Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RBC Studies Midterm
Uploaded by
Dee GeeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RBC Studies Midterm
Uploaded by
Dee GeeCopyright:
Available Formats
TRANSCRIBED GEN CAMATO
RBC
STUDIES
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
RBC series of maturation
1.
Rubriblast
n
also known as normoblast, pronormoblast
n
makes up 5 to 10% of the total nucleated red cell in bone
marrow
n
youngest form of RBCs
[
cytoplasm
deeply basophilic and relatively of small
amout
[
nucleus
relatively large, round or slightly oval with
1-2 nucleoli
[
nucleus to cytoplasm ratio
8:1
2.
Prorubricyte
n
also known as basophilic normoblast
[
cytoplasm
intensely basophilic and relatively small
amount
[
nucleus
relatively large, round and slightly oval
centrally located
if there's a presence of nucleoli they are
not visible
[
nucleus to cytoplasm ratio
6:1
3.
Rubricyte
n
also known as polychromatophilic normoblast
[
cytoplasm
gray-blue to pink in color
shows a wide range of colors because of
the start in hemoglobin formation
[
nucleus
still round, nucleoli in absent
[
nucleus to cytoplasm ratio
4:1
4.
Metarubricyte
n
also known as acidophilic normoblast, orthochromic
normoblast
n
fully hemoglobinated red cell that comprises 50% of the
total nucleated RBC in the bone marrow.
n
Last to contain nucleus
[
cytoplasm
pink to orange in color (similar to adult red
cell.
[
nucleus
having a pyknotic nucleus, relatively small
[
nucleus to cytoplasm ratio
1:2
5.
Reticulocyte
n
also known as retics, polychromatophilic erythrocyte
n
you will observed basophilic fine reticulum of RNA in the
cytoplasm
n
this is demonstrated by the supravital stain.
[
nucleus
none
[
cytoplasm
pink to reddish brown
fibro
Wright stain most commonly used stain in Hematology
Methylene alcohol as FIXATIVE; w/o will washed
away
Methylene blue used to stain NUCLEUS (acidic)
Eosin
Phosphate Buffer saline
Supravital stain stains the living cells
New Methylene Blue
Brilliant Cresyl Blue
6.
Requirements for the maturation of RBC
1.
There must be adequate amount of hematopoeitic factor
2.
There must be an adequate supply of Fe in usuable form.
3.
There must be an adequate amount of protoporphyrin(Protoporphyrin 9)
4.
There must be an adequate supply of globin (Protein)
Statistical factor that could affect the RBC count
1)
Posture
r
there is a decrease around 5.7% of hemoglobin and
hematocrit level in the recumbent position.
2)
Exercise/emotion/excited
r
may increase the RBC count.
3)
Dehydration
r
may also attribute to increase the RBC count
4)
Age
r
the younger the patient the higher the value of hemoglobin,
hematocrit
5)
Gender
r
Male: may increase RBC count
6)
Altitude
r
High altitude
decrease of oxygen, the BM will produce more
Rbc to compensate the decrease of oxygen.
1
Erythrocyte
n
Aka mature RBC
[
size
8.2 m (or cubic micra)
[
thickness
biconcave disc shape (0.8-2.8u3)
[
life span
120 days
*transfused RBCs 120days lifespan
[
for every 100 rbc there is approximately 3-8
platelets found
[
for every 1000 rbc there is one WBC
[
Normal Value
Million
3
Female: 4.5 5.5
/ mm
Million
3
Male: 5.5 6.5
/ mm
increase level of testosterone (MALE)
Objectives used:
HPO WBC; factor 2,000
OIO Platelets; 20, 0000
Hirisutism excessive hairs (FEMALE)
[
Cytoplasm
biconcave disc shape with orange to pink
color that is pale staining at the venter
that occupies 1/3 of cell size of rbc area.
[
RBC is compose of protein lipid stroma that
contains Hb in solution and condense in lipid rich
peripheral cell membrane.
> Hypochromia
< Hyperchromia
Normal Value:
0.5 1.5% found in circulation
98.5 99.5% found in bone
marrow
TRANSCRIBED GEN CAMATO
RBC
STUDIES
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
RBC anomalies
I.
d)
Anisocytosis variation in size
a)
Normocyte
normal RBC size: 6.2-8.2 um
b)
Microcyte
less than 6.2um small rbc
c)
Macrocyte
large RBC, greater than 9um
d)
Megalocyte
giant rbc seen in megalocytic anemia due to
deficiency of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) or
folic acid.
Size: from 12-21um
e)
II.
Elliptocytes
Elliptical shape of rbc (also called ovalocytes)
Found in Pernicious Anemia
9 Hypersegmented neutrophil
* > 5 lobules
Blister cell
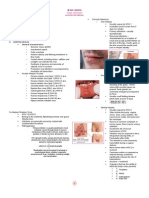
Poikilocytosis variation shape of RBC
a)
Acanthocytes
Also known as Thorn cell, spur cell
Round rbc with around 5-10 irreversible thorn like
projection
Indicative of permanent cell damage
Found in patient with abetalipoproteinemia
Abetalipoproteinemia
absence of Low Density Lipoprotein;
if NO LDL will cause permanent cell damage because
LDL is responsible for the distribution of cholesterol
b)
f)
Helmet cell
Burr cell
c)
RBC with thin peripheral cell membrane.
Found in microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
RBC with reversible thorn-like projection and
is some what elongated.
g)
(triangle cell, keratocyte of bessis /
contracted RBC)
Results after the blistered or ruptured blister cell
that would become a helmet/triangle cell.
Sickle cell
Crenated RBC
Also known as echinocyte
RBC with short blunt spicules found all over the
cell.
Finely serrated RBC
No clinical significance, this condition only occurs
in RBC that has been placed under
hypertonic NaCl solution I > 0.9 %
Normal Saline Solution (0.85 0.9% NaCl solution)
(drepanocyte, meniscocyte)
C shape, crescent shape, sickled RBC
Occurs in the presence of Hb S and found in
sickle cell anemia
Refers also as resistant cell, irreversible reaction
TRANSCRIBED GEN CAMATO
RBC
STUDIES
h)
Spherocyte
i)
HEMATOLOGY 1 | LECTURE
m)
Small, round, darkly staining rbc found in
hereditary spherocytosis and some hemolytic
anemia.
Fragile cell
Erythrocyte Osmotic Fragility Test (EOFT)
Useful in identifying fragile cell and resistant
cell
If spherocyte or sickle cell identification.
Use different concentration of hypotonic NaCl
solution. (0.5 % NaCl 50-85)
n)
o)
j)
Fragmenting or disintegrating RBC found in
hemolytic anemia, patient with severe burns and
who suffers in DIC (Diffuse Intravascular
Coagulation syndrome)
III.
k)
l)
Mouth cell
RBC with mouth-like clear central area found in
hereditary stomatocytosis, alcoholism and liver
diseases.
Stellar cell
(Astrocyte)
Star-like RBC found in some anemias
Tear drop RBC
Target cell
Dacrocytes, pear-shaped
Found in thalassemia
RBC with peripheral and central condensation of
Hb. With clear zone in between.
Found in thalassemia.
Anisochromasia variation in color of RBC
a)
Normochromic/ normochromasia
Normal hb content of RBC
b)
Hypochromic/ hypochromasia
Decrease of hb content and normally RBCs are
with pale central area
c)
Hyperchromic/ hyperchromasia
Increase hb content due to a thick cell wall.
d)
Polychromic/ polychromasia
RBC with uneven distribution of Hb so the RBC
stains unevenly
e)
Anulocyte
(pessary cells, ghost cell)
RBC with thin rim of hb with clear central area
seen in Fe deficiency anemia
9
Lacks Intrinsic Factor (IF)
9
Absorption site of Fe Duodenum
9
Absorption site of Folate Jejunum
9
Absorption site of Vitamin B12 Ileum
f)
Irregular contracted distorted rbc
Found among infants less that 3 months old.
Target cell
Stomatocyte
Similar to tear drop except that it has a longer tail
forming like a racket handle
Pyknotic cell (pyknocyte)
Schistocyte
Racket cell
May categorized as poikilocytosis
Dont let anyone look down on you because you are young, but
set an example for the believers in speech, in life, in love, in faith
and in purity.
1 Timothy 4:12
3
You might also like
- III. Quality Assessment & ManagementDocument3 pagesIII. Quality Assessment & ManagementDee Gee100% (1)
- IV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDocument7 pagesIV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- II. Renal FunctionDocument3 pagesII. Renal FunctionDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- II. Renal FunctionDocument3 pagesII. Renal FunctionDee GeeNo ratings yet
- III. Quality Assessment & ManagementDocument3 pagesIII. Quality Assessment & ManagementDee Gee100% (1)
- IV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDocument7 pagesIV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDee GeeNo ratings yet
- III. Quality Assessment & ManagementDocument3 pagesIII. Quality Assessment & ManagementDee Gee100% (1)
- II. Renal FunctionDocument3 pagesII. Renal FunctionDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- I. Safety in The Clinical LabDocument3 pagesI. Safety in The Clinical LabDee GeeNo ratings yet
- IV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDocument7 pagesIV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDee GeeNo ratings yet
- III. Quality Assessment & ManagementDocument3 pagesIII. Quality Assessment & ManagementDee Gee100% (1)
- 2HDocument6 pages2HDee GeeNo ratings yet
- IV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDocument7 pagesIV. Urinalysis Lab Test & Chemical ScreeningDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Scripture SongsDocument2 pagesScripture SongsDee GeeNo ratings yet
- GENDocument2 pagesGENDee GeeNo ratings yet
- God's Love LetterDocument1 pageGod's Love LetterDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Ix. CSF AnalysisDocument3 pagesIx. CSF AnalysisDee GeeNo ratings yet
- 4 HDocument10 pages4 HDee GeeNo ratings yet
- ABBDocument16 pagesABBDee GeeNo ratings yet
- 5 HDocument4 pages5 HDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Practice Test CCDocument3 pagesPractice Test CCDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Haemoglobin Opa ThiesDocument4 pagesHaemoglobin Opa ThiesDee GeeNo ratings yet
- PH Le BotomyDocument4 pagesPH Le BotomyDee Gee100% (1)
- CC2 ChartDocument2 pagesCC2 ChartDee Gee100% (1)
- Dna VirusesDocument3 pagesDna VirusesDee GeeNo ratings yet
- Hematology LaboratoryDocument3 pagesHematology LaboratoryDee GeeNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Kumpulan Quiz CourseraDocument13 pagesKumpulan Quiz CourseraNadya Azzahra Salsabilla SaragihNo ratings yet
- MSC Genetics SyllabusDocument36 pagesMSC Genetics SyllabusMohak SahuNo ratings yet
- MGR University SyllabusDocument33 pagesMGR University SyllabussanjviewsNo ratings yet
- Tugas ApolipoproteinDocument8 pagesTugas ApolipoproteinSeptiany Christin PalilinganNo ratings yet
- Lecture at University of IndonesiaDocument58 pagesLecture at University of IndonesiaFikriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Facts of Life: Chemistry Is The Logic of Biological Phenomena The Inorganic PrecursorsDocument1 pageChapter 1 The Facts of Life: Chemistry Is The Logic of Biological Phenomena The Inorganic PrecursorsAlbertochoNo ratings yet
- Fonc 13 1226289Document19 pagesFonc 13 1226289Shady tantawyNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lipids NotesDocument9 pagesBiochem Lipids NotesPatricia AnneNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Watson - Summer AQA - Biology - Cell Biology - KnowIT - GCSEDocument71 pagesBenjamin Watson - Summer AQA - Biology - Cell Biology - KnowIT - GCSEboobooNo ratings yet
- Blood PhysiologyDocument17 pagesBlood Physiologymuhammad sadiqNo ratings yet
- Scientist Behind The Cell TheoryDocument20 pagesScientist Behind The Cell TheoryBERNA MAE TAMAYONo ratings yet
- DahliaDocument14 pagesDahliaHiNo ratings yet
- Pre Trial MRSM Biology ObjectivesDocument16 pagesPre Trial MRSM Biology ObjectivesKhusyairy Daeng SailendraNo ratings yet
- Sonu 26S00230050665Document1 pageSonu 26S00230050665Rakesh KoliNo ratings yet
- Plants and Society 7th Edition Levetin Test BankDocument35 pagesPlants and Society 7th Edition Levetin Test Bankconjectxanthinev76r100% (23)
- Agascalm Brossúra01Document21 pagesAgascalm Brossúra01vukicsvikiNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 2Document25 pagesBio Unit 2benlucag5No ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 11 - Cytogenetic TechniquesDocument7 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 11 - Cytogenetic TechniquesAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- Physiology Notes 1Document193 pagesPhysiology Notes 1Sivaranjini BhalaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/23 October/November 2021Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/23 October/November 2021lllllisaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Biosel Serial Endosymbiosis TheoryDocument4 pagesJurnal Biosel Serial Endosymbiosis TheoryHeny SinagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 LodishDocument52 pagesChapter 19 LodishablucNo ratings yet
- Aqa Byb2 W MS Jun06Document5 pagesAqa Byb2 W MS Jun06iluvmcr88No ratings yet
- RBC&WBC AbnormalitiesDocument10 pagesRBC&WBC AbnormalitiesDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - CellStructureSEDocument3 pagesKami Export - CellStructureSEDohnovan RankinsNo ratings yet
- TiroidDocument26 pagesTiroidJoni Riana MustaqimNo ratings yet
- MMC 3Document33 pagesMMC 3Bogdan A. GireadăNo ratings yet
- 10 1038@nrdp20156Document17 pages10 1038@nrdp20156Desi DwiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter FINAL EXAM General Biology 1Document2 pages2nd Quarter FINAL EXAM General Biology 1Cherrina Aguila71% (7)
- MainDocument13 pagesMainIkmah FauzanNo ratings yet