Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.ploarization and Types of Polarization
Uploaded by
Ashutosh SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document3.ploarization and Types of Polarization
Uploaded by
Ashutosh SinghDIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
THEORY
POLARIZABILITY:
The dipole moment per unit volume is defined as the polarization vector
P=
( ) =
Where,
is the total dipole moment.
Polarization vector:
The dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric material is called
polarization vector.
If is the average dipole moment per molecule and N is the number of
molecules per unit volume then the Polarization vector P=N .
Electric flux density (D):
The flux density or electric displacement D at a point in a material is
given by D=r 0E.
www.studyleague.com
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
THEORY
Where E is the electric field strength, 0 is the dielectric constant and r
is relative permitivity of the material.
The 3 vectors D,E and P are related by the equation D= 0 E+P
P= 0 (r -1)E.
Dielectric constant (r ):
Dielectric constant (r ) is the ratio between the permitivity of the
medium and the permitivity of free space.
i.e.
r = / 0.
r has no units.
r =C1/C.
DIELECTRIC POLARIZATION:
Dielectric polarization is the term given to describe the behaviour of a
material when an external electric field is applied on it.
www.studyleague.com
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
THEORY
Dielectric polarization occurs when a dipole moment is formed in an
insulating material because of an externally applied electric field.
TYPES OF POLARIZATION:
1. ELECTRONIC / INDUCED POLARIZATION:
The Electric Polarization P is the dipole moment per unit volume
at a given point.
P = Np where p is the average dipole moment per molecule 1.
N is the number of molecules per unit volume.
Any molecule develops a dipole moment which is proportional
to the applied field. The induced electronic dipole moment is
proportional to the electric field applied to the atom
E
i.e
= e E
where
e is the polarizability (electronic).
www.studyleague.com
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
Pe = N
Pe = N
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
As we know that
Pe = 0 (r -1 )E
0 (r -1 )E = N
Therefore,
e =
( )
Therefore it is given by the formula,
e = 4
www.studyleague.com
THEORY
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
THEORY
Orientational Polarization:
This polarization is exhibited by polar dielectric in the absence of
an external field the permanent dipole are randomly oriented
and the net magnetic moment of the dielectric is zero.
When an electric field is applied on the dielectric the molecular
dipoles tend to align themselves along the direction of the filed.
This result in a polarization of the dielectric called orientational
polarization.
When the external electric field is applied, the individual dipoles
experience a torque of moment
Were,
= E sin ()
= dipole moment
The dipole moment align themselves along the filed
The dipole moment can be given as
www.studyleague.com
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
THEORY
2 E
o
3KT
The orientational polarizability is given by,
Pe = No E
Pe
=N
2 E
3KT
Ionic Polarization:
In the absence of electric field,
The polarization of a given volume, however, is exactly zero because for
every dipole moment there is a neighboring one with exactly the same
magnitude, but opposite sign.
www.studyleague.com
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
THEORY
In an electric field, the ions feel forces in opposite directions. For a field
acting as shown, the lattice distorts a little bit
The Na+ ions moved a bit to the right, the Cl ions to the left.
The dipole moments between adjacent NaCl - pairs in field direction are
now different and there is a net dipole moment in a finite volume now.
The Na+ ions moved a bit to the right, the Cl ions to the left
The distance between the ions increases by d
www.studyleague.com
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
THEORY
Internal fields in solids
The total electric field at the site of the atom within the dielectric is
called the local field or the internal field.
It is also called the Lorentz field.
We have,
P=NEi
Ei=[ 0 (r -1)E]/N .
Ei=E+(P/ 0 ).
Claussius-Mosotti relation:
It gives the relation between the microscopic polarizability and the
macroscopic dielectric constant.
Clasius Mossotti equation is given by
(r -1)/( r +2)= N /3 0 .
www.studyleague.com
DIELECTRIC & MAGNETIC MATERIALS
POLARIZATION AND ITS TYPE
Dielectrics in alternating fields:
According to Maxwells theory of wave propagation
V=1/ .
C= 1/ 00.
Hence ,
C/V=n= r r.
If the materials are non-magnetic,
r=1
n= r( or) r =n2.
Then the Clasius Mossotti relation becomes
(n2-1)/( n2 +2)= N /3 0 .
This is known as Lorentz-Lorentz relation
www.studyleague.com
THEORY
You might also like
- AtomsDocument60 pagesAtomsRohit Kumar BaghelNo ratings yet
- Piezo Electric, Ferroelectric and Pyroelectric MaterialsDocument24 pagesPiezo Electric, Ferroelectric and Pyroelectric MaterialsGauri Deshmukh KaranjgaokarNo ratings yet
- MMP AssignmntDocument3 pagesMMP AssignmntNitasha HussainNo ratings yet
- Clausius-Mossotti Relation - Knowino PDFDocument3 pagesClausius-Mossotti Relation - Knowino PDFSurajNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Energy Gap by The Four Probe Method: Experiment-265 SDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Energy Gap by The Four Probe Method: Experiment-265 SAsheesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Plane Waves Propagations in An Arbitrary Direction: EE2060 Engineering ElectromagneticDocument9 pagesPlane Waves Propagations in An Arbitrary Direction: EE2060 Engineering ElectromagneticAsdcxzNo ratings yet
- Unit-I - Topic-PolarizationDocument12 pagesUnit-I - Topic-PolarizationMUSICAL MASTI RINGTONENo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Structure and Bonding ModelsDocument18 pagesUnit-1 Structure and Bonding ModelsAbhi PathaanNo ratings yet
- Jones Matrix LectureDocument21 pagesJones Matrix LectureDer Untiringe KäferNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (Xiii) Teaching NotesDocument16 pagesWave Optics (Xiii) Teaching NotesSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Viva Voice-Engineering Mechanics: Experiment No.-1Document28 pagesViva Voice-Engineering Mechanics: Experiment No.-1Achint Verma100% (1)
- Unit 1 Oscillation, Ultrasonics and Dieletrical Material - Physic-1Document16 pagesUnit 1 Oscillation, Ultrasonics and Dieletrical Material - Physic-1All About Youtuber'sNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Chemical Kinetics - TopperlearningDocument5 pagesRevision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Chemical Kinetics - TopperlearningRishabh Bhandari0% (1)
- Franck Hertz ExperimentDocument4 pagesFranck Hertz ExperimentAman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Newton's Ring ExperimentDocument3 pagesNewton's Ring ExperimentRoshnee BoseNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics Lab Viva Question AnsweersDocument17 pagesEngineering Physics Lab Viva Question AnsweersXenonNo ratings yet
- WWW - Thinkiit.in: Important DefinitionsDocument37 pagesWWW - Thinkiit.in: Important Definitionsthinkiit100% (2)
- Physics of Solids' MCQsDocument9 pagesPhysics of Solids' MCQsMuhammad Rehan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ManualDocument55 pagesPhysics Lab Manualvncharymsc100% (1)
- UNIT - 3 (Light Semiconductor Interaction)Document26 pagesUNIT - 3 (Light Semiconductor Interaction)Comp105Jyot Kalathiya100% (1)
- UNIT III - PhotochemistryDocument27 pagesUNIT III - PhotochemistrykuthappadyNo ratings yet
- 29777-10546-LAB VIVA Part-1Document3 pages29777-10546-LAB VIVA Part-1Reddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Domains and HysteresisDocument20 pagesDomains and HysteresisMuhammad Salman AttariNo ratings yet
- Aqm Lecture 2Document12 pagesAqm Lecture 2sayandatta1No ratings yet
- Tangent GalvanometerDocument19 pagesTangent GalvanometerChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Physics Book HandwrittenDocument183 pagesPhysics Book Handwritten20IT027 Vinayak40% (5)
- Einstein's Coefficient TheoryDocument8 pagesEinstein's Coefficient TheoryBhagirath sinh ZalaNo ratings yet
- Signal and System by TK Rawat PDF FreeDocument752 pagesSignal and System by TK Rawat PDF FreeTanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument39 pagesElectrostaticsshreyas bulbule100% (1)
- ATOMIC MODELS AtomicphysicsDocument24 pagesATOMIC MODELS Atomicphysicsahsanbgayo100% (1)
- Applied Physics2 - VIVA VOCE PDFDocument22 pagesApplied Physics2 - VIVA VOCE PDFKaran DwivediNo ratings yet
- To Determine The Wavelength of Laser Light Using Single Slit Diffrac-Tion PatternDocument8 pagesTo Determine The Wavelength of Laser Light Using Single Slit Diffrac-Tion PatternNiteshNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument33 pagesCircuit Theoryavi713331No ratings yet
- Viva Questions For HALL EffectDocument2 pagesViva Questions For HALL EffectYashveer YadavNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetism and Conduction ElectronsDocument3 pagesParamagnetism and Conduction Electronsjose miranda100% (1)
- Solid State Viva QuestionsDocument7 pagesSolid State Viva QuestionsAnanya SNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Electromagnetic Waves Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFDocument9 pagesJEE Main Electromagnetic Waves Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFTarun Krishna ManivannanNo ratings yet
- Lloyd's MirrorDocument8 pagesLloyd's Mirrorchiranjib214No ratings yet
- Question Bank Ty 04Document7 pagesQuestion Bank Ty 04Arshad PathanNo ratings yet
- Carrier Generation and RecombinationDocument9 pagesCarrier Generation and RecombinationwaveletNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionDocument11 pagesRelation and FunctionydasjnvNo ratings yet
- 16 - Central Force Motion PDFDocument21 pages16 - Central Force Motion PDFUltrazordNo ratings yet
- Phy Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument16 pagesPhy Kinetic Theory of GasesSachinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Quantum Physics PDFDocument30 pagesUnit 3 Quantum Physics PDFprithwiraj chatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Calculus of Residue and Contour IntegrationDocument78 pagesCalculus of Residue and Contour IntegrationPrateekKumarJaysinghaniNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Conservation LawsDocument48 pagesSymmetry and Conservation Lawshjprast7591No ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics-I Previous Year Question Papers (MSC Physics Delhi University)Document2 pagesQuantum Mechanics-I Previous Year Question Papers (MSC Physics Delhi University)Neerav Kumar0% (2)
- 08 Chapter1 PDFDocument27 pages08 Chapter1 PDFBestin Saly BabuNo ratings yet
- Van Hove SingularityDocument3 pagesVan Hove SingularityChang Jae LeeNo ratings yet
- Born-Oppenheimer ApproximationDocument5 pagesBorn-Oppenheimer ApproximationIjaz TalibNo ratings yet
- Interference and DiffractionDocument27 pagesInterference and DiffractionphydotsiNo ratings yet
- Differntial Equations ProjectDocument28 pagesDifferntial Equations ProjectSai CharanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics IIDocument10 pagesQuantum Mechanics IIAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Lectures 10-11 and 12Document28 pagesLectures 10-11 and 12learncoursegrbNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Properties of SolidsDocument15 pagesDielectric Properties of SolidsMahesh Lohith K.S100% (11)
- Dielectric Properties of Solids PP 1Document15 pagesDielectric Properties of Solids PP 1jainam sharma100% (1)
- Unit-III Dielectrics, Magnetic & EnergymaterialsDocument26 pagesUnit-III Dielectrics, Magnetic & EnergymaterialsudayNo ratings yet
- Dielectrics IntroductionDocument4 pagesDielectrics IntroductionagnirailwaysNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform of IntegralDocument3 pagesLaplace Transform of IntegralAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 Harmonic Function Solved NumericalsDocument3 pages4 Harmonic Function Solved NumericalsAshutosh Singh100% (2)
- Effect of Division by T UnsolvedDocument2 pagesEffect of Division by T UnsolvedAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Harmonic FunctionDocument2 pagesHarmonic FunctionAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- First Shifting TheoremDocument3 pagesFirst Shifting TheoremAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Effect of Multiplication by T THEORYDocument2 pagesEffect of Multiplication by T THEORYAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 Harmonic Function Solved NumericalsDocument3 pages4 Harmonic Function Solved NumericalsAshutosh Singh100% (2)
- Harmonic FunctionDocument2 pagesHarmonic FunctionAshutosh Singh100% (1)
- Change of Scale PropertyDocument1 pageChange of Scale PropertyAshutosh Singh100% (1)
- First Shifting Theorem UnsolvedDocument1 pageFirst Shifting Theorem UnsolvedAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- First Shifting TheoremDocument2 pagesFirst Shifting TheoremAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The IntegralDocument1 pageEvaluation of The IntegralAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Change of Scale Property UnsolvedDocument1 pageChange of Scale Property UnsolvedAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 Cauchy - Riemann Equation in Polar Co-Ordinates Unsolved ProblemDocument1 page3 Cauchy - Riemann Equation in Polar Co-Ordinates Unsolved ProblemAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 Cauchy - Riemann Equation in Polar Co-OrdinatesDocument2 pages3 Cauchy - Riemann Equation in Polar Co-OrdinatesAshutosh Singh100% (1)
- 2 Analytic FunctionDocument5 pages2 Analytic FunctionAshutosh Singh100% (2)
- 2 Analytic Solved ProblemDocument7 pages2 Analytic Solved ProblemAshutosh Singh100% (7)
- Presented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Document56 pagesPresented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Bela GhummanNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Jaynes-Cummings Model: Paul EasthamDocument30 pagesPhysics of The Jaynes-Cummings Model: Paul Easthamharry37No ratings yet
- Vector Model For Orbital Angular MomentumDocument6 pagesVector Model For Orbital Angular MomentumAgrupación Astronomica de Alicante100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Semiconductor Physics and DevicesDocument786 pagesFundamentals of Semiconductor Physics and Devicestolentino.jason1222No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Based Diode: Schottky Diode: (6023 Exp 1) : 1. Experiment ObjectiveDocument7 pagesSemiconductor Based Diode: Schottky Diode: (6023 Exp 1) : 1. Experiment ObjectiveHamza KHNo ratings yet
- GW Approximation and Its Implementation in VASPDocument22 pagesGW Approximation and Its Implementation in VASPRajasekarakumar Vadapoo100% (3)
- Manufacturing ProcessDocument10 pagesManufacturing Processmanya vatsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions - Page 3 of 5 - ICSEHELPDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions - Page 3 of 5 - ICSEHELPlionelkenethNo ratings yet
- Variation of Fermi Level in Intrinsic and Extrinsic SemiconductorsDocument5 pagesVariation of Fermi Level in Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductorsagnirailways100% (4)
- DeGroot - Models For XAS and XMCDDocument94 pagesDeGroot - Models For XAS and XMCDbuddlightbeerlogNo ratings yet
- Biphasic Liquid Dosage FormDocument18 pagesBiphasic Liquid Dosage FormSai Nath NNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Deposition Using Physical Vapor DepositionDocument20 pagesThin Film Deposition Using Physical Vapor DepositionakivedNo ratings yet
- A Direct Calculation of The Tunnelling Current. II. Free Electron DescriptionDocument14 pagesA Direct Calculation of The Tunnelling Current. II. Free Electron DescriptionGianlucaTirimbòNo ratings yet
- Ch20 EmulsionSelectionDocument7 pagesCh20 EmulsionSelectionKee SarakarnkosolNo ratings yet
- Chapter4b - Crystal DefectsDocument55 pagesChapter4b - Crystal DefectsJONATHAN RAJ A/L SEMANNo ratings yet
- Hemt Technology For High Speed Logic &communicationDocument19 pagesHemt Technology For High Speed Logic &communicationvivek gangwarNo ratings yet
- Pnas 1003052107Document6 pagesPnas 1003052107MitzuNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices - CircuitsDocument355 pagesElectronics Devices - CircuitsEman AlbinoNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension and AdsorptionDocument52 pagesSurface Tension and AdsorptionNAVYA BHANDARUNo ratings yet
- Ms. Krishally Joy O. Patalinjug, RPH: Bsph-1102 Quantum NumbersDocument3 pagesMs. Krishally Joy O. Patalinjug, RPH: Bsph-1102 Quantum NumbersOrianna SanoNo ratings yet
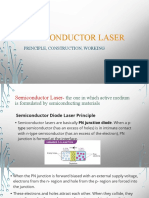
- Semiconductor Laser: Principle, Construction, WorkingDocument17 pagesSemiconductor Laser: Principle, Construction, WorkingRohith50% (2)
- Ionic Bond Formation: General ChemistryDocument20 pagesIonic Bond Formation: General Chemistryyoona stewartNo ratings yet
- Quantum Chemistry Program in FortranDocument41 pagesQuantum Chemistry Program in FortranSoumya GangulyNo ratings yet
- PHY1002 Materials-Science ETH 1 AC40Document4 pagesPHY1002 Materials-Science ETH 1 AC40heena50% (2)
- Aenm 201701797Document97 pagesAenm 201701797rajanadarajanNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Crystal PhysicsDocument62 pagesUNIT I Crystal Physicsvivek sainiNo ratings yet
- Materials Science - Crystal StructureDocument24 pagesMaterials Science - Crystal StructureNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Alloys and CompoundsDocument5 pagesJournal of Alloys and Compoundsmanjeet redduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3bDocument96 pagesLecture 3blaylaylinNo ratings yet