Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lower Limb
Uploaded by
Yusri Arif100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
551 views6 pagesThe document summarizes the major muscles of the lower limb, including:
1) The quadriceps femoris muscle which extends the knee and is the main extensor. It originates from the femur and inserts into the patella.
2) The gluteus maximus muscle which is the main extensor of the hip joint and a strong lateral rotator/abductor of the thigh. It originates from the pelvis and inserts into the femur.
3) The adductor muscles including the adductor longus, brevis, and magnus which adduct and flex the thigh. They originate from the pubis and insert into the femur or tibia.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the major muscles of the lower limb, including:
1) The quadriceps femoris muscle which extends the knee and is the main extensor. It originates from the femur and inserts into the patella.
2) The gluteus maximus muscle which is the main extensor of the hip joint and a strong lateral rotator/abductor of the thigh. It originates from the pelvis and inserts into the femur.
3) The adductor muscles including the adductor longus, brevis, and magnus which adduct and flex the thigh. They originate from the pubis and insert into the femur or tibia.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
551 views6 pagesLower Limb
Uploaded by
Yusri ArifThe document summarizes the major muscles of the lower limb, including:
1) The quadriceps femoris muscle which extends the knee and is the main extensor. It originates from the femur and inserts into the patella.
2) The gluteus maximus muscle which is the main extensor of the hip joint and a strong lateral rotator/abductor of the thigh. It originates from the pelvis and inserts into the femur.
3) The adductor muscles including the adductor longus, brevis, and magnus which adduct and flex the thigh. They originate from the pubis and insert into the femur or tibia.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
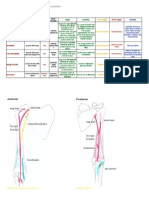
Muscles of Lower Limb
Muscle of the Front of the Thigh
Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Action
1. Sartorius Flexion hip and knee joint
Upper part medial surface of Femoral nerve
ASIS Lateral rotation of thigh
shaft of tibia (L2, L3, L4)
Medial rotation of leg
2. Quadriceps 2 heads 4 heads of muscles join each main extensor of knee joint
Femoris straight head = AIIS other insertions rectus femoris share
a. Rectus femoris reflected head = groove in upper border of patella flexion of hip joint
above acetabulum through patellar ligament articularis genu pull
b. Vastus medialis Linear origin from to tubercle of tibia synovial membrane of
lower part of knee joint upward during
intertrochanteric line extension of knee-prevent
spiral line Femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4) by rolling of synovial
medial lip of linea aspera separate branch for each membrane between bones
medial part of muscle of knee joint
supracondylar ridge
c. Vastus lateralis Upper part of trochanteric
line
root of greater trochanter
lateral of linea aspera
d. Vastus Anterior and lateral surface of
intermedialis upper 3/4 of shaft of femur
3. Psoas Major Lumbar transverse Flexion and medial rotation
processes of thigh
Intervertebral discs in Assist in flexion of trunk
th Posterior part of lesser Roots of femoral nerve (L2, L3,
between 12 thoracic and together with iliacus
st trochanter L4 sometime L1)
1 lumbar spines muscle (=ilopsoas)
Tendinous arch above
lumbar artery
4. Illiacus Tendon of psoas major in assist in psoas major
lesser trochanter muscle (=iliopsoas) to flex
adjoined part of femur the trunk
Femoral nerve in abdomen (L2, flexion and medial rotation
Floor of iliac fossa
L3, L4) of thigh
If neck of the femur
fractured, it will do lateral
rotation of thigh
Fatnulhani – Kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine
5. Pectineus Pectineal surface and Upper half of pectineal line of Originally femoral nerve
Pectineal line of superior femur extending from lesser Additional supply from Adduct and flex the thigh
pubic ramus trochanter down to linea accessory obturator nerve
aspera
6. Gracilis Lower 1/2 of ant surface of Upper part of medial side of Adduction of thigh
body of pubis tibia between sartorious and Flexion of knee
Side of pubic arch semitendinosus insertions Medial rotation of leg
7. Adductor Longus Front of body of pubis just below Anterior division of obturator
Middle part of linea aspera
pubic tubercle nerve
8. Adductor Brevis Lower part of pectineal line of
Adduct and flexion of thigh
Front of body of pubis between femur extending from lesser
obturatur externus and gracilis trochanter down to linea
aspera
9. Adductor Magnus Pubic part
gluteal tuberosity
Anterior surface of pubic arch linea aspera Posterior division of obturator
Adduction and flexion of thigh
medial supraconylar ridge nerve
Ischial part
Lateral area of lower part of
Adductor tubercle Sciatic nerve Extend hip joint
ischial tuberosity
Muscle of Gluteal Region
Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Action
1. Gluteus Maximus Gluteal surface of ilium Deep ¼: floor of gluteal Main extensor of hip joint
behind post gluteal line tuberosity of femur – when force is needed:
Back of lateral mass of Superficial ¾: posterior o Rising from sitting
sacrum border of iliotibial tract o Climbing
Back of sacro-tuberous Inferior gluteal nerve
o Running
ligament Strong lateral rotator and
(L5, S1, S2)
abductor of thigh
Tenses iliotibial tract thus
helps to extend the knee
and maintain knee joint in
full extension
2. Gluteus Medius Posteriorsuperior angle of Abduction of thigh
greater trochanter Medial rotation of thigh
Gluteal surface of ilium between
Oblique ridge of lateral Stabilize pelvis
posterior and middle gluteal line
surface of greater Superior gluteal nerve
trochanter
3. Gluteus Minimus Gluteal surface of ilium between Anterior surface of greater
middle and inferior gluteal line trochanter
4. Piriformis Anterior surface of middle 3 Upper border (top) of greater Lateral rotation of thigh
Root of sacral plexus, S1 & S2
pieces of sacrum trochanter Help in abduction of thigh
Fatnulhani – Kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine
5. Obturator Internus Inner surface of obturator
membrane
Inner surface of greater Nerve to obturator internus (from
Front & side walls of pelvic
trochanter superior to its fossa sacral plexus)
cavity around the margins
of obturator foramen
6. Obturator Externus Outer surface of obturator
Tendon passes below capsule
membrane Posterior division of obturator
of hip joint to be inserted into
Outer margin of obturator nerve Lateral rotation to thigh
trochanteric fossa
foramen
7. Quadratus Femoris Lateral border upper lateral part
Quadrate tubercle of femur Nerve to quadratus femoris
of ischial tuberosity
8. Superior Gemellus Upper boundary of lesser sciatic Nerve to obturator internus, L5,
notch Lower border of obturator S1, S2 (ant)
9. Inferior Gemillus Lower boundary of lesser sciatic internus tendon Nerve to quadratus femoris, L4,
notch L5, S1 (ant)
Muscles of Back of Thigh
Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Action
1. Biceps Femoris Long head (med) = Sciatic nerve by separate Long head – weak
common origin with branch for every head extensor of hip join
semitendinosus from lower Long head – tibial part of Short head – flexion and
medial area of upper sciatic nerve lateral rotation of knee
quadangular of ischial Short head – common joint
Head of fibula
tuberosity peroneal part of sciatic
Short head (lat) lateral lip of nerve
linea aspera and upper part
of lateral supracondylar
ridge
2. Semitedinosus Common origin with long head Flexion and medial
of biceps femoris from lower rotation of knee joint
Upper part of medial surface of
medial area of upper
tibia Extention of hip joint
quadrangular of ischial
tuberosity
3. Semimembranosus groove at the back of Tibial part of sciatic nerve
medial condyle of tibia (Medial popliteal nerve)
Upper lateral area of upper post oblique ligament of
quadrangular of ischial knee joint
tuberosity fascia covers popliteus
muscle and insertion
reaches soleal line
Fatnulhani – Kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine
Muscles of Anterior Compartment of Leg
Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Action
1. Tibialis anterior Upper 2/3 of lateral surface Medial surface of medial Dorsiflexion of ankle
of shaft of tibia cuneiform Inversion of foot
Interosseous membrane Base of 1st metatarsal Helps to maintain medial
Intermuscular septum bone longitudinal arch of the
foot
2. Extensor Hallucis Middle 1/2 of medial Extension of all joints of
Base of terminal phalanx of big
Longus surface of fibula big toe
toe
Interosseous membrane Dorsiflexion of ankle joint
3. Extensor Digitorum Upper 3/4 of medial 4 tendons in lateral 4 toes Extension of joints of
Longus surface of fibula each tendons ends in extensor lateral 4 toes
Interosseous membrane expansion at dorsum of Anterior tibial nerve Dorsiflexion of ankle joint
proximal phalanx
4. Extensor digitorum Extends proximal phalanx
brevis of big toe
Anterior part of upper surface of Base of the proximal phalanx
Extend middle and
calceneus of the big toe
terminal phalanges of 2-4
toes (dorsiflexion of foot)
5. Peroneus Tertius Lower 1/4 medial surface Dorsiflexion of ankle joint
of fibula Dorsal aspect of base of 5th Eversion of foot
Interosseous membrane metatarsal bone
Intermuscular septum
Muscles of Lateral Compartment of Leg
Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Action
st
1. Peroneus Longus Head and upper 2/3 of Lateral side of base of 1 Plantar flexion of ankle
lateral surface of fibula metatarsal bone joint
Anterior and posterior Lateral side of medial Eversion of foot
intermuscular septa of leg cuneiform bone Maintain lateral
Deep fascia of leg longitudinal and
Musculocutaneous (Superficial
transverse arches of foot
peroneal) nerve
2. Peroneus Brevis Lower 2/3 of lateral surface Plantar flexion of ankle
of shaft of fibula Tuberosity of 5th metatarsal joint
Anterior and posterior bone Eversion of foot
intermuscular septa of leg
Deep fascia of leg
Fatnulhani – Kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine
Muscles of Posterior Compartment of Leg
Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Action
1. Gastrocnemius Medial head: popliteal Powerful plantar flexor of
surface of femur just above Tendon + tendon of soleus = ankle
medial condyle tendocalcaneus which insert Tibial (medial popliteal) nerve by Helps flexion knee joint
Lateral head: lateral into middle 1/3 of posterior separate branch for each head Antigravity muscle acting
surface of lateral condyle surface of calcaneus with soleus
of femur
2. Plantaris Lower part of Long slender tendon pass
supracondylar ridge between gastrocnemius and
Oblique popliteal ligament soleus fused with
Tibial (medial popliteal) nerve Accesory to gastrocnemeus
tendocalcaneus to be inserted
on posterior surface of
calcaneus
3. Soleus Fibular origin: Tibial (medial popliteal) Major flexor of the foot
Upper 1/3 of posterior nerve Strong antigravity muscle
surface of its shaft Posterior tibial nerve (in
Back of head of fibula the middle of the leg
Tibial origin: Back of calcaneus through
Soleal line tendocalcaneus
Middle 1/3 of medial
border of tibia
Fibrous arch between tibia and
fibula
4. Popliteus By a strong rounded tendon Tibial nerve Flexion and medial
from anterior part of groove on Posterior tibial nerve rotation of leg
lateral surface of lateral femoral Medial 2/3 of the triangular Unlock knee joint at
condyle (femoral sulcus) lying area above the soleal line beginning of flexion
below lateral epiconcyle
(intracapsular extrasynovial)
5. Flexor Hallucis Lower 2/3 of posterior Plantar flexion of foot
Tendon descends and passes
Longus surface of fibula (below the Flexion of all small joint of
in a groove on posterior
origin of soleus muscle) big toe
surface of talus deep to flexor
Lower part of posterior Support medial
retinaculum.
surface of interosseous longitudinal arch of foot
Passes 2nd layer of foot to be
membrane
inserted in base of terminal
Posterior intermuscular phalanx of big toe Posterior tibial nerve
septum
6. Flexor Digitorum Tendon passes Flex all joints of lateral 4
Longus Upper 2/3 of medial part of superficial to tendon of toes
posterior aspect of tibia, medial tibialis posterior and cross Plantar flexion of foot
to vertical line below lateral to it.
popliteus/soleal line Passes deep to flexor
retinaculum.
Fatnulhani – Kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine
Divides into 4 smaller
tendon.
To be inserted in bases of
terminal phalanges of
lateral 4 toes
7. Tibialis Porterior Posterior surface of Tendon passes in groove at Plantar flexion
interosseus membrane back of medial malleolus, Inversion of foot
Upper 2/3 of posterior passes deep to flexor Maintain medial
surface of tibia (lateral to retinaculum to be inserted in: longitudinal arch of foot
the vertical line) Tuberosity of navicular
Upper 2/3 of posterior bone
surface of fibula All tarsal except talus
Bases of 2 , 3 and 4
nd rd th
Intermuscular septa of the
back of the leg metatarsal bones
Fatnulhani – Kasr Al-Ainy School of Medicine
You might also like
- Muscles of The Upper Limb Made EasyDocument7 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb Made Easynss92% (26)
- Lower Limb Mnemonics (Highlighted)Document8 pagesLower Limb Mnemonics (Highlighted)Saajid Amra100% (5)
- Muscles of Lower LimbsDocument7 pagesMuscles of Lower LimbsFong Yu-hengNo ratings yet
- MOINA Flashcards (Upper Limb)Document63 pagesMOINA Flashcards (Upper Limb)jnthnrsj50% (2)
- Built by Science PDFDocument73 pagesBuilt by Science PDFHeidi Y. Matos GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb: Muscle Table + PicturesDocument3 pagesLower Limb: Muscle Table + Picturesrichard_yin_397% (31)
- MCQ Upper & Lower Limb 2Document92 pagesMCQ Upper & Lower Limb 2Fakhar Uz Zaman87% (31)
- Nerve of The Lower Limb Edited LagiDocument159 pagesNerve of The Lower Limb Edited Lagifathizu100% (1)
- Anatomy - Head and Neck Table of NervesDocument11 pagesAnatomy - Head and Neck Table of NervesIke Ononiwu100% (3)
- Upper Limbs Blood Supply and NervesDocument6 pagesUpper Limbs Blood Supply and Nervesmarksterxxx78% (9)
- Lower LimbDocument27 pagesLower LimbAira Maranan100% (1)
- List of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1Document6 pagesList of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1chitrojan142269% (13)
- Upper Limb MCQsDocument12 pagesUpper Limb MCQsTennyson Machiwenyika91% (11)
- Muscle Innervation Chart IIDocument7 pagesMuscle Innervation Chart IIkimsue9448No ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ - Upper LimbDocument37 pagesAnatomy MCQ - Upper LimbHome Arfaj100% (2)
- Lower Limb Anatomy TablesDocument8 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Tableskep1313No ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper Limb Q Bank MCQDocument19 pagesAnatomy - Upper Limb Q Bank MCQsssaji88% (17)
- 30 SEQs of Lower Limb Anatomy by DR RoomiDocument2 pages30 SEQs of Lower Limb Anatomy by DR RoomiMudassar Roomi50% (2)
- Anatomy Final ReviewDocument35 pagesAnatomy Final ReviewMarie100% (1)
- Viva Questions Final Stage Upper LimbDocument7 pagesViva Questions Final Stage Upper LimbMaria Cheema100% (1)
- Clinical Notes of Lower LimbDocument5 pagesClinical Notes of Lower Limbbeia21100% (1)
- Anatomy Mcqs With AnswersDocument8 pagesAnatomy Mcqs With AnswersJk Flores67% (6)
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument44 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsKaushal Reddy100% (11)
- Clinical Assessment of The Musculoskeletal System: A Guide For Medical Students and Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument40 pagesClinical Assessment of The Musculoskeletal System: A Guide For Medical Students and Healthcare ProfessionalsButchay LumbabNo ratings yet
- Summary of Nerves of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesSummary of Nerves of Lower LimbYusri Arif100% (6)
- Summary of Nerves of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesSummary of Nerves of Lower LimbYusri Arif100% (6)
- Summary of Nerves of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesSummary of Nerves of Lower LimbYusri Arif100% (6)
- Muscle of Upper LimbsDocument5 pagesMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- 07 Upper Limb FinalDocument50 pages07 Upper Limb FinalRavishan De Alwis100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Joints and MusclesDocument92 pagesClinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Joints and Musclesgechanatomy100% (1)
- Upper Limb McqsDocument48 pagesUpper Limb McqsFarhad Ali100% (2)
- Table of Lower Limb Muscles RWDocument9 pagesTable of Lower Limb Muscles RWVirronChahalNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb ReviewDocument24 pagesLower Limb ReviewRyan SilberNo ratings yet
- Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and NeckFrom EverandEssential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and NeckNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb MusclesDocument6 pagesUpper Limb MusclesMarina CasavecchiaNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneDocument2 pagesMnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneLaura Tapia89% (28)
- Lower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletAsif HanifNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb-MCQ With AnswersDocument20 pagesUpper Limb-MCQ With AnswersMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Mnemonics PDFDocument31 pagesAnatomy Mnemonics PDFNonoy JoyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Mnemonics PDFDocument31 pagesAnatomy Mnemonics PDFNonoy JoyaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb MusclesDocument8 pagesLower Limb Musclesbilal_kmu020% (1)
- Table of Upper Limb MusclesDocument7 pagesTable of Upper Limb MusclesLjubica Nikolic100% (7)
- Firearm InjuriesDocument17 pagesFirearm InjuriesYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Upper LimbDocument44 pagesTeach Yourself Upper LimbSambili Tonny100% (2)
- Lower Limp MnemonicsDocument6 pagesLower Limp MnemonicsScott Yee67% (6)
- 5 The Knee PDFDocument515 pages5 The Knee PDFjongski100% (2)
- Wrist and Ankle Acupuncture Book, by Josep CarrionDocument199 pagesWrist and Ankle Acupuncture Book, by Josep Carrionjosep100% (2)
- External Fixation Principles and Applications.5Document8 pagesExternal Fixation Principles and Applications.5Leonardo Rocha100% (1)
- 11 Tibia & Fibula (A)Document29 pages11 Tibia & Fibula (A)idaramaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Anatomy Class NotesDocument87 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Class NotesSalina Amir88% (16)
- Snell Lower LimbDocument44 pagesSnell Lower LimbBen100% (3)
- Bone Limb UpperDocument59 pagesBone Limb UpperGuneyden Guneyden100% (3)
- Lower Limb McqsDocument55 pagesLower Limb McqsKeshav NagpalNo ratings yet
- Ankle AnatomyDocument50 pagesAnkle AnatomyLiao WangNo ratings yet
- Eponymous Fractures 2Document48 pagesEponymous Fractures 2Sllavko K. KallfaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Test QuestionsDocument19 pagesLower Limb Test QuestionsKazim Hussain50% (2)
- Physio - MCQDocument21 pagesPhysio - MCQAmitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsFrom EverandAnatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Lower Limb RegionalDocument75 pagesLower Limb Regionalsponnaboina100% (1)
- Back Anatomy TableDocument7 pagesBack Anatomy TableJeffrey XieNo ratings yet
- Tips For Studying MusclesDocument2 pagesTips For Studying Musclesapi-19510625100% (11)
- Closed Fracture Tibia FibulaDocument41 pagesClosed Fracture Tibia FibulaThathmainnul Qulub100% (1)
- Neurology: Self-Assessment for MRCP(UK) Neurology SCEFrom EverandNeurology: Self-Assessment for MRCP(UK) Neurology SCERating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Study Guide For Students of Tong's AcupunctureDocument63 pagesStudy Guide For Students of Tong's AcupuncturemattNo ratings yet
- Palpation of Bony LandmarksDocument4 pagesPalpation of Bony LandmarksNur Ashriawati BurhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Human Movement: Structure and FunctionFrom EverandAnatomy and Human Movement: Structure and FunctionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- MCQ April 2015 PDFDocument9 pagesMCQ April 2015 PDFZ TariqNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Foot Mcqs ExplainedDocument5 pagesAnkle and Foot Mcqs ExplainedRobert Edwards100% (2)
- Multiple Choice Questions in Anatomy and Neurobiology for UndergraduatesFrom EverandMultiple Choice Questions in Anatomy and Neurobiology for UndergraduatesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Upper Limb MCQDocument7 pagesUpper Limb MCQTendai Chirisa100% (1)
- Lower Limb Anatomy (Mneumonics)Document3 pagesLower Limb Anatomy (Mneumonics)Faisal RehmanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ 2Document63 pagesAnatomy MCQ 2Pirabakar MahendranNo ratings yet
- Clinical Findings in Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageClinical Findings in Respiratory SystemYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- Nerve Supply of FaceDocument1 pageNerve Supply of FaceYusri Arif100% (2)
- Short Stature: - CausesDocument18 pagesShort Stature: - CausesYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- CVS History Taking in PediatricsDocument11 pagesCVS History Taking in PediatricsYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- MacCallan's Classification of TrachomaDocument1 pageMacCallan's Classification of TrachomaYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Drainage of The ThoraxDocument1 pageLymphatic Drainage of The ThoraxYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- Neural Crest DerivativesDocument1 pageNeural Crest DerivativesYusri Arif0% (1)
- Greater Sciatic ForamenDocument2 pagesGreater Sciatic ForamenYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Left & Right LungsDocument1 pageDifferences Between Left & Right LungsYusri Arif100% (1)
- Anastomosis Around The ScapulaDocument1 pageAnastomosis Around The ScapulaYusri Arif67% (3)
- BTEC Sport Level 3 Revision Guide Muscular SystemDocument19 pagesBTEC Sport Level 3 Revision Guide Muscular SystemkanukuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Martini Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Martini Solutions Manual 1toddvaldezamzxfwnrtq97% (29)
- Lab Manual - Appendicular - Skeleton - AtlasDocument58 pagesLab Manual - Appendicular - Skeleton - AtlasShao KahnNo ratings yet
- Legion KneeDocument48 pagesLegion Kneekrueg3rNo ratings yet
- Powers N Ed Human Osteology Method StateDocument64 pagesPowers N Ed Human Osteology Method StateVLAKORADOSNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Bone PalpationDocument9 pagesMuscle and Bone PalpationIzzati WanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Spot Test 1Document18 pagesAnatomy Spot Test 1Uday BarooahNo ratings yet
- PIP Training Program - IIDocument10 pagesPIP Training Program - IISundar PrabhuNo ratings yet
- BKA ProsthesisDocument3 pagesBKA ProsthesisAditi Lakhwara KohliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Section A - OrTHOPEDIC - HomeworkDocument15 pagesLesson 8 - Section A - OrTHOPEDIC - Homework11-MH-HU-ALEXANDER NIELSEN CLEMENTE ESCOBARNo ratings yet
- The 16 Xi-Cleft Points: Lu6 (Kongzui) : 7 Cun Above Lu9Document7 pagesThe 16 Xi-Cleft Points: Lu6 (Kongzui) : 7 Cun Above Lu9See Hing KokNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesLesson Plan 1api-379149339No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument29 pagesAnatomyazeemNo ratings yet
- Article With BhajanDocument4 pagesArticle With BhajanBibek SutradharNo ratings yet
- PFC RP Surgical Technique (DePuy)Document43 pagesPFC RP Surgical Technique (DePuy)Sagaram Shashidar100% (1)
- Opinion WritingDocument20 pagesOpinion WritingnirmalaNo ratings yet
- Ankle JointDocument6 pagesAnkle JointIfeanyichukwu OgbonnayaNo ratings yet