Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unconsolidated Undrained Triaxial Test
Uploaded by
harinderCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unconsolidated Undrained Triaxial Test
Uploaded by
harinderCopyright:
Available Formats
CVE20004
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED
TRIAXIAL TEST
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED
TRIAXIAL TEST
ASSIGNMENT NUMBER :4
CREATED BY : HARINDER SINGH REHAL
STUDENT ID NO :
Due date : 16/10/2015
CVE20004
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED
TRIAXIAL TEST
Introduction
In unconsolidated undrained test sample is not to drain . The sample is
compressed at a different rate . the UU test is applicable to undisturbed
sample in which no change in moisture content from out site can be
permitted . test can be carried out over a range of moisture content to
enable Mohr envelopes for the required to be interpolated . UU test
procedure is useful for determining the total strength parameter for soils
that have suffered disturbances or moisture change during sampling .
Aim
To study the shear strength behaviour of a clay type soil using the triaxial
apparatus under undrained conditions using a multi-stage testing
approach.
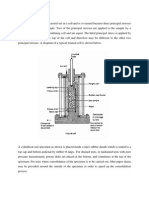
Procedure
Familiarise yourself with the mechanics of the triaxial testing
apparatus.
Record the details of the clay sample (dimensions and wet mass
in order to determine the wet density).
Set up the sample for testing: Place the cylindrical clay sample on
the bottom plate of the triaxial apparatus and cover with the top
loading plate. Then fit the rubber membrane over the sample (and
top loading plate). Use o-rings to seal each end of the sample and
then position the triaxial cell and loading ram over the sample.
Flood the cell with water, maintaining a small amount of air in the
top of the cell to enable pressurisation.
Apply the cell pressure (3): Once the triaxial cell is near full of
water, apply the cell pressure (or confining stress) by simply
releasing pressurised air into triaxial cell 100 kPa for the first stage
of the test.
Apply the deviator stress (1 3): Start the axial loading motor
and record the load ring readings for each 0.75 mm of vertical
displacement, or for every 1% strain of the sample. Continue the
test until the sample fails (the corrected deviator stress reaches a
maximum value).
Increase the cell pressure to 200 kPa to allow the sample to fail
again (i.e. multi-stage testing). Once the sample fails under the
increased cell pressure.
Repeat step 6 for a further increase in cell pressure to 400 kPa.
CVE20004
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED
TRIAXIAL TEST
Remove the sample at the end of the test and observe the failure
mechanism of the soil sample. Sketch the failed sample noting any
shear planes or bulging present. Try to measure / estimate the angle
of the shear plane at failure.
Determine the moisture content, wet density and dry density of the
soil sample.
A description of the sample in accordance with the
terminology used in AS1726
Based on AS1726 sample is Dark brown , moist , firm , med high
with plasticity clay .
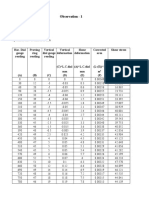
Data Table
Longitudinal Strain vs. Corrected Deviator Stress for Multi-Stage Testing
Cell
Pressure
(kPa)
100
Longitudinal
Deformation
( x 0.01
mm) and
Longitudinal
Strain (%) of
sample
0
75
150
225
300
375
450
525
600
675
750
825
900
975
1050
1125
1200
0
1%
2%
3%
4%
5%
6%
7%
8%
9%
10%
11%
12%
13%
14%
15%
16%
Deviator
Stress
Calibration
and
Correction
Factor
4.40
4.385
4.370
4.356
4.341
.4.326
4.311
4.296
4.281
4.267
4.252
4.237
4.222
4.207
4.193
4.178
4.163
Stage No. 1
Stage No. 2
Stage No. 3
(Cell Pressure = 100 kPa) (Cell Pressure = 200 kPa) (Cell Pressure = 400 kPa)
Load Ring
Readings
(Divisions)
0
10
16
18
17
Corrected
Deviator
Stress
(kPa)
Load Ring
Readings
(Divisions)
Corrected
Deviator
Stress
(kPa)
Load Ring
Readings
(Divisions)
Corrected
Deviator
Stress
(kPa)
38.67
61.66
69.14
65.07
20
23
24
25
26
76.3
87.43
90.92
94.4
97.83
32
34
36
36
37
37
37.5
119.99
127.35
134.03
133.56
136.81
136.32
137.66
CVE20004
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED
TRIAXIAL TEST
1275
1350
1425
1500
1575
1650
1725
1800
17%
18%
19%
20%
21%
22%
23%
24%
38
38
39
39
39
39
4.148
4.133
4.119
4.104
4.089
4.074
4.060
4.004
139
138.49
141.65
141.14
140.62
140.11
Graph shows the relationship between corrected deviator stress
vs longitudinal stress .
Corrected Deviator Stress Vs. Logitudinal Stress
160
140
120
100
Corrected Deviator stress (KPa)
80
60
40
20
0
CVE20004
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED
TRIAXIAL TEST
Result
Sample NO :
Stress 3^1
1
2
3
100
200
300
Discussion / conclusion
Stress 1-Stress
3
69.14
97.83
141.66
Stress 1^1
169.14
297.83
541.66
CVE20004
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED
TRIAXIAL TEST
Value for C = 20 kpa, Value for = 7.5 degree following equation been
produced to check the result of Mohr circles of each stage f = 20 +
Stress (n) tan7.5.
The experiment reaches the aim which was to study the shear strength
behaviour of a clay using unconsolidated undrained triaxle test.
Hand plotting of cell pressure and deviator stress shows the failure point
of all 3 stress and result being calculated as Value for C = 20 kpa. Three
different test been conducted to find failure stress using different normal
stress. After all plotting line of best been drawn tangent to circle to find
out the failure stress and result represents that failure stress occurred
only at 400 Kpa and 200 kpa .
From the graph can be seen that corrected deviator stress vs longitudinal
stress are both linear and nonlinear however as longitudinal stress
increases so does corrected deviator stress increases too .
Mohr circle failure graph been drawn on the 2 different scales Horizontal
scale is 1:50 and vertical scale is : 1:10.
You might also like
- Report Full Direct Shear Test Edit (Repaired)Document15 pagesReport Full Direct Shear Test Edit (Repaired)Asyraf Malik100% (15)
- Shear Box Lab ReportDocument12 pagesShear Box Lab ReportAhmad Al-Rifai100% (4)
- Warehouse Architectural DrawingsDocument6 pagesWarehouse Architectural Drawingsharinder0% (1)
- Manual K5 e K5-ADocument194 pagesManual K5 e K5-AGlauber Tenorio de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument234 pagesPhysicsshugufta nazneenNo ratings yet
- UU Triaxial TestDocument11 pagesUU Triaxial Testprinces_anaNo ratings yet
- 4 Unconfined CompressionDocument12 pages4 Unconfined CompressionShoaib Alam100% (1)
- Triaxial TestDocument14 pagesTriaxial TestSi Rerumpai LautNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Box TestDocument4 pagesDirect Shear Box Testarid132No ratings yet
- Unconsolidated Undrained TestDocument16 pagesUnconsolidated Undrained TestHuzz Ellieyza50% (8)
- Consolidation TestDocument10 pagesConsolidation TestMostafa NouhNo ratings yet
- Consolidation TestDocument8 pagesConsolidation TestCasper da MagnificientNo ratings yet
- Consolidation Test: The University of Hong Kong Department of Civil Engineering Soil Mechanics - CIVL2006Document20 pagesConsolidation Test: The University of Hong Kong Department of Civil Engineering Soil Mechanics - CIVL2006Nicholas Kwong100% (1)
- Standard Proctor Compaction TestDocument3 pagesStandard Proctor Compaction TestSami Sami80% (5)
- Direct Shear TestDocument24 pagesDirect Shear TestObaid Khalid100% (14)
- CBRDocument8 pagesCBRbinod gurungNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Test PDFDocument30 pagesDirect Shear Test PDFM Sohail Ashraf100% (1)
- Direct Shear TestDocument19 pagesDirect Shear Testshahrolhazrien75% (4)
- Shear Box TestDocument7 pagesShear Box Testcedric iradukundaNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Unconfined TestDocument6 pagesExp 4 Unconfined TestumarNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Box TestDocument9 pagesDirect Shear Box TestMuhammad Yusoff Zakaria100% (1)
- Triaxial Test IntroductionDocument4 pagesTriaxial Test IntroductionAshadi Hamdan100% (2)
- UU Triaxial Test - Lab ManualDocument6 pagesUU Triaxial Test - Lab ManualmmNo ratings yet
- Unconsolidated Undrained Triaxial Test On ClayDocument16 pagesUnconsolidated Undrained Triaxial Test On Claygrantyboy8450% (2)
- Faculty of Engineering Bellville Campus Laboratory Report (Oedometer)Document10 pagesFaculty of Engineering Bellville Campus Laboratory Report (Oedometer)Makaveli08k100% (1)
- Direct Shear Test: CEP 701 PG LabDocument32 pagesDirect Shear Test: CEP 701 PG Labneeru143No ratings yet
- Experiment 11 ConsolidationDocument26 pagesExperiment 11 ConsolidationRajeev Kusugal100% (1)
- Unconfined Compression TestDocument11 pagesUnconfined Compression TestAmiruddin JSNo ratings yet
- Shear Box Test ProcedureDocument1 pageShear Box Test ProcedureElson KongNo ratings yet
- Falling Heat Permeability TestDocument10 pagesFalling Heat Permeability TestAiryn UyienNo ratings yet
- Exp 7 Field Density (Sand Replacement Method) PDFDocument21 pagesExp 7 Field Density (Sand Replacement Method) PDFAnonymous DR3NznNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Yunus Salehi I11007770 Experiment 4: Unconfined Compression TestDocument6 pagesMohammad Yunus Salehi I11007770 Experiment 4: Unconfined Compression TestMohammad Yunus Salehi75% (4)
- DCP TestDocument10 pagesDCP TestChathura ChamikaraNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Permeability of Granular SoilDocument19 pagesDetermination of The Permeability of Granular SoilKaluki Judy Rosebell100% (1)
- Consolidation TestDocument16 pagesConsolidation Test1man1bookNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear TestDocument11 pagesDirect Shear TestKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Falling Head Permeability Lab TestDocument6 pagesFalling Head Permeability Lab TestHamierul MohamadNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration TestDocument6 pagesStandard Penetration TestDanica Alejo100% (1)
- O.E.Lab - Docx For Direct Shear TestDocument14 pagesO.E.Lab - Docx For Direct Shear TestAmirah SyakiraNo ratings yet
- CEGB231 EXP 7 Compaction TestDocument11 pagesCEGB231 EXP 7 Compaction TestNur FarehaNo ratings yet
- 1D Consolidation Test Lab ManualDocument15 pages1D Consolidation Test Lab Manualogul100% (2)
- Standard Oedometer TestDocument8 pagesStandard Oedometer TestHiro Cerce Wilhelm ALDEN Abareta TonioNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear TestDocument19 pagesDirect Shear TestAh Gus100% (9)
- Consolidation Test ReportDocument8 pagesConsolidation Test Reportemre usluNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear TestDocument16 pagesDirect Shear TestNishanth Nanthakumar25% (4)
- Standard Proctor TestDocument28 pagesStandard Proctor TestShuja MalikNo ratings yet
- Unbound Aggregates in RoadsFrom EverandUnbound Aggregates in RoadsR.H. JonesNo ratings yet
- Tri Axial TestDocument10 pagesTri Axial TestAskart Nano Crime-artNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1: Direct Shear TestDocument10 pagesExperiment No 1: Direct Shear TestAmir SultanNo ratings yet
- Triaxial TestingDocument5 pagesTriaxial TestingAakash Budhiraja100% (2)
- 5 CVP321 Unconfined Compression Test Memorandum 2023Document10 pages5 CVP321 Unconfined Compression Test Memorandum 2023bvsbsgfb37663No ratings yet
- UCTDocument10 pagesUCTMohd Syafiq AkmalNo ratings yet
- Unconfined CSDocument6 pagesUnconfined CSNaba Kumar BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Cid CiuDocument4 pagesCid CiuRazakMaidenNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Test (UC)Document3 pagesTriaxial Test (UC)Aisha MalikNo ratings yet
- UU Triaxial TestDocument11 pagesUU Triaxial Testredz00100% (1)
- Shear Box TestDocument13 pagesShear Box TestNoor100% (1)
- 1.103 Civil Engineering Materials Laboratory (1-2-3)Document5 pages1.103 Civil Engineering Materials Laboratory (1-2-3)prieten20006936No ratings yet
- Triaxial Test Report - Group 2Document20 pagesTriaxial Test Report - Group 2Khalidah RosmanNo ratings yet
- Standard Test Procedures Manual: 1. ScopeDocument5 pagesStandard Test Procedures Manual: 1. ScopeAeron RodriguezNo ratings yet
- UU TestDocument7 pagesUU TestVenu Gopal Mudhiraj100% (1)
- 5239 Position Description - Traffic and Transport EngineerDocument6 pages5239 Position Description - Traffic and Transport EngineerharinderNo ratings yet
- Career Planning and Mobility Workshop 2 Job Application WorkbookDocument60 pagesCareer Planning and Mobility Workshop 2 Job Application Workbookkalam1989No ratings yet
- Project Engineer PDDocument5 pagesProject Engineer PDharinderNo ratings yet
- Position Description - PD - Coordinator Engineering 2020Document4 pagesPosition Description - PD - Coordinator Engineering 2020harinderNo ratings yet
- Stage 4 Industries - DistributionDocument7 pagesStage 4 Industries - DistributionharinderNo ratings yet
- VicRoads Supplement To AGRD Part 3 Geometric Design PDFDocument36 pagesVicRoads Supplement To AGRD Part 3 Geometric Design PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Edition: June 2016 Specification: Part R49 Installation of SignsDocument15 pagesEdition: June 2016 Specification: Part R49 Installation of SignsharinderNo ratings yet
- Key Selection Criteria Guide: Application StageDocument1 pageKey Selection Criteria Guide: Application StageharinderNo ratings yet
- Project H - West ST North Pde BlackSpot PDFDocument1 pageProject H - West ST North Pde BlackSpot PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Project C - Ashley ST Sherriff ST Intersection PDFDocument1 pageProject C - Ashley ST Sherriff ST Intersection PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Maribyrnong Bicycle Strateg 2020 2030 PDFDocument66 pagesMaribyrnong Bicycle Strateg 2020 2030 PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Traffic Calming Devices Policy PDFDocument4 pagesTraffic Calming Devices Policy PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- TorrensvilleThebarton LATM Feb 2015 PDFDocument122 pagesTorrensvilleThebarton LATM Feb 2015 PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- TorrensvilleThebarton LATM Feb 2015 PDFDocument122 pagesTorrensvilleThebarton LATM Feb 2015 PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Activity DataDocument27 pagesModule 3 Activity DataharinderNo ratings yet
- Frankston City Council: Local Area Traffic Management Study - Fairway Precinct FINAL ReportDocument61 pagesFrankston City Council: Local Area Traffic Management Study - Fairway Precinct FINAL ReportharinderNo ratings yet
- Project C - Ashley ST Sherriff ST Intersection PDFDocument1 pageProject C - Ashley ST Sherriff ST Intersection PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Traffic Calming Devices Policy PDFDocument4 pagesTraffic Calming Devices Policy PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Project H - West ST North Pde BlackSpot PDFDocument1 pageProject H - West ST North Pde BlackSpot PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Frankston City Council: Local Area Traffic Management Study - Fairway Precinct FINAL ReportDocument61 pagesFrankston City Council: Local Area Traffic Management Study - Fairway Precinct FINAL ReportharinderNo ratings yet
- Excel Week 5Document2 pagesExcel Week 5harinderNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument9 pagesCase StudyharinderNo ratings yet
- CVE40002 S1 2018 Assignment 1 Part ADocument1 pageCVE40002 S1 2018 Assignment 1 Part AharinderNo ratings yet
- CVE40004 Assignment 1 Formatting Rules 2017Document36 pagesCVE40004 Assignment 1 Formatting Rules 2017harinderNo ratings yet
- CVE40004 Assignment 1Document2 pagesCVE40004 Assignment 1harinderNo ratings yet
- Healh and Wellbeing ProfileDocument66 pagesHealh and Wellbeing ProfileharinderNo ratings yet
- Reflective WritingDocument5 pagesReflective WritingharinderNo ratings yet
- CVE40004 Assignment 1Document36 pagesCVE40004 Assignment 1harinderNo ratings yet
- Environments 01 00031 PDFDocument11 pagesEnvironments 01 00031 PDFharinderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Lecture 5 Part 2 AmendedDocument40 pagesChapter 7 Lecture 5 Part 2 AmendedChee HoeNo ratings yet
- MITRES2 002S10 Nonlinear Lec1 13 PDFDocument285 pagesMITRES2 002S10 Nonlinear Lec1 13 PDFropmachadoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExperimentsDocument70 pagesLaboratory ExperimentsKarl TristanNo ratings yet
- Geometry Sectional Area Bending: H (MM) B (MM) T (MM) T (MM) H (MM) R (MM) D (MM) A (CM) I (CM) I (CM) I (CM) I (MM)Document25 pagesGeometry Sectional Area Bending: H (MM) B (MM) T (MM) T (MM) H (MM) R (MM) D (MM) A (CM) I (CM) I (CM) I (CM) I (MM)Bagas SuryasatyaNo ratings yet
- KnjigaDocument671 pagesKnjigaIgor VasićNo ratings yet
- Annual Examination - 2020: PhysicsDocument1 pageAnnual Examination - 2020: PhysicsRajNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan-2 ChemistryDocument7 pagesLesson-Plan-2 ChemistryLeslayy CelizNo ratings yet
- KinemaTics KineticsDocument246 pagesKinemaTics KineticsAlejandro Romero MejiaNo ratings yet
- LRB Non-LinearDocument24 pagesLRB Non-LinearGeEs AnggaNo ratings yet
- Steel Moment-Connection-Beam-Column (IS800)Document11 pagesSteel Moment-Connection-Beam-Column (IS800)Selva KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap05 P121Document21 pagesThermo 5th Chap05 P121IENCSNo ratings yet
- Use of Dissipative SilencersDocument9 pagesUse of Dissipative SilencersmukeshkumarjNo ratings yet
- HMT Question PaperDocument1 pageHMT Question PaperSanjay GomastaNo ratings yet
- MEE1002 Engineering Mechanics L8Document22 pagesMEE1002 Engineering Mechanics L8Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1Document6 pagesAssignment #1Deniz GüneşNo ratings yet
- Pace Final Lap 2 PhysicsDocument219 pagesPace Final Lap 2 PhysicsBhavesh KriplaniNo ratings yet
- MMEN 226 - Worked Examples On Torsion, Set 7Document10 pagesMMEN 226 - Worked Examples On Torsion, Set 7nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Turbulence PDFDocument11 pagesTurbulence PDFphutd09No ratings yet
- Thermo SolutionDocument9 pagesThermo SolutionNitty MeYaNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Generator PDFDocument58 pagesSteam Power Generator PDFprajeesh100% (1)
- Do I Need Prism Layers? How Many Should I Use?: Annabella Grozescu 10/20/2017Document2 pagesDo I Need Prism Layers? How Many Should I Use?: Annabella Grozescu 10/20/20179629330773No ratings yet
- VVVDocument108 pagesVVVapi-19827675No ratings yet
- Electrical Charges and Coulomb's Law: Physics II Note-1Document24 pagesElectrical Charges and Coulomb's Law: Physics II Note-1Helping purpose onlyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Tension MembersDocument55 pagesLecture 2 Tension Memberssamiullah034050100% (1)
- ChairDocument7 pagesChairapi-487109487No ratings yet
- Static/dynamic Contact FEA and Experimental Study For Tooth Profile Modification of Helical GearsDocument9 pagesStatic/dynamic Contact FEA and Experimental Study For Tooth Profile Modification of Helical Gearsanmol6237No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Assignments 02Document5 pagesHeat Transfer Assignments 02Konark SharmaNo ratings yet