Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Madagascar 04
Uploaded by
Sonora147Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Madagascar 04
Uploaded by
Sonora147Copyright:
Available Formats
Madagascar - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Madagascar
running parallel to it for some
600 km (370 mi). The western
and southern sides, which lie in
the rain shadow of the central
highlands, are home to dry
deciduous forests, spiny forests,
and deserts and xeric
shrublands. Due to their lower
The grassy plains that dominate the western landscape are dotted with stony massifs
population densities,
(left), patches of deciduous forest, and baobab trees (center), while the south is
Madagascar's dry deciduous
characterized by desert and spiny forests (right).
forests have been better
preserved than the eastern rain
forests or the original woodlands of the central plateau. The western coast features many protected harbors, but
silting is a major problem caused by sediment from the high levels of inland erosion carried by rivers crossing the
broad western plains.[16]
Climate
See also: Geography of Madagascar Climate
The combination of southeastern trade winds and northwestern monsoons produces
a hot rainy season (NovemberApril) with frequently destructive cyclones, and a
relatively cooler dry season (MayOctober). Rain clouds originating over the Indian
Ocean discharge much of their moisture over the island's eastern coast; the heavy
precipitation supports the area's rain forest ecosystem. The central highlands are
both drier and cooler while the west is drier still, and a semi-arid climate prevails in
the southwest and southern interior of the island.[15] Tropical cyclones annually
cause damage to infrastructure and local economies as well as loss of life.[17] In
2004 Cyclone Gafilo became the strongest cyclone ever recorded to hit Madagascar.
The storm killed 172 people, left 214,260 homeless[18] and caused more than
US$250 million in damage.[19]
Ecology
Biogeographic timetable of
Madagascar over the last 200
million years
Main articles: Wildlife of Madagascar, Flora of Madagascar, Fauna of
Madagascar, Agroecology in Madagascar, Ecoregions of Madagascar and List of World Heritage Sites in
Madagascar
As a result of the island's long isolation from neighboring continents, Madagascar is
home to an abundance of plants and animals found nowhere else on Earth.[20][21]
Approximately 90% of all plant and animal species found in Madagascar are
endemic,[22] including the lemurs (a type of strepsirrhine primate), the carnivorous
fossa and many birds. This distinctive ecology has led some ecologists to refer to
Madagascar as the "eighth continent",[23] and the island has been classified by
Conservation International as a biodiversity hotspot.[20]
More than 80 percent of Madagascar's 14,883 plant species are found nowhere else
in the world, including five plant families.[24] The family Didiereaceae, composed
of four genera and 11 species, is limited to the spiny forests of southwestern
Madagascar.[15] Four-fifths of the world's Pachypodium species are endemic to the
island.[25] Three-fourths[26] of Madagascar's 860[24] orchid species are found here
alone, as are six of the world's eight baobab species.[27] The island is home to
around 170 palm species, three times as many as on all of mainland Africa; 165 of
4 of 27
The island's iconic traveler's
palm (ravinala) features in
the national emblem.
11/9/2015 2:08 PM
You might also like
- Ecosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Savanna and Tundra Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandEcosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Savanna and Tundra Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Most Dangerous Deserts In The World | Deserts Of The World for Kids | Children's Explore the World BooksFrom EverandMost Dangerous Deserts In The World | Deserts Of The World for Kids | Children's Explore the World BooksNo ratings yet
- Rainforests of The Atsinanana: AfricaDocument10 pagesRainforests of The Atsinanana: AfricaAlexander LoscinNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial, Aquatic, Marine Ecology and CommunitiesDocument26 pagesTerrestrial, Aquatic, Marine Ecology and CommunitiesArnel AngelesNo ratings yet
- Madagascar Dry Deciduous ForestsDocument1 pageMadagascar Dry Deciduous ForestsIgnacio AllamiNo ratings yet
- Madagascar Forest CC Final 12nov07Document4 pagesMadagascar Forest CC Final 12nov07aliceadslNo ratings yet
- Manaus, Brazil: BiodiversityDocument2 pagesManaus, Brazil: BiodiversityManuel MendozaNo ratings yet
- A Biodiversity HopspotDocument6 pagesA Biodiversity HopspotJessica DaviesNo ratings yet
- SUNDARBANDocument27 pagesSUNDARBANMizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- College of Criminal Justice Education: Savannas and Temperate Grasslands Temperate GrasslandsDocument5 pagesCollege of Criminal Justice Education: Savannas and Temperate Grasslands Temperate GrasslandsDanica JuanNo ratings yet
- ECosystem and Biomes in PakistanDocument21 pagesECosystem and Biomes in PakistanMuhammad HabibNo ratings yet
- Equatorial ForestDocument2 pagesEquatorial ForestPrashant Bhagat100% (1)
- Madagascar (Madagascar (Malagasy: Repoblikan'i MadagasikaraDocument5 pagesMadagascar (Madagascar (Malagasy: Repoblikan'i MadagasikaraGeorgeNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument3 pagesNotesLokesh OriginalsNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument4 pagesEnvironmental ScienceDelia Mae Tao-ingNo ratings yet
- Upper Intermediate Student's Book: A World of Its OwnDocument3 pagesUpper Intermediate Student's Book: A World of Its OwnYovana BizarroNo ratings yet
- MadagascarDocument2 pagesMadagascarslovak.jaNo ratings yet
- An Ecosystem Consists of All The Organisms and The Physical Environment With Which They InteractDocument2 pagesAn Ecosystem Consists of All The Organisms and The Physical Environment With Which They InteractCharanjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Southern North America: Southeastern MexicoDocument2 pagesSouthern North America: Southeastern MexicoIsis ReyesNo ratings yet
- Great Migration: Serr GhetDocument3 pagesGreat Migration: Serr GhetrNo ratings yet
- Forest EcosystemDocument10 pagesForest EcosystemHarish NatrajNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity of RodriguesDocument12 pagesBiodiversity of Rodriguesjimmy sewNo ratings yet
- Madagascar Information and History: The Island of MadagascarDocument22 pagesMadagascar Information and History: The Island of MadagascarHeanary Viera GamboaNo ratings yet
- Rainforest: For Other Uses, SeeDocument8 pagesRainforest: For Other Uses, SeeSachaNo ratings yet
- Science (Tundra, Grassland, Desert) Only Information (No Pictures)Document4 pagesScience (Tundra, Grassland, Desert) Only Information (No Pictures)samikshameenuNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Meghalaya and Antarctica-1Document20 pagesComparison Between Meghalaya and Antarctica-1Abhinav ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Emag-April-Western GhatsDocument6 pagesEmag-April-Western GhatsAparna AnandNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Hotspot: MadagascarDocument1 pageBiodiversity Hotspot: MadagascarMr Cornish100% (2)
- Biomes InformationDocument15 pagesBiomes Informationapi-26319781050% (2)
- Desert Ecosystems: Case Study by Kim KerrDocument13 pagesDesert Ecosystems: Case Study by Kim KerrMohamad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- Western Ghats: Nidhi RaghuwanshDocument16 pagesWestern Ghats: Nidhi RaghuwanshShubhankar ShobuNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity HotspotsDocument6 pagesBiodiversity HotspotsTapan Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Sabina Virk: Citation NeededDocument1 pageSabina Virk: Citation NeededYekitaSNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGY 7937 SolutionsDocument2 pagesPSYCHOLOGY 7937 SolutionsSothorn HENGNo ratings yet
- Madagascar Information and History: The Island of MadagascarDocument22 pagesMadagascar Information and History: The Island of MadagascaralexNo ratings yet
- Biomas de La Tierra en InglesDocument2 pagesBiomas de La Tierra en InglesSAAM_BLDNo ratings yet
- Types and Characteristics of Outdoor EnvironmentsDocument36 pagesTypes and Characteristics of Outdoor Environmentsapi-276706274100% (1)
- Lecture # 8 Geogrphy and Physical Environment of PaksitanDocument104 pagesLecture # 8 Geogrphy and Physical Environment of PaksitanFaik AhmedNo ratings yet
- RainforestDocument7 pagesRainforestmaddydooggNo ratings yet
- The Organisms That Live in 4 Types of Terrestrial Ecosystem (Taiga, Tundra, Deciduous Forest, and Grassland) TaigaDocument3 pagesThe Organisms That Live in 4 Types of Terrestrial Ecosystem (Taiga, Tundra, Deciduous Forest, and Grassland) TaigaKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Sundal and Book ChapterDocument7 pagesSundal and Book ChapterUCOK SINAGANo ratings yet
- Steppe: Steppe in Ukraine Steppe in Russia Steppe in MongoliaDocument7 pagesSteppe: Steppe in Ukraine Steppe in Russia Steppe in MongoliaJohn Gil A. LunesNo ratings yet
- Handout - Biomes of The WorldDocument7 pagesHandout - Biomes of The WorldJonel BarrugaNo ratings yet
- Ecological Jewel in Danger PDFDocument2 pagesEcological Jewel in Danger PDFfranciscogarridoNo ratings yet
- Hutan PantaiDocument9 pagesHutan PantaiYuriza KeumalaNo ratings yet
- 25 Hot SpotsDocument3 pages25 Hot Spotsx5trawb3rriNo ratings yet
- Unit I BioidiversityDocument45 pagesUnit I BioidiversityRidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Forest: The Rainforests by The SeaDocument39 pagesMangrove Forest: The Rainforests by The SeaJitu MishraNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument14 pagesBiomesJerico MarcosNo ratings yet
- Wetlands of The WorldDocument2 pagesWetlands of The WorldVeronica Duque PardoNo ratings yet
- White Creative Doodle Brainstorming PresentationDocument17 pagesWhite Creative Doodle Brainstorming PresentationZyra AbordsNo ratings yet
- Rain Forest: Rainforests Are Forests Characterized by High Rainfall, WithDocument56 pagesRain Forest: Rainforests Are Forests Characterized by High Rainfall, WithSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- North South University Department of Life Science Spring 2011Document12 pagesNorth South University Department of Life Science Spring 2011Abanti Binte FarookNo ratings yet
- THE NIGERIAN VEGETATION Forest Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesTHE NIGERIAN VEGETATION Forest Lecture NotesTimson MantimNo ratings yet
- Biomes - Docx Summary 1 &2Document7 pagesBiomes - Docx Summary 1 &2shathaNo ratings yet
- Desert Biomes: By: Arralizze de Guzman (Beediii-B)Document34 pagesDesert Biomes: By: Arralizze de Guzman (Beediii-B)Arra De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- EgethjujyujDocument41 pagesEgethjujyujWALTER ESCALANTE HUAMANINo ratings yet
- Natural Region - WorksheetDocument3 pagesNatural Region - WorksheeteswarmbbeNo ratings yet
- Tundra Taiga Temperate Deciduous Forest Scrub Forest Grassland Desert Tropical Rain Forest Temperate Rain ForestDocument11 pagesTundra Taiga Temperate Deciduous Forest Scrub Forest Grassland Desert Tropical Rain Forest Temperate Rain Forestvenus caalemNo ratings yet
- Ethnic Groups: Religion in Rome (2015), PercentageDocument1 pageEthnic Groups: Religion in Rome (2015), PercentageSonora147No ratings yet
- Language: Passion of The Christ, Gangs of New York, HBO's Rome, The Life Aquatic and DinoDocument1 pageLanguage: Passion of The Christ, Gangs of New York, HBO's Rome, The Life Aquatic and DinoSonora147No ratings yet
- Fashion: Internal View of The ColosseumDocument1 pageFashion: Internal View of The ColosseumSonora147No ratings yet
- Culture: Entertainment and Performing ArtsDocument1 pageCulture: Entertainment and Performing ArtsSonora147No ratings yet
- Rome - 11Document1 pageRome - 11Sonora147No ratings yet
- Rome - 17Document1 pageRome - 17Sonora147No ratings yet
- Rome - 12Document1 pageRome - 12Sonora147No ratings yet
- Rome (Italian and Latin: Roma ( Ro Ma) : (Listen) 2Document1 pageRome (Italian and Latin: Roma ( Ro Ma) : (Listen) 2Sonora147No ratings yet
- Summer 11Document1 pageSummer 11Sonora147No ratings yet
- EUROPE: 1.8 Week On Average ( )Document1 pageEUROPE: 1.8 Week On Average ( )Sonora147No ratings yet
- Favorite Destinations and Choice Criteria: 13 © 2017 IpsosDocument1 pageFavorite Destinations and Choice Criteria: 13 © 2017 IpsosSonora147No ratings yet
- International Relations: Twin Towns and Sister CitiesDocument1 pageInternational Relations: Twin Towns and Sister CitiesSonora147No ratings yet
- Anticipation of Booking/ Payment For A Trip (%) : More Than 4 Months in AdvanceDocument1 pageAnticipation of Booking/ Payment For A Trip (%) : More Than 4 Months in AdvanceSonora147No ratings yet
- Summer 10Document1 pageSummer 10Sonora147No ratings yet
- Summer 04Document1 pageSummer 04Sonora147No ratings yet
- Summer 03Document1 pageSummer 03Sonora147No ratings yet
- Summer Holiday Plans: USA Europe BrazilDocument1 pageSummer Holiday Plans: USA Europe BrazilSonora147No ratings yet
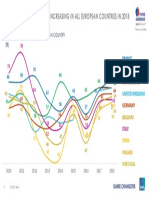
- Holiday Plans: Stable or Increasing in All European Countries in 2018Document1 pageHoliday Plans: Stable or Increasing in All European Countries in 2018Sonora147No ratings yet
- Europe: Consolidating A Positive Trend Since 2016Document1 pageEurope: Consolidating A Positive Trend Since 2016Sonora147No ratings yet
- Summer Holiday Plans: 5 © 2017 IpsosDocument1 pageSummer Holiday Plans: 5 © 2017 IpsosSonora147No ratings yet
- Let's Get Started: SOMETIMES IT'S NECESSARY To Take A Break and Unwind From The Stresses of Real Life and SpendDocument1 pageLet's Get Started: SOMETIMES IT'S NECESSARY To Take A Break and Unwind From The Stresses of Real Life and SpendSonora147No ratings yet
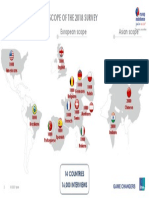
- Scope of The 2018 Survey: European Scope American Scope Asian ScopeDocument1 pageScope of The 2018 Survey: European Scope American Scope Asian ScopeSonora147No ratings yet
- Summer Holiday Plans Among Europeans, Americans and Asians: Ipsos/Europ Assistance Survey 18 EditionDocument1 pageSummer Holiday Plans Among Europeans, Americans and Asians: Ipsos/Europ Assistance Survey 18 EditionSonora147No ratings yet
- Drone Photography: Capture From AboveDocument1 pageDrone Photography: Capture From AboveSonora147No ratings yet
- Romantic 02Document1 pageRomantic 02Sonora147No ratings yet
- Colmar en Troisième Position Du Classement Des Meilleures Destinations Européennes 2018Document24 pagesColmar en Troisième Position Du Classement Des Meilleures Destinations Européennes 2018Aymeric RobertNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgments: Brianna Halloran Shutterstock Chris WoodmanDocument1 pageAcknowledgments: Brianna Halloran Shutterstock Chris WoodmanSonora147No ratings yet
- About This Book: Santorini Cyclades Islands, GreeceDocument1 pageAbout This Book: Santorini Cyclades Islands, GreeceSonora147No ratings yet
- 30 Romantic Getaways: World Destinations To Enjoy and Inspire Your PhotographyDocument1 page30 Romantic Getaways: World Destinations To Enjoy and Inspire Your PhotographySonora147No ratings yet
- Jakarta - Wikitravel3Document2 pagesJakarta - Wikitravel3Sonora147No ratings yet
- Remember How To Recognise and Understand Similes: Lost at SeaDocument1 pageRemember How To Recognise and Understand Similes: Lost at SeaGabriela QuerevalúNo ratings yet
- News Writing Chapter Inside Reporting Part 1 PDFDocument15 pagesNews Writing Chapter Inside Reporting Part 1 PDFGaevs Salinas100% (1)
- Loss Prevention and Safety in Sugar MillsDocument20 pagesLoss Prevention and Safety in Sugar MillsRavi ChandarNo ratings yet
- Weather Modification Test Technology Symposium 1997 USAF DR Arnold A Barnes JRDocument21 pagesWeather Modification Test Technology Symposium 1997 USAF DR Arnold A Barnes JRJim Lee ClimateViewer100% (1)
- Projected Population - 158,590 (As of 2011)Document19 pagesProjected Population - 158,590 (As of 2011)Cdrrmc DigosNo ratings yet
- FM 3-14 Nuclear, Biological and Chemical (NBC) Vulnerability Analysis PDFDocument93 pagesFM 3-14 Nuclear, Biological and Chemical (NBC) Vulnerability Analysis PDFsergey62No ratings yet
- DRR Grade 11 2Document4 pagesDRR Grade 11 2Ashna Nahida MTakiri LptNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental HazardDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Hazard03151206639No ratings yet
- Tos DRRDocument2 pagesTos DRRRyan San Luis100% (2)
- Earthquake Drill 2022Document42 pagesEarthquake Drill 2022Joyce CarreonNo ratings yet
- The Devastating Aftermath of Cyclone - UNHCRDocument3 pagesThe Devastating Aftermath of Cyclone - UNHCREmma Vivian O'ShaughnessyNo ratings yet
- Warsini+28 36Document9 pagesWarsini+28 36Amalia eka PutriNo ratings yet
- RDRP For Hydromet 1st Version 1Document82 pagesRDRP For Hydromet 1st Version 1Al CrisNo ratings yet
- Gated by Amy Christine ParkerDocument87 pagesGated by Amy Christine ParkerRandom House TeensNo ratings yet
- OPLAN MT - kANLAONDocument14 pagesOPLAN MT - kANLAONgary ann jimenez100% (3)
- Ocean Prediction Center's Radiofacsimile Charts User's GuideDocument42 pagesOcean Prediction Center's Radiofacsimile Charts User's GuideLemos FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Awareness of The World and The EnvironmentDocument5 pagesAwareness of The World and The EnvironmentRaian Daduyo QuelbioNo ratings yet
- 12 JSanMiguel EFFIS EuropeFireDocument29 pages12 JSanMiguel EFFIS EuropeFireValPal2013No ratings yet
- Tate No Yuusha No Nariagari 06 - 126-150Document299 pagesTate No Yuusha No Nariagari 06 - 126-150Chucea100% (1)
- Waba Dam Permanent DeformationDocument9 pagesWaba Dam Permanent DeformationccaapprrNo ratings yet
- Prestressed PilingDocument32 pagesPrestressed PilingCQ100% (1)
- Development and Validation of A Test To Measure Student's Climate Change Awareness (CCA) Toward Sustainable Development GoalsDocument9 pagesDevelopment and Validation of A Test To Measure Student's Climate Change Awareness (CCA) Toward Sustainable Development GoalsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Plane Crash Report For Miramar CrashDocument3 pagesPlane Crash Report For Miramar CrashAmanda RojasNo ratings yet
- Use of English Worksheets-Unit-13Document2 pagesUse of English Worksheets-Unit-139k2cwnnk8tNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Zones of India - Wikipedia ReferenceDocument18 pagesEarthquake Zones of India - Wikipedia ReferenceDurga Prasad SharmaNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class IX 20190530122220276Document2 pagesHoliday Homework Class IX 20190530122220276Lakshay GargNo ratings yet
- Explanation TextDocument6 pagesExplanation TextNur ArinaNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment ReportDocument4 pagesAccomplishment ReportPlanning and DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- PETITION To Save People Residing in Seismic Zone III, IV & V of Earthquake Prone AreasDocument41 pagesPETITION To Save People Residing in Seismic Zone III, IV & V of Earthquake Prone AreasSanjay Jain100% (1)