Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GSM Identity
Uploaded by
aazamkhaanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GSM Identity
Uploaded by
aazamkhaanCopyright:
Available Formats
GSM IDENTITY NUMBERS(IMSI,TMSI,CGI,MSRN,IMEI)
GSM identities
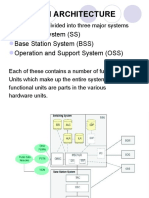
The GSM network is complex and consists of the Switching System (SS) and the Base
Station System (BSS). The switching system, which consists of HLR, MSC, VLR, AUC
and EIR, interfaces both the Base Station System and also other networks like
PSTN/ISDN, data networks or other PLMNs.
In order to switch a call to a mobile subscriber, the right entities need to be involved. It is
therefore important to address them correctly. The numbers used to identify the
identities in a GSM/PLMN network is described in this chapter. See also Figure 56.
Numbering plans are used to identify different networks. For a telephone number in the
PSTN/ISDN network, numbering plans E.164 is used.
Mobile Station ISDN Number (MSISDN)
The MSISDN is a number which uniquely identifies a mobile telephone subscription in
the public switched telephone network numbering plan. According to the CCITT
recommendations, the mobile telephone number or catalogue number to be dialled is
composed in the following way:
MSISDN = CC + NDC + SN
CC = Country Code
NDC = National Destination Code
SN = Subscriber Number
A National Destination Code is allocated to each GSM PLMN. In some countries, more
than one NDC may be required for each GSM PLMN. The international MSISDN
number may be of variable length. The maximum length shall be 15 digits, prefixes not
included.
Each subscription is connected to one Home Location Register (HLR).
The length of the MSISDN depends on the structure and numbering plan of each
operator, as an application of CCITT recommendation E.164.
The following is an example of dialling a GSM subscriber.
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
The IMSI is the information which uniquely identifies a subscriber in a
GSM/PLMN.
For a correct identification over the radio path and through the GSM PLMN
network, a specific identity is allocated to each subscriber. This identity is
called the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and is used for all
signalling in the PLMN. It will be stored in the Subscriber Identity Module
(SIM), as well as in the Home Location Register (HLR) and in the serving
Visitor Location Register (VLR).
The IMSI consists of three different parts:
IMSI = MCC + MNC + MSIN
MCC = Mobile Country Code (3 digits)
MNC = Mobile Network Code (2 digits)
MSIN = Mobile Subscriber Identification Number (max 10 digits)
According to the GSM recommendations, the IMSI will have a length of
maximum 15 digits.
All network–related subscriber information is connected to the IMSI. See also
Figure 56.
Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN)
HLR knows in what MSC/VLR Service Area the subscriber is located. In order
to provide a temporary number to be used for routing, the HLR requests the
current MSC/VLR to allocate and return a Mobile Station Roaming Number
(MSRN) for the called subscriber, see Figure 56.
At reception of the MSRN, HLR sends it to the GMSC, which can now route
the call to the MSC/VLR exchange where the called subscriber is currently
registered.
The interrogation call routing function (request for an MSRN) is part of the
Mobile Application Part (MAP). All data exchanged between the GMSC - HLR
- MSC/VLR for the purpose of interrogation is sent over the No. 7 signalling
network.
The Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN), according to the GSM
recommendations, consists of three parts:
MSRN = CC + NDC + SN
CC = Country Code
NDC = National Destination Code
SN = Subscriber Number
Note: In this case, SN is the address to the serving MSC.
Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI)
The TMSI is a temporary number used instead of the IMSI to identify an MS. It raises
the subscriber’s confidentiality and is known within the serving MSC/VLR-area and
changed at certain events or time intervals. The structure of the TMSI may be chosen
by each administration but should have a maximum length of four octets (8 digits).
International Mobile station Equipment Identity (IMEI)
The IMEI is used for equipment identification. An IMEI uniquely identifies a mobile
station as a piece or assembly of equipment. (See IMEI, chapter 5.)
IMEI = TAC + FAC + SNR + sp
TAC = Type Approval Code (6 digits), determined by a central GSM body
FAC = Final Assembly Code (2 digits), identifies the manufacturer
SNR = Serial Number (6 digits), an individual serial number of six digits uniquely
identifying all equipment within each TAC and FAC
sp = spare for future use (1 digit)
According to the GSM specification, IMEI has the length of 15 digits.
Location Area Identity (LAI)
LAI is used for location updating of mobile subscribers.
LAI = MCC + MNC + LAC
MCC = Mobile Country Code (3 digits), identifies the country. It follows the same
numbering plan as MCC in IMSI.
MNC = Mobile Network Code (2 digits), identifies the GSM/PLMN in that country and
follows the same numbering plan as the MNC in IMSI.
LAC = Location Area Code, identifies a location area within a GSM PLMN network. The
maximum length of LAC is 16 bits, enabling 65 536 different location areas to be
defined in one GSM PLMN.
Cell Global Identity (CGI)
CGI is used for cell identification within the GSM network. This is done by adding a Cell
Identity (CI) to the location area identity.
CGI = MCC + MNC + LAC + CI
CI = Cell Identity, identifies a cell within a location area, maximum 16 bits
Base Station Identity Code (BSIC)
BSIC allows a mobile station to distinguish between different neighboring base stations.
BSIC = NCC + BCC
NCC = Network Colour Code (3 bits), identifies the GSM PLMN.
Note that it does not uniquely identify the operator. NCC is primarily used to distinguish
between operators on each side of border.
BCC = Base Station Colour Code (3 bits), identifies the Base Station to help distinguish
between BTS using the same BCCH frequencies
Location Number (LN)
Location Number is a number related to a certain geographical area, as specified by the
network operator by ”tying” the location numbers to cells, location areas, or MSC/VLR
service areas.
The Location Number is used to implement features like Regional /Local subscription
and Geographical differentiated charging.
You might also like
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Ismsc 2 4Document354 pagesIsmsc 2 4Anonymous Ie0oEXP2e0% (1)
- GSM Identities: If You Like This Than Become Our Friend On FacebookDocument4 pagesGSM Identities: If You Like This Than Become Our Friend On FacebookhmzgNo ratings yet
- GSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriDocument137 pagesGSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriSaNo ratings yet
- GSM IdentitiesDocument3 pagesGSM IdentitiesSameer SulemanNo ratings yet
- GSM - Addresses and Identifiers (Imei, Imsi, Tmsi, Lmsi, Msisdn, MSRN)Document2 pagesGSM - Addresses and Identifiers (Imei, Imsi, Tmsi, Lmsi, Msisdn, MSRN)Avanti Mukhopadhaya100% (1)
- Module 2Document24 pagesModule 2shreya harishNo ratings yet
- GSM - Addresses and IdentifiersDocument3 pagesGSM - Addresses and IdentifiersFereidoun SadrNo ratings yet
- The Diference Between A Imsi and A TsmiDocument3 pagesThe Diference Between A Imsi and A TsmiYoel OrueNo ratings yet
- GSM Introduction: Ada Cellworks PVT LTDDocument257 pagesGSM Introduction: Ada Cellworks PVT LTDAffo AlexNo ratings yet
- International Mobile Station Equipment Identity (IMEI)Document2 pagesInternational Mobile Station Equipment Identity (IMEI)Tashi DorjiNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 & 4 GSMNetArchitecture (Revised)Document63 pagesLec 3 & 4 GSMNetArchitecture (Revised)Duy LeNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument8 pagesGSM ArchitectureAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- GSM Mobile Services: Project Report ONDocument67 pagesGSM Mobile Services: Project Report ONRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- GSMDocument68 pagesGSMjananiit_88No ratings yet
- What Is GSM?Document7 pagesWhat Is GSM?Nitish NaglakshNo ratings yet
- GSM Identifiers ExplainedDocument5 pagesGSM Identifiers ExplainedkrishkarnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GSMDocument3 pagesIntroduction To GSMYasir LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication SystemsDocument136 pagesMobile Communication SystemsJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument11 pagesGSM ArchitectureHemangi Priya Devi DasiNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliDocument66 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemNo ratings yet
- Nepal Nepal TelecomDocument7 pagesNepal Nepal TelecomSigurko MatthewNo ratings yet
- MD - Hasanuzzaman Assignment01Document17 pagesMD - Hasanuzzaman Assignment01MD HasanNo ratings yet
- GSM Signal Processing Lecture on Channel Coding, Interleaving, Authentication & CipheringDocument46 pagesGSM Signal Processing Lecture on Channel Coding, Interleaving, Authentication & CipheringMuti Ul BariNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture FreeDocument20 pagesGSM Architecture FreeTDMA2009No ratings yet
- DT DocumentsDocument10 pagesDT DocumentsSobaan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Chapter XVIII 2020Document23 pagesChapter XVIII 2020Faiyaz AlamNo ratings yet
- GSM SystraDocument67 pagesGSM SystraHi_Lev100% (1)
- 2G Network: Elecom EtworkDocument13 pages2G Network: Elecom Etworkpg5555No ratings yet
- Introduction To GSM 2Document12 pagesIntroduction To GSM 2mba_1604No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 ECE4009 ETH VL2023240102914 2023-10-04 Reference-Material-IDocument24 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 ECE4009 ETH VL2023240102914 2023-10-04 Reference-Material-IPraneshNo ratings yet
- Mobility Management, Call Routing & SecurityDocument49 pagesMobility Management, Call Routing & SecurityIslam BarakatNo ratings yet
- Protocals: Um InterfaceDocument7 pagesProtocals: Um InterfaceRajashekar BhimanathiniNo ratings yet
- Training Program: Network ServicesDocument80 pagesTraining Program: Network ServicesMuhammadwaqasnaseem100% (1)
- GSM System Introduction 1Document0 pagesGSM System Introduction 1Shami TahirNo ratings yet
- TN_SP023_E1_1 - Mobile Number Plan in CS DomainDocument9 pagesTN_SP023_E1_1 - Mobile Number Plan in CS DomainAmirpasha FatemiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Comm Securiy 5Document27 pagesWireless Comm Securiy 5abdulsahibNo ratings yet
- MOBILE STATION FUNCTIONS AND IDENTITIESDocument51 pagesMOBILE STATION FUNCTIONS AND IDENTITIESSathish RajaNo ratings yet
- WC - Unit 5Document18 pagesWC - Unit 5Gopalakrishna Murthy C R100% (1)
- GSM For DummiesDocument82 pagesGSM For DummiesVivek MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument27 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communicationsdecent_ajaiNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument13 pagesGSM Network ArchitectureZameer HussainNo ratings yet
- GSM and GPRS SecurityDocument12 pagesGSM and GPRS Securityphandaka100% (5)
- 2.2.3 The Mobile Services Switching CentreDocument4 pages2.2.3 The Mobile Services Switching CentreTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Cellular CommunicationDocument96 pagesWireless Cellular CommunicationArjun P MNo ratings yet
- Introduction to GSM Network ComponentsDocument8 pagesIntroduction to GSM Network ComponentsWeedhat Utol UyoNo ratings yet
- Network ArchitectureDocument17 pagesNetwork ArchitecturesumantabhuinNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument15 pagesGSM Architectureashok_rudraNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument13 pagesGSM ArchitectureTechnically ExplainedNo ratings yet
- Notes Optimization 2GDocument11 pagesNotes Optimization 2Gisaac brineNo ratings yet
- Security Issues in Wireless NetworkDocument50 pagesSecurity Issues in Wireless NetworkdeardestinyNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)Document19 pagesGSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)aimslifeNo ratings yet
- GSM SIM & SecurityDocument31 pagesGSM SIM & SecuritymanthasaikarthikNo ratings yet
- Automatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandAutomatic Number Plate Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications Security: Solutions for the Internet of ThingsFrom EverandWireless Communications Security: Solutions for the Internet of ThingsNo ratings yet
- Root CLI TreeDocument4 pagesRoot CLI TreeaazamkhaanNo ratings yet
- Cisco Evolved Packet Core Gennady Sirota Vice President PDFDocument46 pagesCisco Evolved Packet Core Gennady Sirota Vice President PDFaazamkhaanNo ratings yet
- 200 125 Ccna v3Document7 pages200 125 Ccna v3Azaz Dobiwala100% (1)
- LTE Nubering & AddressingDocument3 pagesLTE Nubering & AddressingaazamkhaanNo ratings yet
- LTE Glossary PDFDocument3 pagesLTE Glossary PDFaazamkhaanNo ratings yet
- EPC: An Overview of the Evolved Packet Core NetworkDocument28 pagesEPC: An Overview of the Evolved Packet Core NetworkJaved HashmiNo ratings yet
- IELTS General Training Writing Sample ScriptsDocument7 pagesIELTS General Training Writing Sample ScriptsHarktheDarkNo ratings yet
- Ielts WritingDocument3 pagesIelts WritingaazamkhaanNo ratings yet
- GSM IdentityDocument5 pagesGSM IdentityaazamkhaanNo ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS RAN Sharing Feature GuideDocument97 pagesZTE UMTS RAN Sharing Feature GuideRehan Haider Jaffery50% (2)
- ZTE RAN Sharing Solution For Workshop V1.1Document46 pagesZTE RAN Sharing Solution For Workshop V1.1Mav Riz100% (1)
- Etsi TS 141 101Document24 pagesEtsi TS 141 101mozbalNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 26.071Document12 pages3GPP TS 26.071mzyptNo ratings yet
- GPRS A Mobile Internet Architecture-CTDCDocument20 pagesGPRS A Mobile Internet Architecture-CTDCariful_islam_20067643No ratings yet
- Tecore Icore 2G / 3G / 4G Multi-Technology Core Network SpecificationsDocument2 pagesTecore Icore 2G / 3G / 4G Multi-Technology Core Network Specificationsyuyong717No ratings yet
- Huawei IMSI Based HandoverDocument23 pagesHuawei IMSI Based HandoverLiviu Marin100% (1)
- MNP PP PresentationDocument37 pagesMNP PP PresentationNealNo ratings yet
- 21905-d00 Vocabulary For 3GPP SpecificationsDocument65 pages21905-d00 Vocabulary For 3GPP Specificationsحمودي حموديNo ratings yet
- BACHELOR of Technology IN Information Technology: On Third Generation (3G)Document44 pagesBACHELOR of Technology IN Information Technology: On Third Generation (3G)Tanu YadavNo ratings yet
- MSC Pool VMS6 PresentationDocument101 pagesMSC Pool VMS6 Presentationnguyenmanhcuong3No ratings yet
- 08 Tm51108en03gla3 NSN ProductsDocument66 pages08 Tm51108en03gla3 NSN ProductsEdward OkothNo ratings yet
- GSM TrainingDocument554 pagesGSM Trainingdelafinca55No ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS Cell Selection and Reselection GuideDocument83 pagesZTE UMTS Cell Selection and Reselection GuideSefyuNo ratings yet
- SS7 IntroductionDocument51 pagesSS7 Introductionfiras1976No ratings yet
- UCP-Protokoll Emi4 1Document52 pagesUCP-Protokoll Emi4 1userppNo ratings yet
- BSNL Training ReportDocument38 pagesBSNL Training Reportvishal sainiNo ratings yet
- Challenge Networks PresentationDocument17 pagesChallenge Networks PresentationKamaldeep Singh DhanotaNo ratings yet
- Global MOCN Case Sharing-HuaweiDocument14 pagesGlobal MOCN Case Sharing-HuaweiMuhammad Irfan Hassan Khan100% (1)
- Alcatel-Lucent W-CDMA UMTS Radio Principles: Training ManualDocument188 pagesAlcatel-Lucent W-CDMA UMTS Radio Principles: Training Manualbigpack1982No ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23Document202 pages3GPP TS 23tkp98099No ratings yet
- Evdo 2Document29 pagesEvdo 2Win LinnNo ratings yet
- FN1168 Multiple PLMN and Inter-PLMN Handover SupportDocument25 pagesFN1168 Multiple PLMN and Inter-PLMN Handover SupportRazvan Corban50% (2)
- 5 ERAN Sharing and S1-FlexDocument42 pages5 ERAN Sharing and S1-FlexBejetaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Virtual Network OperatorDocument8 pagesMobile Virtual Network Operatorfaiz_grwNo ratings yet
- Netmanias.2013.08.20-LTE Identification I-UE and ME Identifiers (En) PDFDocument15 pagesNetmanias.2013.08.20-LTE Identification I-UE and ME Identifiers (En) PDFFiras Ibrahim Al-HamdanyNo ratings yet
- Axe 10Document65 pagesAxe 10bleua1100% (3)
- ZTE UMTS Idle Mode and Common Channel Behavior Feature Guide - V8.5 - 201312Document147 pagesZTE UMTS Idle Mode and Common Channel Behavior Feature Guide - V8.5 - 201312Faiz Salih Maebed100% (2)
- Basic Knowledge For CDMA SystemDocument42 pagesBasic Knowledge For CDMA SystemSanjay GiriNo ratings yet