Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MOdule II 2 Page
Uploaded by
Vyshakh SunilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MOdule II 2 Page
Uploaded by
Vyshakh SunilCopyright:
Available Formats
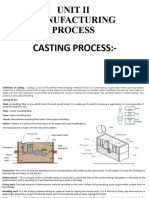
CASTING DEFECTS :-
The defects in a casting
may be due to pattern and molding box equipment , molding
sand, cores, gating system or molten metal. Some of the
defects are :- 1) Mould Shift:- It results in a mismatching of
the top and the bottom parts of the casting, usually at the
parting line. Cause :- i)Worn or loose dowels in patterns
made in halves ii)Worn out, loose, bent or ill-fitting molding
box calming pins. Remedies:-involve removing the causes.
2)Fins & Flash:-These are thin
projection of the metal not
intended as a part of casting.
These usually occurs at the
parting line of the mold. Causes
:-Occurs when:- i)bottom boards
are too flexible ii) pattern plates
are not sufficiently rigid to keep straight during ramming. 3)
Sand Blow or Blow Holes:-It is smooth depression on the
outer surface of the casting work piece. They are entrapped
bubbles of gas with smooth walls. Causes:-Excessive
moisture in molding sand ii) low permeability & excessive
fine grain sands iii) Molds being not adequately vented iv)
Presence of gas producing ingredients in the mold. 4)
Scabs:-These are patches of sand on the upper surface of the
casting component. Cause :-i) too fine sand ii) Sand having
low permeability iii) High moisture content of sand iv)
Uneven mold ramming. 5) Hot Tear:-It is an internal or
external ragged discontinuously in the metal casting
resulting just after the metal has solidified. Cause:- i)Very
hard ramming ii) High dry & hot strength of sand mold. iii)
Too much shrinkage of metal while solidifying. iv) Slow
small gates or metal lacking fluidity. v) High sulphur
content. 6) Cold shuts &Misruns :-These happens when the
mold cavity is not completely filled by the molten &
insufficient material or metal. Causes: - Too cold molten
metal. ii) Too thin casting section iii) too small gates. iv)
Metal lacking in fluidity 7) Honey combing or Slag holes:
- These are smooth depressions on the upper surface of the
castings. They usually occur near the ingate. Causes: - Slag
holes result when slag enters the mould cavity, hence they
can be obviated by inserting slag traps in the gating systems.
8) Shrinkage: - It is a crack or breakage in the casting on
the surface of the work piece, which results from unequal
contraction of the metal during solidification. 9) Runouts &
Bustouts: - These permit drainage of the metal from the
cavity and result in incomplete casting. Causes :- i) Faulty
moulding box equipment ii) Faulty molding. 10) Sand Cuts
& Washes: - It usually occurs near the ingates as rough
lumps another surface of a casting causes: - i) Soft ramming
ii)insufficient draft on patterns iii)Improper gating system
iv)Insufficiently bonded or over baked cores.
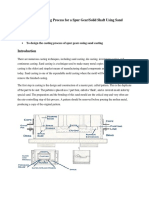
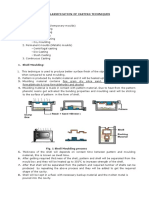
SHELL MOULDING :-Shell
molding replaces
conventional sand molds by shell molds made up of
relatively thin, rigid shells of approximately uniform wall
thickness. Steps :- 1) A metal pattern having the profile of
the reqd casting is heated to 180*c-250*c in an oven
maintained at 300*- 400*c. 2)Pattern after being heated is
taken out of the oven & sprayed with soln of lubricating
agent. 3) Metal pattern is then turned face down & clamped
over the open end of the dump box. 4) The dump box is
inverted so that dry sand-resin mixture falls onto the face of
hot metal pattern 5) As the dump box is turned to its original
position, excess sand rein mixture falls back into the dump
box leaving a shell adhering closely to the pattern. 6) The
pattern along with the shell adhering to it is passed directly
into an oven for 1 to 2 minutes when the resin in the resinsand mixture cures and the shell acquires rigidity. 7) The
shell is then stripped from the pattern plate with the help of
ejector pins which are an integral part of the metal pattern.
8) After the shell so obtained have cooled, two mating shells
are securely fastened together to form a complete mold. 9)
shell molds may be poured either by keeping the parting
surface vertical or horizontal.
INVESTMENT CASTING:-Invest
casting is a
manufacturing process in which a wax pattern is coated with
a refractory ceramic material. Once the ceramic material is
hardened its internal geometry takes the shape of the
casting. The wax is melted out and molten metal is poured
into the cavity where the wax pattern was. The metal
solidifies within the ceramic mold and then the metal
casting is broken out. This manufacturing technique is also
known as the lost wax process. Parts manufactured in
industry by this process include dental, fixtures, gears,
cams, ratchets, jewelry, turbine, blades. etc..
Steps:-1)Producing a die for making wax patterns 2)Making
of expendable patterns and gating system 3)Percolating the
pattern assembly 4)Investing the wax pattern assembly for
the production of molds 5)Removing wax pattern from the
investment mold 6)Pouring metals into the molds 7)After
they are solidified, the castings are removed from the mold
8) Cleaning, Finishing & Inspection.
CENTRIFUGAL CASTING ADVANTAGES :-
CONTINUOUS CASTING :- is the process whereby
1) Cylinders and shapes with rotational symmetry are most
commonly cast by this technique. "Tall" castings are always
more difficult than short castings. In the centrifugal casting
technique the radius of the rotation, along which the
centrifugal force acts, replaces the vertical axis. The casting
machine may be rotated to place this in any convenient
orientation, relative to gravity's vertical. Horizontal and
vertical axis machines are both used, simply to place the
casting's longest dimension conveniently horizontal. 2)
Thin-walled cylinders are difficult to cast by other means,
but centrifugal casting is particularly suited to them. To the
rotation radius, these are effectively shallow flat castings
and are thus simple. 3) Centrifugal casting is also applied to
the casting of disk and cylindrical shaped objects such as
railway carriage wheels or machine fittings where the grain,
flow, and balance are important to the durability and utility
of the finished product. 4) Impurities ligther than metal gets
collected in centre, giving a good product. 5) Longer Life
:Parts made from centrifugals, with the castings finer
grained, denser structure provide increased service life and
withstand greater overloads and impact without fracturing.
6) Reduction of Manufacturing Costs: As a result of the
uniformity and other desirable characteristics of centrifugal
castings, machining time and material waste are
significantly reduced. Hard spots, sand residue, cavities,
blowholes and porosity are virtually eliminated.
CASTING CLEANING :- Cleaning the casting is major
problem in manufacturing industry. Due to sticky sand and
roughness, life of castings decreases. Hence it is necessary
to clean the castings in a certain cleaning value, but it also
increases the lead time. The lead-time raises the cost of
production. Hence casting protection is essential from the
economic point of view. The application of cleaning of
casting increases the life of product. Jet cleaning is generally
used after shot blasting or any other machining process to
remove the impurity like core sand particle inside the
casting and burr. After the metal has solidified and cool in
the mold. These molds go to a shake out station where the
sand and casting are dumped from the flask. The casting
are shaken free from the molding and some dry sand cores
are knocked out. This process of shake out is called the
cleaning of castings.
FETTLING : - The complete process of cleaning of
castings called fettling. It involves the removal of the cores,
gates, sprues, runners, risers and chipping of any of
unnecessary projections on the surface of the castings. The
fettling operation may be divided in to different stages.
Knocking out of dry sand cores. Dry sand cores may be
removed by knocking with iron bar. For quick knocking
pneumatic or hydraulic devices are empolyed, this method
is used for small, meduim work. For large castings the hydro
blast process is mostly employed.
molten metal is solidified into a "semifinished" billet,
bloom, or slab for subsequent rolling in the finishing mills.
This process is used most frequently to cast steel.
Aluminium and copper are also continuously cast.
DIE CASTING :- is a metal casting process that is
characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure
into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two
hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into
shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the
process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous
metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium,
lead, pewter and tin based alloys. Depending on the type of
metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used.
The following are the four steps in traditional die casting,
also known as high-pressure die casting,these are also the
basis for any of the die casting variations: die preparation,
filling, ejection, and shakeout. The dies are prepared by
spraying the mold cavity with lubricant. The lubricant both
helps control the temperature of the die and it also assists in
the removal of the casting. Advantages :Excellent
dimensional accuracy, Smooth cast surfaces,Reduces or
eliminates secondary machining operations. Disadvantage:
the very high capital cost. Both the casting equipment
required and the dies and related components are very costly
You might also like
- Huskystar 219 224 Manual enDocument56 pagesHuskystar 219 224 Manual enkaroodreamerNo ratings yet
- Project Title:: Checklist For PlasteringDocument2 pagesProject Title:: Checklist For Plasteringalfie100% (6)
- Introduction 1.. FoundryDocument112 pagesIntroduction 1.. FoundryDhananjay Shimpi100% (1)
- Playtime Onesies: 2800 Hoover Road - Stevens Point, WI 54481 © Willow Yarns. All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesPlaytime Onesies: 2800 Hoover Road - Stevens Point, WI 54481 © Willow Yarns. All Rights ReservedNounaNo ratings yet
- Types of CastingDocument14 pagesTypes of CastingRamoji Aditya Chary100% (1)
- Lec 5Document39 pagesLec 5Omar AssalNo ratings yet
- Investment Casting ProcessesDocument10 pagesInvestment Casting ProcessesPragyan Kumar PradhanNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument69 pagesMetal CastingMohd Mansoor HasanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222Document66 pagesManufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222shahnawaz875No ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument70 pagesBasic Mechanical EngineeringHemachandran100% (6)
- Casting ProcessesDocument20 pagesCasting ProcessesVv4HNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering MaterialDocument14 pagesBasic Engineering MaterialNur Husnina NinaRamanNo ratings yet
- MME 512 Note 1Document36 pagesMME 512 Note 1faithNo ratings yet
- Dr. Chaitanya Sharma Phd. Iit RoorkeeDocument40 pagesDr. Chaitanya Sharma Phd. Iit RoorkeeTrung Quoc LeNo ratings yet
- Long AnswerDocument3 pagesLong AnswerVarinder MouryaNo ratings yet
- Castingitstypes 140222031231 Phpapp02Document85 pagesCastingitstypes 140222031231 Phpapp02Harmain Ahmed CMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Anteneh AssefaNo ratings yet
- DM-1 CO-1 Special Castings MaterialDocument9 pagesDM-1 CO-1 Special Castings MaterialSree vishnu Sai chandan guntupalliNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process 1 (Casting Processes (B.eng) - 10092014Document129 pagesManufacturing Process 1 (Casting Processes (B.eng) - 10092014bananaNo ratings yet
- BME UNIT2 ClasssDocument30 pagesBME UNIT2 ClasssUpendra NeravatiNo ratings yet
- Casting Its TypesDocument84 pagesCasting Its Typesanmanjunath086No ratings yet
- Differences Between Metal Forming Process and Casting ProcessDocument21 pagesDifferences Between Metal Forming Process and Casting ProcessFarhana Eyla75% (4)
- Ae15301 AMMTDocument98 pagesAe15301 AMMTDurai Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument20 pagesCastingCHANDRAJEET AMARNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting NotesDocument14 pagesMetal Casting NotesMathew Joel MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Casting: Manufacturing ProcessesDocument52 pagesChapter 2 Casting: Manufacturing ProcessesnunuNo ratings yet
- Found AryDocument14 pagesFound Aryluv_leo007No ratings yet
- UNit 3 Part A RevisedDocument76 pagesUNit 3 Part A Revisedraymon sharmaNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument8 pagesCastingTody IsfitazliNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Metal CastingDocument31 pagesTopic 4 - Metal CastingKelvin KVNo ratings yet
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument3 pagesPermanent Mold CastingNirav patelNo ratings yet
- ME364 Casting ProcessesDocument5 pagesME364 Casting Processesjegan_tamilNo ratings yet
- Overviews: Estimators Parts Widgets Processes Materials Suppliers NewsDocument113 pagesOverviews: Estimators Parts Widgets Processes Materials Suppliers Newsrupesh89890% (1)
- Casting Process: Steps of Casting AreDocument10 pagesCasting Process: Steps of Casting AreReham Emad Ezzat MohamedNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Metal Casting ProcessDocument48 pages4.0 Metal Casting ProcessSyed MoizNo ratings yet
- Special CastingDocument46 pagesSpecial CastingJith Viswa100% (1)
- Seminar Special CastingDocument16 pagesSeminar Special CastingAjith SreenathNo ratings yet
- PNC3 - Casting IIDocument4 pagesPNC3 - Casting IIAlpNo ratings yet
- Casting QuestionDocument5 pagesCasting QuestionAvishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cassting 1Document10 pagesCassting 1steve ogagaNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument40 pagesMetal CastingFahmi Sanji AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Quiz FundiciónDocument5 pagesQuiz FundiciónJeankCantorNo ratings yet
- 4castingprocesses 120526012606 Phpapp01Document28 pages4castingprocesses 120526012606 Phpapp01Chennai TuitionsNo ratings yet
- Special CastingDocument24 pagesSpecial CastingManohara ErlaNo ratings yet
- Ae15301-Aircraft Materials and Manufacturing Technology PDFDocument115 pagesAe15301-Aircraft Materials and Manufacturing Technology PDFDurai Raj Kumar100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Manufacturing and Process Report (Group - 4)Document6 pagesFundamentals of Manufacturing and Process Report (Group - 4)Lovely VisakhaNo ratings yet
- Special Casting MethodsDocument73 pagesSpecial Casting Methods359 Srinivasa RamanNo ratings yet
- Sand Casting and Other Casting ProcessesDocument74 pagesSand Casting and Other Casting ProcessesRashid KareemNo ratings yet
- It Is ConsiderationDocument17 pagesIt Is ConsiderationTulasabai JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Mte New Workshop BmeDocument27 pagesMte New Workshop BmeSahil YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 w10 Djj3213 (Metal Processing Casting)Document44 pagesUnit 6 w10 Djj3213 (Metal Processing Casting)Syfull musicNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Processes & Its Advances - An Overview: - Dr.S.P.Kumaresh Babu Professor Dept. of MME N.I.T. TrichyDocument58 pagesMetal Casting Processes & Its Advances - An Overview: - Dr.S.P.Kumaresh Babu Professor Dept. of MME N.I.T. TrichyAditya UNo ratings yet
- MT Merged PDFDocument273 pagesMT Merged PDFavcNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument69 pagesMetal CastingChalamaiah GuntupalliNo ratings yet
- Design of The Casting Process For A Spur Gear/Solid Shaft Using Sand Casting Process ObjectiveDocument17 pagesDesign of The Casting Process For A Spur Gear/Solid Shaft Using Sand Casting Process ObjectiveYonas YG100% (2)
- Foundry Processes: "Why Whittle When You Can Cast?"Document21 pagesFoundry Processes: "Why Whittle When You Can Cast?"lucasNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ahmed Khalifa Ahmed - Khalifa@mhiet - Edu.egDocument46 pagesDr. Ahmed Khalifa Ahmed - Khalifa@mhiet - Edu.egØŠMÄÑ MØHÂMĒDNo ratings yet
- Classification of Casting TechniquesDocument16 pagesClassification of Casting TechniquesRehan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Learn Critical Aspects of Pattern and Mould Making in FoundryFrom EverandLearn Critical Aspects of Pattern and Mould Making in FoundryNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- CSWIP Welding InspectionDocument31 pagesCSWIP Welding InspectionVyshakh SunilNo ratings yet
- TWI Training CSWIP 3.1 PlateDocument8 pagesTWI Training CSWIP 3.1 PlateSepthian DS100% (2)
- BISP-TWI Assessment Form For CSWIPDocument4 pagesBISP-TWI Assessment Form For CSWIPVyshakh SunilNo ratings yet
- Enrolment W.E.F. 13-4-2015Document4 pagesEnrolment W.E.F. 13-4-2015Vyshakh SunilNo ratings yet
- CSWIP-WI-6-92 12th Edition May 2012Document17 pagesCSWIP-WI-6-92 12th Edition May 2012Shaju ShamsudheenNo ratings yet
- RRB Engineering Solved Question PapersDocument5 pagesRRB Engineering Solved Question Paperssantanu_1310No ratings yet
- List of CompaniesDocument4 pagesList of CompaniesVyshakh SunilNo ratings yet
- Contact Us - Seaswift IndiaDocument1 pageContact Us - Seaswift IndiaVyshakh SunilNo ratings yet
- Pattern by Namsom Pan 1Document37 pagesPattern by Namsom Pan 1Paola Cascante100% (1)
- Shot PeeningDocument5 pagesShot Peeningcaddcentre velacheryNo ratings yet
- Panda Bear Amigurumi Crochet Pattern - Free! - Angie's Art StudioDocument2 pagesPanda Bear Amigurumi Crochet Pattern - Free! - Angie's Art Studiotaynahb_1No ratings yet
- Atkins Saw Book For Home Craftsmen 1931Document36 pagesAtkins Saw Book For Home Craftsmen 1931OSEAS GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: CNC Machine Tools & Control Systems: Prepared By: MR.B.K Patil, DTCDocument45 pagesUnit 4: CNC Machine Tools & Control Systems: Prepared By: MR.B.K Patil, DTCDEVARAJU VNo ratings yet
- RailwayBrochure enDocument7 pagesRailwayBrochure enM. AguiarNo ratings yet
- QCS Section 16Document59 pagesQCS Section 16MurugananthamParamasivam67% (3)
- Drinking - Beverages - Tea Cups & SaucersDocument19 pagesDrinking - Beverages - Tea Cups & SaucersThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource Center100% (4)
- Sheet MetalDocument75 pagesSheet MetalVenkata ChakradharNo ratings yet
- List of Yarn Manufacturing Member Mills of BTMADocument26 pagesList of Yarn Manufacturing Member Mills of BTMAMd. Monowarul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chewbacca Amigurumi Doll: Materials NeededDocument5 pagesChewbacca Amigurumi Doll: Materials NeededMaria Lúcia Pereira100% (1)
- MCQDocument4 pagesMCQcc83% (12)
- 5 Router Table UpgradesDocument3 pages5 Router Table Upgradesgmand68100% (3)
- Lorica SegmentataDocument19 pagesLorica SegmentataCipri PopNo ratings yet
- RDS - GMS Qoutation ProposalDocument2 pagesRDS - GMS Qoutation ProposalLemuel Kim Cera TabinasNo ratings yet
- Mosaic DC Envelope Border Photo TutorialDocument3 pagesMosaic DC Envelope Border Photo TutorialAshlee Brotzell100% (1)
- Basic Sewing TechniquesDocument17 pagesBasic Sewing TechniquesOllè WorldwideNo ratings yet
- Bi1000 TocDocument2 pagesBi1000 TocInterweave20% (5)
- Fairy Night Light TotalDocument7 pagesFairy Night Light Totalmonicamauder100% (1)
- How Camera Light Meters WorkDocument18 pagesHow Camera Light Meters WorkomarszNo ratings yet
- Total Solution For Heavy Equipment: Description Size Oem No. Material WeightDocument7 pagesTotal Solution For Heavy Equipment: Description Size Oem No. Material WeightAlexander RuizNo ratings yet
- Knuth Part 1Document100 pagesKnuth Part 1Mesias GuamantarioNo ratings yet
- Name: Claire P. Cabactulan Section: BTVTED-4A: IndustrialDocument12 pagesName: Claire P. Cabactulan Section: BTVTED-4A: IndustrialClaire CabactulanNo ratings yet
- Advance SpinningDocument14 pagesAdvance SpinningArun Yadav100% (1)
- First Summative Test in Tle 6 Fourth Quarter: Francisco F. Illescas Elementary SchoolDocument6 pagesFirst Summative Test in Tle 6 Fourth Quarter: Francisco F. Illescas Elementary SchoolSofia ZafraNo ratings yet
- Guide: CNC Milling 20-07-2016Document27 pagesGuide: CNC Milling 20-07-2016mecanica2000No ratings yet
- Lns125-I Mio M3 Side Cover PDFDocument1 pageLns125-I Mio M3 Side Cover PDFTeguhNugroho100% (1)