Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pollination and Its Agents
Uploaded by
debbyhooiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pollination and Its Agents
Uploaded by
debbyhooiCopyright:
Available Formats
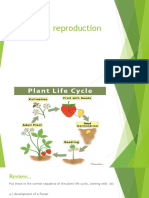
Pollination and its agents
1. There are 2 types of pollination : a) Self pollination : the same flower
: two flowers of the same plant
b) Cross pollination : two flowers of two different plants
2. Both of these pollination happens with the help of different pollination agents.
3. Land plants are commonly pollinated by animals or insects and by wind.
4. Aquatic plants (plants in water) are pollinated by water itself.
5. Characteristic of plants pollinated by animals or insect :
Insect Pollinated
large, brightly coloured petals - to attract insects
Wind Pollinated
small petals, often brown or dull green - no need
to attract insects
often sweetly scented - to attract insects
no scent - no need to attract insects
usually contain nectar - to attract insects
no nectar - no need to attract insects
moderate quantity of pollen - less wastage than with
pollen produced in great quantities - because
wind pollination
most does not reach another flower
pollen often sticky or spiky - to stick to insects
pollen very light and smooth - so it can be blown
in the wind and stops it clumping together
anthers firm and inside flower - to brush against
anthers loosely attached and dangle out - to
Insect Pollinated
Wind Pollinated
insects
release pollen into the wind
stigma inside the flower - so that the insect brushes
stigma hangs outside the flower - to catch the
against it
drifting pollen
stigma has sticky coating - pollen sticks to it
stigma feathery or net like - to catch the drifting
pollen
Insects or animals pollinated flower
Wind pollinated
flower
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed away from each other and from the parent plant so that there is less competition. The
commonest methods of seed dispersal are:
wind e.g. dandelion, sycamore fruits are light and have extensions which act as parachutes or
wings to catch the wind
animal internal e.g. tomato, plum, raspberry, grape have brightly coloured and succulent fruits
which contain seeds with indigestible coats which allow the seeds to pass through the animal undamaged
animal external e.g. goose grass, burdock, the fruits have hooks which attach them to the fur of
passing animals.
explosive/ self propelled e.g. pea pod. The pod burst open when ripe projecting the seeds away
from the plant.
Asexual reproduction in plants
It is possible for plants to reproduce asexually (i.e. without flowers or fertilisation). Two of the most
important methods of asexual reproduction are:
runners - e.g. strawberry, spider plant
tubers - e.g. potatoes, dahlias
Humans are able to propagate plants by artificial propagation.
Taking cuttings and grafting are the methods of artificial propagation which
you need to know. They are a quick way of propagating large numbers of
identical plants.
Plants which are produced in these ways are genetically identical to each
other and to the parent; a group like this is called a clone.
A clone is a group of cells or organisms which are genetically identical to
each other.
Advantages for the plant of asexual reproduction:
only one parent plant is required
young plants are identical to the parent, so that good features will always be passed on
Advantages for the plant of sexual reproduction:
characteristics are inherited from two parents - this produces variation in the offspring;
this gives a good chance of at least a few surviving diseases, changes of climate, etc.
Growing plants - Test
1. Water and a suitable temperature are needed
for germination. What gas is also needed?
carbon dioxide
E
oxygen
F
nitrogen
4. Which letter points to the stamen?
D
hydrogen
F
2. For questions 2 - 7 identify the named
structures on the above diagram.
G
5. Which letter points to the anther?
D
F
Which letter points to the sepals?
A
6. Which letter points to the stigma?
E
3. Which letter points to the petals?
Ovule
7. Which letter points to the ovary?
Stigma
B
11. Questions 11 - 13 are about methods of seed
dispersal.
Which method uses hooks on the seeds? Burdock
and goose grass are examples.
H
Wind
8. Where is pollen produced?
Anther
Animal (internal)
Stigma
Animal (external)
12. Which method is used by gooseberries?
Ovary
Wind
9. Which part of the flower develops into the
fruit?
Animal (internal)
Ovary
Animal (external)
Ovule
13. Which method of dispersal is used by
dandelions?
Stigma
Wind
10. Where does fertilisation occur?
Ovary
Animal (internal)
Animal (external)
You might also like
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument75 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsEdward BradshawNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument26 pagesBiology ProjectSaptarsi BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 16 ReproductionDocument20 pages16 ReproductionEmanuel SafiNo ratings yet
- Bioproject 160202142704Document26 pagesBioproject 160202142704Omm Narayan SethiNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory FileDocument22 pagesBio Investigatory FileTRICKS BY YOGESH100% (1)
- Good Afternoon: CHAPTER NAME: Self IncompatibilityDocument30 pagesGood Afternoon: CHAPTER NAME: Self IncompatibilitylkokodkodNo ratings yet
- Pollination Full NotesDocument10 pagesPollination Full Notes720 026 Promita GhoruiNo ratings yet
- FlowaringDocument21 pagesFlowaringMohamad HattaNo ratings yet
- Pollination, Fertilisation and GerminationDocument41 pagesPollination, Fertilisation and GerminationMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in VegetablesDocument46 pagesModes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in Vegetablessyamkavitha100% (4)
- Reproduction - PlantDocument24 pagesReproduction - PlantCarlos MasNo ratings yet
- K DevadharshanDocument24 pagesK DevadharshanGK addsNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885No ratings yet
- Week 4a-PollinationDocument5 pagesWeek 4a-Pollinationchukwuemekacollins058No ratings yet
- Alberto P. Navarette Jr. Earth and Life Gas 11 Boyle Mrs. CruzDocument4 pagesAlberto P. Navarette Jr. Earth and Life Gas 11 Boyle Mrs. CruzJobadzNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesNotes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsAdnan SathikNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument26 pagesPollinationᏉᏋᏋᏕᏂᏗᏝ Ꮄ. ᏰᎧᎴᎧᏕᏗNo ratings yet
- PERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesDocument11 pagesPERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesErnie Rosemarie T. BucalenNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Types of PollinationDocument22 pagesTypes of Pollinationransingvedika99No ratings yet
- Reproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceDocument20 pagesReproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceSharina GeraldNo ratings yet
- Pollination NotesDocument6 pagesPollination Notesketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document3 pagesChapter 13Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- Science - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesScience - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument14 pagesPollinationmnasainiNo ratings yet
- Pollination and FertilizationDocument21 pagesPollination and FertilizationShriyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- 16 ReproductionDocument9 pages16 ReproductionEmanuel SafiNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument30 pagesPollinationAparna SinghNo ratings yet
- Pollination: Name: Sheryl Bhatnagar Roll No: 2047 Sub: Reproductive Biology Course: Botany 2 YrDocument27 pagesPollination: Name: Sheryl Bhatnagar Roll No: 2047 Sub: Reproductive Biology Course: Botany 2 YrAnny LovibNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesReproduction in PlantsrupeshNo ratings yet
- Gr12 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesGr12 - Reproduction in PlantsZelNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - STUDENTSDocument18 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce - STUDENTSAnshika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants 1Document8 pagesReproduction in Plants 1subhroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PlantsDocument78 pagesIntroduction To PlantsAzizah ManzurNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument10 pagesBiologyNur FarhanimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument45 pagesChapter 23 Plant ReproductionSara SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Non-Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesNon-Flowering PlantsJimmy SerendipNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notesalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument4 pagesReproduction in PlantsYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument5 pagesPollinationMenakadevi MarkandanNo ratings yet
- Reproduciton in Crops Plant 2023Document68 pagesReproduciton in Crops Plant 2023lemma4aNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsRenuNo ratings yet
- CHP 04 - Pollination and FertilizationDocument9 pagesCHP 04 - Pollination and FertilizationKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionExceil Matthew Carpio100% (1)
- LSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument64 pagesLSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsAbraham KangNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes FlowersDocument9 pagesBio Notes FlowersYeo JhNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plantsanish kanthethiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument10 pagesReproduction in PlantsTIMEOFFICE KHARAGPURWORKSHOPNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants - RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants - RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plants and AnimalsAnuradha DhavalaNo ratings yet
- Class X Reproduction Notes 1Document13 pagesClass X Reproduction Notes 1vratNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Heredity: OutcomesDocument22 pagesModule 5: Heredity: OutcomesNavtej DeyalNo ratings yet
- Flowers Fruit and SeedsDocument3 pagesFlowers Fruit and SeedsJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument12 pagesReproduction in PlantsAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument5 pagesPollinationAntonio DiakosNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 4 1Document4 pagesPlant Reproduction 4 1Belen MartinezNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument15 pagesAsexual Reproductioneugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Chemistry Group 1 and 7Document11 pagesChemistry Group 1 and 7debbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Black Pepper White Pepper Aji Black Pepper Aji White PepperDocument1 pageBlack Pepper White Pepper Aji Black Pepper Aji White PepperdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- SDT Questions PDFDocument7 pagesSDT Questions PDFdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Smoked Paprika Thai Super Hot Celery Salt A.P. Seasoning Org Chilli Powder Na-Rok Chilli 25% Pla-Duk-Fu Chilli 17%Document1 pageSmoked Paprika Thai Super Hot Celery Salt A.P. Seasoning Org Chilli Powder Na-Rok Chilli 25% Pla-Duk-Fu Chilli 17%debbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Answer Topic 1-16Document18 pagesAnswer Topic 1-16debbyhooiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 8 StatisticsDocument15 pagesMODULE 8 StatisticshasnitajbNo ratings yet
- I) Aim (1 Mark) :: Do Not Write!!!!: The Apparatus Is Set Up As Shown in The Diagram)Document1 pageI) Aim (1 Mark) :: Do Not Write!!!!: The Apparatus Is Set Up As Shown in The Diagram)debbyhooiNo ratings yet
- A Simple View of Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesA Simple View of Atomic StructuredebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Travel WritingDocument5 pagesTravel WritingdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- 1 6Document7 pages1 6debbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Year 6 ForcesDocument1 pageYear 6 ForcesdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Eye and EarsDocument5 pagesEye and EarsdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Maform 5 Test Maths PDFDocument179 pagesMaform 5 Test Maths PDFdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules and EnzymesDocument16 pagesBiological Molecules and EnzymesdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument26 pagesThe HeartdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Writing To PersuadeDocument3 pagesWriting To PersuadedebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Calculations With Upper and Lower BoundsDocument2 pagesCalculations With Upper and Lower BoundsdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Measur MentsDocument7 pagesMeasur MentsdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Acid ExperimentDocument1 pageAcid ExperimentdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Writing To InformDocument6 pagesWriting To InformdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismDocument2 pagesMicroorganismdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Recipe SoupDocument2 pagesRecipe SoupdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Travel Writing 2Document7 pagesTravel Writing 2debbyhooi0% (1)
- Questions 2 Circles Uni PDFDocument2 pagesQuestions 2 Circles Uni PDFdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Questions 3 Circles Uni PDFDocument2 pagesQuestions 3 Circles Uni PDFdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Set Notation Final WorksheetDocument2 pagesSet Notation Final WorksheetdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Writing TaskDocument2 pagesWriting TaskdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Questions 2 Circles No Uni PDFDocument2 pagesQuestions 2 Circles No Uni PDFdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- A1G Set Worksheet 3 PDFDocument1 pageA1G Set Worksheet 3 PDFdebbyhooiNo ratings yet
- A1G Set Worksheet 1Document1 pageA1G Set Worksheet 1debbyhooiNo ratings yet
- Annual Troop PlanningDocument15 pagesAnnual Troop PlanningArvin CruzNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian Gardens (The Ostrakon, Bigelow, 2000)Document6 pagesAncient Egyptian Gardens (The Ostrakon, Bigelow, 2000)MithotNo ratings yet
- List of Collective NounDocument2 pagesList of Collective NounSya SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- Woodcarving PDFDocument84 pagesWoodcarving PDFReza AldavoodNo ratings yet
- English For BuildersDocument17 pagesEnglish For BuildersAnonymous erkddV1fyDNo ratings yet
- Update Given On Removal of Trees: Seneca Tops Cherry Hill West, 5-3Document16 pagesUpdate Given On Removal of Trees: Seneca Tops Cherry Hill West, 5-3elauwitNo ratings yet
- UTS Bahasa Inggris Semester 1 2017 - Kelas 6Document2 pagesUTS Bahasa Inggris Semester 1 2017 - Kelas 6Elista GeulisNo ratings yet
- Old Time WhittlingDocument12 pagesOld Time WhittlingRemember TheSnow33% (3)
- Steam Recipes For The Culinary EnthusiastDocument95 pagesSteam Recipes For The Culinary EnthusiastJeffrey PeekoNo ratings yet
- The Dallas Post 07-10-2011Document18 pagesThe Dallas Post 07-10-2011The Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Tropical Flowering PlantDocument425 pagesTropical Flowering Plantyorg yorogo100% (3)
- Revised HOA Architectural Guidelines For CommentDocument18 pagesRevised HOA Architectural Guidelines For CommentSan DeepNo ratings yet
- Reading & Listening Extra: Intermediate Unit 8Document1 pageReading & Listening Extra: Intermediate Unit 8nadin nNo ratings yet
- Mughal ArchitectureDocument10 pagesMughal ArchitectureDeepaliGupta100% (1)
- Catalog Custom Pergolas ChadsworthDocument44 pagesCatalog Custom Pergolas ChadsworthEugen IliesiuNo ratings yet
- Garden Staff Position Description 2015Document1 pageGarden Staff Position Description 2015congressheightsontheriseNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Plants Progress Test SY 2017 With AnswersDocument16 pagesGrade 8 Plants Progress Test SY 2017 With Answerspixelhobo100% (1)
- MicropropagationDocument6 pagesMicropropagationEmmanuel OcanseyNo ratings yet
- Basic English For College StudentsDocument66 pagesBasic English For College Studentswastu widya100% (1)
- Backyard Farming On A Acre or LessDocument434 pagesBackyard Farming On A Acre or LessMatt Lawson88% (8)
- 5 TrenchingDocument2 pages5 TrenchingAdjgnf AA100% (1)
- Patterns For EmbroideryDocument34 pagesPatterns For EmbroideryEllen Anne Eddy100% (4)
- ASEAN National FlowersDocument5 pagesASEAN National FlowersNajida FadliyahNo ratings yet
- Time-Life, The Art of Woodworking Vol 07 Encyclopedia of WooDocument147 pagesTime-Life, The Art of Woodworking Vol 07 Encyclopedia of WoorodolfoNo ratings yet
- Grafting and Budding Nursery Crop PlantsDocument20 pagesGrafting and Budding Nursery Crop PlantsArt Del R SalongaNo ratings yet
- Paul Acker - Les Deux Cahiers - 1912Document158 pagesPaul Acker - Les Deux Cahiers - 1912matwashereNo ratings yet
- Designing Pier Footings PDFDocument7 pagesDesigning Pier Footings PDF63ragtopNo ratings yet
- Legend of The Banana PlantDocument3 pagesLegend of The Banana PlantJan Mikel Riparip100% (1)
- Posessive Adjectives and Pronouns - ExercitiiDocument2 pagesPosessive Adjectives and Pronouns - ExercitiiGabriel CizmaritaNo ratings yet
- Dishoom The Permit Room MenuDocument15 pagesDishoom The Permit Room MenuSaurabh WadhwaNo ratings yet