Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differential Diagnosis of Most Common Symptoms - DR - Ahmados
Uploaded by
Rashed ShatnawiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differential Diagnosis of Most Common Symptoms - DR - Ahmados
Uploaded by
Rashed ShatnawiCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr.
Ahmados
Differential diagnosis of most common symptoms
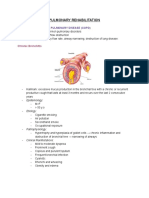
Chest
Dyspnea
Airways
Laryngeal tumour
Foreign body
Asthma
COPD
Bronchiectasis
Lung cancer
Acute Bronchitis.(V-B)
Cystic fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis
Alveolitis
Others causes:
Anaemia, Metabolic acidosis ,
Obesity, Psychogenic
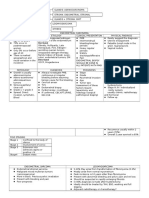
Chronic dyspnea :
1- Asthma precipitated by
allergens.
2- COPD
3- Pulmonary fibrosis
4- Pulmonary hypertension
5- LVF
Acute dyspnea :
with wheeze + cough :
1Exacerbation
of Asthma
2Exacerbation
of COPD
3Acute
bronchitis
4-
Parenchyma
Cardio
Pulmonary
circulation
Pleural
Pneumothorax
Pleural effusion
Diffuse Pleural fibrosis
Chest wall
Sarcoidosis
Neuromuscular
Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
Tumour (metastatic,
lymphangitis)
Acute LV
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary vasculitis
Left ventricular failure
Mitral valve disease
Constrictive pericarditis
Pericardial effusion
Cardiomyopathy
Kyphoscoliosis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Causes of orthopnea :
Cardiac M.S. , LVF (left sided failure)
Chestsever asthmatic attack- emphysema
Abdomen tense ascites.
Myasthenia gravis
Neuropathies
Muscular dystrophies
Guillain-Barr syndrome
Causes of P.N.D :
1- Pulmonary edema due to LVF- CHF
2- Asthma .
3- Cardiac asthma .
4- COPD
Abdomen
1- Ascites escapes into Rt.lung
pleural effusion with dyspnea.
2- Tense Ascites
Cause mechanical orthopnea
failure.
5-
Pulmonary
embolism
6-
Pneumothora
x
7-
Inhaled body
Non central
Chest Pain
Acute chest pain:
Pleural (pleurisy)
Chest wall
1- Pneumothorax
2- Pulmonary infarction
Cardiac
1- Angina & MI
2- Dissecting aortic
aneurysm
3- Acute pericarditis
central
3- Infection:
- Pneumonia
- TB
- Bronchiectasis
- Lung abcess.
Chest
4- Malignancy:
1- Pneumothorax
- mesothelioma
2- Pulmonary embolism
- metastatic
3- Pleurisy
4- Oesophageal spasm
5- C.T. disease:
5- H. zoster
- R.arthritis
- SLE .
1- Malignancy:
- lung cancer
- mesothelioma
- bony metastases
2- Muscles:
- strains/tears
- Myositis
- Bornholm's disease
(Coxsackie B infection)
3- Ribs:
- costochondritis(Tietze's sy.)
- Periostitis
- Fracture .
4- Nerves:
1- Coronary HD :
angina
Myocardial infarction
Tracheal
Infection
Irritant dusts
Oesophageal
Oesophagitis
Oesophageal achalasia
Oesophageal spasm
Rupture
2- Pericardial disease:
Pericarditis
Pericardial effusion
Mediastinitis
Mediastinal emphysema.
Lymphadenopathy
3- Pulmonary embolism:
Massive Pulmonary mbolism
Pulmonary infarction
4- Aorta diseases:
Dissecting aneurysm of aorta
Aortic aneurysm
Mediastinal
Cardiac &
Great vessels
-Intercostal nerve compression
- herpes zoster
Referred Pain
- Gastritis & peptic ulcer
- Gall bladder disease
- Amebic liver abcess
- Subphernic abcess
- Peritonitis
- Cardiac neurosis.
5- Persistent cough/ dysp.
False haemoptysis : blood originating above level of vocal cords .
Hemoptysis
Hematological
causes :
1- Leukemia
2- Purpura
3- Anti-coagulation
4- Blood dyscrasias
Tumour:
Infection
Frank Haemptysis:
1- TB
2- Bronchogenic
Carcinoma
3- Bronchial
adenoma
4- Bronchiectasis
Vascular
1- bleeding from gum
2- Pharyngeal causes
3- Epistaxis, of blood is post. nares is inhaled & coughed up.
Bronchogenic carcinoma Vasculitis Wegener's granulomatosis
(Systemic dis.) Goodpasture's syndrome
Bronchial adnemoa
Acute bronchitis (main)
Bronchiectasis
Lung abscess
TB
Cystic fibrosis
Mycetoma
Pulmonary infarction
Arteriovenous malformation
Trauma
- Inhaled foreign body
- Chest trauma
- Iatrogenic:
bronchoscopic biopsy
transthoracic lung biopsy
bronchoscopic diathermy
LVF
Hematemesis
Frank :
M.S
Acute left ventricular
failure
Pulmonary infarction
-
Frothy blood tinged sputum :
- Acute pulmonary edema
Causes of upper GIT bleeding :
- Oesophagogastric varices
- Mallory-Weiss tear
- Gastric ulcer
- Duodenal ulcer
- Oesophagitis,gastritis, duodenitis
- Oesophageal or gastric cancer
- Profuse nose bleeds (false)
- Vascular malformation
N.B.
Bright red hematemsis occurs if :
1- Bleeding is massive.
2- Presence of hypochlorhydria
Pulmonary congestion
Pulmonary edema
sicca haemorrhagica.
Haematemesis is vomiting blood. The blood can be fresh
and red, or degraded by gastric pepsin, when it is dark in
colour and resembles 'coffee grounds'.
-Upper GIT bleeding results in melaena.
- Spurious melaena :
Ingestion of blood of epistaxis or haemoptysis.
Cough
Others :
1- Encephalitis &
meningitis
2- Hysterical
Acute
(<3 weeks)
with strido & horseness of voice )
asthma
Extrinsic
alveolitis
3-
Recurrent
pulmonary embolism
4Neurosis
5-
Mediastinal
Sydrome
6-
Chronic
(>8 weeks)
Whooping
cough.
Suppurative lung
diseases :
1- Bronchiectasis
2- Lung abcess
- Tracheitis ( brassy painful cough )
-Inhaled foreign body
-Inhaled irritants (dusts/fumes)
-GORD
-Asthma
-Post-viral bronchial hyperreactivity
-Rhinitis / sinusitis post nasal drip
-Cigarette smoking
-Drugs: ACE inhibitors
-Irritant dusts/fumes.
Causes of Paroxysmal dyspnea :
1- Pulmonary venous congestion
(with frothy sputum)
2- Pulmonary edema ( with frothy
pink sputum )
-Laryngitis (whooping, barking in character may
Bronchial
2-
Abnormal chest x-ray
- Pneumonia.
-Acute extrinsic allergic alveolitis.
throat)
Paroxysmal cough:
1-
Normal chest x-ray
-Acute episode of asthma.
- Viral infection
- Bacterial infection (acute bronchitis)
-Pharyngitis( expolsive , painful with sore
(Dry cough)
1- Subdiaphragmatic infection.
2- Vagal stimulation e.g.
gastroduodenal disease
3- Cardiac asthma. (with wheezy chest)
-Lung tumor.
-T.B
-Bronchiectasis.
-Interstitial lung disease.
The patients wakes up 1-2 hours after sleep with
marked dyspnea , cough, with frothy expectoration.
Cough of suppurative lung diseases ( or cavitary syndrome) :
- With huge amount of yellow-greenish fluid sputum ( > teecupful/day )
- Cough & expectoration is related to posture
3- Empyema with
brocho-pleural fistula
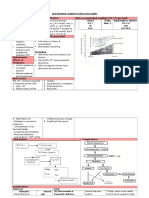
Types of sputum
Type
Serous
Others
Mucoid
Appearance
Clear, watery
Frothy, pink
Clear, grey
White, viscid
Yellow
Purulent
Cause
Acute pulmonary oedema
Alveolar cell cancer
Chronic bronchitis/COPD
Asthma
Acute bronchopulmonary infection
Asthma .
Long-Standing infection :
Palpitation
1- Rapid heart pain :
Sinus or paroxysmal tachycardia
2- Forcible heart contraction :
A.R M.S
3- Arrhythmias :
Extrasystole or A.F.
4- Cardiac neurosis.
Syncope
Rectal Bleeding
Haemorrhoids
Anal fissure
Colorectal polyps
Colorectal cancer
Inflammatory bowel disease
Ischaemic colitis
Dr.Ahmados
1- Cardiac syncope: (due to low COP )
Hemorrhage AS HF P.embolism & infarction
Massive M.infarction .
2- Neurocardiogenic syncope :
- Vasovagal attack: exposure to fear, emotions
- Stimulation of hypersensitive
3- Orthostatic syncope "postural" :
Autonomic neuropathy(DM) huge varicose veins
essential postural hypotension.
4- Neurological :
Transient ischemic attacks , hypertensive
encephalopathy sever anemia hypoglycemia F4
Complicated diverticular disease
Vascular malformation
Massive upper gastrointestinal
bleeding
Aorto-enteric fistula
Endometriosis in the rectum
You might also like
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- GI Signs and SymptomsDocument40 pagesGI Signs and SymptomsJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnosis Information OverviewDocument119 pagesPhysical Diagnosis Information OverviewNarcis PopaNo ratings yet
- YEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas PayneDocument30 pagesYEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas Payneminayoki100% (1)
- Heart MurmursDocument16 pagesHeart MurmursPriyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Schwartz 9th Ed: Chapter Outline: The SpleenDocument22 pagesSchwartz 9th Ed: Chapter Outline: The SpleenKathryn Reunilla100% (1)
- Hepatobiliary Notes 2.0Document18 pagesHepatobiliary Notes 2.0Sri VathanahNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Vs Cyanotic Congenital Heart DefectsDocument2 pagesAcyanotic Vs Cyanotic Congenital Heart Defectstainah07No ratings yet
- IM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitDocument12 pagesIM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitCzara DyNo ratings yet
- Path MnemonicsDocument7 pagesPath MnemonicsDrAbhilash RMNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia Approach and ManagementDocument41 pagesTachycardia Approach and ManagementChadi Alraies100% (5)
- 3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraDocument6 pages3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraCassey Koi FarmNo ratings yet
- Child With Bruises 00Document36 pagesChild With Bruises 00Awatef AbushhiwaNo ratings yet
- أدوية الطوارىءDocument162 pagesأدوية الطوارىءManar22No ratings yet
- DDX Gastrointestinal Disorders ChartDocument20 pagesDDX Gastrointestinal Disorders ChartDavid UribeNo ratings yet
- Shock, Sirs & ModsDocument37 pagesShock, Sirs & ModsambitioustamannaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanDocument27 pagesThyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanMarrah Avila Acuin100% (1)
- Female Genital TractDocument5 pagesFemale Genital Tractsarguss14100% (1)
- Aquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45Document8 pagesAquifer InternalMedicine11 - 45JulieNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergencies FlashcardsDocument109 pagesMedical Emergencies Flashcardsmkct111No ratings yet
- Trusted Medical Answers-In Seconds.: Chest PainDocument22 pagesTrusted Medical Answers-In Seconds.: Chest PainntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- CARAS SCUTSHEET 2nd EditDocument2 pagesCARAS SCUTSHEET 2nd EditFrances Katrina Siruno100% (1)
- Medical MneumonicsDocument139 pagesMedical MneumonicsdrtpkNo ratings yet
- IM NotesDocument79 pagesIM NotesInri Dumlao100% (1)
- Part IIDocument64 pagesPart IIhussainNo ratings yet
- History and Physical Exam SkillsDocument7 pagesHistory and Physical Exam SkillsAnonymous Sfcml4GvZNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular BigDocument37 pagesCardiovascular Bigfaiz nasirNo ratings yet
- Gyne Case COCDocument37 pagesGyne Case COCLian BaylosisNo ratings yet
- Dermatopathology Quick Reference Guide for Inflammatory Superficial Perivascular DisordersDocument2 pagesDermatopathology Quick Reference Guide for Inflammatory Superficial Perivascular DisordersBob LoblawNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Achalasia DysphagiaDocument14 pagesEsophageal Achalasia DysphagiaTirtha Taposh100% (1)
- Pre Exam Surgical Notes 2Document166 pagesPre Exam Surgical Notes 2flor vickyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsDocument22 pagesPediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument29 pagesPericarditisPavin KumarNo ratings yet
- Sherif EL Hawary, MD Professor of Internal Medicine Kasr AL AiniDocument35 pagesSherif EL Hawary, MD Professor of Internal Medicine Kasr AL Aini670411No ratings yet
- History Taking 2. Physical Examination 3. Diagnostic TestsDocument33 pagesHistory Taking 2. Physical Examination 3. Diagnostic TestsAmalNo ratings yet
- Approach To Cough and HemoptysisDocument24 pagesApproach To Cough and Hemoptysisbansaleliza26No ratings yet
- Respiratory Diseases 2Document20 pagesRespiratory Diseases 2Fares KhaledNo ratings yet
- Acute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDDocument49 pagesAcute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDHendraDarmawanNo ratings yet
- Emergency in Respiratory Medicine HandbookDocument73 pagesEmergency in Respiratory Medicine HandbookIndra MahaputraNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hypertension: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms and DiagnosisDocument40 pagesPulmonary Hypertension: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms and DiagnosisAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- Part III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersDocument91 pagesPart III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersFırat GüllüNo ratings yet
- Clinical Physiology of Respiration: Dr. M Qathar RF TDocument76 pagesClinical Physiology of Respiration: Dr. M Qathar RF TTiwi Lestari TiwiNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Respiratory DiseaseDocument70 pagesSymptoms of Respiratory DiseaseDr-i BarreNo ratings yet
- A.respiratory HistoryDocument3 pagesA.respiratory HistoryEl SpinnerNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfDocument49 pagesPulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfKrisno ParammanganNo ratings yet
- Sesak Napas Arimbi (PBL)Document50 pagesSesak Napas Arimbi (PBL)Endik SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument8 pagesResearch MethodsSilver DrakeNo ratings yet
- Systemic Disorders of The LungDocument74 pagesSystemic Disorders of The Lungjhay-r reyesNo ratings yet
- HemoptysisDocument32 pagesHemoptysisbudiNo ratings yet
- COPD:RLDDocument11 pagesCOPD:RLDKhiara Yapha AlfarNo ratings yet
- DyspneaDocument6 pagesDyspneaIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfDocument49 pagesPulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfSef NengkoNo ratings yet
- An Approach To A Patient With BreathlessnessDocument35 pagesAn Approach To A Patient With Breathlessnessgl tousifNo ratings yet
- 5. Hemoptysis 讲稿Document4 pages5. Hemoptysis 讲稿mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Signs of Pulmonary DiseasesDocument29 pagesSymptoms and Signs of Pulmonary DiseasesDiana_anca6No ratings yet
- History Taking and Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument48 pagesHistory Taking and Examination of Respiratory SystemAlfina Aulia RizkiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DDXDocument3 pagesRespiratory DDXKathryn BrooksNo ratings yet
- 4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyDocument56 pages4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyReynandriel100% (1)
- Approach To The Patient With Cough and Hemoptysis 15 11 13Document34 pagesApproach To The Patient With Cough and Hemoptysis 15 11 13Sanchit PeriwalNo ratings yet
- IM NotesDocument74 pagesIM NotesRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Obsandgyne Tables 200pagesDocument221 pagesObsandgyne Tables 200pagesRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Sga IugrDocument6 pagesBelle Sga IugrRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle PuerperiumDocument11 pagesBelle PuerperiumRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle RH IsoimmunizationDocument3 pagesBelle RH IsoimmunizationRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- PRETERM BIRTH CLASSIFICATION, ETIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENTDocument3 pagesPRETERM BIRTH CLASSIFICATION, ETIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENTRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle STDDocument8 pagesBelle STDRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle-Fetal Growth AssessmentDocument10 pagesBelle-Fetal Growth AssessmentRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle-Premature Rupture of MembraneDocument5 pagesBelle-Premature Rupture of MembraneRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Vaginal DischargeDocument12 pagesBelle Vaginal DischargeRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle PuerperiumDocument10 pagesBelle PuerperiumRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dystocia Risks & ManagementDocument2 pagesShoulder Dystocia Risks & ManagementRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle-Preterm Labour ManagementDocument4 pagesBelle-Preterm Labour ManagementRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Prolonged PregnancyDocument2 pagesBelle Prolonged PregnancyRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Preterm BirthDocument9 pagesBelle Preterm BirthRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Preinvasive Invasive Cervical DiseaseDocument5 pagesBelle Preinvasive Invasive Cervical DiseaseRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle PPHDocument4 pagesBelle PPHRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Infertility Management ARTDocument6 pagesBelle Infertility Management ARTRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Ovarian NeoplasmDocument6 pagesBelle Ovarian NeoplasmRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle PIDDocument2 pagesBelle PIDRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle MenopauseDocument7 pagesBelle MenopauseRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Multiple GestationsDocument2 pagesBelle Multiple GestationsRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Induction of LaborDocument5 pagesBelle Induction of LaborRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- (Belle) MalpresentationDocument4 pages(Belle) MalpresentationAray Al-AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Belle Malignant Lesions of The Body of UterusDocument2 pagesBelle Malignant Lesions of The Body of UterusRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle-Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesBelle-Gestational Diabetes MellitusRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Medical Disorders in PregnancyDocument4 pagesBelle Medical Disorders in PregnancyRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Instruments For OGDocument1 pageBelle Instruments For OGRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle-Drugs in PregnancyDocument17 pagesBelle-Drugs in PregnancyRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Belle Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDocument6 pagesBelle Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Cell Salts William BoerickDocument525 pagesCell Salts William BoerickSorabh Sharma100% (1)
- Management of Orthostatic Hypotension.12-1Document24 pagesManagement of Orthostatic Hypotension.12-1Cristina GhizdavetNo ratings yet
- Bowel Nosodes - John PatersonDocument25 pagesBowel Nosodes - John PatersonIkram Manzoor100% (1)
- Orthodontics in Medically CompromisedDocument189 pagesOrthodontics in Medically CompromisedAshish MathewNo ratings yet
- Common OSCE CasesDocument6 pagesCommon OSCE CasesRosa AlersNo ratings yet
- Introductory Training PacketDocument8 pagesIntroductory Training Packetdonna summersNo ratings yet
- Kasturi Sonawane - FYReportDocument62 pagesKasturi Sonawane - FYReportKasturi SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Cto 16 02Document29 pagesCto 16 02sivakumar GNo ratings yet
- Bhatti NotesDocument100 pagesBhatti NotesSergio Chang100% (2)
- Long QT SyndromeDocument15 pagesLong QT Syndromeprudhvi gallaNo ratings yet
- FDocument197 pagesFAneuk Agam JinoeNo ratings yet
- Post Operative Emergency Management in Periodontics PeioDocument40 pagesPost Operative Emergency Management in Periodontics PeioFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergencies in DentistryDocument1 pageMedical Emergencies in Dentistrylaur_rbNo ratings yet
- Informative Speech: Thinking About This AssignmentDocument6 pagesInformative Speech: Thinking About This AssignmentChaosJNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergencies in OSDocument62 pagesMedical Emergencies in OSAditi RapriyaNo ratings yet
- iTIJ:: P4Yicai. Etfal - Uati OnDocument4 pagesiTIJ:: P4Yicai. Etfal - Uati OnBartolome MercadoNo ratings yet
- N174 Physical Assessment-Final Study GuideDocument14 pagesN174 Physical Assessment-Final Study GuideMark Angelo Picar AbelleraNo ratings yet
- FaintingDocument5 pagesFaintingJothilavinia VD100% (1)
- HT of Cardiovasc Diseases - Kelompok 1Document54 pagesHT of Cardiovasc Diseases - Kelompok 1Nadya Auliarahma SamiadjiNo ratings yet
- Heart Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1136 - Heartjnl-2017-312112) Ruwald, Martin H - Syncope andDocument3 pagesHeart Volume Issue 2017 (Doi 10.1136 - Heartjnl-2017-312112) Ruwald, Martin H - Syncope andZauzaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias: Self-Learning GuideDocument74 pagesMechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias: Self-Learning Guideyasahswi91No ratings yet
- Patient desire most important factor to quit smokingDocument96 pagesPatient desire most important factor to quit smokingAsif Newaz0% (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation - Geeky MedicsDocument10 pagesAtrial Fibrillation - Geeky MedicsJahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- General Health Questions: The Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire For EveryoneDocument4 pagesGeneral Health Questions: The Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire For EveryoneLenard PagsisihanNo ratings yet
- كورس اللابDocument110 pagesكورس اللابgaber 230No ratings yet
- 3rd Year OSCE StationsDocument6 pages3rd Year OSCE StationsrutendonormamapurisaNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument4 pagesIsosorbide DinitrateManelle Singzon100% (1)
- Principles of Medication AdministrationDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Medication AdministrationTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- CMS Neuro 1 AnswersDocument13 pagesCMS Neuro 1 AnswersKomal Menon100% (14)
- Anaphylactic ShockDocument36 pagesAnaphylactic ShockCarmelli Mariae Calugay100% (1)