Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SBP Series With ICD200 UM 2013-05 R200
Uploaded by
Jose LunaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SBP Series With ICD200 UM 2013-05 R200
Uploaded by
Jose LunaCopyright:
Available Formats
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Pen type syringe pump
SBP-100G series
I/O start type drive controller
ICD200-1120A-03
Users Manual
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Foreword
Accessories
This users manual explains usage of ICD200-1120A
with SBP-100G series. Before commencing operation,
please read this users manual thoroughly and
operate the product accordingly.
SBP-100G series
Name
CD-R
Description
Containing this users manual
Unit
1
ICD200-1120A
Name
Power cable
Motor cable
Sensor I/F cable
Start signal I/F
cable
RS485 I/F cable
USB/RS485
conversion cable
General Safety Instructions
Use the following safety guidelines to help ensure
your own personal safety and to help protect your
equipment and working environment from potential
damage.
Warning Symbols
WARNING
CAUTION
Failure to observe instructions given
with this symbol may result in injury
or death by fire or electric shock.
Failure to observe instructions given
with this symbol may result in injury
or damage to property by electric shock
or other reason.
CD-R
Description
YS-OPCXHP2P15
YS-OMCPHR4P15-TOKU
YS-OSCZHR9P15-TOKU
Unit
1
1
1
YS-OSCZHR13P15-TOKU
YS-OSCZHR3P20WRS
UTS-485
Containing ICD200 users
manual and software
Description of Symbols
Symbol for WARNING and CAUTION
Symbol for PROHIBITION
Symbol for INSTRUCTION
WARNING
Do not disassemble, repair or modify the
product. Doing so may result in fire or
electric shock.
Protect the product from strong impacts and
do not drop it. Impacts may cause injury.
Provide appropriate back-up mechanisms to
avoid the situation that result in human
death, injury or any other serious
consequences.
Do not use in a wet environment. Doing so
may result in electric shock.
Do not use a fluid media which may corrode
the wetted materials. Doing so may result in
fire, electric shock or pollution by chemical
substance.
CAUTION
Do not store in extremely humid, dusty or
oily places, or near heat generating
equipment. Doing so may result in
malfunction, fire or electric shock.
Do not impose excess pressure on the lead
wires or needles. Doing so may result in
performance deterioration or malfunction.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Specifications
SBP-100G Series (excerpts)
ITEMS
MODEL NUMBER
SYRINGE CAPACITY
FULL STROKE
RESOLUTION
ACCURACY
REPEATABILITY (CV)
PRESSURE
FLUID MEDIA
WETTED MATERIALS
MEDIA
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE
RANGE
MOTOR
MAXIMUM CURRENT
DUTY CYCLE
DIELECTRIC STRENGTH
MODEL
INPUT VOLTAGE
SENSOR
OUTPUT
OPERATING
FROM ORIGIN
DISTANCE
DESCRIPTION
SBP-100G Series
100 L
12 mm (9600 STEPS)
10.5 nL (THEORETICAL RESOLUTION)
10 % (FULL STROKE, INCLUDING BACKLASH)
1 % (FULL STROKE, INCLUDING BACKLASH)
100 kPa
LIQUIDS CHEMICALLY COMPATIBLE WITH WETTED MATERIALS
BELOW
STAINLESS STEEL, PTFE, BOROSILICATE GLASS
5 - 40
5 - 40
BIPOLAR TYPE 2 PHASE STEPPER MOTOR
4.4 /PHASE, 2.6 mH/PHASE
0.25 A (CONSTANT CURRENT CONTROL)
CONTINUOUS
200 VDC
PHOTOINTERRUPTER, RPI-0226 MANUFACTURED BY ROHM
24 VDC 10 %
CURRENT LIMITING
RESISTANCE 5.6 k
OPEN COLLECTOR OUTPUT
ABSOLUTE
MAXIMUM
RATING:
COLLECTOR-EMITTER
VOLTAGE 30 V.
SET THE COLLECTOR CURRENT VALUE TO UNDER 0.4 mA.
OUTPUT CHANGES FROM LOW LEVEL TO HIGH LEVEL
ACCORDING TO SUCTION / DISCHARGE DIRECTION.
DISCHARGE DIRECTION : 9600 STEPS
SUCTION DIRECTION 960 STEPS
The above specifications are applicable when the pump is set to operate at full step using a controller ICD200.
For more detailed information, please see the users manual for SBP-100G series.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
ICD200-1120A-03
Specifications for Controller part
ITEMS
MODEL NUMBER
NUMBER OF APPLICABLE AXIS
USE OF ASIC
DIMENSIONS
CONTROL TYPE
INPUT POWER
CONSUMPTION POWER
COMMUNITCATION I/F
NUMBERS OF REWRITING SERIAL
ROM
STANDARD
ENVIRONMENTAL TEMPERATURE
OPERATING HUMIDITY
STORING HUMIDITY
WEIGHT
Specification of driver part
ITEMS
DRIVING TYPE
DRIGVING CURRENT
DESCRIPTION
ICD200-1120A-03
1 AXIS
1 pc. MCD 1201
60(D) x 90(W) x 36(H)
I/O START TYPE
DC 24 V 10 %
LESS THAN 24 W
RS485 (DATA DOWNLOAD AND START COMMNAD ETC. FROM
PC)
1 MILLION TIMES
EU RoHS COMPLIANT
0 40 (NO FREEZING)
OPERATING
0 60 (NO FREEZING)
STORING
LESS THAN 80 % (NO CONDENSATION)
LESS THAN 80 % (NO CONDENSATION)
130 g
AUTO-CURRENT DOWN
DRIVING CURRENT ADJUSTMENT
OVER HEAT DETECTION
DESCRIPTION
BI-POLAR CONSTANT CURRENT TYPE
MAX. 1.2 A (TOTAL OUTPUT CURRENT)
Default 0.25 A
1, 2, 2.5, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50 OR 100 DIVISION (10 KINDS) OF
STANDARD STEP.
ABOUT 50 % OF DRIVING CURRENT
BY VOLUME ON THE BOARD
ALARM OUTPUT AT HIGHTER THAN ABOUT 70
Specification of ICDRS_GUI
ITEMS
APPLICABLE OS
DESCRIPTION
Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows 7 (32 bit, 64 bit)
RESOLUTION
For more details, please see the users manual for ICD200 series issued by MYCOM, INC.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
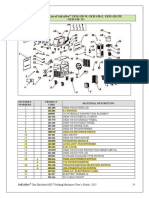
External Appearance and Name of Each Part
SBP-100G Series
Note: External appearance of SBP-100G-N(Needle:22G)
ICD200-1120A-03
For External Appearance and Name of Each Part of ICD200-1120A-03, please see the users manual for
ICD200 series issued by MYCOM, INC.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
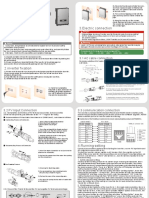
Wiring Diagram and Circuit Diagram
Cable Connection
1.
Motor cable
SBP-100G series
Name
A
/A
B
/B
2.
Exciting Sequence (Full Step)
Cable Color
Orange
Brown
Red
Yellow
ICD200-1120A
Motor cable
Name Cable Color
A
Orange
/A
Brown
B
Red
/B
Yellow
Step
/A
/B
1
2
Operating directions are as follows:
Step Sequence Motor
Syringe pump
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 CW rotation
Suction
4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 CCW rotation Discharge
Sensor cable
ICD200-1120A
Sensor cable
Name
Cable Color Name Cable Color
+COM Brown
SEN1 Red
-COM Orange
+24 VDC Green
+COM Yellow
SIGNAL Purple
SEN2 Green
GND
Blue
-COM Blue
+COM Purple
SEN3 Gray
-COM White
This is when operating one syringe pump at Relative
Positioning Drive Mode or PC Drive Mode, with
using the sensor as the one for returning to the
origin.
SBP-100G series
Motor Circuit Diagram
Sensor Circuit Diagram
Set the collector current value to under 0.4 mA.
Output changes from low level to high level
according to suction / discharge direction.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
SBP-100G Series Users Manual
Method of Starting with ICD200
Pen-type syringe pump SBP-100G series is a small
syringe pump designed by Takasago Electric, Inc. Its
feature is its compact size (12 mm diameter) and
light weight. When driving at full-step, theoretical
resolution is 10.5nL. It has a built-in sensor to
prevent overrun.
For using ICD200, I/O drive that uses external I/O as
a start signal, and PC drive that is operated by a
personal computer through RS485 I/F is available.
In I/O drive, starting/moving point specification is
made by input signal from start signal I/F connecter
or Sensor I/F connecter. For I/O drive, sensor mode,
absolute positioning drive mode, relative positioning
drive mode are available.
The user's manual below is available for SBP-100G
series. Read through the user's manual before use,
and make sure that the product is used properly.
In PC drive, starting/moving point specification is
made through RS485 I/F with a communication
software ICDRS GUI. If one wishes to operate the
pump easily, this mode is recommended.
SBP-100G series Users Manual
A user's manual for SBP-100G series. Specifications
and usage is explained in it.
ICD-200 Users Manual
This user's manual explains the usage to operate one
pump by either I/O drive with relative positioning
drive mode or PC drive through using the sensor for
origin returning.
I/O start type drive controller ICD200 is a controller
& driver designed by MYCOM, INC. As a controller
and a driver are unified, operating the syringe pump
is made possible with this unit. Original Nano-drive
method enables the basic step angular to be divided
into 100 at the maximum.
ICD200-1120A-03, the exclusively used model for
SBP-100G series' drive, is a improved model of a
basic ICD200-1120A. It is designed to make the
driver part's driving current at the optimum value.
Method of
Starting
PC Drive
Sensor Mode
I/O
Drive
Absolute
Positioning
Drive Mode
Relative
Positioning
Drive Mode
3 user's manuals below are available for ICD200.
Read through the user's manual before use, and
make sure that the product is used properly.
ICD200 Series Users Manual
A user's manual for ICD200. It includes the usage
and detailed information for hardware.
ICDRS_GUI_EN Users Manual
A user's manual for controlling ICD200 through a
personal computer. It includes the usage of ICDRS
GUI for Windows.
ICD200/201 Communication Specification
A user's manual for ICD-200 - host communication.
It includes detailed information of communication,
such as commands and response.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
How to Use (Setting)
Operation1. Assemble the syringe pump
Table 1 Setting of DIP switch
The needle is packed having been removed from the
syringe pump for protection. Please assemble
according to the instructions below when using.
SW No.
SW1-1
SW1-2
SW1-3
SW1-4
SW1-5
SW1-6
SW2-1
SW2-2
SW2-3
SW2-4
In order starting from the tip the parts are the cap,
spring, needle and syringe. When you screw the
needle into the syringe, insert the needle into the
hole at the center of the PTFE inside the syringe. Be
careful not to scratch the surface of PTFE by
inserting it in the wrong position. In addition,
although it may sometimes be hard to insert, please
insert it slowly with your hands (not using any tools).
For PC
For Relative
Drive Mode Positioning Drive Mode
()
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
either ON/OFF is acceptable.
Operation4. (Option: For Relative Positioning
Drive Mode) Wire PLC and the drive
WARNING
WARNING
For PC drive, see Operation 5
i.
Prepare Programmable logic controllerreferred
to as PLC(or switch for start signal).
ii.
Do the cable end treatment on Start signal I/F
cable (opposite side of the connector), and wire
Protect the product from strong
to PLCs input/output terminal and power
impacts and do not drop it. Impacts
terminal.
may cause injury.
iii.
Insert Start signal I/F cable to ICD200.
Handle the needle carefully. The tip of
the needle is sharp and may cause an
injury.
Table 2 Start Signal I/F cable
(Relative Positioning Drive Mode)
Operation2. Wire the syringe pump and driver
Connect the motor cable and sensor cables of the
syringe pump to a driver. Please refer to the figure
How to connect SBP-100G series, ICD200 and PC
on Page 10.
Cable
Number
and Color
1(Brown)
2(Red)
3(Orange)
4(Yellow)
5(Green)
6(Blue)
7(Purple)
8(Gray)
9(White)
10(Black)
11(Brown)
12(Red)
13(Orange)
Operation3. Setting of ICD200
Check that the JP for termination is inserted, and
then set the DIP switch as below.
SW1
SW2
JP
Name
PLC
Connection
+COM
ST1
ST2
ST3
DIR
ORG
CO
STOP
FIN1
FIN2
FIN3
ALARM
-COM
+24V
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
GND
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Operation5. Wire Power and the driver
i.
ii.
iii.
Prepare DC power supply DC24V 10 .
Power is not turned on during the preparation.
Cut Power cable for a certain length, and do the
cable end treatment.
Attach Power cables connector to ICD200.
Table 3 Power Cable
Cable Color
Red
Black
Connection
+24 VDC
GND
Figure 1 USB/RS485 I/F cable
For PC drive, procedure below is required.
i.
Cut Start signal I/F cable to a certain length,
and do the cable end treatment for cables
(1(Brown) and 13(Orange)).
ii.
Attach the connector of Start signal I/F cable to
ICD200.
iii.
Connect the terminals of Start signal I/F cable
and Power cable to the DC power supply.
Operation7. Power Supply
Apply the DC power supply to ICD200. Check if
LED is as the state below.
Table 5 State of LED
LED No.
PWR
MONI
Table 4 Start signal I/F cable (PC Drive Mode)
ERR
Cable Number and Color
1 (Brown)
13 (Orange)
Connection
+24 VDC
GND
State
Green light
Lights out
First time Red light
After setting Lights out
Operation8. Setting communication between
PC and ICD200
Set the port for USB/RS-485 conversion cable.
Open USB Serial Port from Port at device
manager, and set the port as below. Port number
needs to be set as COM1 COM9.
Operation6. PC Setting
i.
ii.
iii.
Install ICDRS GUI to a personal computer. For
detailed information, see ICDRS_GUI_EN
Users Manual.
Install driver for USB/RS-485 conversion cable
to a personal computer. For detailed information,
see the manual attached to USB/RS-485
conversion cable. Driver and manual can be
downloaded from the website below.
http://www.cabling-ol.net/cabledirect/UTS-485.p
hp
Connect USB/RS-485 conversion cable to the
computers USB port. Attach one side of
RS485/IF cable to USB/RS-485 conversion cable,
and then connect the other side to ICD200s
connector.
Table 6 Port setting
Items
Baud rate
Data bit
Parity
Stop bit
Flow Control
Description
19200
8
Even
1
None
Set the communication of ICDRS GUI. Set the
appropriate COM port and Baud rate from
menu communication setting.
Check if the communication is established on the
menu.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Figure 2 How to connect SBP-100G series, ICD200 and PC.
Operation9. Default Setting of ICD200
Do the initial setting of ICDRS GUI. Set the each
parameter as below. Transmit the setting to ICD200, and
write them to ICD200s memory.
Table 7 Default setting of ICD200
Items
ERR output
FIN output
STOP input
CO input
DIR input
SEN1 input
SEN2 input
SEN3 input
Current down time
Position compensation movement retry
Wait time until sensor state
confirmation
Description
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
300 ms
1 time
1 ms
10
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
How to Use (PC Drive Mode)
Preparation Setting ICDRS GUI
i.
Table 9 Movement Execution (10 L discharge)
Select Setting in PC Start tab, and select drive
pattern data 1, data 2, origin return, and set
them as below.
Items
Axis
Movement
Pattern
Table 8 Setting in PC Start
Items
Data 1
Data 2
Axis
Speed mode
1
Low
1500
Hz
300 Hz
0.1 %
1
Low
1500
Hz
300 Hz
0.1 %
Maximum speed
Origin
return
1
Low
Upload with Application button.
iii.
Press Data transmission to ICD button,
transmit the setting above to ICD200, and write
them to ICD200s memory.
WARNING
Forwardtips edge is at 50
- 100 L
or
Reversetips edge is at 0
- 49 L
Direction of
rotation
When one changes the resolution from
1/1, driving current value needs to be
changed. See How to Use (Step
Drive).
ii.
Select ICDRS GUIs Movement Execution tab,
and set as below. Change the direction of the
rotation depending on the position of the tips
edge in the syringe (In order not to make the tip
touch the edge of the syringe, or not to make it
continues its operation going beyond the origin).
Press Start button, and check that it stops after
operating for 10 L. Slowdown Stop button,
Instant Stop button can stop its operation at
any time.
Operation2. Origin Return
i.
Select ICDRS GUIs Movement Execution tab,
and set as below.
Table 10 Movement Execution (Origin Return)
Items
Axis
Movement Pattern
Direction of rotation
ii.
Description
1
Origin Return
Forward
Start button makes the tip moves toward
suction direction, and the motor stops
automatically when it reaches the origin.
Operation3. Suction/Discharge of liquids
i.
Select ICDRS GUIs Movement Execution tab,
and set as below.
Table 11 Movement Execution (100 L discharge)
Item
Operation1. Test Run (10 L discharge)
i.
Data 1
1000 Hz
Start speed 1
300 Hz
Average slope
0.1 %
Practice in S-curve
None
None
None
slope
Amount of
960
9600
1 pulse
Movements 1
pulse
pulse
Resolution
1/1
1/1
1/1
Accumulation
counter is clear when None
None
None
starting
Rounding off
Invalid Invalid Invalid
protection
Forward direction
CCW
CCW
CCW
Data 1 : 10 L suction / discharge setting
Data 2 : 100 L suction / discharge setting
Origin Return : Origin return setting
ii.
Description
1
Axis
Movement Pattern
Direction of rotation
ii.
iii.
11
Description
1
Data 2
Forward
Start button makes the tip moves toward
discharge direction to 100 L (9600 steps),
discharging air in the syringe .
Select ICDRS GUIs Movement Execution tab,
and set as below.
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Table 12 Movement Execution Setting (100 L suction)
Item
Axis
Movement Pattern
Direction of rotation
Insert the needle into liquids for suction. Start
button makes the tip moves toward suction
direction to 100 L (9600 steps) for suction into
syringe.
v.
Discharge the air left in the syringe by repeatedly
conducting discharge and suction. Air would be
discharged more easily when needle is faced
upper direction.
WARNING
Due to backlash, the pumps suction/discharge is
not conducted for a short time when changing the
direction of the motors rotation. Use as follows for
avoiding the variation caused by backlash.
Description
1
Data 2
Reverse
iv.
WARNING
Operation5. Elimination of backlash
Example Eliminate backlash and discharge
50L
i. Set to the origin.
ii. Moves toward suction direction for 960 steps.
iii. Moves toward discharge direction for 960 steps
to eliminate backlash.
iv. Moves toward discharge direction for 4800
steps to discharge 50 L.
NoteBacklash is a striking back of connected wheels. With
backlash, the pumps suction/discharge temporarily stops
because the rotary motion is not transmitted when the
motor rotates to the other direction. Backlash is not created
if the motor rotates in a same direction.
Do not make the tip contact to the edge
of the syringe. This may cause worse
performance or malfunction.
Do not make the tip continues to go for
suction direction beyond the origin
sensor. This may cause worse
performance or malfunction.
Operation4. Syringe Pump Operation
Operate the pump for suction/discharge by driving
the stepper motor. The range for discharge is 9600
steps from origin, the range for suction is 960 steps.
WARNING
WARNING
Do not allow the temperature of the
motors surface goes beyond 90 . The
heat
generation
may
cause
malfunction on the motor.
Do not keep operating the pump while
there is no liquid in the syringe. The
tip will wear and it causes worse
performance or malfunction. Follow
Operation5 to replace the air with
liquids.
12
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
How to Use (I/O Drive Relative Positioning Drive Mode)
Preparation: Setting ICDRS GUI
i.
Table 14 PLC Setting 1 (10 L suction / discharge)
Select Setting in PC Start tab, and select drive
pattern data 1, data 2, origin return, and set
them as below.
ii.
Press Application button to update the content.
iii.
Select Data -transmission to ICD button, and
transmit the setting to ICD200 and write them to
ICD200s memory.
Name
ST1
ST2
ST3
DIR
Setting
HL
H
H
L
H
Table 13 Setting in Relative Position Mode
Items
Data 1
Data 2
ORG
CO
STOP
Origin
Return
1
Low
Axis
1
1
Speed mode
Low
Low
Maximum
1500 Hz 1500 Hz
1000 Hz
speed
Start speed 1 300 Hz
300 Hz
300 Hz
Average slope 0.1 %
0.1 %
0.1 %
Practice in
None
None
None
S-curve slope
Amount of
960
9600
1 pulse
Movements 1 pulse
pulse
Resolution
1/1
1/1
1/1
Accumulation
counter is
None
None
None
clear when
starting
Rounding off
Invalid
Invalid
Invalid
protection
Forward
CCW
CCW
CCW
direction
Data 1 : 10 L suction / discharge setting
Data 2 : 100 L suction / discharge setting
Origin Search : Origin return setting
Operation1.
Test
run
(10
uL
suction
Operation2. Origin Return
i.
ii.
Set PLCs output as below.
Table 15 PLC Setting 2 (Origin Return)
Name
ORG
ii.
Setting
HL
Description
Start Origin Search
By making ORG L, the tip moves toward suction
direction, and as it reaches the origin, the motor
stops.
Operation3. Suction/Discharge of liquids
i.
Set PLCs output as below.
Table 16 PLC Setting 3 (100 L discharge)
Name
ST1
ST2
ST3
DIR
Setting
HL
L
H
L
Description
Start 100 L discharge
select parameter
parameter2
Forward
discharge)
i.
H
H
H
Description
starting
select parameter
parameter1
Forwardtips edge is at 50 100 L
Reversetips edge is at 0 49 L
Origin Searchinvalid
Current OffON
Stopinvalid
ii.
Change the direction of the rotation depending on
the position of the tips edge in the syringe (In
order not to make the tip touch the edge of the iii.
syringe, or not to make it continues its operation
going beyond the origin).
By making ST1 L, the tip moves toward
discharge/suction direction for 10 L (960 steps).
By making ST1 L, the tip moves toward
discharge direction for 100 L(9600 steps) to
discharge the air inside the syringe.
Set PLCs output as below.
Table 17 PLC Setting 4 (100 L suction)
Name
ST1
ST2
ST3
DIR
13
Setting
HL
L
H
H
Description
Start 100 L suction
select parameter
parameter2
Reverse
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
iv.
Insert the needle into liquids for suction. By
making ST1 L, the tip moves toward suction
direction for 100 L (9600 steps) for suction.
v.
Operation5. Elimination of backlash
Due to backlash, the pumps suction/discharge is
not conducted for a short time when changing the
direction of the motors rotation. Use as follows for
avoiding the variation caused by backlash.
Discharge the air left in the syringe by repeatedly
conducting discharge and suction. Air would be
discharged more easily when needle is faced
upper direction.
WARNING
WARNING
NoteBacklash is a striking back of connected wheels. With
backlash, the pumps suction/discharge temporarily stops
because the rotary motion is not transmitted when the
motor rotates to the other direction. Backlash is not created
if the motor rotates in a same direction.
Do not make the tip contact to the edge
of the syringe. This may cause worse
performance or malfunction.
Do not make the tip continues to go for
suction direction beyond the origin
sensor. This may cause worse
performance or malfunction.
Operation4. Syringe Pump Operation
Operate the pump for suction/discharge by driving
the stepper motor through PLC. The range for
discharge is 9600 steps from origin, the range for
suction is 960 steps.
WARNING
WARNING
Do not allow the temperature of the
motors surface goes beyond 90 . The
heat
generation
may
cause
malfunction on the motor.
Do not keep operating the pump while
there is no liquid in the syringe. The
tip will wear and it causes worse
performance or malfunction. Follow
Operation5 to replace the air with
liquids.
14
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
How to Use (Step Drive)
1. What is Step Drive?
SBP-100G series is capable of 2 drive modes below.
Full StepResolution : 1
StepResolution : More than 2)
C.ADJ Volume
Step drive enables to hold down the oscillation and
lower the noise by raising resolution.
Figure:
Current Adjust Volume
ICD-200 is capable of 10 kinds of standard step as 1 /
Table 18 Setting driving current value for Step drive
2 / 2.5 / 4 / 5 / 10 / 20 / 25 / 50 / 100. In order to
operate SBP-100G series on Step drive, current
value is required to be adjusted to the resolution.
2. Preparation: Setting driving current value
i.
Resolution
Current
250 mA (initial value)
More than 2
200 mA
See How to Use (PC Drive Mode) for setting as
below. Set an ammeter as the current on A
iv.
Return the state of
SW1(4 poles ON, 6 poles
OFF)
phase of the motor cable can be monitored. Turn
4 poles on SW1 OFF, 6 poles ON.
WARNING
If C.ADJ volume is fully rotated to
clockwise, current beyond the rated
current is applied, and it causes failure
on the motor. Set as the current does
not go beyond the rated value.
Figure 3 Wiring diagram for setting driving current
ii.
Apply the drivers power after checking that the
Current Adjust (C.ADJ) volume is fully rotated
to counter clockwise.
iii.
Adjust the motors rated driving current with
C.ADJ volume. Set the current value as below.
15
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Note:
Driving current is measured by repeatedly suction/discharging on 5 seconds cycle at the condition below.
Table 19 Note:Step setting
Items
Resolution
1/1
Resolution
1/4
Resolution
1/10
Resolution
1/100
Axis
Speed mode
Low
Low
Low
Medium
Maximum speed
2,500 Hz
10 kHz
25kHz
250 kHz
Start speed 1
300 Hz
1,200 Hz
3 kHz
30 kHz
Average slope
0.1 %
0.4 %
1.0 %
1.0 %
Practice in S-curve slope
None
None
None
None
Amount of Movements 1
9,600 pulse
38,400 pulse
96,000 pulse
960,000 pulse
Accumulation counter is clear when starting
None
None
None
None
Rounding off protection
Invalid
Invalid
Invalid
Invalid
Forward direction
CCW
CCW
CCW
CCW
16
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Usage Precautions
If you have any trouble, please check the following. If
the problem persists after performing these
inspections, please contact us.
Specifications and appearance are subject to
change without notice.
Do not apply excess pressure to the lead wires or
needle. Doing so may result in performance
deterioration or malfunction.
Protect the product from strong impacts and do not
drop it. Impacts may cause injury.
Do not use liquids containing foreign matter. Doing
so may cause performance deterioration or
malfunction.
Flush the inside of the barrel after use. Liquids
remaining within the barrel may cause performance
deterioration or malfunction.
Do not apply excessive pressure that exceeds
specifications. Applying a higher pressure than the
specification value may result in leakage, explosion,
or malfunction.
Do not use in a wet environment. Especially do not
get the motor or the sensor wet. A shortcircuit may
occur, resulting in performance deterioration or
malfunction.
Keep the surface temperature of motor under 90 C.
The motor may be damaged by the generation of
heat. We recommend monitoring the surface
temperature of the motor after a change in operating
conditions.
Do not operate the pump with the syringe full of air.
The tip inside the syringe will wear away, possibly
resulting
in
performance
deterioration
or
malfunction.
Symptom
Motor does
not work.
Motor
rotates
unstably.
Motor is out
of step or
races.
The motor is
out of step or
races when
the pump is
operated
over the limit
in
the
suction
/
discharge
direction.
Inspection
Check if the power is ON.
Check if the motor and the driver
are correctly wired.
Check if the motor and the driver
are connected.
Check if the input pulse frequency
is high. If the frequency is high,
the
torque
of
the
motor
deteriorates.
Check that the liquid does not
contain foreign matter.
If the pump is operated over the
limit in the suction / discharge
direction, it requires a large torque
to return to the original position.
<Tip>
Increase the torque of the motor by
increasing the applied current in
addition to lowering the operating
frequency of the stepper motor so
that
it
recovers
from
the
out-of-step situation. At this time,
keep the surface temperature of
motor under 90 . The motor may
be damaged by the generation of
heat.
17
2nd edition
TAKASAGO ELECTRIC, INC.
Warrantee
WARRANTY CONDITIONS AND
INSTRUCTIONS (attached separately)
Please read thoroughly and keep for your record.
Contact
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us
at any time.
Takasago Electric, Inc.
Sales and Engineering
66 Kakitsubata Narumi-cho Midoriku Nagoya
458-8522 JAPAN
Tel: +81-52-891-2301 Fax: +81-52-891-7386
E-mail: info@takasago-elec.co.jp
URL: http://www.takasago-fluidics.com
All rights reserved. Any unauthorized distribution or
reproduction of this manual is prohibited.
The contents of this Users Manual are current as of
May 2013.
Specifications and appearance are subject to
change without notice.
All company and product names are trademarks or
registered
trademarks
of
their
respective
companies.
18
2nd edition
You might also like
- Ups Multi DialogDocument49 pagesUps Multi DialogDavid Bernis100% (2)
- Domino - Vision Teknik - Serialization Solution - Hisfarin Material PDFDocument48 pagesDomino - Vision Teknik - Serialization Solution - Hisfarin Material PDFwisang geniNo ratings yet
- MTC Software Manual (Current Use)Document28 pagesMTC Software Manual (Current Use)Sharath Teja ReddyNo ratings yet
- FC 1 Do 12Document12 pagesFC 1 Do 12veroljubdjNo ratings yet
- AC Servo Drive: Operation ManualDocument116 pagesAC Servo Drive: Operation ManualjassemNo ratings yet
- 369 Motor Management Relay - Communications Guide PDFDocument170 pages369 Motor Management Relay - Communications Guide PDFrafaelfbacharelNo ratings yet
- TC3001 With COMMDocument139 pagesTC3001 With COMMmd3001abcNo ratings yet
- 13.4. Spare Part List of Gekamac GKM 420-2GDocument2 pages13.4. Spare Part List of Gekamac GKM 420-2GBa MamadouNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Magnetic Flowmeters 10DS3111 Design Level E Sizes 1 Through 12 InchesDocument57 pagesInstruction Manual: Magnetic Flowmeters 10DS3111 Design Level E Sizes 1 Through 12 InchesAlejandro GuerraNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: FeaturesDocument2 pagesOperating Manual: FeaturesTahera SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Kinetix 300Document222 pagesKinetix 300Raul Villalvazo0% (1)
- 6sr41 SeriesDocument202 pages6sr41 Seriesfireza husnulNo ratings yet
- ISO9001 Quality Management System AuthenticationDocument139 pagesISO9001 Quality Management System AuthenticationrzrasaNo ratings yet
- WRL Power Series 10-400K User ManualDocument81 pagesWRL Power Series 10-400K User ManualShahan Mehboob100% (1)
- Ett-6 PD enDocument2 pagesEtt-6 PD enyounesNo ratings yet
- 1LG0 Catalogue (En)Document23 pages1LG0 Catalogue (En)Sandi AslanNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting For Unidrive SP Commander GP20Document4 pagesTroubleshooting For Unidrive SP Commander GP20castkarthickNo ratings yet
- Mobile Manipulator Application GuideDocument29 pagesMobile Manipulator Application GuideEdson Pires da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Kewo Solar Pump Drive CatalogDocument15 pagesKewo Solar Pump Drive Catalogiulius299No ratings yet
- 05 - FK CF PTZ 3612 IQ - enDocument2 pages05 - FK CF PTZ 3612 IQ - entrung2iNo ratings yet
- Polaris Dp30Document74 pagesPolaris Dp30joseNo ratings yet
- C4505 Deh-4250sd, Deh-4290sd, Deh-3200ubDocument82 pagesC4505 Deh-4250sd, Deh-4290sd, Deh-3200ubW_JaimesNo ratings yet
- Cordex 110-1.1kW - Tehnicke KarakteristikeDocument34 pagesCordex 110-1.1kW - Tehnicke KarakteristikeTomislav BjelicaNo ratings yet
- Soft Drive 200 DesignDocument22 pagesSoft Drive 200 DesignMine RHNo ratings yet
- BMD4064 Input/Output Module ApplicationDocument8 pagesBMD4064 Input/Output Module Applicationreza rifqil aziz100% (1)
- Digsi 5 Quick Notes Digsi-5-Qn0020: Device Modes & Test SuiteDocument5 pagesDigsi 5 Quick Notes Digsi-5-Qn0020: Device Modes & Test SuiteWalter Andres Estevez VasquezNo ratings yet
- STR58U Mastepact ACBDocument74 pagesSTR58U Mastepact ACB322399mk7086No ratings yet
- FK3u Analog 485Document18 pagesFK3u Analog 485Vitex Ascensores GaliciaNo ratings yet
- 3-5.5KVA Inverter User ManualDocument29 pages3-5.5KVA Inverter User ManualAron IonutNo ratings yet
- POWER FACTOR CONTROLLER RG-TDocument4 pagesPOWER FACTOR CONTROLLER RG-THafizudin Md IsaNo ratings yet
- ACS800 Democase Default ParametersDocument14 pagesACS800 Democase Default ParametersRemigio MendozaNo ratings yet
- Touch Screen Numerical Control: SIAX A100Document2 pagesTouch Screen Numerical Control: SIAX A100Mounir BelalaNo ratings yet
- Operator's Manual For Collins MP-20 Radio SetDocument27 pagesOperator's Manual For Collins MP-20 Radio Setm38a1guy100% (1)
- Spectral Pyrometer ARDOMETER MPA 1x, 2x, 3x 7MC3030-.Document92 pagesSpectral Pyrometer ARDOMETER MPA 1x, 2x, 3x 7MC3030-.Aissa MidouneNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Temperature SwitchesDocument4 pagesInstruction Manual Temperature Switchesdel110001No ratings yet
- Service: LCD-TVDocument107 pagesService: LCD-TVLeandro BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Keli D30-2 Calibrate ManualDocument11 pagesKeli D30-2 Calibrate ManualTakaSenseiNo ratings yet
- CXD2861ERDocument30 pagesCXD2861ERZaegorNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa 616G5Document332 pagesYaskawa 616G5Hernan A Villadiego VNo ratings yet
- Gd200 ManualDocument252 pagesGd200 ManualTrien DoNo ratings yet
- R-G2 Controller Maintenance PDFDocument336 pagesR-G2 Controller Maintenance PDFpabs2604No ratings yet
- Siemens LR560 HART Man 7ML19985KB01 PDFDocument157 pagesSiemens LR560 HART Man 7ML19985KB01 PDFcesarNo ratings yet
- Wartsila o P Ihimu CRPDocument6 pagesWartsila o P Ihimu CRPNguyễn Tấn TrưởngNo ratings yet
- SG 60 KTLDocument104 pagesSG 60 KTLadjiNo ratings yet
- SYS001-02 00 Flusarc (En)Document36 pagesSYS001-02 00 Flusarc (En)Ursula JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Teknic MCPV Manual Frame 56Document209 pagesTeknic MCPV Manual Frame 56jnbxyzNo ratings yet
- Aqua Mon 4000 PH Red Ox AnalyserDocument4 pagesAqua Mon 4000 PH Red Ox Analyserarvindgupta_2005No ratings yet
- OHD Thermal Guard: ApplicationsDocument11 pagesOHD Thermal Guard: ApplicationsJoseNo ratings yet
- DSE Link 5000 Software ManualDocument61 pagesDSE Link 5000 Software ManualAnonymous vqsuRyNo ratings yet
- Arcnet: 1. Revision OverviewDocument13 pagesArcnet: 1. Revision OverviewEduardo Perin de FreitasNo ratings yet
- Baldor VS1MD Micro Series ManualDocument163 pagesBaldor VS1MD Micro Series ManualSteve WozniakNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi - WS-55809 Service ManualDocument68 pagesMitsubishi - WS-55809 Service ManualDaniel MorganNo ratings yet
- 611U Manual PDFDocument976 pages611U Manual PDFBaldev SinghNo ratings yet
- PTM-6V Position Transmitter ManualDocument14 pagesPTM-6V Position Transmitter ManualMohd SamirNo ratings yet
- Resistive Level Measurement ManualDocument21 pagesResistive Level Measurement Manualatheb12345100% (1)
- Working Instructions DOC25 ACW6x4 Nxr12i RevdDocument43 pagesWorking Instructions DOC25 ACW6x4 Nxr12i RevdJezer Lugo100% (1)
- Moog ServoDrives DS2000 Manual enDocument142 pagesMoog ServoDrives DS2000 Manual enBojan MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Rm5 Operation Manual (1-38Document45 pagesRm5 Operation Manual (1-38tonnytoons67% (3)
- MANUAL For Inverter 3.5 KW LNCDocument78 pagesMANUAL For Inverter 3.5 KW LNCEduardo Gonzalez OleaNo ratings yet
- PWD - Electronic For Proportional Directional Control Valves - Installation ManualDocument9 pagesPWD - Electronic For Proportional Directional Control Valves - Installation ManualCrz Mdfkr0% (1)
- Powerlogic Energy Meter: Instruction Boletín de Bulletin Instrucciones EnglishDocument28 pagesPowerlogic Energy Meter: Instruction Boletín de Bulletin Instrucciones EnglishJose LunaNo ratings yet
- 7 7725 Pamod 03eDocument15 pages7 7725 Pamod 03eJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Logic Controller - Modicon M221 - TM221CE16RDocument17 pagesLogic Controller - Modicon M221 - TM221CE16RJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Pac3200 PDFDocument117 pagesPac3200 PDFJose LunaNo ratings yet
- 7 7000 Pamod 05eDocument18 pages7 7000 Pamod 05eJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Design Strategy For A 3-Phase Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) PDFDocument37 pagesDesign Strategy For A 3-Phase Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) PDFSamuel Mushaka100% (1)
- CP1L ModbusRTUDocument6 pagesCP1L ModbusRTUJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Technical Description Sigma Air Manager: Process Data V0.23Document15 pagesTechnical Description Sigma Air Manager: Process Data V0.23Jose LunaNo ratings yet
- Kaeser Process MapDocument17 pagesKaeser Process MapJose LunaNo ratings yet
- PID Closed Control Loop of A Knudsen PumpDocument21 pagesPID Closed Control Loop of A Knudsen PumpJose LunaNo ratings yet
- User Manual TLBDocument49 pagesUser Manual TLBJose Luna100% (1)
- Eaton9130UPSBrochure9130TFXA PDFDocument2 pagesEaton9130UPSBrochure9130TFXA PDFJose LunaNo ratings yet
- DynamixelLibrary (English)Document17 pagesDynamixelLibrary (English)wanttosmartNo ratings yet
- Programming PIC Microcontrollers to Control Dynamixel Robot ActuatorsDocument8 pagesProgramming PIC Microcontrollers to Control Dynamixel Robot ActuatorsJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Angular Position Control of Stepper Motor Using Parallel Port on PCDocument11 pagesClosed Loop Angular Position Control of Stepper Motor Using Parallel Port on PCJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Laurel Electronics Quadrature TransmitterDocument4 pagesLaurel Electronics Quadrature TransmitterJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Totally Integrated Automation Portal ProgramDocument117 pagesTotally Integrated Automation Portal ProgramJose LunaNo ratings yet
- RotaryEncoders Overview PDFDocument48 pagesRotaryEncoders Overview PDFJose Daniel Fuquen VargasNo ratings yet
- H540113 2Document436 pagesH540113 2Jose LunaNo ratings yet
- Zero Speed Switch PDFDocument2 pagesZero Speed Switch PDFsunilbakoliya786No ratings yet
- Read VarDocument5 pagesRead VarJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Becker SteffenDocument320 pagesBecker SteffenJose LunaNo ratings yet
- TuserDocument442 pagesTuserJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Burker Actuador MotorizadoDocument7 pagesBurker Actuador MotorizadoJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Direct 15mm Micro Solenoid ValvesDocument2 pagesDirect 15mm Micro Solenoid ValvesJose LunaNo ratings yet
- 7SR23 (DAD) High Impedance Protection: For Internal Use Only / © Siemens AG 2012. All Rights ReservedDocument34 pages7SR23 (DAD) High Impedance Protection: For Internal Use Only / © Siemens AG 2012. All Rights Reservedhizbi7100% (1)
- TOCSIN 750 - Datasheet NEWDocument7 pagesTOCSIN 750 - Datasheet NEWabcd8482No ratings yet
- Dixell Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument4 pagesDixell Installation and Operating InstructionsiuliastarNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operating Instructions Zeverlution 3680 4000 5000 enDocument75 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions Zeverlution 3680 4000 5000 enTiên Lê Trần MỹNo ratings yet
- InsulGard ManualDocument111 pagesInsulGard ManualPriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Wiring Rs-485 Networks: Keymaster SystemsDocument26 pagesWiring Rs-485 Networks: Keymaster Systemsnicky_balan100% (1)
- ELM325 J1708 Interpreter: Description FeaturesDocument39 pagesELM325 J1708 Interpreter: Description FeaturesMarco Aurélio BorgesNo ratings yet
- Convertidor LBNP16301B-UserManualDocument16 pagesConvertidor LBNP16301B-UserManualJosé Ramón Rivera BarriosNo ratings yet
- MGate MB3180 QIG v2Document2 pagesMGate MB3180 QIG v2RobertoFuentesNo ratings yet
- CP Plus DVR User's Manual V1.03Document185 pagesCP Plus DVR User's Manual V1.03Tissara Nalin79% (19)
- Pantallas - STON - STAD070WT-05Document14 pagesPantallas - STON - STAD070WT-05jorge armando vega prietoNo ratings yet
- 02A EclipseLaunchDocument5 pages02A EclipseLaunchHJNo ratings yet
- EMU RS485 Communication Cable - External AlarmsDocument3 pagesEMU RS485 Communication Cable - External AlarmsCloud BeezerNo ratings yet
- KSG 5K DM3 Installation Manual PDFDocument2 pagesKSG 5K DM3 Installation Manual PDFMIchelle SmithNo ratings yet
- CX3G PLC User Manual V22.11Document2 pagesCX3G PLC User Manual V22.11Lalo MendezNo ratings yet
- 06 - Variable Speed DrivesDocument12 pages06 - Variable Speed DrivesMermillon JulienNo ratings yet
- 1S9A30 25-2-10 AVyQS-en PDFDocument156 pages1S9A30 25-2-10 AVyQS-en PDFTaufik Hidayat KurniansyahNo ratings yet
- Posicionador Digital Valtek Logix Series 2000Document24 pagesPosicionador Digital Valtek Logix Series 2000GustavoCruzNo ratings yet
- Taktis ® Vision: Configurable Fire Alarm Repeater SolutionDocument2 pagesTaktis ® Vision: Configurable Fire Alarm Repeater SolutionChaosNo ratings yet
- AS1 RS485 Communications Manual - 3281Document74 pagesAS1 RS485 Communications Manual - 3281hiloactiveNo ratings yet
- Nuflo MC III Plus ManualDocument136 pagesNuflo MC III Plus ManualJonathanNo ratings yet
- N Din FDocument4 pagesN Din Fpinku_thakkarNo ratings yet
- Abb Price ListDocument340 pagesAbb Price ListyogeshNo ratings yet
- K Uniflair Ug30Document48 pagesK Uniflair Ug30Myka MykNo ratings yet
- User Manual: HGM6100K Series Genset ControllerDocument31 pagesUser Manual: HGM6100K Series Genset ControllerW MoralesNo ratings yet
- FR1200 Installation Guide V1.1Document2 pagesFR1200 Installation Guide V1.1Kashif Aziz Awan100% (1)
- Fieldserver Driver - Serial YorktalkDocument2 pagesFieldserver Driver - Serial YorktalkPlay-O FarmsNo ratings yet
- MK120S Users ManualDocument306 pagesMK120S Users ManualKrittaphak HacheyramNo ratings yet
- Emax Ep1501Document2 pagesEmax Ep1501Gregory Virhuez NietoNo ratings yet
- Deep Sea 335Document88 pagesDeep Sea 335nestor arias castNo ratings yet