Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ai 20
Uploaded by
ml0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pagesdf
Original Title
ai_20
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageAi 20
Uploaded by
mlsdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
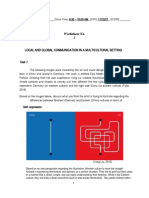
intelligence.
Musk donated ten million dollars to the Future of Life
Institute to fund research on understanding AI decision making. The goal
of the institute is to "grow wisdom with which we manage" the growing
power of technology. He also funds companies developing artificial
intelligence such as Google DeepMind and Vicarious in order to just keep
an eye on whats going on with artificial intelligence.[207] I think
there is potentially a dangerous outcome there.[208][209]
There is also no connection between superintelligence and the desire to
destroy all of humanity. It is unclear where this assumption comes from,
as the logical conclusion would be to assist humanity. This irrational
belief in the inherent malevolence and hostility of artificial
intelligence may be the result of human guilt or ignorance, and its
causes should be further explored.[210]
The possibility that Artificial Intelligence may come to be a threat to
mankind cannot be eliminated, should new discoveries be made, but with
regards to current research, there is little evidence for the possibility
of a superintelligent computer coming into existence at all.
In fiction
Main article: Artificial intelligence in fiction
The implications of artificial intelligence have been a persistent theme
in science fiction. Early stories typically revolved around intelligent
robots. The word "robot" itself was coined by Karel apek in his 1921
play R.U.R., the title standing for "Rossum's Universal Robots". Later,
the SF writer Isaac Asimov developed the three laws of robotics which he
subsequently explored in a long series of robot stories. These laws have
since gained some traction in genuine AI research.
Other influential fictional intelligences include HAL, the computer in
charge of the spaceship in 2001: A Space Odyssey, released as both a film
and a book in 1968 and written by Arthur C. Clarke.
Since then, AI has become firmly rooted in popular culture.
Notes
Definition of AI as the study of intelligent agents:
Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, p. 1, which provides the version that
is used in this article. Note that they use the term "computational
intelligence" as a synonym for artificial intelligence.
Russell & Norvig (2003) (who prefer the term "rational agent") and
write "The whole-agent view is now widely accepted in the field" (Russell
& Norvig 2003, p. 55).
Nilsson 1998
Legg & Hutter 2007.
The intelligent agent paradigm:
Russell & Norvig 2003, pp. 27, 3258, 968972
Poole, Mackworth & Goebel 1998, pp. 721
Luger & Stubblefield 2004, pp. 235240
Hutter 2005, pp. 125126
The definition used in this article, in terms of goals, actions,
perception and environment, is due to Russell & Norvig (2003). Other
definitions also include knowledge and learning as additional criteria.
Although there is some controversy on this point (see Crevier (1993, p.
50)), McCarthy states unequivocally "I came up with the term" in a c|net
You might also like
- SGDGSDFG SDFDocument1 pageSGDGSDFG SDFmlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 27Document1 pageAaa 27mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 24Document1 pageAaa 24mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 26Document1 pageAaa 26mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 25Document1 pageAaa 25mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 28Document1 pageAaa 28mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 30Document1 pageAaa 30mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 23Document1 pageAaa 23mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 28Document1 pageNew 1 - 28mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 26Document1 pageNew 1 - 26mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 22Document1 pageAaa 22mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 27Document1 pageNew 1 - 27mlNo ratings yet
- Aaa 21Document1 pageAaa 21mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 24Document1 pageNew 1 - 24mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 13Document1 pageNew 1 - 13mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 25Document1 pageNew 1 - 25mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 21Document1 pageNew 1 - 21mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 20Document1 pageNew 1 - 20mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 09Document1 pageNew 1 - 09mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 22Document1 pageNew 1 - 22mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 14Document1 pageNew 1 - 14mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 11Document1 pageNew 1 - 11mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 14Document1 pageNew 1 - 14mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 10Document1 pageNew 1 - 10mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 06Document1 pageNew 1 - 06mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 04Document1 pageNew 1 - 04mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 07Document1 pageNew 1 - 07mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 08Document1 pageNew 1 - 08mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 05Document1 pageNew 1 - 05mlNo ratings yet
- New 1 - 03Document1 pageNew 1 - 03mlNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Course Syllabus LS127 PDFDocument4 pagesCourse Syllabus LS127 PDFBlah BlamNo ratings yet
- GEEng1 - Worksheet No. 3Document4 pagesGEEng1 - Worksheet No. 3Jeremae EtiongNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis of Nike and Adidas Commercials: A Multimodal Approach To Building Brand StrategiesDocument67 pagesA Comparative Analysis of Nike and Adidas Commercials: A Multimodal Approach To Building Brand StrategiesPrince Leō KiñgNo ratings yet
- CYP Case Study Assignment Virginia Toole 20260933 Dec 3, 2019 Part 2Document9 pagesCYP Case Study Assignment Virginia Toole 20260933 Dec 3, 2019 Part 2Ginny Viccy C TNo ratings yet
- AIDocument2 pagesAITedo HamNo ratings yet
- TKT Young Learners Worksheets: With Trainer NotesDocument92 pagesTKT Young Learners Worksheets: With Trainer NotesThu NaingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17: Planning For Laboratory and Industry-Based InstructionDocument34 pagesLesson 17: Planning For Laboratory and Industry-Based InstructionVARALAKSHMI SEERAPUNo ratings yet
- Twenty Little Poetry ProjectsDocument3 pagesTwenty Little Poetry Projectsapi-260214370% (1)
- Sociology ReportingDocument9 pagesSociology ReportingMichelle UpodNo ratings yet
- For D.R. S.I.M.O.N.S.O.N DiEiMIiRiAiY About Mieitia CioimimiuiniiiciaitiiioiiniDocument324 pagesFor D.R. S.I.M.O.N.S.O.N DiEiMIiRiAiY About Mieitia CioimimiuiniiiciaitiiioiiniJk McCreaNo ratings yet
- Teacher Reflection FormDocument8 pagesTeacher Reflection FormJff Reyes100% (11)
- Grammar - 1-ADocument7 pagesGrammar - 1-AB20L7-Choun Vey -Gram & WriteNo ratings yet
- CS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) - Fall 2011: Antonina KolokolovaDocument3 pagesCS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) - Fall 2011: Antonina KolokolovaZhichaoWangNo ratings yet
- Automation Industry PPT 2-3 ADocument16 pagesAutomation Industry PPT 2-3 AVijay Vj100% (1)
- Assignment Life Long October2016Document5 pagesAssignment Life Long October2016Arvin KovanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 KEYDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 KEYSzilagyi Barna BelaNo ratings yet
- The Double As The Unseen of Culture - Toward A Definition of DoppelgangerDocument9 pagesThe Double As The Unseen of Culture - Toward A Definition of DoppelgangerDaniel FloquetNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument39 pagesPresent Perfect Tensemiraflores19100% (1)
- HHGGFDocument25 pagesHHGGFgbrbbNo ratings yet
- Writing ObjectivesDocument22 pagesWriting ObjectiveswintermaeNo ratings yet
- Dog Training BlueprintDocument46 pagesDog Training Blueprintoljavera67% (3)
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: A. Content StandardDocument3 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: A. Content StandardPrecious Gabrillo GabagatNo ratings yet
- Vila-Henninger, L. Bringing The HumanDocument8 pagesVila-Henninger, L. Bringing The HumanCarlos Manuel Uribe GómezNo ratings yet
- DLunit 5Document17 pagesDLunit 5EXAMCELL - H4No ratings yet
- EL 108 DLP Phrasal Verb 1Document21 pagesEL 108 DLP Phrasal Verb 1Kisha Mae FronterasNo ratings yet
- Verbal Ability Test 3Document10 pagesVerbal Ability Test 3ankit0076No ratings yet
- Top 100 Commonly Misspelled WordsDocument28 pagesTop 100 Commonly Misspelled WordsFebe NievaNo ratings yet
- Information Theory and Coding PDFDocument214 pagesInformation Theory and Coding PDFMohan Raj100% (1)
- DBM-CSC Form No. 1 Position Description Forms - SHS HUMMS-T2Document2 pagesDBM-CSC Form No. 1 Position Description Forms - SHS HUMMS-T2CHARLYN TOYHACAONo ratings yet
- "Designing & Teaching Learning Goals & Objectives" SummaryDocument10 pages"Designing & Teaching Learning Goals & Objectives" SummaryAltamira International School100% (1)