Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BP: HR: RR: Temp:: CBC Count Pulse Oximetry (Oxygen Saturation) Creatinine
Uploaded by
roshmaeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BP: HR: RR: Temp:: CBC Count Pulse Oximetry (Oxygen Saturation) Creatinine
Uploaded by
roshmaeCopyright:
Available Formats
SUBMITTED TO:
SUBMITTED BY:
REPRESENTATIVE CASE
IDENTIFYING DATA:
CHIEF COMPLAINT:
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS:
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY:
FAMILY HISTORY:
PERSONAL AND SOCIAL HISTORY:
REVIEW OF SYSTEMS
General Survey:
HEENT:
Chest and Lungs:
Cardiovascular:
Gastrointestinal:
Musculoskeletal:
Genitourinary:
CNS:
SILLIMAN UNIVERSITY MEDICAL SCHOOL
DATE:
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
General Survey:
Vital Signs:
BP:
RR:
Skin:
HEENT:
Neck:
Pulmonary:
Cardiovascular:
Abdomen:
Genitourinary:
Extremities:
CNS:
HR:
Temp:
II. PRIMARY IMPRESSION
DIAGNOSIS
RULE IN
RULE OUT
III. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
DIAGNOSES
RULE IN
RULE OUT
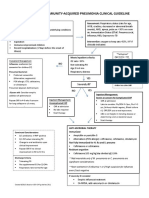
IV. RATIONAL LABORATORY & DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
LABORATORY WORKUPS
CBC Count
Pulse Oximetry
(Oxygen
Saturation)
Creatinine
Sputum Gram
stain and culture
Sputum AFB
Smear for 3
consecutive days
Chest radiograph
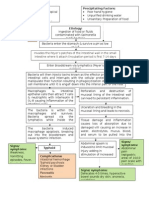
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
INTERPRETATION/NECESSITY
This is used to determine the hematologic profile of the patient, to detect if there is
anemia, infection, and other possible blood disorders. Leukocytosis with a left shift may be
observed in any bacterial infection. Leukopenia (usually defined as a WBC count < 5000
cells/L) may be an ominous clinical sign of impending sepsis.
A pulse oximetry finding of < 90-92% indicates significant hypoxia. It is performed to
assess the adequacy of oxygen levels (or oxygen saturation) in the blood and could help in
the management of the patient.
Some patients presenting with pneumonia have elevated creatine kinase (CK) levels. In
patients with severe respiratory failure and profound hypoxemia, cellular death can occur
with the release of CK into the circulation. Destruction of alveolar epithelial cells by both
bacteria and bacterial toxins can result in CK release into the circulation.
Sputum Gram stain and culture should be performed before initiating antibiotic therapy (if
a good-quality, contaminant-sparse specimen containing < 10 squamous epithelial cells
per low-power field can be obtained). The white blood cell (WBC) count should be more
than 25 per low-power field in non-immunosuppressed patients. A single predominant
microbe should be noted at Gram staining. Mixed flora may be observed with anaerobic
infections.
AFB testing may be used to detect several different types of acid-fast bacilli, but it is most
commonly used to identify an active tuberculosis (TB) infection caused by the most
medically important AFB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sputum AFB Smear helps in rulingout Pulmonary Tuberculosis for suspected cases.
Chest radiography is considered the standard method for diagnosing the presence of
pneumonia, that is, the presence of an infiltrate is required for the diagnosis. pleural
effusions can be identified by chest radiographs. The presence of a parapneumonic pleural
fluid can have inportant therapeutic implications. In H influenzae pneumonia, pleural
effusion is present in approximately half of infected individuals.
V. THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT (DE LOS SANTOS, GARSUTA, GOROY)
LIST OF PROBLEMS
THERAPEUTIC OBJECTIVES
1.
ADVICE AND INFORMATION
NON-PHARMACOLOGIC MANAGEMENT
1.
PHARMACOLOGIC MANAGEMENT
DRUG NAME
P-DRUGS
DRUG NAME
EFFICACY
EFFICACY
VI. MONITORING AND FOLLOW-UP
1.
SAFETY
SAFETY
SUITABILITY
SUITABILITY
COST
You might also like
- The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology System for Reporting Respiratory Cytology: Definitions, Criteria, Explanatory Notes, and Recommendations for Ancillary TestingFrom EverandThe Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology System for Reporting Respiratory Cytology: Definitions, Criteria, Explanatory Notes, and Recommendations for Ancillary TestingNo ratings yet
- Unusual Case of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion and Abdominal MassDocument4 pagesUnusual Case of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion and Abdominal MassRofi IrmanNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia:: Current Management GuidelinesDocument100 pagesPneumonia:: Current Management Guidelinesinterna MANADONo ratings yet
- How To Diagnose: Colorado Tuberculosis ManualDocument74 pagesHow To Diagnose: Colorado Tuberculosis ManualChinette de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 05 Investigations For PneumoniaDocument4 pages05 Investigations For Pneumoniause4meNo ratings yet
- Case JadiDocument24 pagesCase JadiIndadiah LestariNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Panel GuidelineDocument8 pagesPneumonia Panel Guidelineilham perdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Myeloperoxidase and Protein Oxidation in The Airways of Young Children With Cystic FibrosisDocument7 pagesMyeloperoxidase and Protein Oxidation in The Airways of Young Children With Cystic FibrosisMichael StudiofourteenohnineNo ratings yet
- Kansasiiand M. Avium), May Be Positive For AFB Stain. Thus, A PositiveDocument8 pagesKansasiiand M. Avium), May Be Positive For AFB Stain. Thus, A PositiveMarisa PetersonNo ratings yet
- Bal 3BDocument29 pagesBal 3BLian Marie ViñasNo ratings yet
- The Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Lung Biopsy Pathology andDocument8 pagesThe Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Lung Biopsy Pathology andHeru SigitNo ratings yet
- Bal & TBBDocument40 pagesBal & TBBvivekanand78waghNo ratings yet
- Clinical Predictors of Ileocecal Tuberculosis: A Case SeriesDocument14 pagesClinical Predictors of Ileocecal Tuberculosis: A Case SeriesChristopher AsisNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis Literature Reviewafdtvwccj100% (1)
- DIAGNOSIS OF MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS OfficeDocument4 pagesDIAGNOSIS OF MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS OfficeSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- Comparison OF Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology and Biopsy in Lung MalignancyDocument5 pagesComparison OF Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology and Biopsy in Lung MalignancyDyahSavitriKusumoningtyasNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis - AiimsrisDocument118 pagesBronchiectasis - AiimsrisElteyb Nor eldaimNo ratings yet
- Nosocomial Pneumonia: Self AssessmentDocument10 pagesNosocomial Pneumonia: Self AssessmentZali AhmadNo ratings yet
- Usefulness of Tumor Marker CA-125 Serum Levels For The Follow-Up of Therapeutic Responses in Tuberculosis Patients With and Without SerositisDocument6 pagesUsefulness of Tumor Marker CA-125 Serum Levels For The Follow-Up of Therapeutic Responses in Tuberculosis Patients With and Without Serositishumayun kabirNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument3 pagesCase Reportyena hillNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diagnostic NTMDocument12 pagesMicrobial Diagnostic NTMdicky wahyudiNo ratings yet
- 8.11.08 Davis-Hovda. TB PleurisyDocument13 pages8.11.08 Davis-Hovda. TB Pleurisyrisda aulia putriNo ratings yet
- DR Agus Specimen CultureDocument2 pagesDR Agus Specimen CultureAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Nodulos Pulmonares 2Document10 pagesNodulos Pulmonares 2Dani BelloNo ratings yet
- Sputum Cultures For The Evaluation of Bacterial PneumoniaDocument13 pagesSputum Cultures For The Evaluation of Bacterial Pneumoniamayteveronica1000No ratings yet
- Case Report: A Case Report of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Challenging DiagnosisDocument4 pagesCase Report: A Case Report of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Challenging DiagnosisDumitru RadulescuNo ratings yet
- Al-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal Aamj, Vol 13, No 4, October 2015 Suppl-2Document6 pagesAl-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal Aamj, Vol 13, No 4, October 2015 Suppl-2Vincentius Michael WilliantoNo ratings yet
- Utility of Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal) Specimens in Clinically and Radiologically Suspected Cases of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in HIV-Seronegative PatientsDocument1 pageUtility of Bronchoalveolar Lavage (Bal) Specimens in Clinically and Radiologically Suspected Cases of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in HIV-Seronegative PatientsVadivel N P PillaiNo ratings yet
- Radiologic Manifestations of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Patients of Intensive Care UnitsDocument6 pagesRadiologic Manifestations of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Patients of Intensive Care UnitsAnonymous qwH3D0KrpNo ratings yet
- Brief CommunicationDocument3 pagesBrief CommunicationanrihmNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Laboratory Testing Methods For The Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleurisy in ChinaDocument5 pagesComparison of Laboratory Testing Methods For The Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleurisy in ChinaclaryntafreyaaNo ratings yet
- PK - Aspek Laboratorium Respirasi - Dr. AnnaDocument48 pagesPK - Aspek Laboratorium Respirasi - Dr. AnnaMUHAMMAD ILHAM PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Diadnosis and Treatment of Extra Pulmonary TB PDFDocument9 pagesDiadnosis and Treatment of Extra Pulmonary TB PDFteyim pride mbuhNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Between CAP and TuberculosisDocument36 pagesDifferentiating Between CAP and TuberculosisMd Azhar InamdarNo ratings yet
- Tuberculous Salpingitis: A Case Report: - 2013 Jun 7 (6) : 1186-1188. Published Online 2013 Jun 1. Doi: PMCID: PMC3708232Document5 pagesTuberculous Salpingitis: A Case Report: - 2013 Jun 7 (6) : 1186-1188. Published Online 2013 Jun 1. Doi: PMCID: PMC3708232Lucky PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Delay in Diagnosis of Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Its Rare Manifestations: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesDelay in Diagnosis of Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Its Rare Manifestations: A Case ReportSneeze LouderNo ratings yet
- Hemoptysis: A Symptom Not Well Explored in The Primary Care Setting in The Developing WorldDocument4 pagesHemoptysis: A Symptom Not Well Explored in The Primary Care Setting in The Developing WorldAditya RamdaniiNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 3 TopicDocument27 pagesLiterature Review 3 TopicBharathi Sneha PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Ajtccm 27 1 054Document5 pagesAjtccm 27 1 054Saniska NCTNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Recent Advances and Diagnostic AlgorithmsDocument8 pagesDiagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Recent Advances and Diagnostic AlgorithmsJulissapenacNo ratings yet
- Title Use of Fibreoptic Bronchoscopy in Diagnosing Sputum Smear-Negative Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument46 pagesTitle Use of Fibreoptic Bronchoscopy in Diagnosing Sputum Smear-Negative Pulmonary TuberculosisHam FGNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Tuberculosis Presenting As Ascites in An Older Indigenous Woman: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesAbdominal Tuberculosis Presenting As Ascites in An Older Indigenous Woman: A Case ReportauliaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Profile, Etiology, and Management of Hydropneumothorax: An Indian ExperienceDocument5 pagesClinical Profile, Etiology, and Management of Hydropneumothorax: An Indian ExperienceSarah DaniswaraNo ratings yet
- BronchopneumoniaDocument2 pagesBronchopneumoniaAzette AgpiNo ratings yet
- Investigate CAP Severity & CausesDocument27 pagesInvestigate CAP Severity & CausesRoshana Mallawaarachchi0% (1)
- Ultrasonography: A Cost - Effective Modality For Diagnosis of Rib Tuberculosis - A Case ReportDocument3 pagesUltrasonography: A Cost - Effective Modality For Diagnosis of Rib Tuberculosis - A Case ReportAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Tuberculosis: ReviewDocument5 pagesPeritoneal Tuberculosis: ReviewEvellyna MeilanyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of TuberculosisDocument51 pagesClinical Presentation and Diagnosis of TuberculosisRestu MegantaraNo ratings yet
- En V38n2a04Document7 pagesEn V38n2a04Ana MercadoNo ratings yet
- Imp bn1Document5 pagesImp bn1Karito FloresNo ratings yet
- Revision 2019 TurciosDocument19 pagesRevision 2019 TurciosAdriana AsturizagaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Cytology: DR Mohammed Shahin, JR (Academic), Dept of Pathology & Lab Medicine, AIIMS BhubaneswarDocument62 pagesRespiratory Cytology: DR Mohammed Shahin, JR (Academic), Dept of Pathology & Lab Medicine, AIIMS BhubaneswarShruthi N.RNo ratings yet
- Chest X Ray in CAPDocument7 pagesChest X Ray in CAPsahatmanurungNo ratings yet
- 58 JMSCRDocument4 pages58 JMSCRhumayun kabirNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Bahasa InggrisDocument12 pagesJurnal Bahasa InggrisVanessa Angelica SitepuNo ratings yet
- AdultOI CryptococcosisDocument18 pagesAdultOI CryptococcosisricardoatejassNo ratings yet
- Empyema SGIM Poster 2007Document1 pageEmpyema SGIM Poster 2007sys_manusNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medicine Case Reports: Lauren A. Sharan, Thea P. Price, Boyd Hehn, David Manoff, Scott W. CowanDocument4 pagesRespiratory Medicine Case Reports: Lauren A. Sharan, Thea P. Price, Boyd Hehn, David Manoff, Scott W. CowanJha BhoenkNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Pneumonia Caused by Rare Granular Cell TumorDocument7 pagesRecurrent Pneumonia Caused by Rare Granular Cell TumorJoshua MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hiv Medicine: Objective Specific Clinical Assessment Report (OSCAR) Module - 1Document3 pagesHiv Medicine: Objective Specific Clinical Assessment Report (OSCAR) Module - 1Matin Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- CAP Flow Sheet PDF 62015 PDFDocument1 pageCAP Flow Sheet PDF 62015 PDFroshmaeNo ratings yet
- SHEDocument3 pagesSHEroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Cascade: Difference Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic PathwayDocument10 pagesCoagulation Cascade: Difference Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathwayroshmae100% (1)
- Cap PDFDocument1 pageCap PDFroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Causes and Symptoms of HypothyroidismDocument3 pagesCauses and Symptoms of HypothyroidismroshmaeNo ratings yet
- IM - Focal Seizure ReportDocument2 pagesIM - Focal Seizure ReportroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Surgery - PAODDocument4 pagesSurgery - PAODroshmaeNo ratings yet
- CPG Pcap 2012 PDFDocument54 pagesCPG Pcap 2012 PDFroshmae67% (3)
- CAP Flow Sheet PDF 62015 PDFDocument1 pageCAP Flow Sheet PDF 62015 PDFroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Sentinel Lymph Node DissectionDocument9 pagesSentinel Lymph Node DissectionroshmaeNo ratings yet
- FCM IiiDocument2 pagesFCM IiiroshmaeNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument3 pagesResearchroshmaeNo ratings yet
- IM - Focal Seizure ReportDocument8 pagesIM - Focal Seizure ReportroshmaeNo ratings yet
- PD Surgery - Incarcerated Hernia - Dr. RanaDocument2 pagesPD Surgery - Incarcerated Hernia - Dr. RanaroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Obejctives Content TA T-L Activitie S Materials Resources Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesTopic:: Obejctives Content TA T-L Activitie S Materials Resources Evaluatio NroshmaeNo ratings yet
- POT - NutritionDocument18 pagesPOT - NutritionroshmaeNo ratings yet
- PD - CopdDocument3 pagesPD - CopdroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Recommendations 1Document1 pageRecommendations 1roshmaeNo ratings yet
- PD - Heart Failure ReportDocument28 pagesPD - Heart Failure ReportroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Surgery 1Document2 pagesSurgery 1roshmaeNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Congenital HypothyroidismDocument3 pagesGyne - Congenital HypothyroidismroshmaeNo ratings yet
- ACS WorksheetDocument6 pagesACS WorksheetroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument32 pagesCervical CancervvmgkikiNo ratings yet
- ACS WorksheetDocument6 pagesACS WorksheetroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Functional Ovarian Cysts Treatment and ManagementDocument1 pageGyne - Functional Ovarian Cysts Treatment and ManagementroshmaeNo ratings yet
- After Bea's PPT Psych Reports. 4.5 - 4.6Document51 pagesAfter Bea's PPT Psych Reports. 4.5 - 4.6roshmaeNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever PathophysiologyDocument1 pageTyphoid Fever PathophysiologyroshmaeNo ratings yet
- Case 1 Gyne ID, PEDocument2 pagesCase 1 Gyne ID, PEroshmaeNo ratings yet
- PD - Heart Failure ReportDocument28 pagesPD - Heart Failure ReportroshmaeNo ratings yet
- WHO WPE GIH 2020.2 Eng PDFDocument11 pagesWHO WPE GIH 2020.2 Eng PDFMaicon MarquesNo ratings yet
- What Is Infusion Pump?Document4 pagesWhat Is Infusion Pump?BMTNo ratings yet
- OSCE PracticeDocument8 pagesOSCE PracticeU$er100% (2)
- PATHFit 1 Module 1 1Document9 pagesPATHFit 1 Module 1 1Danielle Jhon Tevdcian OmegaNo ratings yet
- Einc Lectures - CeDocument5 pagesEinc Lectures - Ceboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot ComplicaDocument25 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot Complicafebyan yohanesNo ratings yet
- DCA-Coalition Insulin GuidelinesDocument5 pagesDCA-Coalition Insulin GuidelinesNabihah BarirNo ratings yet
- 3M Mask and AntisepticDocument2 pages3M Mask and AntisepticДимитър ПетровNo ratings yet
- Professional Football Club Registration & Consent Form: Personal Information - Child / Young PersonDocument2 pagesProfessional Football Club Registration & Consent Form: Personal Information - Child / Young PersonanilNo ratings yet
- INI-CET Corrigendum No.23-2020. & Sponsorship Certificate PDFDocument2 pagesINI-CET Corrigendum No.23-2020. & Sponsorship Certificate PDFpriyathileepan-1No ratings yet
- Format Pencatatan Hasil Pelayanan Vaksinasi Manual Pusk Fasyankes PosDocument48 pagesFormat Pencatatan Hasil Pelayanan Vaksinasi Manual Pusk Fasyankes PosluveliaNo ratings yet
- Ob Nursing Care Plan For Maternal Database Maternal and NewbornDocument2 pagesOb Nursing Care Plan For Maternal Database Maternal and Newbornapi-403051801No ratings yet
- Simulation Program For Clinical Performance Improvement: Improving Clinical Care and Patient Safety Through SimulationDocument11 pagesSimulation Program For Clinical Performance Improvement: Improving Clinical Care and Patient Safety Through SimulationiloilocityNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Dancing BenefitsDocument4 pagesAerobic Dancing BenefitsDal.giNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Health Seeking Behavior of Women in Green Valley Health Center in The Year 2016Document29 pagesPrenatal Health Seeking Behavior of Women in Green Valley Health Center in The Year 2016Grace TayagNo ratings yet
- University of Dentistry Medicine .: Department of Dermatology and D VenerologyDocument4 pagesUniversity of Dentistry Medicine .: Department of Dermatology and D VenerologyEriola FrrokuNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1 EXPANDED AND EXTENDED ROLE OF PEDIATRIC NURSEDocument15 pagesSeminar 1 EXPANDED AND EXTENDED ROLE OF PEDIATRIC NURSESuganthi Parthiban100% (7)
- BeWell Assignment 2 W22Document8 pagesBeWell Assignment 2 W22Christian SNNo ratings yet
- Ignaz Semmelweis Handwashing Discovery Saves LivesDocument18 pagesIgnaz Semmelweis Handwashing Discovery Saves LivesSamjhana NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Path Fit100: Physical Activities Towrds Health and Fitness Movement CompetencyDocument1 pagePath Fit100: Physical Activities Towrds Health and Fitness Movement CompetencyChristian Fel MoralitaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Item CardDocument2 pagesPathology Item CardBir Mohammad SonetNo ratings yet
- Eur J Clin Investigation - 2023 - Schmeling - Batch Dependent Safety of The BNT162b2 mRNA COVID 19 VaccineDocument3 pagesEur J Clin Investigation - 2023 - Schmeling - Batch Dependent Safety of The BNT162b2 mRNA COVID 19 VaccineLeblancNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Disease in PregnancyDocument37 pagesHepatic Disease in PregnancyElisha Joshi100% (1)
- Nursing Career Ladder System in Indonesia The Hospital ContextDocument9 pagesNursing Career Ladder System in Indonesia The Hospital Contextners edisapNo ratings yet
- Systemic Routes of Drug Administration:: Hind B. Almufty BS.C Clinical PharmacyDocument14 pagesSystemic Routes of Drug Administration:: Hind B. Almufty BS.C Clinical PharmacySana SarwarNo ratings yet
- Student's Handbook 2014Document52 pagesStudent's Handbook 2014Ahmed MawahibNo ratings yet
- Department of Oral Pathology Professor ProfileDocument5 pagesDepartment of Oral Pathology Professor ProfileAmaradeepika JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube (NGT)Document31 pagesNasogastric Tube (NGT)annyeong_123No ratings yet
- What Vaccines Do BC Adults NeedDocument2 pagesWhat Vaccines Do BC Adults NeedCatalina VisanNo ratings yet
- Coma Dfiferential DiagnosisDocument23 pagesComa Dfiferential DiagnosisGeorge GeorgeNo ratings yet
- War on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicFrom EverandWar on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicFrom EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceFrom EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineFrom EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineNo ratings yet
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsFrom EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusFrom EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismFrom EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- The War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardFrom EverandThe War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.From EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Arthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefFrom EverandArthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefNo ratings yet
- Epidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentFrom EverandEpidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- The HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedFrom EverandThe HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Quick Fixes: Drugs in America from Prohibition to the 21st Century BingeFrom EverandQuick Fixes: Drugs in America from Prohibition to the 21st Century BingeNo ratings yet
- Blood Runs Coal: The Yablonski Murders and the Battle for the United Mine Workers of AmericaFrom EverandBlood Runs Coal: The Yablonski Murders and the Battle for the United Mine Workers of AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Anti-vaxxers: How to Challenge a Misinformed MovementFrom EverandAnti-vaxxers: How to Challenge a Misinformed MovementRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (12)
- The Transformation: Discovering Wholeness and Healing After TraumaFrom EverandThe Transformation: Discovering Wholeness and Healing After TraumaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (70)
- The Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthFrom EverandThe Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthNo ratings yet
- The Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryFrom EverandThe Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoFrom EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (40)
- Doctored: The Disillusionment of an American PhysicianFrom EverandDoctored: The Disillusionment of an American PhysicianRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- My House Is Killing Me!: A Complete Guide to a Healthier Indoor Environment (2nd Edition)From EverandMy House Is Killing Me!: A Complete Guide to a Healthier Indoor Environment (2nd Edition)No ratings yet
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyFrom EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)