Professional Documents
Culture Documents
f3 c1 Breathing Revision
Uploaded by
chinpy0884640 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views2 pagesHAND OUTS FOR CLASS LESSONS
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHAND OUTS FOR CLASS LESSONS
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views2 pagesf3 c1 Breathing Revision
Uploaded by
chinpy088464HAND OUTS FOR CLASS LESSONS
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The Management and Continuity of 7 Which of the following characteristics
Life : The Human Breathing of the alveolus facilitates the exchange
Mechanism of respiratory gases?
I Its wall is moist.
1. Which of the following is not part of II Its wall is one-cell thick.
the respiratory system in humans? III Its wall is thin and dry.
A The heart
B The lungs A I only
C The alveolus B I and II only
D The intercostal muscles C II and III only
D I, II and III
2. The function of the human rib cage is
to 8. The exchange of gases takes place
I protect vital organs such as the between
lungs. A the alveolus and the capillaries.
II assist in the breathing B the alveolus and the bronchus.
mechanism. C the bronchioles and the capillaries.
III separate the chest cavity from D the bronchioles and the bronchus.
the abdominal cavity.
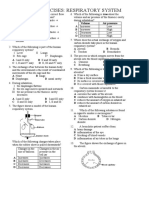
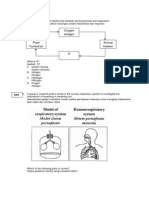
9. The diagram below shows a model of
A I only the respiratory organs involved in the
B I and II only breathing mechanism.
C I and III only What will happen when the structure
D I ,II and III labelled X is pulled downwards as
shown?
3. The function of very small hairs or A The balloon expands.
cilia in the trachea is to B The balloon contracts.
A kill the bacteria in the inhaled air. C The balloon will burst.
B absorb oxygen from the inhaled D The balloon remains the same
air. size.
C move mucus upward and out into
the throat. 10. During exhalation, which of the
D warm and moistened the air as it following statements
passes through the trachea. are correct?
I The ribs moves
4. Which one of the following upward and
statements is true? outward.
A Breathing is a chemical process. II The diaphragm
B The bronchi end in clusters of air relaxes
sacs called the alveoli. III The pressure
C Exhalation is the process inside the lungs
whereby air is taken into the and chest cavity
lungs. increases.
D The wall of the alveolus is very
thin and moist to facilitate gas
exchange. A I and II only
B I and III only
5 The human lung is protected by the C II and III only
A sternum. D I, II and III
11.
B rib cage. Which of the following happens during
C diaphragm. inhalation?
D intercostals muscles.
I The external intercostal muscles
6 The exchange of respiratory gases contracts.
occurs in the II The ribs moves upwards and
A pharynx. outwards.
B trachea. III The pressure inside the lungs and
C alveolus. thoracic cavity decreases.
D bronchioles.
A
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
Carbon monoxide is a waste
product of respiration.
12. The diagram
B Secondary smokers refers to those
below shows a
who smokes occasionally.
model of the
C Carcinogens are substances that
respiratory
originates from carbon
organs involwd in
compounds.
the breathing
D Hydrocabons can interact with
mechanism.
pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide
What will happen when the structure
to form haze.
labeled P is pushed upwards as
shown?
4. Which of the following is incorrectly
paired?
A The balloon will become bigger.
B The balloon will become smaller.
Chemica Harmful effect on
C The balloon will burst
l the respiratory
D The balloon remains the same
substan system
size.
ce
A Carbon Reduces the
monoxid ability of blood to
e transport oxygen
B Tar Corrodes the
respiratory tract
13. The diagram below shows a C Nicotine Causes addiction
model of the respiratory organs to smoking
involved in the breathing D Sulphur Damages lung
mechanism. dioxide tissues
Which of the structure labeled A, B,
C and D represents the bronchus?
Transport of Oxygen in the Human
Body
1. The red pigment found in red blood
cells that helps in oxygen transport is
called
A globulin
B haemoglobin
C oxyhaemoglobin
D immunoglobulin
2. Oxygen passes through the wall of
the alveolus via a process known as
A osmosis
B diffusion
C transpiration
D active transport
3. Which one of the following
statements is true?
You might also like
- Resepiratory Quiz PDFDocument4 pagesResepiratory Quiz PDFapi-448873912No ratings yet
- SK BANDARAN SIBU NO.2 DIGNOSTIC TEST 2021 SCIENCE YEAR 4 (PAPER 1Document14 pagesSK BANDARAN SIBU NO.2 DIGNOSTIC TEST 2021 SCIENCE YEAR 4 (PAPER 1LAU SING WAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Science Examjenefer100% (2)
- PUSAT TUISYEN PENGUKUHAN PINTAR SCIENCE - MONTHLY TEST 1Document10 pagesPUSAT TUISYEN PENGUKUHAN PINTAR SCIENCE - MONTHLY TEST 1Abram Calinton JustinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 11 REVISIONDocument3 pagesRespiratory System 11 REVISIONchinpy088464No ratings yet
- Modul 1Document28 pagesModul 1aszmadie81No ratings yet
- Summative Test in Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesSummative Test in Respiratory SystemJay CervantesNo ratings yet
- Modul 1Document28 pagesModul 1Irrinna Shakinah100% (1)
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocument25 pagesCH 7 Respiration StudentHamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 1: RESPIRATION Structure QuestionsDocument6 pagesForm 5 Chapter 1: RESPIRATION Structure QuestionsChee Jin TangNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Grade 5 Study GuideDocument7 pagesRespiratory System Grade 5 Study Guidelil pony ssiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - 2 - WsDocument5 pagesRespiratory - 2 - WsRatna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Grade 5Document5 pagesRespiratory System Grade 5lil pony ssiNo ratings yet
- Self Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Document3 pagesSelf Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Dr DolittleNo ratings yet
- Evaluate - Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageEvaluate - Gas ExchangeRaquel LizardoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerDocument6 pagesRespiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerRatna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System: Mcqs Quiz - 4Document2 pagesHuman Respiratory System: Mcqs Quiz - 4Iman TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 Gas Excgange - SDocument14 pagesChapter 08 Gas Excgange - SFelix CheungNo ratings yet
- 9B Respiration - Gaseous Exchange in Man PDFDocument18 pages9B Respiration - Gaseous Exchange in Man PDFabdulrehman mughalNo ratings yet
- PH 1 8FLC Ipa GenapDocument5 pagesPH 1 8FLC Ipa GenapNurtri NunuNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument5 pagesRESPIRATIONShatviga VisvalingamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Wednesday, 23 March 2022 5:54 AmDocument3 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Wednesday, 23 March 2022 5:54 AmDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology MCQ'SDocument5 pagesRespiratory Physiology MCQ'SayashanpNo ratings yet
- Major parts and functions of male and female reproductive systemsDocument17 pagesMajor parts and functions of male and female reproductive systemsmarife gupaalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Respiration Sec 3Document11 pagesChapter 2 Respiration Sec 3Qian hui TanNo ratings yet
- Science form answers respiratory system quizDocument5 pagesScience form answers respiratory system quizSadlyNot SadNo ratings yet
- TERM 2 Chapter 7 Topical Revision Bio STPMDocument59 pagesTERM 2 Chapter 7 Topical Revision Bio STPMKeertana SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- F2 - IS - 1213 - 1st Exam 20.0 PDFDocument8 pagesF2 - IS - 1213 - 1st Exam 20.0 PDF羅天佑No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesMaitri RoyNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Test in Grade 9 Science: Caraga Administrative RegionDocument3 pagesFirst Quarter Test in Grade 9 Science: Caraga Administrative RegionCary Clark OriasNo ratings yet
- Soalan Objektif Bab 7 & Bab 8Document19 pagesSoalan Objektif Bab 7 & Bab 8SACHEETHA MoeNo ratings yet
- New Draft For Third Term Second C.ADocument10 pagesNew Draft For Third Term Second C.AEni marylueNo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (40 MarksDocument11 pagesOBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (40 MarkszilaNo ratings yet
- DPP XI Chapter - 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 12Document12 pagesDPP XI Chapter - 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases 12Riya Mondal100% (1)
- Respiratory System QuizDocument6 pagesRespiratory System QuizKryzel Reyca Dawn Alatan100% (1)
- Respiratory System - LECDocument5 pagesRespiratory System - LECDexter DelcarmenNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Collections.Document335 pagesScience Form 3 Collections.Fazil JayNo ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 18 SummaryDocument9 pagesRespiration Chapter 18 SummaryMohamad Harith100% (1)
- Summative Test in Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageSummative Test in Respiratory SystemMelvin Cabonegro100% (7)
- IT Sci F3 Topical Test 1 (E)Document6 pagesIT Sci F3 Topical Test 1 (E)Nad Ramli0% (1)
- Bio4 5Document11 pagesBio4 5ミーチェルNo ratings yet
- 1st MT Test - Science 9Document3 pages1st MT Test - Science 9April AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Biology MCQs on RespirationDocument10 pagesBiology MCQs on RespirationKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Test QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesScience 9 Test QuestionnaireJevy Rose Molino MayonteNo ratings yet
- Legacy of Wisdom Academy Dasmariñas Inc. Golden City, Salawag, Dasmariñas CityDocument3 pagesLegacy of Wisdom Academy Dasmariñas Inc. Golden City, Salawag, Dasmariñas CityJhen Bon100% (1)
- 1Document14 pages1hanafizaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesScienceCHRISTINE GASPACHONo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QP PDFDocument12 pagesGas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QP PDFSyakir Fahmie100% (2)
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document7 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Princess Arjona BaluranNo ratings yet
- Human RespirationDocument9 pagesHuman RespirationMona MohtarNo ratings yet
- Full HND Nursing Revision Questions .Document326 pagesFull HND Nursing Revision Questions .lalixs71No ratings yet
- Ulangan Harian Materi Sistem Pernapasan & EkskresiDocument3 pagesUlangan Harian Materi Sistem Pernapasan & EkskresiRizka MaylindaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Summative Test in Science 9Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Summative Test in Science 9KRISTA MAE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledLyshanya HymanNo ratings yet
- Reathing AND Xchange OF Ases: HapterDocument5 pagesReathing AND Xchange OF Ases: HapterAnannya Deshmukh100% (1)
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 9Document4 pagesFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 9Chai Barcelon86% (7)
- Lung Development Biological and Clinical Perspectives: Biochemistry and PhysiologyFrom EverandLung Development Biological and Clinical Perspectives: Biochemistry and PhysiologyPhilip FarrellNo ratings yet
- Inhaled Particles and Vapours: Proceedings of an International Symposium Organized by the British Occupational Hygiene Society, Cambridge, 28 September — 1 October 1965From EverandInhaled Particles and Vapours: Proceedings of an International Symposium Organized by the British Occupational Hygiene Society, Cambridge, 28 September — 1 October 1965No ratings yet
- Cakeless Sponge CakeDocument1 pageCakeless Sponge Cakechinpy088464No ratings yet
- Labelling The Human HeartDocument6 pagesLabelling The Human Heartchinpy088464No ratings yet
- Labelling The Human HeartDocument6 pagesLabelling The Human Heartchinpy088464No ratings yet
- Tanggung Jawab Pembantu MakmalDocument3 pagesTanggung Jawab Pembantu Makmalchinpy088464No ratings yet
- Tanggung Jawab Pembantu MakmalDocument3 pagesTanggung Jawab Pembantu Makmalchinpy088464No ratings yet
- 2 Respiratory System 10Document2 pages2 Respiratory System 10chinpy088464No ratings yet
- 1 Breathing Mechanism 10Document2 pages1 Breathing Mechanism 10chinpy088464No ratings yet
- Stay AwakeDocument1 pageStay Awakewilko sNo ratings yet
- Rat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyDocument10 pagesRat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyValar Mathei PadmanadhanNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument25 pagesLymphatic Systemumar khanNo ratings yet
- Children's Sleep QuestionnaireDocument9 pagesChildren's Sleep QuestionnaireAravind Babu100% (1)
- Chapter 43 The Immune SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 43 The Immune System蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Guyton Respiration QuestionsDocument23 pagesGuyton Respiration QuestionsAli WalayNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument24 pagesBloodapi-310193189No ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument5 pagesVital SignsFrances Kaye Sta. CruzNo ratings yet
- The Link Between Fatigue and Safety PDFDocument18 pagesThe Link Between Fatigue and Safety PDFAndre MarsNo ratings yet
- Digestive System FunctionsDocument5 pagesDigestive System Functionsقى قىNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System ExamDocument2 pagesLymphatic System ExamJacobNo ratings yet
- After 30 Minutes To 1 Hour of Nursing InterventionDocument2 pagesAfter 30 Minutes To 1 Hour of Nursing InterventionBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in SCIENCE UPDATED 1Document10 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in SCIENCE UPDATED 1Denver Jewel AlcaydeNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument47 pagesHematologySalim Hussain ThebaNo ratings yet
- Sleep NewletterDocument7 pagesSleep Newletterapi-270796252No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 13 Respiratory SystemMaria Nichole JavarNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument9 pagesGas Exchange in HumanscherylrachelNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8 By: Cherry Mae B. CorriaDocument4 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 8 By: Cherry Mae B. CorriaCherry MaeNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) Definition of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA)Document4 pagesObstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) Definition of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA)Abdul JalilNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WebquestDocument6 pagesNervous System Webquestapi-294104473No ratings yet
- Zaslon LoadoutDocument2 pagesZaslon LoadoutElise WolfeNo ratings yet
- The Health Benefits of Deep BreathingDocument7 pagesThe Health Benefits of Deep BreathingMastersam888No ratings yet
- Human Biology Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesHuman Biology Lecture NotesGrace Melissa ChoiNo ratings yet
- Claudio Stampi - Why We NapDocument291 pagesClaudio Stampi - Why We NapMarco ZanellaNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asia's Land of PagodasDocument3 pagesSoutheast Asia's Land of PagodasAyeAyeMoeNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesGas ExchangeDemi Ruth ElenNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System HistologyDocument14 pagesLymphatic System HistologySilhouette SignNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Respiration and MovingDocument8 pagesLesson 1 Respiration and MovingCHENNAIAH GARI SAI BABUNo ratings yet
- AKC Histo Drawings PDFDocument130 pagesAKC Histo Drawings PDFDanDeleanuNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Text BookDocument24 pagesUrinary System Text Bookapi-209542414No ratings yet