Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vii. Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders
Uploaded by
Dee Gee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
141 views4 pagesreviewer only
Original Title
Vii. Urine Screening for Metabolic Disorders
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentreviewer only
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
141 views4 pagesVii. Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders
Uploaded by
Dee Geereviewer only
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Denielle
Genesis B. Camato
VII. URINE SCREENING FOR METABOLIC DISORDERS
ANALYSIS O F URINALYSIS AND BODY FLUIDS | REVIEWER
OVERFLOW VERSUS RENAL DISORDERS
PHENYLALANINE TYROSINE DISORDERS
TWO CATEGORIES IN RENAL DISORDERS
a)
OVERFLOW TYPE
Results from the disruption of a normal metabolic pathway
that causes increased plasma concentrations of nonmetabolized substances.
PHENYLKETONURIA
b)
Metabolic defects cause production of excessive amounts
of melanin.
RENAL TYPE
caused by malfunctions in the tubular reabsorption
mechanism (see Chap 8; Tubular Disorders)
Metabolic Disturbances- most encountered abnormalities that
produce urinary overflow of substances involved in CHON and CHO
metabolism
Inborn Error of Metabolism- disruption of enzyme function
can be caused by failure to inherit the gene to produce a
particular enzyme, or by organ malfunction from disease or toxic
reactions.
ABNORMAL METABOLIC CONSTITUENTS FOR CONDITIONS DETECTED IN
THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS
Most well-known of the aminoacidurias; may lead to mental
retardation if remain undetected
first identified in NORWAY by Ivan Folling, 1934
Mousy-odor to urine
Increased amts of keto-acids including phenylpyruvate
Decrease production of tyrosine and its pigmentation
metabolite, melanin
Failure to inherit gene, phenyalanine hydroxylase
PHENYLALANINE, major constituent of milk from infants
diet
GUTHRIE TEST, most well-known test for PKU
Blood from heelstick is absorbed into filter paper; blood
impregnated disks are then placed on culture media streaked with
Bacillus subtilis
Beta-2-thienylalanine, inhibitor of B. subtilis
Tube test based on ferric chloride reaction; addition of ferric
chloride to urine with phenylpyruvic acid produces permanent
blue-green color
TYROSYLURIA
MAJOR DISORDERS OF PROTEIN & CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
ASSOCIATED WITH ABNORMAL URINARY CONSTITUENTS CLASSIFIED
AS TO FUNCTIONAL DEFECT
Accumulation of excess tyrosine in the plasma (tyrosinemia)
Urine may contain excess tyrosine or its degradation
products p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid & phydroxyphenyllactic acid
most frequently seen is a transitory tyrosinemia in
premature infants; under development of the liver function
Reaction can be distinguished from the PKU reaction in the
ferric chloride tube test because green color fades rapidly
when tyrosine is present
Nitroso-naphthol test, recommended urinary screening
test, orange-red is positive color
ALKAPTONURIA
AMINO ACID DISORDERS
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Tyrosinuria
Alkaptonuria
Melanuria
Maple syrup urine disease
Organic acidemias
Indicanuria
Cystinuria
Cystinosis
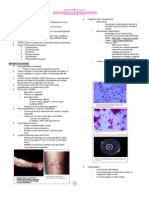
Observed form urine of patients that has darkened urine
after becoming alkaline from standing at room
temperature; described by GARROD (1902)
alkali lover or alkaptonuria term adopted
Failure to inherit the gene to produce the enzyme
homogentisic acid oxidase
Brown-stained or black-stained cloth diapers; in later life
brown pigment becomes deposited in body tissues
(particularly in ears)
Ferric chloride test blue color
Benedicts test/ Clinitest yellow color (indicating presence
of reducing substance)
More specific screening test for urinary homogentisic acid is
to add alkali to freshly voided urine to observe darkening of
the color
Addition of silver nitrate and ammonium hydroxide will also
produced black urine
Denielle Genesis B. Camato
VII. URINE SCREENING FOR METABOLIC DISORDERS
ANALYSIS O F URINALYSIS AND BODY FLUIDS | REVIEWER
MELANURIA
MELANIN- the pigment responsible for the dark color of
hair, skin, and eyes. Deficient production of melanin results in
albinism
Increased urinary melanin will produced darkening of urine
(just like homegentisic acid); elevation of urine melanin is a
serious finding that indicates the overproliferation of the
normal melanin-producing cells (melanocytes) producing
malignant melanin.
5,6-dihydroxyindole- colorless precursor of melanin
Ferric chloride test gray or black precipitate
Sodium nitroprusside test red color
Intereference sources: Acetone & Creatinine; to avoid,
just add glacial acetic acid w/c will cause melanin to revert to
a green-black color whereas acetone turns purple and
Creatinine becomes amber.
BRANCHED-CHAIN AMINO ACID DISORDERS
The branched-chain amino acids differ from other amino
acids by having a methyl group that branch from the main
aliphatic carbon chain.
2 GROUPS:
Accumulation of one or more of the early amino acid
degradation products g eg: Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Disorders in the other group are termed organic acidemias
and result in accumulation of organic acids produced further
down in the amino acid metabolic pathway
TRYPTOPHAN DISORDERS
The major concern of the urinalysis laboratory in the
metabolism of tryptophan is the increased urinary excretion
of the metabolites indicant and 5-hydroxylindoleacetic acid
(5-HIAA)
MAPLE-SYRUP URINE DISEASE
INDICANURIA
Cause by an inborn error of metabolism, inherited as an
autosomal recessive trait.
Amino acids involve: leucine, isoleucine, & valine
Three amino acids in liver (-ketoisovaleric, ketoisocaproic, & -keto--methylvaleric). Failure to
inherit the gene for the enzyme necessary to produce
oxidative decarboxylation of these keto acids results in their
accumulation in blood and urine.
Urine produces strong odor resembling maple syrup, which is
caused by the rapid accumulation of keto acids in urine
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH)- screening test most
frequent performed for keto acids yellow turbidity or
precipitate
Interference: large dose of ampicillin
5-HYDROXYINDOLEACETIC ACID (5-HIAA)
ORGANIC ACIDEMIAS
Tryptophan usually enters the body to be reabsorbed for
use of the body in the production of protein or is converted
to indole by the intestinal bacteria & excreted in the feces;
however if there are intestinal disorders (eg: obstruction,
Hartnup disease, etc) increases amount of tryptophan are
converted to indole.
Hartnup disease g blue staining of infants diapers refer to
as blue-diaper syndrome
Ferric chloride g deep blue or violet color; can subsequently
be extracted into chloroform
SEROTONIN- used for the stimulation of smooth muscles;
produced from tryptophan by the argentaffin cells in the
intestine and is carried through the body primarily by the
platelets; major constituent of foods: bananas, pineapples,
tomatoes
When carcinoid tumors involving the argentaffin
(enterochromaffin) cells develop, excess amounts of
serotonin are produced, resulting in the elevation of urinary
5-HIAA levels
Nitrous acid + 1-nitroso-2-naphthol g urine with 5-HIAA =
purple to black color
Normal daily excretion of 5SEROTONIN m olecular
structure
HIAA: 2-8 mg (argentaffin cells
tumors will produce from 160 to
628 mg/24 hours)
Specimen: Random or First morning
urine
Specimen: if 24 hour urine g preserved with HCL or Boric
Acid
Interference: Phenothiazines and Acetanilids
Denielle Genesis B. Camato
VII. URINE SCREENING FOR METABOLIC DISORDERS
ANALYSIS O F URINALYSIS AND BODY FLUIDS | REVIEWER
CYSTINE DISORDERS
PHORPHYRIN DISORDERS
CYSTINURIA- defect in the renal tubular transport of
amino acids
CYSTINOSIS- inborn error of metabolism
A noticeable odor of sulfur may be present in the urine in
disorders of cystine metabolism
CYSTINURIA
Marked by elevated amounts of the amino acid cysteine in
the urine
Inability of the renal tubules to reabsorbed cysteine
filtered by the glomerulus
2 MODES:
R
Reabsorption of all four amino acids (cysteine,
lysine, arginine, & ornithine)
R
The other in which only cysteine & lysine are not
reabsorbed
65% of these people can be expected to produce calculi
early in life
Cyanide-Nitroprusside- chemical screening test redpurple color
False Positives: presence of Ketones & homocystine
CYSTINOSIS
Regarded as genuine inborn error of metabolism
Incomplete metabolism of cystine results in crystalline
deposits of cysteine in many areas of the body, including the
cornea, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and internal organs
FANCONIS SYNDROME- major defect in the renal tubular
reabsorption mechanism
Urinalysis: Polyuria, Aminoaciduria, (+) test for reducing
substances, lack of urinary concentration
Progression to total renal failure
Renal transplants & use of cystine-depleting medications to
prevent cysteine build up in other tissues are extending lives
MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDE DISORDERS
HOMOCYSTINURIA
Increased urinary homocystine gives a positive result with
the cyanide-nitroprusside test
Positive cyanide-nitroprusside test result must be followed
by silver-nitroprusside test in which only homocystine will
react
The use of silver nitrate in place of sodium cyanide will
reduce homocystine to its nitroprusside reactive-form but
will not reduce cysteine.
Positive reaction in the silver-nitroprusside test confirms
the presence of homocytinuria
Specimen: Fresh Urine
Porphyrins are the intermediate compunds in the production
of heme
Three primary porphyrins: (uroporphyrin,
coproporphyrin, protoporphyrin)
Porphyrin precursors: (-aminolevulinic acid [ALA] &
porphobilinogen)
ALA, porphobilinogen & uroporphyrin are the most soluble &
readily appear in the urine.
Coporphyrin is less soluble but is found in the urine
Protoporphyrin is not seen in urine
Fecal Analysis usually performed for detection of
coproporphyrin & protoporphyrin; however to avoid false
positive BILE is more acceptable specimen.
FREE ERYTHROCYTE PORPHYRIN (FEP)- analysis of whole
blood recommended by Centers for Disease Control (CDC) as
screening test for lead poisoning
PORPHYRIAS- disorders of porphyrin metabolism; can be
inherited or acquired from erythrocytic& hepatic
malfunctions or exposure to toxic agents
Port-wine/Red color to the urine
Congenital Porphyria is sometimes suspected from a red
discoloration of an infants diapers
ERHLICHS Reaction & Fluorescence under ultraviolet
light in 550 to 600nm are two screening tests for
porphyrinuria
ERHLICHS g detection of ALA & Porphobilinogen only
Acetylacetone g added to specimen to convert ALA to
porphobilinogen prior to performing Ehrlich test
FLUORESCENT TECHNIQUE g used for other porphyrins
Ehrlich Test & Watson-Schwartz test & Hoesch testfor differentiation between presence of urobilinogen &
porphobilinogen
Glycosaminoglycans; group of large compunds located
primarily in the connective tissue.
Products most frequently found in urine are dermatan
sulfate, keratin sulphate, heparin sulphate
Hurlers Syndrome, Hunters Syndrome, San Filipippos
Syndrome- best known disorders of mucopolysaccharides
Hurler & Hunter g skeletal structure are abnormal &
there is severe mental retardation; in Hurlers syndrome
mucopolysaccharides accumulate in the cornea of the eye.
San Filippos syndrome g only abnormality is mental
retardation
Acid-Albumin & Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
(CTAB)- most frequently used screening tests; turbidity
tests and the metachromatic staining spot tests.
Acid-Albumin & CTAB g thick, white turbidity is positive
result
Metachromatic Stain- uses basic dyes to react with acid
mucopolysaccharides (eg: Azure A dye) Positive result: BLUE
spot that cannot be washed away by a dilute acidified
methanol solution
Denielle Genesis B. Camato
VII. URINE SCREENING FOR METABOLIC DISORDERS
ANALYSIS O F URINALYSIS AND BODY FLUIDS | REVIEWER
PURINE DISORDERS
Lesch-Nyhan Disease g inherited as a sex-linked recessive
results in a massive excretion of urinary uric acid crystals
Failure to inherit the gene to produce the enzyme
hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase;
responsible for the accumulation of uric acid throughout the
body.
Patients suffer from severe motor defects, mental
retardation, tendency toward self-destruction, gout & renal
calculi
Uric Acid crytals resembling orange sand in diapers
CARBOHYDRATE DISORDERS
Presence of increased urinary sugar (melituria)
Pentosuria one of Garrods original six inborn errors of
metabolism; ingestion of large amounts of fruits
Presence of galactosuria indicating the ability to properly
metabolize galactose to glucose. Resulting galactosemia with
toxic intermediate metabolic products results in infant
failure to thrive, combined with liver disorders, presence of
cataracts & severe mental retardation.
Lactosuria may be seen during pregnancy
Fructosuria associated with parenteral feeding
You might also like
- Urine Screening of Metabolic DisordersDocument24 pagesUrine Screening of Metabolic DisordersMark Arlo Hernandez SegundoNo ratings yet
- Metab DisordersDocument36 pagesMetab DisordersDaena TimtimanNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument55 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersGlormina Asprec AvenaNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Test Detects Kidney & Metabolic DiseasesDocument5 pagesUrinalysis Test Detects Kidney & Metabolic DiseasesRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Special TopicsDocument8 pagesSpecial Topicskatherine ruizNo ratings yet
- Non Protein CompoundsDocument64 pagesNon Protein CompoundsAbigail Mayled LausNo ratings yet
- History of PhlebotomyDocument46 pagesHistory of PhlebotomyDorothy AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical MethodsDocument119 pagesBiochemical MethodsElias Libay100% (1)
- Lec 2 Anemia Classification1Document17 pagesLec 2 Anemia Classification1Omar MaanNo ratings yet
- Medical TechnologistDocument2 pagesMedical Technologistapi-329932534No ratings yet
- Aubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityDocument38 pagesAubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Basic Clinical Chemistry TestsDocument49 pagesBasic Clinical Chemistry TestsMegbaru100% (1)
- Here, Only 1 Few Stages Undergo Subdivision (Sabi Ni Maam)Document6 pagesHere, Only 1 Few Stages Undergo Subdivision (Sabi Ni Maam)Jaenie Grace AliganNo ratings yet
- Principles of Clinical Chemistry AutomationDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Clinical Chemistry AutomationChristine Rodriguez-Guerrero50% (2)
- Defining The Practice of Medical Technology or Clinical Laboratory Science ProfessionDocument27 pagesDefining The Practice of Medical Technology or Clinical Laboratory Science ProfessionKianna TicsayNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Functions of LiverDocument94 pagesBiochemical Functions of LiverMi PatelNo ratings yet
- Understanding PhlebotomyDocument4 pagesUnderstanding PhlebotomyAngelo Jude CumpioNo ratings yet
- Routine Fecalysis Stool Analysis: Is A Series of Tests Done On A Stool Sample To Help Diagnose Certain ConditionsDocument3 pagesRoutine Fecalysis Stool Analysis: Is A Series of Tests Done On A Stool Sample To Help Diagnose Certain ConditionsSheila GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Liver FunctionDocument41 pagesChapter 1 Liver FunctionDaniel HikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Anemia HematologyDocument30 pagesChapter 18 Anemia HematologyYelnats DatsimaNo ratings yet
- Non Malignant Hereditary Disorders of LeukocytesDocument6 pagesNon Malignant Hereditary Disorders of LeukocytesGilo IlaganNo ratings yet
- Urine Specimen Collection: Ms. Sneha SehrawatDocument36 pagesUrine Specimen Collection: Ms. Sneha SehrawatRajaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument3 pagesLiver Function Testssamdaman001No ratings yet
- Microbiology-Specimens CollectionDocument31 pagesMicrobiology-Specimens Collectionapi-253201876100% (1)
- Clinical ChemistryDocument333 pagesClinical ChemistryshooberNo ratings yet
- Bacte TestDocument10 pagesBacte TestRiondalionNo ratings yet
- WBC AbN MorphologyDocument2 pagesWBC AbN MorphologyTristan Iris100% (2)
- Aubf Lab Types of Urine SpecimenDocument18 pagesAubf Lab Types of Urine SpecimenNerizaNo ratings yet
- Clearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSDocument25 pagesClearance and GFR: Major DR Arabinda Mohan Bhattarai Lecturer (Biochemistry), NAIHSChandan SahNo ratings yet
- The Result of Any Laboratory Test Is Only As Good As The Sample Received in The LaboratoryDocument16 pagesThe Result of Any Laboratory Test Is Only As Good As The Sample Received in The LaboratoryZeeshan YousufNo ratings yet
- Principles in Medical Laboratory Science 2Document2 pagesPrinciples in Medical Laboratory Science 2lai cruzNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast Staining For TBDocument52 pagesAcid Fast Staining For TBtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- UNIT 3.0 Medical Technology CurriculumDocument12 pagesUNIT 3.0 Medical Technology CurriculumJean Carmelette BalalloNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous & Systemic MycosesDocument7 pagesSubcutaneous & Systemic MycosesDee GeeNo ratings yet
- LJ MediaDocument3 pagesLJ MediaJerry ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Review in Clinical MicrosDocument103 pagesReview in Clinical MicrosSyvelmarie Tinte100% (1)
- Staining DocumentDocument4 pagesStaining DocumentsuryabratabanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To ParasitologyRIC JOSEPH PONCIANONo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : Git Block 1 Lecture Dr. Usman GhaniDocument26 pagesLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : Git Block 1 Lecture Dr. Usman Ghaniraanja2100% (1)
- Pre-Analytical Consideration and Venipuncture ComplicationsDocument52 pagesPre-Analytical Consideration and Venipuncture ComplicationsVenomNo ratings yet
- Routine UrinalysisDocument4 pagesRoutine UrinalysisDanica Joy Christelle L. PilarNo ratings yet
- Medical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesDocument1 pageMedical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesAthaliah Del MonteNo ratings yet
- Examination of Urine Formation and CompositionDocument7 pagesExamination of Urine Formation and CompositionDaniel LamasonNo ratings yet
- COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideDocument9 pagesCOMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids2020Document47 pagesUrinalysis and Body Fluids2020MONFOLA100% (1)
- Count the sperm in the central grid and multiply by 10,000 to obtain the sperm concentration per mLDocument81 pagesCount the sperm in the central grid and multiply by 10,000 to obtain the sperm concentration per mLAris ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion in History PDFDocument48 pagesBlood Transfusion in History PDFjozsef10No ratings yet
- Histopathologic TechniquesDocument78 pagesHistopathologic TechniquesSwitzel CustodioNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument8 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringLourdette TorrefielNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Physical Properties of UrineDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Physical Properties of UrineameerabestNo ratings yet
- Al-Rasheed University Urinalysis Lab GuideDocument24 pagesAl-Rasheed University Urinalysis Lab GuideAli RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UrinalysisDocument28 pagesIntroduction To UrinalysisNicnoc RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Nature of The Clinical LaboratoryDocument8 pagesLesson 5: Nature of The Clinical LaboratoryJohn Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- Antigen and Its PropertiesDocument20 pagesAntigen and Its Propertiestusharpremin92% (12)
- URINALYSIS Power Point PresentationDocument20 pagesURINALYSIS Power Point PresentationOlugbenga A AdetunjiNo ratings yet
- Swu Phinma, College of Pharmacy 2020: Wr/Urinalysis - Html#Ixzz6Zxlj RQKH /Product-Manual/3008 - 3B - UrinalysisDocument7 pagesSwu Phinma, College of Pharmacy 2020: Wr/Urinalysis - Html#Ixzz6Zxlj RQKH /Product-Manual/3008 - 3B - UrinalysisTrex MarciiiNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument4 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineIceNo ratings yet
- Aubf Outline EditedDocument16 pagesAubf Outline EditedNoraine Princess TabangcoraNo ratings yet
- Senior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandSenior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- II. Renal FunctionDocument3 pagesII. Renal FunctionDee GeeNo ratings yet
- QA MonitoringDocument3 pagesQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeNo ratings yet
- QA MonitoringDocument3 pagesQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- II. Renal FunctionDocument3 pagesII. Renal FunctionDee GeeNo ratings yet
- II. Renal FunctionDocument3 pagesII. Renal FunctionDee GeeNo ratings yet
- QA MonitoringDocument3 pagesQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing Urinalysis ComponentsDee GeeNo ratings yet
- I. Safety in The Clinical LabDocument3 pagesI. Safety in The Clinical LabDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Scripture Songs: 1 Corinthians, 1 John, 1 PeterDocument2 pagesScripture Songs: 1 Corinthians, 1 John, 1 PeterDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- GENDocument2 pagesGENDee GeeNo ratings yet
- QA MonitoringDocument3 pagesQA MonitoringDee Gee100% (1)
- 4 HDocument10 pages4 HDee GeeNo ratings yet
- 5 HDocument4 pages5 HDee GeeNo ratings yet
- God's Love LetterDocument1 pageGod's Love LetterDee GeeNo ratings yet
- 2HDocument6 pages2HDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobin Opa ThiesDocument4 pagesHaemoglobin Opa ThiesDee GeeNo ratings yet
- ABBDocument16 pagesABBDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Dna VirusesDocument3 pagesDna VirusesDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Hematology LaboratoryDocument3 pagesHematology LaboratoryDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Practice Test CCDocument3 pagesPractice Test CCDee GeeNo ratings yet
- CC2 ChartDocument2 pagesCC2 ChartDee Gee100% (1)
- PH Le BotomyDocument4 pagesPH Le BotomyDee Gee100% (1)
- RBC Studies MidtermDocument3 pagesRBC Studies MidtermDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Rickets and Osteomalacia: Moderator: Dr. P. TahbildarDocument43 pagesRickets and Osteomalacia: Moderator: Dr. P. TahbildarNorman RiyadiNo ratings yet
- 1Document55 pages1abcd efgh0% (1)
- Essential Notes For The MRCP 3rd PDFDocument613 pagesEssential Notes For The MRCP 3rd PDFnayhtun2471100% (1)
- Cystinosis DiseaseDocument10 pagesCystinosis Diseaseapi-485321550No ratings yet
- Urinalysis 2Document9 pagesUrinalysis 2Dawn GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Kidney and Urinary Tract PDFDocument104 pagesDisorders of Kidney and Urinary Tract PDFShaik Istehsan Ul haqNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Urine Screening for Metabolic DisordersDocument41 pagesGroup 4: Urine Screening for Metabolic DisordersBrent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Phenylalanine/Tyrosine Metabolic Pathway Screening DisordersDocument1 pagePhenylalanine/Tyrosine Metabolic Pathway Screening DisordersChynna Izzabelle Alcantara AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Inherited Metabolic, 2nd Edition - Georg F. PDFDocument600 pagesInherited Metabolic, 2nd Edition - Georg F. PDFGrigore VladNo ratings yet
- Vii. Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument4 pagesVii. Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDee GeeNo ratings yet
- NephrocystinosisDocument31 pagesNephrocystinosisEmily EresumaNo ratings yet
- Renal DiseasesDocument26 pagesRenal DiseasesismailcemNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic Disorders: Learning ObjectivesJonalyn LumantasNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology Final ProjectDocument37 pagesHuman Physiology Final ProjectAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Genes For All DisordersDocument86 pagesGenes For All Disordersvenkyreddy97No ratings yet
- Halitosis Causes, Assessment and ManagementDocument14 pagesHalitosis Causes, Assessment and Managementdaniel_siitompulNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument9 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersXyleene Jency Bien IINo ratings yet
- Journal of Suppository Formulations As A Potential Treatment For Nephropathic CystinosisDocument11 pagesJournal of Suppository Formulations As A Potential Treatment For Nephropathic CystinosisApt Ariep Aulia RakhimNo ratings yet
- Inherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalDocument11 pagesInherited Overflow Metabolic Overflow RenalChrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- Fanconi SyndromeDocument9 pagesFanconi SyndromeEduardo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument39 pagesInternship ReportHappy Sunshine50% (2)
- Clinical Microscopy Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument5 pagesClinical Microscopy Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersGlazel TulaganNo ratings yet
- MRCP NephrologyDocument394 pagesMRCP Nephrologyxplaind100% (8)
- AUB - Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument3 pagesAUB - Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersJeanne Rodiño100% (1)
- Lysosomal Storage DiseaseDocument23 pagesLysosomal Storage DiseaseDewi YantiNo ratings yet