Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and Equilibrium
Uploaded by
Ahmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and Equilibrium
Uploaded by
Ahmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidCopyright:
Available Formats
PRE-SPAIN
CHEMISTRY 4 (WCH04)
TUTORIAL 3 EQUILIBRIA
1. State two characteristics of a system in equilibrium.
2. For each of the following systems, sketch graphs that show the change in
concentration against for the reactants A, P and X and the products C, R and Z.
System I: A + B
System II: P + Q
(Only a small amount of Q reacted in this reaction.)
System III: X + Y
(A large quantity of Z was produced in this reaction.)
3. The dissociation of sulfur trioxide to form sulfur dioxide and oxygen is a
reversible process. The figure below shows the composition of an equilibrium
mixture containing SO2 and SO3. Sketch a graph on the figure to show the
variation in the concentration of oxygen as the reaction proceeds until
equilibrium is established. Explain your reasoning.
4.
Consider the following reaction between A and B
to give C.
A(g) + B(g)
2C(g)
If 5 moles of A are allowed to mix and react with 3 moles of B in a 1.00 dm 3
container, 2 moles of C are produced at equilibrium. What is the value of K c for
this reaction?
5. An equilibrium mixture contains 2.00 moles of bromine, 1.25 moles of hydrogen
and 0.50 mole of hydrogen bromide in a 4.0 dm 3 container. Calculate Kc for the
reaction
H2(g) + Br2(g)
2HBr(g)
6. When a mixture of 60 g of ethanoic acid and 69 g of ethanol is heated in the
presence of an acid catalyst until equilibrium is achieved, 78% of the ethanoic
acid is converted to ester. Calculate Kc for the reaction
CH3COOH (l) + C2H5OH (l)
CH3COOC2H5 (l) + H2O (l)
7. What is the relationship between K 1 and K2 in each of the following pairs of
reactions? K1 and K2 are equilibrium constants.
K2
a) N2 (g) + 3H
(g) 2NH3 (g)
N2 (g) + 3/2 H2 (g)
K
2
b) H2 (g) + I2 (g)
K
2HI (g)
NH3 (g)
2HI (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
K
8. A mixture of2 NO2 (g) and N2O4 (g) at equilibrium has a total pressure of 0.135
atm. If the partial pressure of NO2 (g) at equilibrium = 0.0794 atm, calculate Kp
for the following reaction.
2NO2 (g)
N2O4 (g)
9. A mixture containing hydrogen and nitrogen in the ratio 3:1 (by volume) is
allowed to come to equilibrium at 1 atm pressure and 600K. Under these
conditions, the equilibrium mixture mixture contains 15% by volume of
ammonia. Calculate Kp for the reaction
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
2NH3 (g)
10.The oxidation of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide is a reversible reaction.
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2SO3 (g)
An equilibrium mixture in a container 0.40 mole of sulfur dioxide, 0.80 mole of
oxygen and 4.8 moles of sulfur trioxide. If the total pressure in the container is
1.5 x 106 Pa, calculate the value of Kp for the reaction.
11.An equilibrium mixture contains 23.9 g of NH 3, 13.5 g of H2 and 60.2 g N2 at
temperature 450 C. The total pressure of the system is 10 atm. Calculate the
value of Kp and state its unit.
12.The equilibrium constant , Kp, for the reaction
CaCO3 (s)
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
is 1.10 atm at 600 C. If 20.0 g of CaCO3 (s) is put in a 5.0 dm3 vessel and heated
to 600
C,
a) Calculate the number of moles of carbon dioxide produced using the formula
PV = nRT.
[P=pressure in atm; V=volume in dm3; n=number of mole; R=gas constant
(0.0821 atm dm3 mol-1 K-1); T=temperature in Kelvin]
b) Calculate the percentage of calcium carbonate decomposed at equilibrium.
13.Consider the heterogeneous equilibrium,
I2 (s) + 2HCl (g)
2HI (g) + Cl2 (g)
When 0.100 mol of HCl and excess solid iodine are placed in 1.00 L container,
the amount of HI produced is 1.46 x 10-12 mol. Calculate Kc for the reaction.
14.The value of Kc for the following equilibrium is 0.11 dm6 mol-2 at 500 C.
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
2NH3 (g)
Calculate the value of Kp at the same temperature.
[R = 0.0821 atm dm3 K-1 mol-1]
15.At 720 C, the value of Kp for the heterogeneous system shown below is 2.0 x 10 4
atm.
CaCO3(s)
CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Calculate the value of Kc for the system at the same temperature.
[R = 0.0821 atm dm3 K-1 mol-1]
16.a) At 1 atm pressure and 55 C, N2O4 is 50% dissociated. Calculate Kp for the
reaction.
b) Using your answer in (a), calculate the degree of dissociation of N 2O4 at the
same temperature and 10 atm pressure.
17.A chemical equilibrium is achieved when 20% of N 2O4 gas in a closed vessel at T
K dissociates according to the equation
N2O4(g)
2NO2(g)
If the total pressure of the system is p, what is the partial pressure equilibrium
constant, Kp, for this reaction?
18.Consider the reaction,
A(g) + B(g)
C(g) + D(g)
Kc for the reaction at 50 C is 0.78.
In the reacting vessel, the concentrations of these gases before equilibrium are
as follows.
[A] = 0.50 mol dm-3; [B] = 0.04 mol dm-3; [C] = 0.35 mol dm-3; [D] = 0.04 mol
dm-3.
Determine the direction of reaction in order to reach equilibrium.
19.At T C, the value of Kc for the reaction shown below is 4.5 x 10-3 mol dm-3.
N2O4(g)
2NO2(g)
If [N2O4] = 0.5 mol dm-3 and [NO2] = 0.15 mol dm-3, in which direction will the
reaction proceed to reach equilibrium?
20. Kp for chemical equilibrium: N2(g) + 3H2(g)
2NH3(g) at 450 C is 5.0 x 10-5
atm-2. For each of the following mixtures, chemical equilibrium may or may not
have been attained. Show the direction in which the reaction will move in order
to achieve chemical equilibrium.
a) NH3 (140 atm), N2 (20 atm) and H2 (600 atm)
b) NH3 (30 atm), N2 (83 atm) and H2 (60 atm)
c) NH3 (100 atm), N2 (5 atm) and H2 (2 atm)
21.Nickel (II) oxide (NiO) can be reduced by carbon monoxide to nickel according to
the equation
NiO(s) + CO(g)
Ni(s) + CO2(g)
At 1500 K, the equilibrium constant, K p, for the reaction is 650. If the pressure of
CO(g) is 0.40 atm, and the total pressure does not exceed 1 atm, can the
reduction of NiO by CO occur?
22.For each of the following cases, explain the changes that take place when the
chemical equilibrium is disturbed.
a) Water is added to the concentrated solution of bismuth chloride (BiCl 3),
followed by diluted hydrochloric acid.
BiCl3(aq) + H2O(l)
(colorless solution)
BiOCl(s)
(white solid)
2HCl(aq)
b) Iron(III) chloride solution is added to aqueous ammonium thiocyanate,
NH4SCN.
Fe3+(aq) + SCN-(aq)
(yellow)
FeSCN2+(aq)
(dark red)
c) An aqueous solution of cobalt(II) chloride is heated with concentrated
hydrochloric acid.
Co2+(aq) + 4Cl-(aq)
[CoCl4]2-(aq)
H is positive
(endothermic)
(pink)
(blue)
23.With reference to the following equilibrium reaction
2NO2(g)
(dark brown)
N2O4(g)
H < 0
(colorless)
Explain what will happen if a small sealed tube which contains a mixture of
NO2(g) and N2O4(g) is immersed in
a) A beaker containing an ice-water mixture,
b) A conical flask half-filled with hot water.
24.In which of the following reactions would the composition of the equilibrium
mixture be affected by an increase in pressure?
a) C(s) + O2(g)
b) CuO(s) + H2(g)
c) CaCO3(s)
CO2(g)
Cu(s) + H2O(g)
CaO(s) + CO2(g)
25.For the equilibrium system
PCl5(g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
What is the effect on
a) The equilibrium constant,
b) The position of equilibrium,
if some of the PCl5 (g) is removed from the equilibrium mixture?
You might also like
- Aldehydes and Ketones For IitjeeDocument65 pagesAldehydes and Ketones For Iitjeevarundhall1994No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Properties of HaloalkaneDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Properties of HaloalkaneRen Liew Jia QingNo ratings yet
- 235practice Exam 3 AnswerDocument4 pages235practice Exam 3 Answersowmmiya karuppiahNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Part-A I. Answer ALL The Questions (Each Question Carries One Mark) 10x1 10Document3 pagesInstructions:: Part-A I. Answer ALL The Questions (Each Question Carries One Mark) 10x1 10anon_850201470No ratings yet
- Ap Chemistry Acid-Base Exam Part I Multiple Choice: K (Hco) (Co) (H O) K (Co) (Co) (OH)Document8 pagesAp Chemistry Acid-Base Exam Part I Multiple Choice: K (Hco) (Co) (H O) K (Co) (Co) (OH)Max SaubermanNo ratings yet
- Solution-Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesSolution-Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsAnindya AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Kristia Stephanie BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument21 pagesAssignment IChocolaMeilleurNo ratings yet
- Chem52 Su13 PracticeExam1ADocument11 pagesChem52 Su13 PracticeExam1Aamarka01No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halide PDFDocument6 pagesAlkyl Halide PDFTvisha ViraniNo ratings yet
- Inter Ipe Isomerism & Bond PolarizationDocument9 pagesInter Ipe Isomerism & Bond PolarizationNalla Umapathi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1 - Introduction To The Synthesis of Nanomaterials - Molecular SpectrosDocument88 pagesLecture 3.1 - Introduction To The Synthesis of Nanomaterials - Molecular SpectrosGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- Hyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. EvansDocument12 pagesHyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. Evansomkar9996767No ratings yet
- OCHEM Practice FinalsDocument13 pagesOCHEM Practice FinalsNoleNo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Their Alicyclic Couterparts: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHDocument17 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Their Alicyclic Couterparts: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHEllaŠtrbac100% (1)
- Answers To ROH Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAnswers To ROH Tutorial PDFCorvo Haosen Al-Han0% (1)
- Chem 1040 Final Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesChem 1040 Final Exam ReviewUzair AliNo ratings yet
- ADV. I 57 - 64 (Exercise 3)Document8 pagesADV. I 57 - 64 (Exercise 3)Aditya ShahNo ratings yet
- Che 232 Test 1 Sptember 2007Document16 pagesChe 232 Test 1 Sptember 2007BONOLO RANKONo ratings yet
- Organic Problems1Document9 pagesOrganic Problems1Sung-Eun KimNo ratings yet
- Alcohols TestDocument2 pagesAlcohols TestAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument11 pagesHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Alkene ReactivityDocument23 pagesChapter 8 - Alkene ReactivitySimran DhunnaNo ratings yet
- APCHEM Review Practice Test 1Document16 pagesAPCHEM Review Practice Test 1M. JosephNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFDocument37 pagesAlkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFUma JadounNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesLecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsSHUBHAMNo ratings yet
- Houston Community College System: Organic Chemistry II 2425Document19 pagesHouston Community College System: Organic Chemistry II 2425Banele Ezma LambathaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFDocument5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids PDFmadhurima maityNo ratings yet
- Fall 2008 Old - Exam - 4Document12 pagesFall 2008 Old - Exam - 4alfredNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocument29 pagesChapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionAnonymous Ngsu7C4aNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument10 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenesakshatshukla2021No ratings yet
- ACS Review 9 AlkynesDocument9 pagesACS Review 9 AlkynesMohamad HabbabaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Placement Chemistry TestDocument15 pagesAdvanced Placement Chemistry TestBobNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-OctDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-Octolivia.benson9331No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanDocument16 pagesChapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Directions: This Examination Contains A Total of 80 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesDirections: This Examination Contains A Total of 80 Multiple ChoiceLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Practice Test 4u1Document1 pageChapter 8 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument16 pagesAromatic CompoundsadityaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The SDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The Ssweta KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument8 pagesAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNo ratings yet
- My Faculty Is Downloading Question Paper Alkyl HalideDocument4 pagesMy Faculty Is Downloading Question Paper Alkyl HalidesanskritiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 108M Final Exam Practice 1Document8 pagesChemistry 108M Final Exam Practice 1Norma Leticia RamosNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Document10 pagesPractice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Arianne Foster100% (1)
- ALDEHYDES, KETONES, ACIDS-01-170419: Neet-Crash-2017 Chemistry TestDocument6 pagesALDEHYDES, KETONES, ACIDS-01-170419: Neet-Crash-2017 Chemistry TestPoorvaBakshiNo ratings yet
- CH 331/1 Midterm Examination/Summer 2013/Dr. Daniel J. T. MylesDocument8 pagesCH 331/1 Midterm Examination/Summer 2013/Dr. Daniel J. T. MylesAnita MarLaNo ratings yet
- Practices Exam - Organic Chemistry To 2nd PartialDocument10 pagesPractices Exam - Organic Chemistry To 2nd PartialShary MosqueraNo ratings yet
- T1-1 TDocument30 pagesT1-1 TFRENCHONLYNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 231 Final ExamDocument19 pagesOrganic Chemistry 231 Final ExamAlex Rose100% (1)
- Welcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvansDocument22 pagesWelcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvanseraborNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Fang GaoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Problem SetBermonica Alvior SatuitoNo ratings yet
- NEPHAR 109 Practice Problems - 2 - G1&G2-1Document3 pagesNEPHAR 109 Practice Problems - 2 - G1&G2-1Amirabbas SaffariNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument21 pagesQuestion Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsSahilNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationDocument8 pagesReactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationMarc RitzNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- Caieee04fisica PDFDocument15 pagesCaieee04fisica PDFRafaelNo ratings yet
- Alkenes SeatworkDocument5 pagesAlkenes SeatworkJhefNo ratings yet
- Ap Equilibrium WorksheetDocument5 pagesAp Equilibrium Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Test, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFDocument18 pagesTest, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFTarun Gupta0% (2)
- GENTELMEN EQUILIBRIUM (Red)Document25 pagesGENTELMEN EQUILIBRIUM (Red)ewin TijaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C1 Revision Notes PDFDocument22 pagesEdexcel C1 Revision Notes PDFAhmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Entropy and Free EnergyDocument4 pagesEntropy and Free EnergyAhmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Rate of Chemical ChangesDocument3 pagesRate of Chemical ChangesAhmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Experiments Hooke's Law and Young ModulusDocument3 pagesExperiments Hooke's Law and Young ModulusMustafaAsimNo ratings yet
- Experiments Hooke's Law and Young ModulusDocument3 pagesExperiments Hooke's Law and Young ModulusMustafaAsimNo ratings yet
- 04 Membrane Structure NotesDocument22 pages04 Membrane Structure NotesWesley ChinNo ratings yet
- Issue15 - Chirag JiyaniDocument6 pagesIssue15 - Chirag JiyaniDipankar SâháNo ratings yet
- Alto Hotel Melbourne GreenDocument2 pagesAlto Hotel Melbourne GreenShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- AWS Compete CustomerDocument33 pagesAWS Compete CustomerSergeyNo ratings yet
- MMB & DFT 2012 Workshop ProceedingsDocument44 pagesMMB & DFT 2012 Workshop ProceedingsFelipe ToroNo ratings yet
- Family Factors: Its Effect On The Academic Performance of The Grade 6 Pupils of East Bayugan Central Elementary SchoolDocument11 pagesFamily Factors: Its Effect On The Academic Performance of The Grade 6 Pupils of East Bayugan Central Elementary SchoolGrace Joy AsorNo ratings yet
- 4D Beijing (Muslim) CHINA MATTA Fair PackageDocument1 page4D Beijing (Muslim) CHINA MATTA Fair PackageSedunia TravelNo ratings yet
- 4BT3 9-G2 PDFDocument5 pages4BT3 9-G2 PDFNv Thái100% (1)
- HG32High-Frequency Welded Pipe Mill Line - Pakistan 210224Document14 pagesHG32High-Frequency Welded Pipe Mill Line - Pakistan 210224Arslan AbbasNo ratings yet
- Programming MillDocument81 pagesProgramming MillEddy ZalieNo ratings yet
- Alufix Slab Formwork Tim PDFDocument18 pagesAlufix Slab Formwork Tim PDFMae FalcunitinNo ratings yet
- Newsela Teacher Review - Common Sense EducationDocument1 pageNewsela Teacher Review - Common Sense EducationJessicaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report PDFDocument71 pagesInternship Report PDFNafiz FahimNo ratings yet
- CNC - Rdmacror: Public Static Extern Short Ushort Short Short ShortDocument3 pagesCNC - Rdmacror: Public Static Extern Short Ushort Short Short ShortKession HouNo ratings yet
- Iroquois Clothes and WampumDocument3 pagesIroquois Clothes and Wampumapi-254323856No ratings yet
- Assignment & Case Marketing Week 1: Max Van Neerven: 1664172 Mounir Trabelsi: 1705839 Renaldas Zlatkus: 1701775Document8 pagesAssignment & Case Marketing Week 1: Max Van Neerven: 1664172 Mounir Trabelsi: 1705839 Renaldas Zlatkus: 1701775Ren ZkNo ratings yet
- TABEL Sifat Uap Jenuh Tabel Suhu Dan TekananDocument8 pagesTABEL Sifat Uap Jenuh Tabel Suhu Dan Tekanan21-002 Alditua sinabaribaNo ratings yet
- Model No. TH-65JX850M/MF Chassis. 9K56T: LED TelevisionDocument53 pagesModel No. TH-65JX850M/MF Chassis. 9K56T: LED TelevisionRavi ChandranNo ratings yet
- Most Probable Number (MPN) Test: Principle, Procedure, ResultsDocument4 pagesMost Probable Number (MPN) Test: Principle, Procedure, ResultsHammad KingNo ratings yet
- Region: South Central State: Andhra PradeshDocument118 pagesRegion: South Central State: Andhra PradeshpaulinNo ratings yet
- Fall 3050 SyllabusDocument6 pagesFall 3050 Syllabustaher91No ratings yet
- Vtoris 100% Clean Paypal Transfer Guide 2015Document8 pagesVtoris 100% Clean Paypal Transfer Guide 2015Sean FrohmanNo ratings yet
- White Cataract What To AssesDocument2 pagesWhite Cataract What To Assesalif andraNo ratings yet
- Catch Up RPHDocument6 pagesCatch Up RPHபிரதீபன் இராதேNo ratings yet
- NATO Obsolescence Management PDFDocument5 pagesNATO Obsolescence Management PDFluisNo ratings yet
- Gics-In-India Getting Ready For The Digital WaveDocument81 pagesGics-In-India Getting Ready For The Digital Wavevasu.gaurav75% (4)
- Case Study Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesCase Study Managerial EconomicsZaza Afiza100% (1)
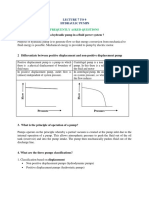
- Frequently Asked Questions: Lecture 7 To 9 Hydraulic PumpsDocument5 pagesFrequently Asked Questions: Lecture 7 To 9 Hydraulic PumpsJatadhara GSNo ratings yet
- CP3 - June2019 2Document5 pagesCP3 - June2019 2Sifei ZhangNo ratings yet
- Net Pert: Cable QualifierDocument4 pagesNet Pert: Cable QualifierAndrés Felipe Fandiño MNo ratings yet