Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assembler Guide
Uploaded by
Mathias EderOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assembler Guide
Uploaded by
Mathias EderCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Geographic Data Management
After creating the catalog, you load raster datasets into it.
After creating the empty raster
catalog, right-click it, point to Load,
and click Load Data. Browse to
the rasters to add, and add them
to the list.
When you create a raster catalog, a table is created that lists each raster. You can display the table by selecting the
catalog in the Catalog tree, selecting the Preview tab, and clicking the Table option at the bottom of the window. You
can add fields to the table (such as source, creation date, and so on) to track the rasters. Right-click the catalog, click
Properties, and select the Fields tab. Then enter the additional fields as you would for any other table (see Creating
feature classes and tables earlier in this chapter).
When you preview the
table for the raster catalog
you can see that each
raster dataset is stored as
a record in the table. You
can add fields to the table,
such as the creation date,
the source, and so on, to
manage the raster datasets
more efficiently.
The input rasters are stored as
individual datasets within the raster
catalogyou can access the
properties for a dataset by rightclicking it.
You can also perform searches to query the raster catalog. You might do this to find only rasters of a specific date or
having a low percentage of cloud cover on an image. You can search by geography to view only those rasters that
coincide with your area of interest. (See Searching for data and maps earlier in this chapter.)
133
udt_ch02.indd 133
10/18/2006 11:13:38 AM
Using ArcGIS Desktop
Adding specialized datasets to a geodatabase
In addition to the basic geodatabase data types of feature classes, tables, and rasters, you can extend your geodatabase
with datasets that are used for specific applications, such as surface modeling and analysis; modeling the flow of people,
goods, or resources over networks; or locating features or incidents along a street or highway network. Usually, these
datasets are built from feature classes and tables that already exist in your geodatabase. While this section describes
how to define these datasets in your geodatabase, Chapter 3, Data Compilation and Editing, contains information on
how to create and edit the features that the datasets contain.
Creating a terrain dataset for surface modeling
A terrain dataset is used to model surfaces using TIN structures within a geodatabase (see also Creating a TIN surface
in Chapter 5). Terrains are also used to manage massive 3D point collectionsfor example, billion point LiDAR
collections. You define and build the terrain dataset from existing feature classes stored in a feature dataset. You can
also specify scales at which to display the terrain at a lower resolution, so it will draw faster.
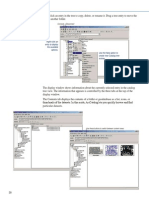
To create a Terrain, right-click the
feature dataset containing the
feature classes that will be used to
build the surface, point to New, and
click Terrain.
Select the feature
classes that will be
used to build the
Terrain. These include
spot elevations,
contour lines, and
breaklines (such as
streams or graded
roadbeds).
Specify the number
of pyramid levels.
Pyramids are used
to draw the Terrain
more quickly (but with
lower resolution) when
zoomed out.
Specify how the
feature classes will be
used for building the
Terrain (or accept the
defaults).
The final panel
summarizes the
settingsclick Finish
to build the Terrain
(or Back to make
changes).
134
udt_ch02.indd 134
10/18/2006 11:13:47 AM
You might also like
- Secrets of Access Database Development and ProgrammingFrom EverandSecrets of Access Database Development and ProgrammingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pivot Tables In Depth For Microsoft Excel 2016From EverandPivot Tables In Depth For Microsoft Excel 2016Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Manual Arcgis2Document2 pagesManual Arcgis2Mathias EderNo ratings yet
- 2 - Geographic Data ManagementDocument2 pages2 - Geographic Data ManagementMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Georeferencing and Digitizing in ArcGISDocument7 pagesGeoreferencing and Digitizing in ArcGISatierah_dsgNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: 1. Getting To Know ArcgisDocument19 pagesExercise 1: 1. Getting To Know ArcgisbirukNo ratings yet
- Arcmap: Ahmad MokhtariDocument31 pagesArcmap: Ahmad Mokhtariripal100% (1)
- Manual ArcgisDocument2 pagesManual ArcgisMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Using Arcgis Desktop: Additional Toolbars Are Available From The View MenuDocument2 pagesUsing Arcgis Desktop: Additional Toolbars Are Available From The View MenuMathias EderNo ratings yet
- The Display Window: 1 - IntroductionDocument2 pagesThe Display Window: 1 - IntroductionMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Tribhuvan University: Institute of EngineeringDocument16 pagesTribhuvan University: Institute of Engineeringphoenix waibaNo ratings yet
- Bsa2a Paraggua FinalsDocument3 pagesBsa2a Paraggua FinalsCherry G. QuibuyenNo ratings yet
- Registering MapDocument41 pagesRegistering MapYaronBabaNo ratings yet
- Access Import SHPDocument3 pagesAccess Import SHPmlgtsamuelNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Introduction To Gis: LBR & WS 188 01.24.2013Document31 pagesLab 1: Introduction To Gis: LBR & WS 188 01.24.2013Windibel Gutierrez SalgueroNo ratings yet
- Gis Lab1 (Intro)Document12 pagesGis Lab1 (Intro)Muhammad Hizbullah BaharomNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Using Data From Factfinder With ArcmapDocument20 pagesExercise 1: Using Data From Factfinder With ArcmapBlacksacerdoteNo ratings yet
- GIS Lab ManualDocument10 pagesGIS Lab Manualsatishkumarkolluru9809100% (2)
- Introduction To Spatial Analyst & Raster Display: Starting Arcgis and Exploring Help SystemDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Spatial Analyst & Raster Display: Starting Arcgis and Exploring Help SystemJames LeeNo ratings yet
- Creation of A Slope MapDocument7 pagesCreation of A Slope MapSaratNo ratings yet
- Creating Feature Classes and Tables: 2 - Geographic Data ManagementDocument2 pagesCreating Feature Classes and Tables: 2 - Geographic Data ManagementMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Gis I: Arcmap Introduction: Fall 2006 WorkshopDocument16 pagesGis I: Arcmap Introduction: Fall 2006 WorkshopTony BuNo ratings yet
- Free Open-Source Cross - Platform Geographic Information SystemDocument3 pagesFree Open-Source Cross - Platform Geographic Information Systemisfsn dfsfNo ratings yet
- 3 TABLEAU TerminolgyDocument12 pages3 TABLEAU TerminolgyOmkar RajNo ratings yet
- Tableau Terminology - Learn Tableau GlossaryDocument5 pagesTableau Terminology - Learn Tableau GlossaryGiri RajNo ratings yet
- Map Making in Arcgis 9.3: Getting StartedDocument15 pagesMap Making in Arcgis 9.3: Getting Startedvasile madalinaNo ratings yet
- ArcGIS 10 Intro Exercise PDFDocument10 pagesArcGIS 10 Intro Exercise PDFDamai WongNo ratings yet
- Actix UserGuide Part 2Document157 pagesActix UserGuide Part 2Thang LK100% (1)
- ArcGIS - Basics - India - World - Data - Final - GIS Center Version PDFDocument37 pagesArcGIS - Basics - India - World - Data - Final - GIS Center Version PDFBioMetNo ratings yet
- I Use ArcGISonlineDocument15 pagesI Use ArcGISonlineGeoBlogsNo ratings yet
- ArcGIS 10 Intro ExerciseDocument10 pagesArcGIS 10 Intro Exerciseandy kayembeNo ratings yet
- Create Geographic Metadata and Review Arccatalog Metadata ApplicationDocument8 pagesCreate Geographic Metadata and Review Arccatalog Metadata Applicationda azcurNo ratings yet
- Geographic Information SystemDocument6 pagesGeographic Information SystemLuis BergNo ratings yet
- Tufts GIS Tip Sheet Working With Elevation DataDocument4 pagesTufts GIS Tip Sheet Working With Elevation DataFlor TsukinoNo ratings yet
- Raster Tutorial ArcGIS 93Document11 pagesRaster Tutorial ArcGIS 93SYifa ShuhaIliNo ratings yet
- Oracle Discoverer DesktopDocument38 pagesOracle Discoverer DesktopjaveedhunkNo ratings yet
- GISArcMAp and Georeferencing ArcGISDocument29 pagesGISArcMAp and Georeferencing ArcGISSenay Horozal100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Microsoft AccessDocument48 pagesChapter 6 Microsoft Access6s6597wvp2No ratings yet
- Exercise 2: 2. Data Storage: Digitizing and Data StructureDocument13 pagesExercise 2: 2. Data Storage: Digitizing and Data StructurebirukNo ratings yet
- Handbuch EsriDocument2 pagesHandbuch EsriMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Manual On GPS Usage in Forest Managment UnitsDocument70 pagesManual On GPS Usage in Forest Managment UnitsSubesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- It 101 DBMS 2023 2024Document40 pagesIt 101 DBMS 2023 2024cbarbiejoy22No ratings yet
- ArcGIS Network Analyst LabDocument22 pagesArcGIS Network Analyst LabnayabNo ratings yet
- C++ PrimerDocument2 pagesC++ PrimerMathias Eder0% (2)
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1ashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Assign Geographic RolesDocument2 pagesAssign Geographic RolesShambhawi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lab4 2Document19 pagesLab4 2Enoch ArdenNo ratings yet
- Surfer 8 Geology TutorialDocument22 pagesSurfer 8 Geology TutorialEdin DivovićNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Exploring ArcGISDocument13 pagesTutorial 1 - Exploring ArcGISAbdNo ratings yet
- Menu Dan Icon Arcgis 9Document8 pagesMenu Dan Icon Arcgis 9harly_bintangNo ratings yet
- Creating GeodatabaseDocument36 pagesCreating Geodatabasedino_becicNo ratings yet
- GIS Lab Experiment Number 2: AIM SoftwareDocument13 pagesGIS Lab Experiment Number 2: AIM SoftwareGaurav ParmarNo ratings yet
- Autocad For DeveloppersDocument2 pagesAutocad For DeveloppersMathias EderNo ratings yet
- 3D WireframesDocument6 pages3D WireframesaymeneNo ratings yet
- Pivot Table and Pivot ChartsDocument2 pagesPivot Table and Pivot ChartsAlieu BanguraNo ratings yet
- QGIS Beginners Manual: Tethys 1.5.0Document34 pagesQGIS Beginners Manual: Tethys 1.5.0Fathoni Mahardika100% (1)
- Getting Started GIS Lab 01Document15 pagesGetting Started GIS Lab 01Muhammad Aamir QadriNo ratings yet
- Lab 6: Georeferencing and Digitization: 1.0 OverviewDocument30 pagesLab 6: Georeferencing and Digitization: 1.0 OverviewComan AlinaNo ratings yet
- Examples: Opengis Simple Features Implementation Specification For SQL 1.1Document2 pagesExamples: Opengis Simple Features Implementation Specification For SQL 1.1Mathias EderNo ratings yet
- Examples: ST - Centroid ST - Point - Inside - CircleDocument2 pagesExamples: ST - Centroid ST - Point - Inside - CircleMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Using Building Height. The Attribute Values Are Used As Relative Heights in The View. You Can Also Combine PerspectiveDocument2 pagesUsing Building Height. The Attribute Values Are Used As Relative Heights in The View. You Can Also Combine PerspectiveMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Centos ManualDocument2 pagesCentos ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- See Also: ST - Asewkt ST - Extent3D ST - Setsrid ST - SridDocument2 pagesSee Also: ST - Asewkt ST - Extent3D ST - Setsrid ST - SridMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Examples: 7.11 Long Transactions SupportDocument2 pagesExamples: 7.11 Long Transactions SupportMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Examples: Postgis 1.5.1 ManualDocument2 pagesExamples: Postgis 1.5.1 ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Postgis 1.5.1 ManualDocument2 pagesPostgis 1.5.1 ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Perl PrimerDocument2 pagesPerl PrimerMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Cobol Doku PDFDocument2 pagesCobol Doku PDFMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Drawing Graphics On A Map: Using The Draw ToolbarDocument2 pagesDrawing Graphics On A Map: Using The Draw ToolbarMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Using Arcgis Desktop: Udt - Ch03.Indd 244 10/18/2006 12:23:05 PMDocument2 pagesUsing Arcgis Desktop: Udt - Ch03.Indd 244 10/18/2006 12:23:05 PMMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Smaltalk GuideDocument2 pagesSmaltalk GuideMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Postgis 1.5.1 ManualDocument2 pagesPostgis 1.5.1 ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- 8.8 Postgis Function Support Matrix: ST - TranslateDocument2 pages8.8 Postgis Function Support Matrix: ST - TranslateMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Smaltalk PrimerDocument2 pagesSmaltalk PrimerMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Prolog GuideDocument2 pagesProlog GuideMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Auditing Quiz - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesAuditing Quiz - Cash and Cash EquivalentsRonel CaagbayNo ratings yet
- Eder606 Albersworth Reality Check FinalDocument16 pagesEder606 Albersworth Reality Check Finalapi-440856082No ratings yet
- 1-P1 P9-AIAG CQI-9 Pre 3rdDocument12 pages1-P1 P9-AIAG CQI-9 Pre 3rdSaravanan MNo ratings yet
- Asking The Right QuestionsDocument72 pagesAsking The Right QuestionsAnubhav MishraNo ratings yet
- PHILIPS RC133V W62L62 1 xLED36S840 OC PDFDocument3 pagesPHILIPS RC133V W62L62 1 xLED36S840 OC PDFNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Desiccant Dryers: KAD, KED and KBD SeriesDocument10 pagesRegenerative Desiccant Dryers: KAD, KED and KBD SeriesNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical-Research-DLL-Week 4Document3 pagesPractical-Research-DLL-Week 4JIMP ISRAEL CABUHATNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Problem Solving and Reasoning: Learner'S Module: Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Problem Solving and Reasoning: Learner'S Module: Mathematics in The Modern WorldkvelezNo ratings yet
- MUFON UFO Journal - December 1997Document24 pagesMUFON UFO Journal - December 1997Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Metallized Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene FilmDocument10 pagesCharacterization of Metallized Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene FilmLaboratory Plant 7No ratings yet
- Infra-View LitDocument2 pagesInfra-View LitGavinsiauNo ratings yet
- GulfSea Turbine Oil Series PDFDocument2 pagesGulfSea Turbine Oil Series PDFObydur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Dual Plate 800 NB-ModelDocument1 pageDual Plate 800 NB-ModelTanmoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Checklist: I. Q & A II. Ôn tập QuizzesDocument19 pagesChecklist: I. Q & A II. Ôn tập QuizzesLê Hoàng Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- Shotcrete Solutions PDFDocument2 pagesShotcrete Solutions PDFBrett HartNo ratings yet
- XL640 User ManualDocument213 pagesXL640 User ManualSIELAB C.A.No ratings yet
- ELEN1000 Lab Cover Sheet - LAB 1Document10 pagesELEN1000 Lab Cover Sheet - LAB 1Francis GomesNo ratings yet
- Using Engineering and Management Principles For Better Patient Care Nikhil BalakrishnanDocument345 pagesUsing Engineering and Management Principles For Better Patient Care Nikhil BalakrishnanYendy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ge7 ModDocument5 pagesGe7 Modaldo galloNo ratings yet
- Screw Pump: Presented By: Padon, Mric Kimjim JDocument24 pagesScrew Pump: Presented By: Padon, Mric Kimjim JJohn A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- REHAU CatalogDocument25 pagesREHAU CatalogGeorge PetziNo ratings yet
- The Green Brain - Chaotic Processing by Arthur Carmazzi PDFDocument3 pagesThe Green Brain - Chaotic Processing by Arthur Carmazzi PDFnur syahidaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universityfeyayel988No ratings yet
- Excavations OSHA Competent Person Course 2Document17 pagesExcavations OSHA Competent Person Course 2MelchezadekNo ratings yet
- Booklist Shubham Kumar PDFDocument11 pagesBooklist Shubham Kumar PDFVivek VishwakarmaPSH'076No ratings yet
- GS - RS - Lite CENTUM VP Integration PackageDocument4 pagesGS - RS - Lite CENTUM VP Integration PackageVijayNo ratings yet
- Giancoli - Physics SolutionsDocument1 pageGiancoli - Physics Solutionspo4xx0% (1)
- Applied - Economics - Q1 - SHS AppliedDocument55 pagesApplied - Economics - Q1 - SHS Appliedjoshua seanNo ratings yet
- BOECO Hydrometer Alcohol Meter PDFDocument5 pagesBOECO Hydrometer Alcohol Meter PDFTianTrafNo ratings yet
- Hassas Döküm Genel HatlarıDocument56 pagesHassas Döküm Genel HatlarıUgur KayaNo ratings yet