Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Fall 2014 Ans
Uploaded by
joeyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Fall 2014 Ans
Uploaded by
joeyCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Examination December 2013
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 1 of 11
Part A. Answer all twelve questions with a few sentences or equations
(5 marks each).
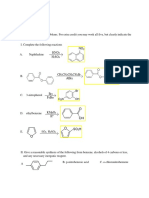
1.
Compare the average molecular kinetic energy of 1 mol of NH3(g) in 1.00 L
at 500oC with that of 3.35 mol of O2(g) in 25.0 L at 500oC, and explain.
The average kinetic energies are the same because the two samples are at the same temperature.
2.
Define the term state function and give three examples of a state function.
A state function is a function whose value does not depend on the path taken from reactants to
products, nor on the reaction rate. Examples are enthalpy (H), internal energy (E), the distance
between two cities, etc.
3.
State the Pauli exclusion principle.
The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom have identical quantum
numbers.
4.
Would you expect Zn2+ ions to be diamagnetic or paramagnetic? Answer with reference to the
ions electronic configuration.
Zns electronic configuration is 4s23d10. That of Zn2+ is therefore 3d10. Thus all 10 electrons
are paired in the filled 3d and other subshells, so the ion is diamagnetic.
5.
Oxygen has a greater electronegativity than carbon. Why is carbon dioxide not polar?
The Lewis structure is O=C=O, i.e. no lone pairs on the central carbon atom. The molecule is
therefore linear. Although each O=C bond is polar, these two dipoles point in opposite directions
and cancel each other out, resulting in zero net dipole.
6.
Name three physical properties of molecules predicted by molecular orbital theory, and not
predicted by hybrid orbital theory.
Magnetic properties, bond length, bond energy
7.
What is the strongest intermolecular force between two molecules of nitrobenzene, shown
below?
The CC and CH bonds are essentially nonpolar. However, the CN and NO bonds are quite
polar, resulting in a polar molecule. The dominant force between two of these molecules is thus a
dipoledipole force. (Note that it is not an Hbond because the H is not bound directly to the N.)
Final Examination December 2013
8.
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 2 of 11
Diamond and graphite are both chemically just solid carbon. Why is diamond so much harder
than graphite? Answer with respect to hybrid orbital theory.
The carbon atoms in diamond are each bound to three other carbon atoms via sp3 hybrid orbitals.
This results in a very strong threedimensional lattice of carbon atoms. In graphite, the bonding
is via sp2 hybrids, with a porbital left over. Bonding between neighbouring porbitals in
adjacent planes of graphite is weak.
9.
Which of the vitamins folic acid or alphaTocopherol would you expect to be more soluble in
water? Why?
Folic acid must have a higher solubility. The folic acid molecule contains more polar groups,
especially OH and NH groups, which will hydrogen bond with water, increasing the solubility.
10.
When you take a carbonated drink from the refrigerator, place it on the kitchen counter and open
it, carbon dioxide evolves from the solution. Name two reasons why this happens.
First, opening the drink exposes the liquid to a lower pressure (atmospheric pressure instead of
the 23 bar pressure in an unopened drink). Henrys law predicts that lower pressure means
lower solubility of the gas. Second, as the solution warms, gases, including carbon dioxide,
become less soluble.
11.
Circle the Newman projection that correctly represents
12.
Name this compound:
3chlorocyclopentene
Final Examination December 2013
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 3 of 11
Part B. Answer all three questions B1, B2 and B3 (20 marks each).
B1.
[20] Silver (Ag) crystallizes in a cubic unit cell. The edge length of the unit cell is 408 pm. The density
of silver metal is 10.6 g cm-3. What type of cubic unit cell does silver form?
Volume of the unit cell = V = (408 x 10-10 cm)3 = 6.79 x 10-23 cm3
Mass of unit cell = m = rV = 10.6 g cm-3 x 6.67 x 10-23 cm3 = 7.20 x 10-22 g
Mass of one Ag atom =
107.9 g mol1
= 1.79 1022 g
6.02 1023 mol1
Number of atoms per unit cell =
7.20 1022 g / unit cell
= 4 atoms / unit cell
1.79 1022 g / atom
Only FCC (face centered cubic) has four atoms per unit cell.
(There are other ways to solve this probelm)
Final Examination December 2013
B2.
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 4 of 11
(a) [6] A 0.15 g sample of a protein is dissolved in water to make 2.0 mL of solution. The osmotic
pressure of this solution is found to be 18.6 Torr at 25C. Calculate the molecular weight of the protein.
= MRT
= 18.6 Torr = (18.6/760) = 0.0245 atm
Thus,
M = /(RT)
= 0.0245 atm / (0.082 L atm K-1 mol-1 x 298 K)
= 0.00100 mol L-1
In this 2.0 mL solution there would be 0.00100 mol L-1 x 0.002 L = 2.00 x 10-6 mol of protein
The molecular weight is therefore 0.15 g / (2.00 x 10-6 mol) = 7.45 x 104 g mol-1
(b) A solution is made by adding 250 g Na2SO4(s) to 1.00 L H2O(l) at 25.0oC.
(i) [6] Calculate the vapor pressure of this solution at 30C (in Pa). The vapor pressure of pure water at
30C is 4242 Pa.
n Na 2SO4
250 g
=
1.76 mol Na 2SO 4
(2(23.0) + 32.1 + 4(16.0)) g mol1
+
2
+ SO 4(aq)
n solute = 3(1.76) = 5.28 mol (because Na 2SO 4 2Na (aq)
)
1.00 L H2O = 997 g H2O
=
n H2O
=
X H2O
997 g
=
55.3 mol
18.0 g mol1
n H2O
55.3
=
= 0.913
n solute + n H2O 5.28 + 55.3
p H2O = p oH2O X H2O
= (4242 Pa(0.913)
= 3872 Pa
Final Examination December 2013
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
(ii) [4] Calculate the freezing point (oC) of the solution. Kf for water is 1.86 oC kg mol1.
iK f msolute
Tf =
1.76 mol
= 3(1.86 o C kg mol1 )
0.997 kg
= 9.85 o C
Tf =
0.00o C 9.86o C =
9.86o C
(iii) [4] Calculate the boiling point (oC) of the solution. Kb for water is 0.51 oC kg mol1.
Tb =
iK b msolute
1.76 mol
= 3(0.51 o C kg mol1 )
0.997 kg
= 2.70 o C
Tb= 100.00o C + 2.70o C= 102.70o C
Page 5 of 11
Final Examination December 2013
B3.
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 6 of 11
(a) [10] Name the following compounds
3chlorophenol
or 1chloro3hydroxybenzene
or 3hydroxychlorobenzene
3,4dibromo2pentene
or 3,4dibromopent2ene
4methylhexanoic acid
4methylN,Ndimethylhexanamide
3bromopropylacetate
or 3bromopropylethanoate
(b) [4] Circle any chirality centres in the molecule shown below, and label each as R or S.
(c) [6] Assign E or Z stereochemical descriptors to each of the following three compounds
Final Examination December 2013
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 7 of 11
Part C. Answer any three of the five questions C1 C5. If you answer more than three, the best
three will be used to calculate your mark (20 marks each).
C1.
(a) [4] Calculate the density of CH3F(g) (in g L1) at 2.00 bar and 50oC.
=
r
pM
2.00 bar(34.03 g mol1 )
=
= 2.53 g L1
RT 0.08314 L bar K 1mol1 (50 + 273.15) K
(b) [6] It takes 85.0 s for 1.00 mol of CH3F(g) to diffuse through a porous barrier. Under identical
conditions, how long (in s) would it take for 1.00 mol of H2(g) to diffuse through the same barrier?
rate H2
rateCH3F
M CH3F
M H2
rate H2 = rateCH3F
=
M CH3F
M H2
1 mol 34.03 g mol1
= 0.0483 mol s 1
85 s 2.02 g mol1
Time required =
1
= 20.7 s mol1
1
0.0483 mol s
(c) [4] Beginning with N2(g) and O2(g), show the reactions responsible for producing ozone in a smoggy
city.
N2 + O2 2 NO(g)
NO(g) + O2(g) NO2(g)
NO2(g) + h NO(g) + O(g)
O(g) + O2(g) O3(g)
(d) [6] Calculate the pressure exerted by 25.0 g CH3F(g) in 2.50 L at 100oC. For this gas, a = 5.009 bar L2
mol2 and b = 0.05617 L mol1.
25.0 g
= 0.735 mol
34.03 g mol1
nRT
n
p
=
a
V nb
V
0.735 mol
0.735 mol(0.08314 L bar K 1mol1 )(100 + 273.15)K
5.009 bar L2 mol2
1
2.50 0.735 mol(0.05617 L mol )
2.50 L
= 9.27 bar 0.43 bar
= 8.84 bar
Final Examination December 2013
C2.
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 8 of 11
(a) [8] Use data in the table to calculate the amount of heat released (in MJ) when 100 mol of C2H2(g) is
burned in excess oxygen according to the reaction C2H2(g) + 2.5 O2(g) 2 CO2(g) + H2O(g).
C2H2(g)
CO2(g)
H2O(g)
227.4
393.5
241.83
H of , kJ/mol
H o = 2H fo (CO 2(g) ) + H fo (H 2 O(g) ) H fo (C2 H 2(g) ) 2.5H of (O 2(g) )
=
2(393.5) + (241.8) 227.4 2.5(0)
= 1256.2 kJ mol1
100 mol =
125620 kJ =
1.26 MJ
(b) [6] Calculate the work done (in J) when a balloon is inflated to a volume of 2.50 L if the atmospheric
pressure is 0.98 bar.
w = pV
= 0.98 bar(2.50 L)
= 2.45 L bar
1 m3 105 Pa
3
= 245 Pa m
=
245 J
1000 L 1 bar
(c) [6] A 2.70 g sample of caffeine (C8H10N4O2) is burned in a constant volume calorimeter that has a
heat capacity of 7.85 kJ oC1. The temperature increases from 19.27oC to 28.05oC. Calculate the energy
of combustion of caffeine (in kJ mol1).
q= CT
= 7.85 kJ o C1 (28.05 19.27)o C
= 68.9 kJ
E =
q
68.9 kJ
=
= 4960 kJ mol1
n
2.70 g
1
194.2 g mol
Final Examination December 2013
C3.
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 9 of 11
(a) [5] Calculate the frequency (in s1) of the light emitted by hydrogen atoms when electrons fall from
level m = 5 to level n = 2.
1
1
1
= R 2 2
m
n
1 1
= 0.01097 nm 1 2 2
2 5
= 0.002304 nm 1
=
1
=
434.0=
nm 434.0 109 m
1
0.002304 nm
c 3.00 108 m s 1
= =
= 6.911014 s 1
9
434.0 10 m
(b) [5] Do a calculation to show whether or not 500 nm light can dissociate O2 molecules, which have a
bond dissociation energy of 498 kJ mol1.
hc 6.63 1034 J s(3.00 108 m s 1 )
=
= 3.98 1019 J
l
500 109 m
6.02 =
=
1023 mol1 239, 000
J mol1 239 kJ mol1
=
E
These photons are therefore not energetic enough to break the bond in the O2 molecule.
(c) [5] Place the following ions in increasing order of radius:
Rb+, As3, Br, Se2, Sr2+
(All of these have the same number of electrons. Thus the lower the atomic number (i.e. the number of
protons), the larger the radius.)
From smallest to largest are therefore Sr2+ < Rb+ < Br < Se2 < As3
(d) [5] Indicate with a check mark whether or not each of the following sets of quantum numbers are
valid in an Mn atom:
ml
ms
Valid
Not Valid
Final Examination December 2013
C4.
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 10 of 11
(a) [5] What type of hybrid orbitals are used by each of the five indicated central atoms shown in the
structure of tryptophan below?
1:__sp3___
2:__sp2___
3:__sp3___
4:__sp3___
5:___sp2__
(b) [10] Predict the shapes of the following four molecules:
AsF5
AsF4
SeO2
NF3
5+(5x7) = 40 e
5+(4x7) = 33 e
6+(2x6) = 18 e
5+(3x7) = 26 e
Thus, AX5
Thus, AX4E
Thus, AX2E
Thus, AX3E
Thus, trigonal bipyramidal
Thus, seesaw
Thus, bent
Thus, Trigonal pyramidal
(c) [5] The highest energy electron in a molecule of NO is in a *2p molecular orbital. Is the bond energy
of NO+ higher or lower than that of NO? Why?
Making the NO+ ion requires removing the electron from NO that is in the highest energy MO. Since
this is an antibonding MO, removing it will result in an increased bond order. This in turn will make the
bond energy in NO+ higher than that in NO.
Final Examination December 2013
C5.
CHEM 1001 A and T
R. Burk
Page 11 of 11
(a) Answer the following question about the phase diagram of CO2 shown below.
(i)
(ii)
[12] Name all phases present at points:
A
Solid
Solid, Gas
Liquid
Solid, Liquid
Gas
Gas, Liquid
Solid, Liquid, Gas
[1] What is the vapour pressure of CO2 at room temperature, approximately?
73 bar
(iii)
[1] What is the name of the point at G?
The triple point
(iv)
[1] What is the name of the point at H?
The critical point
(v)
[2] Why can we not observe liquid CO2 at STP?
The lowest pressure at which the liquid can exist is 5.1 bar, which is higher than standard
pressure.
(vi)
[3] A block of dry ice is taken from the freezer and placed on the lab bench. What temperature is
the block at? How do you know?
Dry ice is solid CO2. Under 1 bar pressure (like the pressure in a lab), the temperature of the
solidgas equilibrium is 78oC.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Ayushman DwivediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 QuizDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Quizapi-296550987No ratings yet
- Chem Notes Chapter 9 - Lewis StructuresDocument53 pagesChem Notes Chapter 9 - Lewis StructuresjohnNo ratings yet
- Biology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankDocument58 pagesBiology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankBrooke Bradley100% (34)
- Basic Design Concepts in Process CalculationsDocument17 pagesBasic Design Concepts in Process CalculationsCalista KawaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank...Document7 pagesChemistry Question Bank...Vansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Cemerlang Persamaan KimiaDocument16 pagesSoalan Cemerlang Persamaan KimiaNorazliana MarzukiNo ratings yet
- Physical Science GRADE 10 STEP AHEAD LEARNER SUPPORT DOCUMENT 2022Document41 pagesPhysical Science GRADE 10 STEP AHEAD LEARNER SUPPORT DOCUMENT 2022TsheguhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - MATTER (Combined PPT) Class VII Help NotesDocument72 pagesCHAPTER - MATTER (Combined PPT) Class VII Help NotesPriyanca JunejaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SpectrosDocument89 pagesFundamentals of SpectrosI BadrNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry (Inorganic Chemistry)Document83 pagesAs Level Chemistry (Inorganic Chemistry)Amani EnkaraNo ratings yet
- HSI2023 Course CatalogDocument11 pagesHSI2023 Course CatalogJaya NataNo ratings yet
- Section Test 1 - Stoichiometry & Chemical Bonding MSDocument2 pagesSection Test 1 - Stoichiometry & Chemical Bonding MSV. G. LagnerNo ratings yet
- Level of Biological OrganizationDocument37 pagesLevel of Biological OrganizationMaria Faye MarianoNo ratings yet
- Henderson Main Group Chemistry, Tutorial Chemistry Texts 2000Document208 pagesHenderson Main Group Chemistry, Tutorial Chemistry Texts 2000mansaribhu_933532508100% (2)
- Chapter 9B General Organic Chemistry IIDocument55 pagesChapter 9B General Organic Chemistry IImrityunjaibharti2502No ratings yet
- Quantum Chemistry: International Journal ofDocument743 pagesQuantum Chemistry: International Journal ofMohammed SoleimanNo ratings yet
- Atoms To MoleculesDocument9 pagesAtoms To Moleculesapi-233567721No ratings yet
- Chemistry-Orgo II Exam 1 Version A (UD) Answer KeyDocument8 pagesChemistry-Orgo II Exam 1 Version A (UD) Answer KeyNesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- Review Guide Moles and Molecular FormulasDocument4 pagesReview Guide Moles and Molecular FormulashejajsNo ratings yet
- Ebook Ebook PDF Principles of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Principles of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition PDFlarry.coleman273100% (36)
- A Comparative Study of Crystal Structures and Inclusion Properties of Fluorinated TriazinesDocument7 pagesA Comparative Study of Crystal Structures and Inclusion Properties of Fluorinated TriazinesPablo de TarsoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision 2Document2 pagesWorksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision 2oscarbecNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Structure & Bonding QDocument115 pagesCHM1 Structure & Bonding QGoutham SivagnanamNo ratings yet
- Chem16 - 2ndLE Reviewers PDFDocument9 pagesChem16 - 2ndLE Reviewers PDFlylwennmacalaladNo ratings yet
- WCH11 01 Que 20210304Document24 pagesWCH11 01 Que 20210304윤소리No ratings yet
- Split Up Syllabus Xi Xii 2019 20 PDFDocument57 pagesSplit Up Syllabus Xi Xii 2019 20 PDFPrabith GuptaNo ratings yet
- Daniel Fry ATOMS GALAXIES AND UNDERSTANDINGDocument44 pagesDaniel Fry ATOMS GALAXIES AND UNDERSTANDINGNyTamasNo ratings yet
- Building Useful Models of Complex Reaction Systems in Petroleum RefiningDocument20 pagesBuilding Useful Models of Complex Reaction Systems in Petroleum RefiningNoheilly VásquezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Central Science 13th Edition Brown Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesChemistry The Central Science 13th Edition Brown Solutions ManualDavidThompsonratz100% (60)