Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kfs Unit II Two Marks With Answer
Uploaded by
Sivakumar K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views2 pagesknitted fabric structure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentknitted fabric structure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views2 pagesKfs Unit II Two Marks With Answer
Uploaded by
Sivakumar Kknitted fabric structure
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1.
List out types of needle used in weft knitting
There are three types of needles namely:
Latch needle
Spring bearded needle,
Compound needle
2. Define knitting
Knitting is a process of fabric forming by the intermeshing of loops of yarns. When one loop is
drawn through another, loop stitch is formed. Stitches may be formed in horizontal or vertical
direction.
3. Mention the types stitches produced in weft knitting
Four principal stitches utilized in knit fabrics
Knit stitch
Purl Stitch
Miss stitch
Tuck stitch
4. Write the characteristics of tuck stitch
Thicker than knit stitch
Less extensible
Loop shape is wider
Stitches are wider than knit stitch
More open and porous
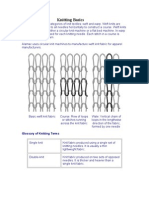
5. Define. Knitting Notations.
A knitting notation is a simple, easily understood, symbolic representation of a knitting repeat
sequence and its resultant fabric structure that eliminates the need for time-consuming and
possibly confusing sketches.
6. List out the methods used for knitting notations.
Verbal Notations
Structural notation Notations
Symbolic Notations
Diagrammatic Notations
7. List out the characteristics of float stitch
Fabric becoming narrower and minimum width
Uniform texture is obtained
Less extensible compared with other
Fabric lighter weight
8. What are advantages of notation in weft knitting?
It is simple
Easily-understand the design,
Symbolic representation used for knitting repeat sequence and its resultant fabric
structure that eliminates the need for time-consuming and possibly confusing sketches.
9. Give the symbolic representations for tuck and miss stitch
Tuck stitch
Miss stitch
10. How tuck stitch is formed in weft knitting?
A tuck stitch is formed when a knitting needle holds its old loop and then receives a new yarn.
Two loops then collect in the needle hook. The previously formed knitted loop is called the held
loop and the loop which joins it is a tuck loop.
11. How knit stitch is formed in weft knitting?
Knit stitch is formed when the needle carries out a complete stroke, reaching the maximum
height on the looping plane.
12. Mention the all basic weft structures.
Plain
Rib
Interlock
Purl
13. How miss stitch is formed in weft knitting
A miss stitch is created when one or more knitting needles are deactivated and do not move into
position to accept the yarn. The yarn merely passes by and no stitch is formed.
14. Distinguish between tuck and knit stitches.
15. Give the symbolic representation for knit, purl, tuck and float stitch?
16. Mention the various patterning mechanisms used in weft knitting.
17. Write the importance of patterning mechanism in knitting.
18. Draw the diagrammatic representation for all stitches.
19. What are tape patterning devices?
20. What is three way techniques?
21. What are limitations of pattern drum in patterning?
22. Give the characteristics of knit stitch.
23. What is two way techniques?
24. List out the effect of tuck stitch in knitted fabric properties.
25. List out the effect of miss stitch in knitted fabric properties.
26. Give the symbolic representation of principal weft knit stitches.
27. State the merits and demerits of verbal and thread diagram representation techniques.
28. Write the advantages of graphical and symbolic representation methods.
29. Draw the symbolic representation of Interlock.
30. What is the influence of tuck stitch on fabric property
31. State importance of patterning mechanism in knitting
32. What are function of wing cam
33. Write the advantage of pattern roll jacquard
34. What are advantages of electronic device used weft knit patterning?
35. Mention the role of pattern wheel in weft knitting
You might also like
- Knitting TechnologyDocument31 pagesKnitting TechnologyOviya CpNo ratings yet
- 09iuytghjkjhgvbnk Ijhjklkjhgfghjkl IuhgjkjhjDocument16 pages09iuytghjkjhgvbnk Ijhjklkjhgfghjkl Iuhgjkjhjsurya rajputNo ratings yet
- Knitting Assignment - MRKDocument5 pagesKnitting Assignment - MRKChandhanaNo ratings yet
- KnittingDocument9 pagesKnittingdevenderpal48No ratings yet
- Textiles and FashionDocument8 pagesTextiles and FashionangelamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document9 pagesLecture 13Arham BajwaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document10 pagesLecture 12Arham BajwaNo ratings yet
- Knitting TechnologyDocument17 pagesKnitting TechnologyMuhammad Ateeb AnsariNo ratings yet
- 13 Warp KnittingDocument3 pages13 Warp KnittingVasant Kothari100% (1)
- Miss, Tuck & Float StitchDocument23 pagesMiss, Tuck & Float StitchKazi Sabbir AhmadNo ratings yet
- knitting Views/January-February 2012 /knitting Views/January-February 2012Document3 pagesknitting Views/January-February 2012 /knitting Views/January-February 2012Sanghamitra KalitaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Fabric Structure and Design (Tt303) : VIGNAN UniversityDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 Fabric Structure and Design (Tt303) : VIGNAN UniversityMohammad Vaseem ChavhanNo ratings yet
- Short Note On Warp KnittingtDocument7 pagesShort Note On Warp KnittingtRezaul Karim Tutul100% (1)
- Theory of Silk Weaving A Treatise on the Construction and Application of Weaves, and the Decomposition and Calculation of Broad and Narrow, Plain, Novelty and Jacquard Silk FabricsFrom EverandTheory of Silk Weaving A Treatise on the Construction and Application of Weaves, and the Decomposition and Calculation of Broad and Narrow, Plain, Novelty and Jacquard Silk FabricsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Single Jersey and Rib FabricDocument5 pagesSingle Jersey and Rib FabricgagunzaNo ratings yet
- Cut Sew PP PDFDocument18 pagesCut Sew PP PDFRafiur Islam RatulNo ratings yet
- Fabric-Construction-Methods (Questions) PDFDocument6 pagesFabric-Construction-Methods (Questions) PDFTamer Farouk Khalifa67% (3)
- Course 224 - 1Document36 pagesCourse 224 - 1Mardiyya SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Historical Background of Knitting TechnologyDocument15 pagesHistorical Background of Knitting TechnologyMd.Shoeb Alom RoxyNo ratings yet
- KNT Final RomanaDocument49 pagesKNT Final RomanaSHAKIBNo ratings yet
- FM 1 KnittingDocument28 pagesFM 1 KnittingTextile Department Help Desk.DiuNo ratings yet
- Fabric ConstructionDocument12 pagesFabric Constructionsaran7ran100% (2)
- 6 Sem. B.Tech (Fashion & Apparel Technology) : PCFT 4304 Knitting & Non WovenDocument20 pages6 Sem. B.Tech (Fashion & Apparel Technology) : PCFT 4304 Knitting & Non WovenBebi WakaNo ratings yet
- Malimo enDocument24 pagesMalimo enHari Tham KhanNo ratings yet
- Knitting Fundamentals LecturesDocument44 pagesKnitting Fundamentals LecturesShohan Mohammad WasiuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Warp and Weft KnittingDocument6 pagesWarp and Weft KnittingPragya Dixit0% (1)
- Question Answer 1 PDFDocument12 pagesQuestion Answer 1 PDFArsalan Ahmed SheikhNo ratings yet
- Basics of Knitting Straight Bar Knitting MachineDocument3 pagesBasics of Knitting Straight Bar Knitting MachineVasant Kothari100% (4)
- Workshop KnittingDocument37 pagesWorkshop Knittingfathi mustafaNo ratings yet
- Knitting for Beginners: The Ultimate Craft Guide. Learn How to Knit Following Illustrated Practical Examples and Create Amazing ProjectsFrom EverandKnitting for Beginners: The Ultimate Craft Guide. Learn How to Knit Following Illustrated Practical Examples and Create Amazing ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Knitting Basics: Glossary of Knitting TermsDocument24 pagesKnitting Basics: Glossary of Knitting TermsrizvifarabiNo ratings yet
- Knitting Basics: Glossary of Knitting TermsDocument21 pagesKnitting Basics: Glossary of Knitting TermsrizvifarabiNo ratings yet
- Knit 1Document92 pagesKnit 1zinabu abrhaNo ratings yet
- .Knitting-1 Theory-Lecture-For Mid + FinalDocument33 pages.Knitting-1 Theory-Lecture-For Mid + FinalSanaullah MuradNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - KnittingDocument33 pagesChapter-2 - KnittingMD Shakil KhanNo ratings yet
- Fabric Construction MethodsDocument6 pagesFabric Construction MethodsgetmamunhoqNo ratings yet
- Yarn Substitution Made Easy: Matching the Right Yarn to Any Knitting PatternFrom EverandYarn Substitution Made Easy: Matching the Right Yarn to Any Knitting PatternNo ratings yet
- PROJECTevs 1Document14 pagesPROJECTevs 1Organ PcNo ratings yet
- Professional Institute of Science & Fashion Technology (PISFT)Document57 pagesProfessional Institute of Science & Fashion Technology (PISFT)ErRajeshNo ratings yet
- Types of Knit FabricDocument31 pagesTypes of Knit Fabricmeenurampal100% (2)
- Professional Institute of Science & Fashion Technology (PISFT)Document58 pagesProfessional Institute of Science & Fashion Technology (PISFT)দীপ্তি হুমাইরাNo ratings yet
- 79 97 ET V1 S1 - Unit - 1Document8 pages79 97 ET V1 S1 - Unit - 1Aruna KumarasiriNo ratings yet
- Textile Science - Unit 3-Q & ADocument98 pagesTextile Science - Unit 3-Q & AISHITA100% (1)
- Lock Stitch MachineDocument4 pagesLock Stitch MachineGaurav ShakyaNo ratings yet
- KnittingDocument13 pagesKnittingrakibNo ratings yet
- Aditya Itp FinalDocument56 pagesAditya Itp FinalAjay Kumar100% (2)
- Home AssignmentDocument6 pagesHome Assignmentshero indiaNo ratings yet
- Knitting: Introduction, History, Types of Needles and Knitting TypesDocument16 pagesKnitting: Introduction, History, Types of Needles and Knitting TypesangelamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Knitting ExplainedDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Knitting ExplainedGarmentLearnerNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - Basics of Fabric Production (Knitting)Document8 pages2.5 - Basics of Fabric Production (Knitting)R G Panneerselvam100% (1)
- Modular Crochet: The Revolutionary Method for Creating Custom-Designed PulloversFrom EverandModular Crochet: The Revolutionary Method for Creating Custom-Designed PulloversRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Knitting Technology IntroductionDocument72 pagesKnitting Technology IntroductionDr Muhammad Mushtaq Mangat100% (3)
- Knitting 2Document8 pagesKnitting 2Sanaullah MuradNo ratings yet
- Crochet Every Way Stitch Dictionary: 125 Essential Stitches to Crochet in Three WaysFrom EverandCrochet Every Way Stitch Dictionary: 125 Essential Stitches to Crochet in Three WaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Knitting Process: Escorts Advanced Textiles Distributor of Dupont PakistanDocument57 pagesKnitting Process: Escorts Advanced Textiles Distributor of Dupont PakistanJazib YaseenNo ratings yet
- Knit, Tuck and Miss StitchDocument4 pagesKnit, Tuck and Miss StitchVasant Kothari100% (11)
- 40 TT 404 - Knitting Technology QUESTION BANKDocument6 pages40 TT 404 - Knitting Technology QUESTION BANKSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Knit Deknit ProcessDocument9 pagesKnit Deknit ProcessSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Warp KnittingDocument93 pagesWarp KnittingSivakumar K100% (1)
- Flat Bed KnitingDocument21 pagesFlat Bed Knitingvasiney100% (1)
- Knit Deknit ProcessDocument9 pagesKnit Deknit ProcessSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Evaulation of False Twist YarnDocument25 pagesEvaulation of False Twist YarnSivakumar K100% (1)
- Knitting Elememts Sinker and CamDocument19 pagesKnitting Elememts Sinker and CamSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Eco FriendlyDocument50 pagesEco FriendlySivakumar K100% (1)
- Unit III - Clothing Science Question Bank WITH ANSWERDocument5 pagesUnit III - Clothing Science Question Bank WITH ANSWERSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Unit I Study Material CsDocument19 pagesUnit I Study Material CsSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Eco FriendlyDocument50 pagesEco FriendlySivakumar K100% (1)
- Unit I Clothing Science Two Marks With Answer and Question BankDocument3 pagesUnit I Clothing Science Two Marks With Answer and Question BankSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Unit III MerchandisingDocument103 pagesUnit III MerchandisingSivakumar K100% (2)
- Ssi IDocument13 pagesSsi ISivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document4 pagesUnit - 1Sivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Angel: College of Engineering and Technology TIRUPUR 641 665Document21 pagesAngel: College of Engineering and Technology TIRUPUR 641 665Sivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Warp Knitting BasicsDocument64 pagesWarp Knitting BasicsSivakumar K100% (1)
- Warp Knitting StructureDocument29 pagesWarp Knitting StructureSivakumar K100% (1)
- Kfs Study Material Unit IIDocument13 pagesKfs Study Material Unit IISivakumar K100% (1)
- Unit - II Kfs Two Marks With AnswerDocument4 pagesUnit - II Kfs Two Marks With AnswerSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Patteren Mechanism in Knitting - JacquardDocument27 pagesPatteren Mechanism in Knitting - JacquardSivakumar K100% (3)
- LykraDocument27 pagesLykraSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Warp Knitting StructureDocument29 pagesWarp Knitting StructureSivakumar K100% (1)
- Interlock StructuresDocument15 pagesInterlock StructuresSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- SpectrophotometerDocument46 pagesSpectrophotometerSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Colour FastnessDocument37 pagesColour FastnessSivakumar K100% (1)
- CC Unit I and Unit II Two Marks Question With AnswerDocument7 pagesCC Unit I and Unit II Two Marks Question With AnswerSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Unit I TCP Study MaterialDocument4 pagesUnit I TCP Study MaterialSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument2 pagesUnit VSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour - Mini Project - Amul Chocolate - Marketing StrategyDocument24 pagesOrganisational Behaviour - Mini Project - Amul Chocolate - Marketing StrategyNaresh RtNo ratings yet
- MDF253 Spirea PatternDocument13 pagesMDF253 Spirea PatternElisa VarhamNo ratings yet
- Ajrakh Printing: Design Resource Traditional Craft of Block Printing and Dyeing by Prof. Nina Sabnani IDC, IIT BombayDocument34 pagesAjrakh Printing: Design Resource Traditional Craft of Block Printing and Dyeing by Prof. Nina Sabnani IDC, IIT BombayparmeetkaurNo ratings yet
- Decoding The PatternDocument3 pagesDecoding The PatternCherry Escolano0% (1)
- Crochet PatternDocument31 pagesCrochet PatternAnca-Andreea HrițuleacNo ratings yet
- Beretta: Spring/Summer 2013 CatalogDocument48 pagesBeretta: Spring/Summer 2013 CatalogR Adhi NoegrohoNo ratings yet
- Events Management Services NC Iii PortfolioDocument31 pagesEvents Management Services NC Iii PortfolioEdwardArribaNo ratings yet
- loveFMD Issue6Document84 pagesloveFMD Issue6loveFMDNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL and 5PL LogisticsDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between 1PL, 2PL, 3PL, 4PL and 5PL LogisticsSuyog Sadanand Shembekar100% (2)
- Gold Anchor F&B and Culinary Review 2010A IndependenceDocument66 pagesGold Anchor F&B and Culinary Review 2010A Independencegellu77No ratings yet
- Silkworm and CocoonDocument4 pagesSilkworm and CocoonRemyaNo ratings yet
- RIDE 2015: Make Life A RideDocument49 pagesRIDE 2015: Make Life A RideMaximus TavusNo ratings yet
- Cypraea LeucodonDocument1 pageCypraea Leucodonshan_vegaNo ratings yet
- Warmaster Painting PDFDocument2 pagesWarmaster Painting PDFJean-Bernard MondoloniNo ratings yet
- RickshawGirl PDFDocument16 pagesRickshawGirl PDFNaseef Amin50% (4)
- Final Revision of HKDocument109 pagesFinal Revision of HKalex princess de castroNo ratings yet
- Describing ChangesDocument7 pagesDescribing Changesferrys37No ratings yet
- MWJRCF Packing List Updated 26 MAR 19Document3 pagesMWJRCF Packing List Updated 26 MAR 19Jim HoftNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Cost & Sales ConceptDocument15 pagesChap 1 - Cost & Sales ConceptAhmad SayutiNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Thread Consumption of GarmentDocument2 pagesEstimation of Thread Consumption of GarmentK.s. Ramesh100% (1)
- Case Study Louis Vuitton in ChinaDocument6 pagesCase Study Louis Vuitton in ChinaalejandraNo ratings yet
- Metal SilosDocument8 pagesMetal Siloswidad alamriNo ratings yet
- Mi 4A PRO 80 CM 32 HD Ready LED Smart Android TV With Google Data SaverDocument2 pagesMi 4A PRO 80 CM 32 HD Ready LED Smart Android TV With Google Data SaverSarvar PathanNo ratings yet
- Pre Shrunk Machine SopDocument6 pagesPre Shrunk Machine SoplanhotelsNo ratings yet
- Manual SPD 505Document1 pageManual SPD 505nahuel915No ratings yet
- Sunrise AB5 Read OnlyDocument93 pagesSunrise AB5 Read Onlybahb1979100% (3)
- New York GuideDocument246 pagesNew York GuideCristina Rinaldi100% (1)
- Ispo Trends and Color Card 15 16Document10 pagesIspo Trends and Color Card 15 16PD MANo ratings yet
- SOPs and Functions of Linen and Laundry DeptDocument17 pagesSOPs and Functions of Linen and Laundry Deptnidhithacker86% (44)
- TTM60 61A Service ManualDocument98 pagesTTM60 61A Service ManualAlexandru DiaconuNo ratings yet