Professional Documents
Culture Documents
V P Inspire : Residual Volume
Uploaded by
Eva GuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
V P Inspire : Residual Volume
Uploaded by
Eva GuCopyright:
Available Formats
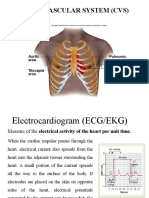
RESPIRATORY BASICS
Lung volumes
V/P mismatch
O2 and CO2 transport
Restriction - Expiratory
- Bronchioles are restrictive i.e. takes effort to force air out
V P Inspire
Compliance - alveolar-gas exchange (= pressure required to open alveoli)
Surfactant - reduces compliance/decreases surface tension so that the alveoli dont
collapse type 2 pneumocytes
* Surface tension compliance
Graph
Tidal volume
Minimum + Maximum Inspiratory/Expiratory volumes (measured from top/bottom
of tidal wave?)
Residual volume - volume always leftover in normal physiological state so that lungs dont
collapse
Emphysema - low compliance - disruption/destruction of alveolus - sac that doesnt contract any
more - air going in but not able to be expelled - residual volume
- would have more trouble expiring than inspiring as it is an obstructive process
Shunt - when alveoli is so collapsed on itself that it is unable to get proper exchange although it
has proper perfusion
Dead Space - when you have no perfusion
V Q mismatch:
V/Q ratio higher than normal dead space, PE
V/Q ratio lower than normal shunt, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, consolidation,
COPD, asthma, bronchitis
Oxygen Curve
- Sigmoid curve
O2 and CO2 transport
- haemoglobin dissolved
- bicarbonate dissolved
Bohr Effect: shifting affinity of O2 with CO2 levels
EXAMPLE MEQ QUESTIONS
1. 53 yr old male crushing chest pains radiating from left arm and dyspnoea
Underlying cause of chest pain
O 2 supply heart Ischaemia necrosis MI
- release of cytokines and inflammatory mediators e.g. bradykinin,
histamine inflammatory response
no ATP channels working influx of Ca 2+
Why radiation
- Referred pain: carried by same afferent fibres pathways from C7-T4, which
converge at one area in the brain, which is unable to specify/localise/demarcate a
particular area.
Dyspnoea
- pulmonary hypertension
- reduced cardiac output reduced gas exchange buildup of CO 2
dyspnoea on exertion
Testing
- troponin
- creatine kinase - delayed chemical released during tissue death (not specific to
cardiac muscle)
- ECG - STEMI (elevated during a MI) (whereas only depressed ST after a prior
case of acute MI)
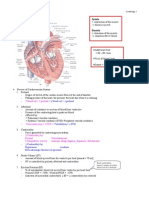
- Lead 2, 3, aVF = inferior infarct
- V3, V5 = anterior infarct
- V5, V6 = lower lateral
Treatment
-
GTN
thrombolytics
supplemental oxygen
angioplasty (normally for STEMI as transmural infarct)
Change in hemodynamic state
Stand blood pooling in legs decreased ventricular filling reduction in BP
baroreceptors sympathetic vasoconstriction to increase venous return
* Include changes in dorsal medulla, adrenergic stimulation, beta-adrenergic stimulation,
change in pulse pressure etc.
Pulse Pressure - difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
You might also like
- System and Disease III ComprehensiveDocument46 pagesSystem and Disease III Comprehensivenasr234No ratings yet
- Oxygenation and CirculationDocument6 pagesOxygenation and Circulationluna lovegoodNo ratings yet
- Notes PhysiologyDocument21 pagesNotes Physiology2070834No ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Blood Flow and MetabolismDocument7 pagesCh. 4 Blood Flow and MetabolismMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- CARDIODocument10 pagesCARDIOMarcel TabucolNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: Presenter: DR Hairul Anuar Bin MahatDocument23 pagesCardiac Cycle: Presenter: DR Hairul Anuar Bin MahatHairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Cardiology-1 ValvDocument34 pagesCardiology-1 ValvMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Trauma NotesDocument8 pagesTrauma NotesaaamirrrNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: TH THDocument2 pagesCardiovascular System: TH THChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- CHF PathophysiologyDocument12 pagesCHF PathophysiologyprofgambhirNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument74 pagesCardiovascular Systemاسامة محمد السيد رمضانNo ratings yet
- Heart failure numbers and termsDocument12 pagesHeart failure numbers and termsKat IvyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle CardiodynamicsDocument29 pagesCardiac Cycle Cardiodynamicseverforyou2023No ratings yet
- UW Notes - 7 - Cardiology ArrangedDocument84 pagesUW Notes - 7 - Cardiology ArrangedAaquib AmirNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds and Cardiac Cycle GuideDocument9 pagesHeart Sounds and Cardiac Cycle GuideAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ConditionsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular System ConditionsNinjaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Assessment of CV Function: Cardiovascular SystemDocument60 pagesOverview of Anatomy & Physiology Assessment of CV Function: Cardiovascular SystemSaputra Tri NopiantoNo ratings yet
- Amboss - Cradiac CycleDocument18 pagesAmboss - Cradiac CycleAllysahNo ratings yet
- ACUTE CHEST PAIN Normal Cardiac Cycle ExplainedDocument11 pagesACUTE CHEST PAIN Normal Cardiac Cycle ExplainedShampa SenNo ratings yet
- Acute Severe Chest Pain: Presented By: Arwa H. Al-OnayzanDocument11 pagesAcute Severe Chest Pain: Presented By: Arwa H. Al-OnayzanShampa SenNo ratings yet
- Lec 3&4 - Pulmonary PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLec 3&4 - Pulmonary PhysiologyDana KostNo ratings yet
- Physiology 09Document36 pagesPhysiology 09Sumeyya Binte BockthierNo ratings yet
- TARev - Respiratory ReviewDocument139 pagesTARev - Respiratory ReviewAashay PatelNo ratings yet
- Circulation WorksheetDocument3 pagesCirculation Worksheetholagato100% (1)
- Topic 1 Biology 5Document21 pagesTopic 1 Biology 5Prachi SavaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument3 pagesCardiac Study GuideLindsay BirnbrichNo ratings yet
- Physiologic and Pathophysiologic Function of The Heart: Cardiac Cycle Graphs, Curves, Loops and CO CalculationsDocument40 pagesPhysiologic and Pathophysiologic Function of The Heart: Cardiac Cycle Graphs, Curves, Loops and CO CalculationsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (1)
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument27 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseOwen J. WieseNo ratings yet
- 1 One-General Scheme For Valvular Heart DiseasesDocument51 pages1 One-General Scheme For Valvular Heart Diseasesمحمد بن الصادقNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Cardiac CycleDocument49 pagesUnderstanding the Cardiac CycleJardee Datsima100% (1)
- Cardiac SystemDocument7 pagesCardiac Systemsccctutor100% (3)
- Alterations in Tissue OxygenationDocument28 pagesAlterations in Tissue OxygenationDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology NOTESDocument3 pagesRespiratory Physiology NOTESJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (1)
- Sylaby - CVS 01Document26 pagesSylaby - CVS 01upul85No ratings yet
- Chemo Receptors: T A T A 2 O2 ADocument8 pagesChemo Receptors: T A T A 2 O2 As7jayn100% (6)
- Shock Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesShock Lecture Notescolek22100% (7)
- NPTE CArdio NotesDocument27 pagesNPTE CArdio NotesAubrey Vale SagunNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Physiology PDFDocument17 pagesCardiac Physiology PDFAli Aborges Jr.No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument49 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Physiology Slides UsmleDocument46 pagesPhysiology Slides Usmlejustseas100% (1)
- Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentDocument4 pagesHeart and Neck Vessels AssessmentAndrei PedrajetaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle JVPDocument70 pagesCardiac Cycle JVPAstrid PramudyaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On CardiologyDocument31 pagesLecture Notes On CardiologyambiskuysNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument6 pagesBio NotesJessica KunderNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System BSN 1Document16 pagesCardiovascular System BSN 1Arianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument172 pagesCardiovascular Anatomy & PhysiologyYS NateNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lecture - Dr. Dominguez: Slow FastDocument3 pagesPhysiology Lecture - Dr. Dominguez: Slow FastJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Ecg 1Document4 pagesEcg 1Lindsay Ann Garcia MariacaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle ActivityDocument3 pagesCardiac Muscle ActivityPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle.: Basic Heart StructureDocument9 pagesCardiac Cycle.: Basic Heart StructureMohammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- FA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDocument15 pagesFA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDrbee10No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes on Anatomy and Physiology of the Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesLecture Notes on Anatomy and Physiology of the Cardiovascular SystemLudwigJayBarayuga100% (5)
- 8 Heart Failure - Notes-DONE - PrintedDocument9 pages8 Heart Failure - Notes-DONE - PrintedKristin SmithNo ratings yet
- Res PH Dental - 2023Document82 pagesRes PH Dental - 2023shozainab2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - HeartDocument3 pagesChapter 12 - HeartAngelyka CabaloNo ratings yet
- Frank-Starling Law of Cardiovascular DynamicsDocument3 pagesFrank-Starling Law of Cardiovascular DynamicsSumirat NurcahyaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: The Heart: Prof. Magidah Alaudi, M.SCDocument62 pagesLecture 2: The Heart: Prof. Magidah Alaudi, M.SCMonicaNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument19 pagesThe Cardiac CycleRebi NesroNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Central Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsFrom EverandCentral Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Auto Dysreflexia InfoDocument8 pagesAuto Dysreflexia InfoEva GuNo ratings yet
- Your Blood Pressure: Information From TheDocument2 pagesYour Blood Pressure: Information From TheEva GuNo ratings yet
- Tone Vs MoodDocument2 pagesTone Vs MoodEva GuNo ratings yet
- Types of Poetry and Narrative PerspectivesDocument3 pagesTypes of Poetry and Narrative PerspectivesEva GuNo ratings yet
- Jacaranda Chemistry Chapter 6 (Indicators)Document14 pagesJacaranda Chemistry Chapter 6 (Indicators)Eva Gu100% (1)
- Red Blood Cells (PBL LO)Document1 pageRed Blood Cells (PBL LO)Eva GuNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells (PBL LO)Document1 pageRed Blood Cells (PBL LO)Eva GuNo ratings yet
- Website Evaluation - Student Handout-4Document1 pageWebsite Evaluation - Student Handout-4Eva GuNo ratings yet
- Film Techniques: Film Study Guidelines (Film Techniques Adapted From Rebecca Mahon, HSC English StudyDocument3 pagesFilm Techniques: Film Study Guidelines (Film Techniques Adapted From Rebecca Mahon, HSC English StudyNick JamesNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalance (PBL LO)Document1 pageElectrolyte Imbalance (PBL LO)Eva GuNo ratings yet
- Cadet Lesson - First Aid - Flow ChartDocument1 pageCadet Lesson - First Aid - Flow ChartEva GuNo ratings yet
- Bohemian Galileo Galilei Rhapsody LyricsDocument2 pagesBohemian Galileo Galilei Rhapsody LyricsEva GuNo ratings yet
- Many FormulasDocument11 pagesMany FormulasErnest MarkovnikovNo ratings yet
- Cadet Lesson - First Aid - Flow ChartDocument1 pageCadet Lesson - First Aid - Flow ChartEva GuNo ratings yet
- Vol 6 CH 01 UniformsDocument11 pagesVol 6 CH 01 UniformsEva GuNo ratings yet
- SHakespeare - King Lear (Critical Study) PreparationDocument1 pageSHakespeare - King Lear (Critical Study) PreparationEva GuNo ratings yet
- Writing Application ShortDocument1 pageWriting Application ShortEva GuNo ratings yet
- Writing Competition Short EditDocument1 pageWriting Competition Short EditEva GuNo ratings yet
- SHakespeare - King Lear (Critical Study) PreparationDocument1 pageSHakespeare - King Lear (Critical Study) PreparationEva GuNo ratings yet
- King Lear Questions Eva Gu 11en5Document2 pagesKing Lear Questions Eva Gu 11en5Eva GuNo ratings yet
- King Lear Questions Eva Gu 11en5Document2 pagesKing Lear Questions Eva Gu 11en5Eva GuNo ratings yet
- Incas & Kickapoo Tribe - Information SheetDocument12 pagesIncas & Kickapoo Tribe - Information SheetEva GuNo ratings yet
- Global Issues Topic NotesDocument8 pagesGlobal Issues Topic NotesEva GuNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesGrade 9 Respiratory SystemChristine Gacula100% (1)
- Ga Machine Slide11Document94 pagesGa Machine Slide11Wong KinYouNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument31 pagesPulmonary Edematanjung panji asmoroNo ratings yet
- Síndrome de Insuficiência Torácica Abordagens para Avaliação e TratamentoDocument7 pagesSíndrome de Insuficiência Torácica Abordagens para Avaliação e TratamentoGuilherme GCNo ratings yet
- 4 6042066894301692928Document307 pages4 6042066894301692928Adiel OjedaNo ratings yet
- Connect FOUR - Exams On Units 2022 1st Term by Ragab AhmedDocument13 pagesConnect FOUR - Exams On Units 2022 1st Term by Ragab AhmedSameh IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Respiration Form 3Document19 pagesRespiration Form 3Akif FarhanNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Items by Strand Grade 7 ScienceDocument31 pagesSample Test Items by Strand Grade 7 ScienceRam Russel Casao PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Development of A Continuous Positive Airway: Group Members: Project Advisor: DR Hans GrayDocument24 pagesDevelopment of A Continuous Positive Airway: Group Members: Project Advisor: DR Hans GrayDamith Buddhika Sri WimalarathnaNo ratings yet
- Handout1 - Normal Changes of AgingDocument3 pagesHandout1 - Normal Changes of Agingpissednachos0123No ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Inverse Relationship of Gas Volume and PressureDocument12 pagesBoyle's Law: Inverse Relationship of Gas Volume and PressureLex PabustanNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma and Chest Wall Surgery GuideDocument67 pagesChest Trauma and Chest Wall Surgery GuideKapil LakhwaraNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument38 pagesMeconium Aspiration Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentGrace Antonette Pati100% (1)
- Gas Exchange in Humans MYP4 BiologyDocument52 pagesGas Exchange in Humans MYP4 Biologydiyar alassafNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment CheatDocument7 pagesPhysical Assessment CheatJepe Urate100% (1)
- ANAPHY Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesANAPHY Respiratory SystemAshley Franceska CansanayNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Laparotomy Post-Op CareDocument5 pagesExploratory Laparotomy Post-Op CareJaru ObenzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles Keytone ReviewDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Basic Biological Principles Keytone ReviewShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- 18 A + B - Lect ModifiedDocument65 pages18 A + B - Lect ModifiedAsad MirzaNo ratings yet
- Ujjayi Pranayama or Ocean Breath For DiabeticsDocument23 pagesUjjayi Pranayama or Ocean Breath For Diabeticssivaprasth_vNo ratings yet
- Hazel Roda Estorque - September 2021: 2. Physiological Changes With AgingDocument4 pagesHazel Roda Estorque - September 2021: 2. Physiological Changes With Agingkassy yeonNo ratings yet
- Chest X-ray Interpretation Methodical ApproachDocument13 pagesChest X-ray Interpretation Methodical ApproachduncanNo ratings yet
- Wilkins Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care 7th Edition Heuer Test BankDocument10 pagesWilkins Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care 7th Edition Heuer Test Bankanthelioncingulumgvxq100% (21)
- Module DLP ANSWERSDocument9 pagesModule DLP ANSWERSStephanie PhangNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument34 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans - 10 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsMenard Velasco100% (1)
- Oxford Bronchoscopy GuideDocument16 pagesOxford Bronchoscopy GuideM Marliando Satria PangestuNo ratings yet
- MFSCDocument28 pagesMFSCFlaviub23No ratings yet
- Greys-Anatomy-Student (1) - CompressedDocument2 pagesGreys-Anatomy-Student (1) - CompressedKaranNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TransportDocument8 pagesOxygen Transportmekar retnoningsihNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quiz 2Document45 pagesAnatomy Quiz 2Upscaled100% (1)