Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 - Covalent and Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
EbadHassan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views4 pagesNotes on Covalent and Metallic Bonding.A part of the topic bonding and structure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNotes on Covalent and Metallic Bonding.A part of the topic bonding and structure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views4 pagesChapter 8 - Covalent and Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
EbadHassanNotes on Covalent and Metallic Bonding.A part of the topic bonding and structure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Chap 8: Covalent and Metallic Bonding
I). Covalent Bonds:
The bond formed between atoms that share electrons is called a covalent bond. After bonding, each
electron attains the electronic configuration of a noble gas, or attains stability. This bond is formed
between a non-metal and a non-metal.
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds. Covalent compounds do not
have chemical formulae; instead, they have molecular formulae.
Formation and Arrangement:
Many non-metallic elements exist as diatomic molecules. This means that they always exist in the
molecular state, with two identical atoms joined together through covalent bonding. For example,
hydrogen gas always exists as H2, which is its diatomic form.
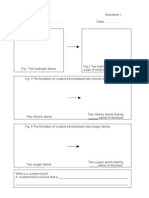
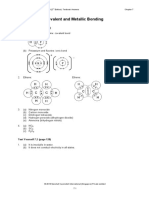
Fig 8.1. Covalent bond in Hydrogen molecule.
Note: always show the electrons of different members with different signs, i.e. one with a dot and the
other with a cross.
There are other ways of representing a hydrogen molecule as well:
Molecular Formula: H2
Dot & cross diagram: HH
Structural Formula: H
H (The single line shows a single covalent bond.)
The sharing of two electrons, or a pair of electrons, forms a single covalent bond.
Between each molecule of a covalent compound, there are weak van der Waals forces holding the
molecules together.
Other Examples:
Fig 8.3. Cl2 molecule, Cl Cl
Fig 8.2. O2 molecule, O=O
Covalent Compounds:
Molecules made from two or more different types of atoms linked together by covalent bonding are called
molecular compounds or covalent compounds.
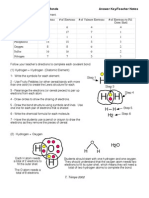
A common example is H2O, water. It is made up of two single covalent bonds.
Fig 8.3. H2O
molecule,
Another example is CH4, methane. It has four single bonds in it.
Fig 8.4. CH4 molecule,
Carbon dioxide, CO2, has two double bonds.
Fig 8.5. CO2 molecule, O=C=O
Physical Properties:
They have low melting and boiling points.
They are mostly gases or volatile liquids at room temperature.
Most are insoluble in water, and soluble in organic compounds.
Most do not conduct electricity in either solid, liquid or gaseous state.
II). Metallic Bonding:
Metal atoms are held strongly to each other by metallic bonding. In the metal lattice, the atoms lose their
valence electrons and become positively charged. The valence electrons no longer belong to any metal
atom and are said to be delocalised. They move freely between the metal ions like a cloud of negative
charge. Hence, this lattice structure is described as a lattice of positive ions surrounded by a sea of
mobile electrons. Therefore a metallic bond can be defined as: the force of attraction between positive
metal ions and the sea of delocalised electrons.
Physical Properties of Metals:
They are good conductors of electricity.
They are good conductors of heat.
They are malleable (can be hammered into different shapes).
They are ductile (can be drawn into wires without breaking).
You might also like
- Bonding, Structure and Periodicity TestDocument8 pagesBonding, Structure and Periodicity Testpaulcampbell37No ratings yet
- Chem Int CC CH 12 - Stoichiometry - Answers (09.15)Document7 pagesChem Int CC CH 12 - Stoichiometry - Answers (09.15)Emma GillesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Periodic TableDocument45 pagesChapter 5 The Periodic Tableapi-30718309No ratings yet
- CHPT 12.2 PowerpointDocument62 pagesCHPT 12.2 PowerpointA ANo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument2 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsGENERAL COCNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic Trends ActivityDocument6 pagesChemistry Periodic Trends ActivityocNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Practice Test GuideDocument10 pagesGas Laws Practice Test GuideTAHA GABRNo ratings yet
- Free Online Science Education ResourcesDocument17 pagesFree Online Science Education ResourcesDIONYSUS100% (1)
- RedoxDocument2 pagesRedoxFiza SakraniNo ratings yet
- Test-2-10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Test 02Document2 pagesTest-2-10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Test 02Ramesh MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Test-2-Key-10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Test 02 Answer 0n4sDocument2 pagesTest-2-Key-10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Test 02 Answer 0n4sRamesh MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 5Document9 pagesWorksheet Chapter 5Maktok Azi RahimNo ratings yet
- Chap15 Periodic TableDocument32 pagesChap15 Periodic TableSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- 7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyDocument8 pages7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyXazerco LaxNo ratings yet
- Organizing Elements Int - Reader - Study - Guide PDFDocument4 pagesOrganizing Elements Int - Reader - Study - Guide PDFMiguel RuizNo ratings yet
- Unit 15 - Reaction Rates and EquilibriumDocument68 pagesUnit 15 - Reaction Rates and EquilibriumGarett Berumen-RoqueNo ratings yet
- Chem M17 Reaction Rates & EquilibriumDocument17 pagesChem M17 Reaction Rates & EquilibriumRosanna LombresNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Binary Ternary and AcidsDocument43 pagesNomenclature Binary Ternary and AcidsSofia PaganNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Test ReviewDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding Test ReviewAlakh Jagtap100% (1)
- Shapes of Molecules and Ions PDFDocument9 pagesShapes of Molecules and Ions PDFMagenta SparklegemNo ratings yet
- POGIL Avg Atomic Mass KEYDocument4 pagesPOGIL Avg Atomic Mass KEYbobNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument4 pagesMolecular PolarityTea RadicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingDocument56 pagesChapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingCharles GibbsNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Guide to Chemical BondingDocument9 pagesGCSE Chemistry Guide to Chemical BondingSabsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Presented By: Mohammad Fayiz Akhtar SP05-AA-0017 Presented To: Afsheen Khalil Presented On: 04-OCT-2006Document12 pagesChemical Bonding: Presented By: Mohammad Fayiz Akhtar SP05-AA-0017 Presented To: Afsheen Khalil Presented On: 04-OCT-2006helperforeuNo ratings yet
- Week12 Mole Student 2019Document35 pagesWeek12 Mole Student 2019api-4915646430% (1)
- Chemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Document6 pagesChemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Anisah MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TestDocument5 pagesChapter 6 TesthelloblargNo ratings yet
- Redox WKSHTDocument4 pagesRedox WKSHTMarco ConopioNo ratings yet
- Dot Structures Practice PacketDocument6 pagesDot Structures Practice Packetgoogley71No ratings yet
- Bonding Test ReviewDocument5 pagesBonding Test ReviewRonaldo ManaoatNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1211 Worksheet Covalent BondingDocument3 pagesCHEM 1211 Worksheet Covalent Bondingyash patel0% (1)
- Addition Polymers and Polyester Student NotesDocument8 pagesAddition Polymers and Polyester Student Notesapi-277345420No ratings yet
- CH 7 Practice Test Honor Chem Naming CompoundsDocument8 pagesCH 7 Practice Test Honor Chem Naming CompoundsBeth0% (1)
- Pre-IB Chemistry Mid-Term Review List (Nagel)Document3 pagesPre-IB Chemistry Mid-Term Review List (Nagel)Helie100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument8 pagesChemical Reactions and Equationsapi-246793885No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document4 pagesChapter 11John Christian De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Names and Formulas: 9.1 Naming IonsDocument53 pagesChemical Names and Formulas: 9.1 Naming IonsLovieAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Document4 pagesChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaNo ratings yet
- Bonding Basics CovalentDocument2 pagesBonding Basics Covalentwosli350% (2)
- Notes and Questions: Aqa GcseDocument12 pagesNotes and Questions: Aqa Gcseapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Kinetic Particle TheorykitoniumNo ratings yet
- Polar Covalent BondsDocument10 pagesPolar Covalent BondsParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Chemical Reactions and EquationsayanNo ratings yet
- History and Models of The AtomDocument26 pagesHistory and Models of The AtomDexter MumaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 - Introduction To Stoichiometry Guided Notes AssignmentDocument15 pagesDay 2 - Introduction To Stoichiometry Guided Notes AssignmentDaveNo ratings yet
- COVALENT BONDING EXPLAINEDDocument91 pagesCOVALENT BONDING EXPLAINEDNorhafiza RoslanNo ratings yet
- I B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingDocument7 pagesI B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingMuy TamNo ratings yet
- Mole Ratio WorksheetDocument2 pagesMole Ratio WorksheetmillsaprunnerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulas All WorksheetsDocument19 pagesChemical Formulas All Worksheetsshivam33% (3)
- Types of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFDocument4 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFStefanie CorcoranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Physical and Chemical Change Law of Conservation of Mass and Balancing Equations PDFDocument44 pagesLesson 1 Physical and Chemical Change Law of Conservation of Mass and Balancing Equations PDFJellyNo ratings yet
- Mole Conversion ClassworkDocument4 pagesMole Conversion ClassworkAdvanced PastryNo ratings yet
- Science Notes For Class 10 Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument4 pagesScience Notes For Class 10 Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elementscrazy about readingNo ratings yet
- Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedDocument13 pagesTest4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedEga SukmaNo ratings yet
- Biophysical Chemistry: Thermodynamics, Electrostatics, and the Biological Significance of the Properties of MatterFrom EverandBiophysical Chemistry: Thermodynamics, Electrostatics, and the Biological Significance of the Properties of MatterNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding1Document26 pagesCovalent Bonding1BaselNo ratings yet
- Molecular Compounds and Covalent BondingDocument19 pagesMolecular Compounds and Covalent BondingHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compound - WikipediaDocument7 pagesChemical Compound - Wikipediatsvmpm1765No ratings yet
- Peek Freans Cake Up Advertisement Analysis (With Advertisement)Document23 pagesPeek Freans Cake Up Advertisement Analysis (With Advertisement)EbadHassanNo ratings yet
- Overcome Communication ApprehensionDocument9 pagesOvercome Communication ApprehensionEbadHassanNo ratings yet
- Selected Qusetions Pakistan Studies Paper 1Document8 pagesSelected Qusetions Pakistan Studies Paper 1oalevels86% (7)
- Computer Studies NotesDocument30 pagesComputer Studies Notessyed_talha_373% (11)
- Economics NotesDocument44 pagesEconomics NotesEbadHassan0% (1)
- Cambridge Learner Guide For o Level PhysicsDocument50 pagesCambridge Learner Guide For o Level PhysicsEbadHassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument4 pagesChapter 8 - Covalent and Metallic BondingEbadHassanNo ratings yet
- General Wave PropertiesDocument5 pagesGeneral Wave PropertiesEbadHassanNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCurrent ElectricityPeter KachouhNo ratings yet
- Guide On DiseasesDocument56 pagesGuide On DiseasesEbadHassanNo ratings yet
- Geography Pakstudies Notes of Chapter 3 4 5 6 o LevelDocument19 pagesGeography Pakstudies Notes of Chapter 3 4 5 6 o LevelMohsin Hassan Khan67% (9)
- Pakistan Studies Paper 1 SectionDocument20 pagesPakistan Studies Paper 1 SectionIraj Aziz100% (1)
- Static ElectricityDocument4 pagesStatic ElectricityMuhammad Wasil KhanNo ratings yet
- Sutton - Electronic Structure of Materials PDFDocument275 pagesSutton - Electronic Structure of Materials PDFHaroldMartinezNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes CHPTR 5Document6 pagesChem Notes CHPTR 5Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Family Study NotesDocument61 pagesNitrogen Family Study NotesBelezza CoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 q3 Slm4Document15 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 q3 Slm4Christine Mae LlabanNo ratings yet
- MCQ UNIT1 Chemical Bonding From Nirali CHEMISTRY - With AnswerDocument6 pagesMCQ UNIT1 Chemical Bonding From Nirali CHEMISTRY - With AnswerSantosh Kulkarni100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Notes MinDocument98 pagesChemical Bonding Notes Minnandhini rajendarNo ratings yet
- STD 12th Perfect Chemistry 2 Notes Science MH Board 1Document50 pagesSTD 12th Perfect Chemistry 2 Notes Science MH Board 1TheGuyWhoLovesTheWorld100% (1)
- Learning Plan For Metallic BondingDocument6 pagesLearning Plan For Metallic BondingFrancisca Catacutan100% (1)
- Presented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Document56 pagesPresented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Bela GhummanNo ratings yet
- Crystal BondingDocument12 pagesCrystal BondingSuyogNo ratings yet
- An Appreciation of The Classic Valence Bond TheoryDocument42 pagesAn Appreciation of The Classic Valence Bond TheoryChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Intermetallische Phasen - Antworten-1-30 en-USDocument30 pagesIntermetallische Phasen - Antworten-1-30 en-USLorena juárezNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument45 pagesChemical BondingFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument16 pagesMetallic Bondingmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise On Structures & Properties: S3 ChemistryDocument16 pagesRevision Exercise On Structures & Properties: S3 Chemistrysimonlee2007No ratings yet
- Electron Theory of Metals: 2.1 ConductivityDocument32 pagesElectron Theory of Metals: 2.1 ConductivityriponkumarNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Periodicity (STUDENT) Edited 20apr2017 PDFDocument116 pages3.2 Periodicity (STUDENT) Edited 20apr2017 PDFAliffuddin MohamadNo ratings yet
- Modern Materials' Atomic StructureDocument47 pagesModern Materials' Atomic StructureAngelica MartinezNo ratings yet
- David Hudson Patent For The Preparation of G-OrMEDocument17 pagesDavid Hudson Patent For The Preparation of G-OrMEGeoff Harris100% (2)
- Covalent and Metallic Bonding: Test Yourself 7.1 (Page 114)Document2 pagesCovalent and Metallic Bonding: Test Yourself 7.1 (Page 114)khalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- CHE 413N Problem Set 1: Materials Science ConceptsDocument1 pageCHE 413N Problem Set 1: Materials Science ConceptsLouie G NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 SenguptaDocument38 pagesPhysics 2 SenguptaSashank PrayagaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFDocument8 pagesStudy Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFNicolyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Materials: Principles of EngineeringDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Materials: Principles of EngineeringPrakharNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding Updated 2Document82 pagesStructure and Bonding Updated 2jadabrown542No ratings yet
- Types of Solids 1Document16 pagesTypes of Solids 1Fern BaldonazaNo ratings yet
- Joanna Eve Alexandra O. Ramos Regine J. Remoroza Glenn Oliver L. Ferrer Allan L. Escanilla Ramdolf GenerDocument44 pagesJoanna Eve Alexandra O. Ramos Regine J. Remoroza Glenn Oliver L. Ferrer Allan L. Escanilla Ramdolf GenerDexter EnthusiastsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HOTS questions on solid stateDocument5 pagesChemistry HOTS questions on solid stateSuparnaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table 2 PDFDocument18 pagesPeriodic Table 2 PDFDiksha Bansal100% (1)
- Chapter 24 - Group IVDocument9 pagesChapter 24 - Group IVNicole MutumhaNo ratings yet