Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Refraction & Superposition Answer
Uploaded by
grace_ng_45Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Refraction & Superposition Answer
Uploaded by
grace_ng_45Copyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 3 : Refraction & Superposition
1.
Direction of travel of light is water air (1)
Angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle (1)
2
[2]
2.
QWC spelling of technical terms must be correct and the answer must be
organised in a logical sequence
Identifies two rays of light (1)
Two rays have same frequency/come from same source/are coherent (1)
Path difference (between the two reflected rays) (1)
They superpose (when they meet) /constructive and destructive
interference occur (1)
If they meet in phase/n / path difference, constructive interference/
bright fringe (1)
If they meet in antiphase / (n+ ) / path difference, destructive
interference/dark fringe (1)
Max 5
[5]
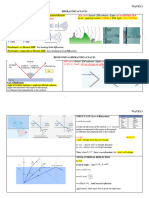
3.
(a)
n = sin 48 / sin 30
n = 1.5 (common answer will be 1.49)
(n = 0.67 scores 1 mark for idea of ratio of sin of angles)
(b)
(i)
QWC spelling of technical terms must be correct and the answer
must be organised in a logical sequence
As x increases, y increases
OR
At a certain angle / critical angle, y = 90 / the light travels along the
boundary (do not allow reflects at 90)
For angles greater than the critical angle (in glass)
total internal reflection occurs
(do not accept TIR)
(ii)
Use of sin c = 1/n
c = 42
ecf n from (a) unless n= 0.67 which scores 0 here
[7]
HELP Academy
Tutorial 3 : Refraction & Superposition
4.
(a)
(b)
Ray drawn along edge of prism (labelled X) (ignore a
reflected ray)
(i)
n = 3 10 1.96 10
n = 1.53
(ii)
(c)
(no unit, ue if one given)
1
1
Use of sin (critical angle) = 1/ n OR use of sin i/sin r = v1/v2 = n
c = 41
Red light: refraction towards normal at first face but less
than refraction for blue light
Refracts into air at second face with angle in air > angle in glass
1
[7]
5.
Use of sin i / sin r = (1)
Use of either 80 or 1.33 (1)
[r = 48] (1)
Example of answer
sin 80 / sin r = 1.33
[r = 48]
Both rays refracted towards the normal
Violet refracted more than red
2
[5]
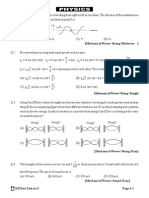
6.
(a)
(b)
(i)
Node correctly placed (1)
(ii)
Arrow at Y moving up (1)
Arrow at Z moving down (1)
Identifies a factor of 3 (1)
Fundamental frequency = 0.5 Hz (1)
2
[5]
7.
(a)
(i)
HELP Academy
v = f (words or symbols not numbers)
1
2
Tutorial 3 : Refraction & Superposition
length of string = /2 OR wavelength = 2 length
OR node to node = /2
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
d /4 OR (D3/2) OR (D3/2)^2
(this mark is lost if there is a * length / A3)
(ignore powers of ten)
E4 * density OR E4 * 7800
(ignore powers of ten)
OR
volume of 1 metre length density
5.12
(spreadsheet answers must be correct to same number dec places so
do not accept 5.116 or 5.11)
(correct answer on spreadsheet scores mark irrespective of whats
written on next page)
See T = v OR T =v (not just quoting given equation)
T = 82 (N)
(do not penalise dec places twice, 82.1 could score both marks if
more than 3 dec places given in (iv))
(correct answer on spreadsheet scores both marks)
(b)
Plot a graph of v T, v T, f T, or f T
Graph should be a straight line through the origin
Statement of what gradient equals (consistent with what has been
plotted)
(For this experiment is a constant. A graph using a variable can
score max 1 mark for the correct gradient)
[10]
8.
(a)
(i)
HELP Academy
How the bow causes the wave pattern
EITHER
3
Tutorial 3 : Refraction & Superposition
Bow alternately pulls and releases string (or sticks and slips) (1)
Creates travelling wave (OR travelling vibration ) (on string) (1)
Wave reflects at the end (OR bounces back) (1)
Incident and reflected waves (OR waves travelling in opposite (1)
directions) superpose (OR interfere OR combine)
[Dont accept collide]
max 3
OR
Bow alternately pulls and releases string (or sticks and slips) (1)
Produces forced oscillation/acts as a driver/exerts periodic force (1)
[Dont accept makes it vibrate] At a natural frequency of the string (1)
Causing resonance (OR large amplitude oscillation) (1)
max 3
(ii)
Determination of wavelength
Use of node to node distance = /2 / recognise diagram shows 2] (1)
Correct answer [0.4 m] (1)
e.g. = 2 0.2 m
= 0.4 m
(iii)
Differences between string wave and sound wave
Any TWO points from:
String wave is transverse, sound wave is longitudinal /
can be polarised, cant
String wave is stationary (OR standing), sound wave is travelling
(OR progressive) / has nodes and antinodes, doesnt /
doesnt transmit energy, does
The waves have different wavelengths
Sound wave is a vibration of the air, not the string (1)(1)
[Dont accept travel in different directions / can be seen, cant be
seen / cant be heard, can be heard / travel at different speeds
The first two marking points require statements about both waves,
e.g. not just sound waves are longitudinal]
(b)
Sketch of the waveform
Sinusoidal wave with T = 1 ms (1)
[Zero crossings correct to within half a small square
Accept a single cycle]
Amplitude 1.6 cm (1)
[Correct to within half a small square]
2
[9]
9.
(a)
Explanation of maximum or minimum
9
path difference = 2 125 10 m = 250 10 m (1)
HELP Academy
Tutorial 3 : Refraction & Superposition
= half wavelength /antiphase (1)
destructive interference / superposition (1)
( minimum intensity)
(b)
Meaning of coherent
remains in phase / constant phase relationship (1)
1
[4]
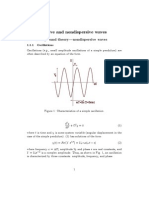
10.
(a)
(b)
Amplitude
Maximum distance/displacement
From the mean position / mid point / zero displacement line / (1)
equilibrium point
[If shown on a diagram, at least one full wavelength must be shown,
the displacement must be labelled a or amplitude and the zero
displacement line must be labelled with one of the terms above.]
Progressive wave
Displacement at A: 2.0 (cm) [accept 2] (1)
Displacement at B: 2.5 (cm) to 2.7 (cm) (1)
Displacement at C: 1.5 to 1.7 (cm) (1)
Diagram
[Minimum] one complete sinusoidal wavelength drawn (1)
Peak between A and B [accept on B but not on A] (1)
y = 0 (cm) at x = +2.6 cm with EITHER x = +6.2 cm OR x = 1.0 (1)
cm
3
[7]
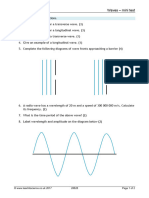
11.
Wavelength
0.30 m (1)
Letter A on graph
A at an antinode (1)
Wavespeed
Use of = f (1)
1
11(10.8) m s (1)
2
1
[allow ecf = 0.15 m ie = 5.4 m s ]
Phase relationship
In phase (1)
Amplitude
2.5 mm (1)
1
[6]
12.
Explanation of words:
HELP Academy
Tutorial 3 : Refraction & Superposition
Coherent
Same frequency and constant phase relationship (1)
Standing wave
Any two points from:
Superposition/interference
Two (or more) wavetrains passing through each other
Having equal A, f,
+ system of nodes and antinodes (1) (1)
Position of one antinode marked on diagram
Correctly marked A (in centre of rings hot zone) (1)
Wavelength demonstration:
= c/f = 3 108 /2.45 109 m
= 12.2 cm (1)
Path difference:
(22.1 + 14) (20 + 10) cm
= 6.1 cm (1)
Explanation:
6.1 cm = (1)
Waves at X in antiphase/ destructive interference (1)
node (1)
Explanation of how two separate microwave frequencies overcomes
uneven heating problem:
Different wavelengths (1)
So a path difference which gives destructive interference at
one wavelength may not do so at another (1)
1
[11]
HELP Academy
You might also like
- 2.3 Waves MSDocument4 pages2.3 Waves MSBenedict YamvwaNo ratings yet
- Waves - Booklet 1 (New IAL) AnsDocument10 pagesWaves - Booklet 1 (New IAL) AnsfedNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Physics Oscillations AnswersDocument26 pagesUnit 5 Physics Oscillations Answersareyouthere92100% (1)
- SHM Set 1 MSDocument7 pagesSHM Set 1 MSRoyal QueenNo ratings yet
- Answers To Oscillations QuestionsDocument27 pagesAnswers To Oscillations QuestionsMimran1994No ratings yet
- Statics & Resolving Forces 2 MSDocument8 pagesStatics & Resolving Forces 2 MSelsieNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: GCE Physics (6PH01) Paper 01 Physics On The GoDocument8 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2012: GCE Physics (6PH01) Paper 01 Physics On The GoCka DohaNo ratings yet
- H2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesH2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics Answers and Mark Schemes: Waves & SoundDocument10 pagesGcse Physics Answers and Mark Schemes: Waves & SoundJason LeeNo ratings yet
- Density, Viscosity & Drag 1 MSDocument8 pagesDensity, Viscosity & Drag 1 MSaayanzubair12125No ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 15Document1 pageEOCQ Ans 15harshanauoc50% (2)
- Jan 11 MSDocument9 pagesJan 11 MSshangardeziNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Assessment Unit AS 2Document8 pagesMark Scheme: Assessment Unit AS 2Mark McKinsnkeyNo ratings yet
- 1A Force MSDocument69 pages1A Force MSShuvashis BiswasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Waves: - Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 1: Waves GCKL 2011Document29 pagesUnderstanding Waves: - Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 1: Waves GCKL 2011rush7240No ratings yet
- Ch15 Properties of WavesDocument11 pagesCh15 Properties of WavesWang Ka YuNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Waves Sound & LightDocument15 pagesGrade 10 Waves Sound & LightMidyondzi ngobeniNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Test 6Document41 pagesJee Main Test 6rs81219952gmailcomNo ratings yet
- 20.1 Stationary Waves CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages20.1 Stationary Waves CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- F GMM/R: 6735 Unit Test Phy5Document5 pagesF GMM/R: 6735 Unit Test Phy5muxadeyNo ratings yet
- Ias-Physics Student Text Book Answer.Document14 pagesIas-Physics Student Text Book Answer.mayaNo ratings yet
- As Prelim P2 2020-2021 (MS Final Draft)Document4 pagesAs Prelim P2 2020-2021 (MS Final Draft)Nathaniel BasukiNo ratings yet
- 15 Oscillations: Answers To Exam Practice QuestionsDocument10 pages15 Oscillations: Answers To Exam Practice QuestionsKoe ChoNo ratings yet
- H1 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesH1 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document7 pagesTutorial 9angel lopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 16 PDFKoe Cho100% (1)
- Tutesheet 7Document2 pagesTutesheet 7Aryan AroraNo ratings yet
- EdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsDocument141 pagesEdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsAravinth Pushparaj100% (2)
- Plane Waves Part I - 2 PDFDocument13 pagesPlane Waves Part I - 2 PDFAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Wave Phenomena PracticeDocument63 pagesWave Phenomena PracticeDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 Waves On StringDocument3 pagesDPP 1 Waves On Stringupanshupandit3No ratings yet
- 9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument14 pages9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersbobNo ratings yet
- Physics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Document29 pagesPhysics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Jo Ey Goh75% (4)
- TWSS 2018 5076 SciPhy 4E5N Prelims MS v2 (Edited)Document5 pagesTWSS 2018 5076 SciPhy 4E5N Prelims MS v2 (Edited)leetaishenNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Light and Waves Exam MSDocument6 pagesExercises For Light and Waves Exam MSVarvaraNo ratings yet
- Waves A Level Questions and AnswersDocument69 pagesWaves A Level Questions and AnswersBunya AnillyNo ratings yet
- 04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - ch9)Document95 pages04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - ch9)JL1206No ratings yet
- 19.2 Ultrasound CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument3 pages19.2 Ultrasound CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- Unit2topic3 Examzone Ms PDFDocument3 pagesUnit2topic3 Examzone Ms PDFNusaiba AminNo ratings yet
- Test 12H Review AnswersDocument7 pagesTest 12H Review Answerstedien252No ratings yet
- JEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2Document28 pagesJEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2Alisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MCQ 2Document52 pagesMCQ 2eka123No ratings yet
- UIC Physics 105: Practice Final ExamDocument7 pagesUIC Physics 105: Practice Final ExamnetrunnrNo ratings yet
- Homework No. 2: Fig. 1. Problem 1Document3 pagesHomework No. 2: Fig. 1. Problem 1victus0110No ratings yet
- Markscheme: International Baccalaureate Baccalauréat International Bachillerato InternacionalDocument7 pagesMarkscheme: International Baccalaureate Baccalauréat International Bachillerato InternacionalEdgarNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Electricity MSDocument13 pages2.4 Electricity MSnaziya begumNo ratings yet
- Markscheme: (232 Marks)Document27 pagesMarkscheme: (232 Marks)Sharavanan Mathivanan TIPSNo ratings yet
- IIT Paper 1 Physics 2012Document14 pagesIIT Paper 1 Physics 2012Yash KuncolienkarNo ratings yet
- Waves 3Document6 pagesWaves 3krichenkyandex.ruNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Formulae Wave OpticsDocument12 pages6 2 Formulae Wave OpticsNathanian50% (2)
- A: Dispersive and Nondispersive WavesDocument10 pagesA: Dispersive and Nondispersive WavesKyungHwan OhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Waves Learning Outcomes 1.1 Understanding Waves A Student Is Able ToDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Waves Learning Outcomes 1.1 Understanding Waves A Student Is Able ToElly SayutiNo ratings yet
- Reflection, Refraction, and DiffractionDocument19 pagesReflection, Refraction, and DiffractionSteven RollinsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Wave Optics GistDocument20 pagesChapter 10: Wave Optics GistNiciitaa SuklaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Latihan Utk Wave Utk SPMDocument19 pagesSoalan Latihan Utk Wave Utk SPMnurulsyafiqah93No ratings yet
- Waves MinitestDocument2 pagesWaves MinitestBarnaby PettiferNo ratings yet
- 32 Sound Waves and Beats StudentDocument5 pages32 Sound Waves and Beats Studentgrace_ng_45No ratings yet
- Refraction & Superposition AnswerDocument6 pagesRefraction & Superposition Answergrace_ng_45No ratings yet
- Academic Calendar Jan 2014 HA16EDocument2 pagesAcademic Calendar Jan 2014 HA16Egrace_ng_45No ratings yet
- Haydn Oboe Concerto-Solo OboeDocument7 pagesHaydn Oboe Concerto-Solo OboeEdLeal90No ratings yet
- Written Report in Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesWritten Report in Instructional PlanningRose Aura HerialesNo ratings yet
- PC's & Laptop Accessories PDFDocument4 pagesPC's & Laptop Accessories PDFsundar chapagainNo ratings yet
- Javascript NotesDocument5 pagesJavascript NotesRajashekar PrasadNo ratings yet
- ERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingDocument3 pagesERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingtpeppermanNo ratings yet
- Business Plan - A TeahouseDocument6 pagesBusiness Plan - A TeahouseJoe DNo ratings yet
- Hailey College of Commerce University of PunjabDocument12 pagesHailey College of Commerce University of PunjabFaryal MunirNo ratings yet
- Caddy Arc 251i Service ManualDocument52 pagesCaddy Arc 251i Service Manualrikycien100% (8)
- Heisenberg, "Über Den Anschaulichen Inhalt Der Quantentheoretischen Kinematik Und Mechanik"Document16 pagesHeisenberg, "Über Den Anschaulichen Inhalt Der Quantentheoretischen Kinematik Und Mechanik"Benjamin Crowell0% (1)
- Errata V0.1 For IT8212F V0.4.2Document2 pagesErrata V0.1 For IT8212F V0.4.2tryujiNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Questions Tnusrb S. I - 2010: Part - A': General KnowledgeDocument21 pagesPrevious Year Questions Tnusrb S. I - 2010: Part - A': General Knowledgemohamed AzathNo ratings yet
- The Dust Bunnies COL FKBDocument36 pagesThe Dust Bunnies COL FKBPradeep ManralNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Guest Experience and Operational Efficiency in Hotels Through Robotic Technology-A Comprehensive Review.Document8 pagesEnhancing Guest Experience and Operational Efficiency in Hotels Through Robotic Technology-A Comprehensive Review.Chandigarh PhilosophersNo ratings yet
- Singer 900 Series Service ManualDocument188 pagesSinger 900 Series Service ManualGinny RossNo ratings yet
- @InglizEnglish-4000 Essential English Words 6 UzbDocument193 pages@InglizEnglish-4000 Essential English Words 6 UzbMaster SmartNo ratings yet
- NDT HandBook Volume 10 (NDT Overview)Document600 pagesNDT HandBook Volume 10 (NDT Overview)mahesh95% (19)
- Geography NotesDocument2 pagesGeography NotesMinethegroundNo ratings yet
- Fire Guard Study MaterialDocument14 pagesFire Guard Study MaterialSerina Sanusi100% (1)
- 2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)Document31 pages2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)VincentNo ratings yet
- Starbucks Progressive Web App: Case StudyDocument2 pagesStarbucks Progressive Web App: Case StudyYesid SuárezNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Reading and Writing (Grade 11)Document5 pagesI. Objectives:: Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Reading and Writing (Grade 11)Shelton Lyndon CemanesNo ratings yet
- Saes T 883Document13 pagesSaes T 883luke luckyNo ratings yet
- 8. Nguyễn Tất Thành- Kon TumDocument17 pages8. Nguyễn Tất Thành- Kon TumK60 TRẦN MINH QUANGNo ratings yet
- CSCU Module 08 Securing Online Transactions PDFDocument29 pagesCSCU Module 08 Securing Online Transactions PDFdkdkaNo ratings yet
- Haymne Uka@yahoo - Co.ukDocument1 pageHaymne Uka@yahoo - Co.ukhaymne ukaNo ratings yet
- Cad32gd - Contactor ManualDocument28 pagesCad32gd - Contactor Manualhassan karimiNo ratings yet
- Development of A Small Solar Thermal PowDocument10 pagesDevelopment of A Small Solar Thermal Powעקיבא אסNo ratings yet
- New Compabloc IMCP0002GDocument37 pagesNew Compabloc IMCP0002GAnie Ekpenyong0% (1)
- D15 Hybrid P1 QPDocument6 pagesD15 Hybrid P1 QPShaameswary AnnadoraiNo ratings yet
- Matokeo CBDocument4 pagesMatokeo CBHubert MubofuNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Module 1 Performing Roughing in Activities For Communication and DistributDocument26 pagesGrade 10 Module 1 Performing Roughing in Activities For Communication and DistributNelshane JohnNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionFrom EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)