriRimple MaheyNo ratings yet
- Lab01 - Metallic Crystal StructuresDocument8 pagesLab01 - Metallic Crystal StructuresPok ThungNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 3 Revision NotesDocument45 pagesMechanics 3 Revision NotesDexter FungNo ratings yet
- Magnetic InteractionsDocument13 pagesMagnetic InteractionsZsuzsa BorsayNo ratings yet
- Antennas PropagationDocument1 pageAntennas Propagationzoe gypsyNo ratings yet
- 05-Dinamika Fluida Lanjut - Turbulent FlowDocument17 pages05-Dinamika Fluida Lanjut - Turbulent FlowSri Peni WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Energy: X. Chen, R.Z. Wang, S. DuDocument9 pagesEnergy: X. Chen, R.Z. Wang, S. DualmadhagiNo ratings yet
- Optical Gyroscope With Whispering Gallery Mode Optical CavitiesDocument6 pagesOptical Gyroscope With Whispering Gallery Mode Optical Cavitiesjalamia8796No ratings yet
- Franck-Hertz Experiment With A Hg-Tube: Physics Modern Physics Quantum PhysicsDocument11 pagesFranck-Hertz Experiment With A Hg-Tube: Physics Modern Physics Quantum PhysicsSebastian M.No ratings yet
- Phototubes: A Concise History of Early Light Detection DevicesDocument5 pagesPhototubes: A Concise History of Early Light Detection Devicesdhananjaymohapatra2009No ratings yet