Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Local Area Network
Uploaded by
sagar pajankarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Local Area Network
Uploaded by
sagar pajankarCopyright:
Available Formats
Local area network - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
1 of 4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_area_network
Local area network
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
"LAN" redirects here. For other uses, see Lan (disambiguation).
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects
computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory,
or office building.[1] A local area network is contrasted in principle to a
wide area network (WAN), which covers a larger geographic distance
and may involve leased telecommunication circuits, while the media for
LANs are locally managed.
Ethernet over twisted pair cabling and Wi-Fi are the two most common
transmission technologies in use for local area networks. Historical
technologies include ARCNET, Token Ring, and AppleTalk.
A conceptual diagram of a local
area network using 10BASE5
Ethernet
Contents
1 History
1.1 Standards evolution
1.2 Cabling
1.3 Wireless media
2 Technical aspects
3 See also
4 References
5 External links
History
The increasing demand and use of computers in universities and research labs in the late 1960s generated the
need to provide high-speed interconnections between computer systems. A 1970 report from the Lawrence
Radiation Laboratory detailing the growth of their "Octopus" network[2][3] gave a good indication of the
situation.
Cambridge Ring (computer network) was developed at Cambridge University in 1974[4] but was never
developed into a successful commercial product.
Ethernet was developed at Xerox PARC in 19731975,[5] and filed as U.S. Patent 4,063,220
(https://www.google.com/patents/US4063220). In 1976, after the system was deployed at PARC, Metcalfe
and Boggs published a seminal paper, "Ethernet: Distributed Packet-Switching for Local Computer
Networks."[6]
ARCNET was developed by Datapoint Corporation in 1976 and announced in 1977.[7] It had the first
commercial installation in December 1977 at Chase Manhattan Bank in New York.[8]
Standards evolution
The development and proliferation of personal computers using the CP/M operating system in the late
1970s, and later DOS-based systems starting in 1981, meant that many sites grew to dozens or even
hundreds of computers. The initial driving force for networking was generally to share storage and printers,
9/3/2015 2:54 PM
Local area network - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
2 of 4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_area_network
which were both expensive at the time. There was much enthusiasm for the concept and for several years,
from about 1983 onward, computer industry pundits would regularly declare the coming year to be the year
of the LAN.[9][10][11]
In practice, the concept was marred by proliferation of incompatible physical layer and network protocol
implementations, and a plethora of methods of sharing resources. Typically, each vendor would have its own
type of network card, cabling, protocol, and network operating system. A solution appeared with the advent
of Novell NetWare which provided even-handed support for dozens of competing card/cable types, and a
much more sophisticated operating system than most of its competitors. Netware dominated[12] the personal
computer LAN business from early after its introduction in 1983 until the mid-1990s when Microsoft
introduced Windows NT Advanced Server and Windows for Workgroups.
Of the competitors to NetWare, only Banyan Vines had comparable technical strengths, but Banyan never
gained a secure base. Microsoft and 3Com worked together to create a simple network operating system
which formed the base of 3Com's 3+Share, Microsoft's LAN Manager and IBM's LAN Server - but none of
these was particularly successful.
During the same period, Unix computer workstations from vendors such as Sun Microsystems, HewlettPackard, Silicon Graphics, Intergraph, NeXT and Apollo were using TCP/IP based networking. Although
this market segment is now much reduced, the technologies developed in this area continue to be influential
on the Internet and in both Linux and Apple Mac OS X networkingand the TCP/IP protocol has now
almost completely replaced IPX, AppleTalk, NBF, and other protocols used by the early PC LANs.
Cabling
Early LAN cabling had generally been based on various grades of coaxial cable. Shielded twisted pair was
used in IBM's Token Ring LAN implementation, but in 1984, StarLAN showed the potential of simple
unshielded twisted pair by using Cat3 cablethe same simple cable used for telephone systems. This led to
the development of 10Base-T (and its successors) and structured cabling which is still the basis of most
commercial LANs today.
Fiber-optic cabling is common for links between switches, but fiber to the desktop is uncommon.
Wireless media
Many LANs are based partly or wholly on wireless technologies. Smartphones, tablet computers and laptops
typically have wireless networking support built-in. In a wireless local area network, users may move
unrestricted in the coverage area. Wireless networks have become popular in residences and small
businesses, because of their ease of installation. Guests are often offered Internet access via a hotspot
service.
Technical aspects
Network topology describes the layout of interconnections between devices and network segments. At the
Data Link Layer and Physical Layer, a wide variety of LAN topologies have been used, including ring, bus,
mesh and star, but the most common LAN topology in use today is switched Ethernet. At the higher layers,
the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) is the standard, replacing NetBEUI, IPX/SPX, AppleTalk and others.
Simple LANs generally consist of one or more switches. A switch can be connected to a router, cable
modem, or ADSL modem for Internet access. Complex LANs are characterized by their use of redundant
links with switches using the spanning tree protocol to prevent loops, their ability to manage differing traffic
types via quality of service (QoS), and to segregate traffic with VLANs. A LAN can include a wide variety
of network devices such as switches, firewalls, routers, load balancers, and sensors.[13]
9/3/2015 2:54 PM
Local area network - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
3 of 4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_area_network
LANs can maintain connections with other LANs via leased lines, leased services, or the Internet using
virtual private network technologies. Depending on how the connections are established and secured in a
LAN, and the distance involved, a LAN may also be classified as a metropolitan area network (MAN) or a
wide area network (WAN).
See also
IEEE 802 family of IEEE standards
Ethernet physical layer
LAN messenger
LAN party
Network card
References
1. Gary A. Donahue (June 2007). Network Warrior. O'Reilly. p. 5.
2. Samuel F. Mendicino (1970-12-01). "Octopus: The Lawrence Radiation Laboratory Network"
(http://www.webcitation.org/5tP07Xoec). Rogerdmoore.ca. Archived from the original
(http://www.rogerdmoore.ca/PS/OCTOA/OCTO.html) on 2010-10-11.
3. "THE LAWRENCE RADIATION LABORATORY OCTOPUS". Courant symposium series on networks
(Osti.gov). 29 Nov 1970. OSTI 4045588 (https://www.osti.gov/energycitations
/product.biblio.jsp?osti_id=4045588).
4. "A brief informal history of the Computer Laboratory" (http://www.webcitation.org/5tP0nKIlL). University of
Cambridge. 20 December 2001. Archived from the original (http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/conference/EDSAC99
/history.html) on 2010-10-11.
5. "Ethernet Prototype Circuit Board" (http://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/object.cfm?key=35&objkey=96).
Smithsonian National Museum of American History. Retrieved 2007-09-02.
6. "Ethernet: Distributed Packet-Switching For Local Computer Networks" (http://www.acm.org/classics/apr96/).
Acm.org. Retrieved 2010-10-11.
7. "ARCNET Timeline" (http://www.webcitation.org/5tP1JOSj5). ARCNETworks magazine. Fall 1998. Archived
from the original (http://www.arcnet.com/resources/HistoryATA.pdf) (PDF) on 2010-10-11.
8. Lamont Wood (2008-01-31). "The LAN turns 30, but will it reach 40?" (http://www.computerworld.com/action
/article.do?command=viewArticleBasic&articleId=9060198). Computerworld.com. Retrieved 2010-10-11.
9. "'The Year of The LAN' is a long-standing joke, and I freely admit to being the comedian that first declared it
in 1982..." (http://books.google.co.nz/books?id=FzsEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA45&lpg=PA45&dq=%E2
%80%9Cthe+year+of+the+LAN%E2%80%9D+bogus&source=bl&ots=hGEgb2Ekvc&sig=y6XBt_XvpiQlqkmVwUSRoYUCe8&hl=en&ei=6YlnTcCmNIjksQP9-tymBA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&
ved=0CBgQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false), Robert Metcalfe, InfoWorld Dec 27, 1993
10. "...you will remember numerous computer magazines, over numerous years, announcing 'the year of the
LAN.'" (http://www.ibiblio.org/java/quotes1999.html), Quotes in 1999
11. "...a bit like the Year of the LAN which computer industry pundits predicted for the good part of a decade..."
(http://herot.typepad.com/cherot/2010/10/connected-health-symposium.html), Christopher Herot
12. Wayne Spivak (2001-07-13). "Has Microsoft Ever Read the History Books?" (http://www.webcitation.org
/5tP23vwBy). VARBusiness. Archived from the original (http://guide.sbanetweb.com/press
/varbiz07116001.html) on 2010-10-11.
13. "A Review of the Basic Components of a Local Area Network (LAN)" (http://networkbits.net/lan-components
/local-area-network-lan-basic-components/). NetworkBits.net. Retrieved 2008-04-08.
External links
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org
/w/index.php?title=Local_area_network&oldid=677045987"
Wikimedia Commons has
media related to Local area
network.
Categories: Local area networks Office equipment
9/3/2015 2:54 PM
Local area network - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
4 of 4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_area_network
This page was last modified on 20 August 2015, at 19:45.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may
apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia is a registered
trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
9/3/2015 2:54 PM
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Cisco White Paper EPCDocument7 pagesCisco White Paper EPCReid_ChangNo ratings yet
- Charging SYSTEMDocument64 pagesCharging SYSTEMThind MalkeetNo ratings yet
- 1Document9 pages1sagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Ceramic: Vessels) or Figurines Made From Clay, Either by Itself or Mixed With OtherDocument12 pagesCeramic: Vessels) or Figurines Made From Clay, Either by Itself or Mixed With Othersagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Chennai Super KingsDocument38 pagesChennai Super Kingssagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Mysore PalaceDocument8 pagesMysore Palacesagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Hitman Hitman Is An Episodic Stealth Video Game Developed by IODocument13 pagesHitman Hitman Is An Episodic Stealth Video Game Developed by IOsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- SamsungDocument26 pagesSamsungsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- SDocument9 pagesSsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- DarjeelingDocument7 pagesDarjeelingsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Great Wall Motors Company LimitedDocument10 pagesGreat Wall Motors Company Limitedsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- REDocument5 pagesREsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Kolkata Knight RidersDocument10 pagesKolkata Knight Riderssagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Sunrisers HyderabadDocument22 pagesSunrisers Hyderabadsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Bajirao IDocument9 pagesBajirao Isagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- ShimlaDocument15 pagesShimlasagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- CrayonDocument11 pagesCrayonsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Colored PencilDocument4 pagesColored Pencilsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Oil Paint: Oil Paint Is A Type of Slow-Drying Paint That ConsistsDocument5 pagesOil Paint: Oil Paint Is A Type of Slow-Drying Paint That Consistssagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- PaintbrushDocument4 pagesPaintbrushsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Coal Mining in IndiaDocument4 pagesCoal Mining in Indiasagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Vernier ScaleDocument5 pagesVernier Scalesagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Cork BallDocument2 pagesCork Ballsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- ArchitectureDocument10 pagesArchitecturesagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- BaseballDocument30 pagesBaseballsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- QuatroDocument1 pageQuatrosagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- DodgeballDocument6 pagesDodgeballsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- 8 Qualities That Make Great Bosses Unforgettable: Jeff HadenDocument22 pages8 Qualities That Make Great Bosses Unforgettable: Jeff Hadensagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Swimming (Sport)Document12 pagesSwimming (Sport)sagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- BasketballDocument21 pagesBasketballsagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Table TennisDocument16 pagesTable Tennissagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- Sketch (Drawing)Document5 pagesSketch (Drawing)sagar pajankarNo ratings yet
- 1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Configure Router InterfacesDocument2 pages1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Configure Router InterfacesGene RodeNo ratings yet
- LTE ENB Feature Description SLR 2 4 V2 0 en PDF 1Document1,021 pagesLTE ENB Feature Description SLR 2 4 V2 0 en PDF 1Swati SiwachNo ratings yet
- Certified Routing Engineer (MTCRE) : Duration: OutcomesDocument2 pagesCertified Routing Engineer (MTCRE) : Duration: OutcomesKayode EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- LKSN 2022 - Module B - Network SystemsDocument7 pagesLKSN 2022 - Module B - Network Systemsani musNo ratings yet
- LAN-Cell 2 Release NotesDocument17 pagesLAN-Cell 2 Release NotesProxicastNo ratings yet
- Ds-3E0326P-E (B) 24-Port 100 Mbps Long-Range Unmanaged Poe SwitchDocument5 pagesDs-3E0326P-E (B) 24-Port 100 Mbps Long-Range Unmanaged Poe SwitchawadalmekawyNo ratings yet
- ICNS PresentationDocument9 pagesICNS PresentationDavidKNo ratings yet
- NKSTPP WiFi Access System DocsDocument6 pagesNKSTPP WiFi Access System DocsPawan VaskarNo ratings yet
- CN Lab - Manual (2023-24) Odd SemDocument58 pagesCN Lab - Manual (2023-24) Odd SemBv shankar RoyalNo ratings yet
- Modbus TCP Kopplung Doku v12 en - pdfuUUffffRLsEDocument80 pagesModbus TCP Kopplung Doku v12 en - pdfuUUffffRLsEMateo QuispeNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios PredicadosDocument399 pagesEjercicios PredicadosIsrael Martin Vargas TorresNo ratings yet
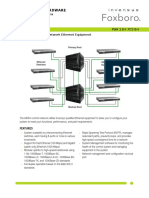
- I/A Series Hardware: ® Product SpecificationsDocument48 pagesI/A Series Hardware: ® Product SpecificationsHani IbrahimNo ratings yet
- LTE Advanced - Carrier Aggregation - ShareTechnoteDocument18 pagesLTE Advanced - Carrier Aggregation - ShareTechnoteGanesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Application Layer NotesDocument23 pagesComputer Networks Application Layer Notess indraneelNo ratings yet
- OSPF Configuration For IPv6 in Packet Tracer PDFDocument9 pagesOSPF Configuration For IPv6 in Packet Tracer PDFadNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Security All ExamsDocument79 pagesCisco CCNA Security All ExamsLiuwal MuñozNo ratings yet
- CCIE Practical Studies: Security (CCIE Self-Study) : Dmitry Bokotey Andrew G. Mason Raymond MorrowDocument1,104 pagesCCIE Practical Studies: Security (CCIE Self-Study) : Dmitry Bokotey Andrew G. Mason Raymond MorrowThomas PSNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Work No. 10: Link Aggregation and EtherchannelDocument7 pagesLaboratory Work No. 10: Link Aggregation and EtherchannelHanțig Eduard-GaborNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of a DNS Cache Poisoning AttackDocument58 pagesAnatomy of a DNS Cache Poisoning Attackwifawan52No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Junos Operating System - 12.A - Lab Guide DetailsDocument108 pagesIntroduction To The Junos Operating System - 12.A - Lab Guide DetailsTrần Đức HiềnNo ratings yet
- SUNDRAY AP S650 Wireless Access Point: Product OverviewDocument10 pagesSUNDRAY AP S650 Wireless Access Point: Product OverviewIrvan SyahNo ratings yet
- Common Industrial Protocol and Family of CIP Networks de ODVDocument134 pagesCommon Industrial Protocol and Family of CIP Networks de ODVAbdenago JesusNo ratings yet
- Congestion Control: Transport Layer 3-1Document14 pagesCongestion Control: Transport Layer 3-1Abhishek RegmiNo ratings yet
- BGP Course Exam R3-0 Release NoteDocument3 pagesBGP Course Exam R3-0 Release NoteNathalyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7ccnaDocument32 pagesChapter 7ccnaashenafi animawNo ratings yet
- Tcpdump f5 CommandDocument2 pagesTcpdump f5 CommandAjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- G120 Fieldbus FCT Man 0418 en-US PDFDocument244 pagesG120 Fieldbus FCT Man 0418 en-US PDFWilson Barco MNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: C# Websocket Server DocumentationDocument4 pagesTable of Content: C# Websocket Server DocumentationJoao AfonsoNo ratings yet