Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SWMS 001 Drilling Soil Bores
Uploaded by
Engr Faheem AkhtarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SWMS 001 Drilling Soil Bores
Uploaded by
Engr Faheem AkhtarCopyright:
Available Formats
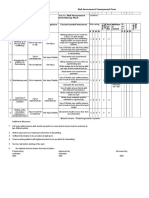
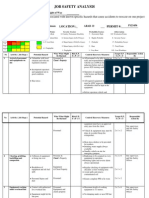
Safe Work Method Statement Drilling Soil Bores
Person responsible for ensuring
compliance with this SWMS:
Field Manager
Revision Date:
23 October 2012
Job Description:
Drilling soil bores and collection of soil samples
Location:
Field
Tasks Involved
Potential Hazards
Hazard Control Measures
Mobilisation / Demobilisation
Heavy lifting
Avoid heavy lifting by loading / unloading individual items at one time.
Seek assistance to lift heavy or awkward loads.
Use trolleys etc. to transport heavy items, where deemed necessary.
Lift with legs rather than back.
Trip hazard
All equipment, soil cuttings and waste to be removed from drilling location prior to moving on to next
location.
No holes to be left unattended unless covered, fenced or backfilled.
No running on-site and avoid walking on uneven surfaces, where possible.
Compact and reinstate core holes in a manner to minimise future subsidence.
Unstable ground
Position drill rig on relatively flat, stable ground.
Use hydraulic stabilising legs to create level drilling platform.
Public entry, movement of site
vehicles / plant
Where public entry or movement of site vehicles / plant is possible; utilise bollards, tape, signage and /
or fencing to create safe work area or visual demarcation barrier.
Do not leave open holes unattended.
At all times wear high visibility vests and or clothing.
Electrocution from overhead
services.
Complete Senversa Underground and Overhead Services Clearance Protocol prior to and drilling
Energy release from underground
services
Complete Senversa Underground and Overhead Services Clearance Protocol prior to and drilling
Drilling
Page 1 of 3
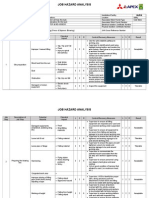
Safe Work Method Statement Drilling Soil Bores
Tasks Involved
Potential Hazards
Hazard Control Measures
Crush points, heat, rotating parts
on drilling rig
Overhead plant
Discuss and observe drilling subcontractors JSA/SWMS control measures.
Ensure rotating rods on drilling rig is guarded.
All personnel except drilling rig operators to remain approximately 3m or greater from drill rig when its
operating.
Prior to drilling works, arrange communication protocol with driller and off-sider.
Hearing protection to be worn when rig noisy (eg down hole hammer, push tube drilling, concrete
coring).
Wear hard hat, safety shoes and safety glasses.
Toxic or explosive gases,
hazardous materials
Cease work if the following conditions are encountered and review the need for additional control
measures:
Soil sampling
Page 2 of 3
Underground service or utility is encountered during drilling.
Strong or persistent odours are noticed.
Suspected asbestos containing materials (ACMs) or fibrous material potentially containing
asbestos is observed.
Suspected ground gas is emitted from borehole.
Non-aqueous phase liquid is identified.
Electrical atmosphere
Temporarily cease work if frequent lightning observed until passed
Noise and dust
Ear muffs or plugs to be worn while rig is in operation (ie hammering or push tube).
P1 dust mask to be worn if persistent dust is generated.
Exposure to soil contamination
Gloves, safety glasses, long sleeves and long pants to be work when handling and sampling soil.
Sampling equipment to be decontaminated before placing into vehicle
Contaminated consumable / disposable equipment preferably disposed on-site; not to be carried in
passenger cabin of vehicle.
Where volatile contaminants are suspected, utilise a photo-ionisation detector (PID) to monitor for
potential vapour exposure. Modify work procedures and / or wear half-face respirator with organic
filter; where deemed necessary or when site derived action levels are exceeded.
Exposure to cleaning chemicals
Wear safety glasses when using undiluted Decon 90.
Wear rubber gloves when decontaminating field equipment.
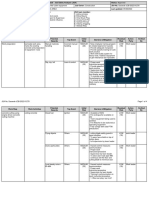
Safe Work Method Statement Drilling Soil Bores
Tasks Involved
Potential Hazards
Hazard Control Measures
Sharp materials
Do not run fingers down push-tube cores.
Use trowel to collect soil samples, where sharp materials are suspected.
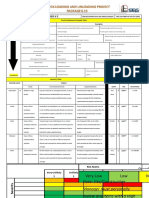
Steps for filling out
1. Discuss with relevant employees, contractors and HSRs what work will be high-risk, the tasks, and associated hazards, risks and controls.
2. In the What are the tasks involved? column, list the work tasks in sequence to how they will be carried out.
3. In the What are the hazards and risks? column, list the hazards and risks for each work task.
4. In the How will the hazards and risks be controlled? column, select the hazard or risk and then work through the control levels 1 4 from top to bottom. Choose a control
measure (and how it is to be used) that is as close to level 1 as is reasonably practicable.
Control levels
1. Eliminate any risk to health or safety associated with construction work.
2. Reduce the risk to health or safety by any one or any combination of the following:
Substituting a new activity, procedure, plant, process or substance
Isolating persons from the hazard, such as barricading, fencing or guardrailing, or
Using engineering controls, such as mechanical or electrical devices.
3. Use administrative controls, such as changing the way the work is done.
4. Provide appropriate personal protective equipment.
5. Brief each team member on this SWMS before commencing work. Ensure team knows that work is to immediately stop if the SWMS is not being followed.
6. Observe work being carried out. If controls are not adequate, stop the work, review the SWMS, adjust as required and re-brief the team.
7. Retain this SWMS for the duration of the work.
Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- 001 JSA Site CompoundDocument15 pages001 JSA Site CompoundRui Ribeiro100% (1)
- Concrete Cutting and Drilling PDFDocument2 pagesConcrete Cutting and Drilling PDFcityofdarwingis100% (1)
- Working at Height - JHA-1Document13 pagesWorking at Height - JHA-1Burhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Deshuttering WorkDocument2 pagesDeshuttering WorkChandru100% (1)
- Excavations JSA Final 2015Document5 pagesExcavations JSA Final 2015jithin shankarNo ratings yet
- Jsa Civil Work (00000002)Document6 pagesJsa Civil Work (00000002)Ali AlahmaNo ratings yet
- Jha RebarsDocument7 pagesJha RebarsJaycee QuinNo ratings yet
- Activity Hazard AnalysisDocument7 pagesActivity Hazard AnalysisAnthony MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Sinopec Northen Construction Camp - Tilenga Job Hazard Analysis (Jha)Document3 pagesSinopec Northen Construction Camp - Tilenga Job Hazard Analysis (Jha)Nora Afzam Abd WahabNo ratings yet
- 07 - JSA Compaction and BackfillingDocument4 pages07 - JSA Compaction and Backfillingsatti100% (2)
- Job Safety Analysis: Manual ExcavationDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Manual Excavationfdfddf dfsdfNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DateDocument1 pageJob Safety Analysis (JSA) - Carpentry Works DatenabeelNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) Worksheet: Perform Forwork, Rebar and Concrete WorkDocument6 pagesJob Hazard Analysis (Jha) Worksheet: Perform Forwork, Rebar and Concrete WorkAbdul Khairul RiduanNo ratings yet
- Rohan Abuilders (India) PVT - LTD: Job Hazard AnalysisDocument2 pagesRohan Abuilders (India) PVT - LTD: Job Hazard AnalysisMc Evans Magallanes100% (1)
- 004 Piling JSADocument5 pages004 Piling JSAmidozotyNo ratings yet
- Jha For RoadworksDocument15 pagesJha For RoadworksHenry RajahNo ratings yet
- Part-A: Jsa Date: 23.11.16 Work Permit No: HW-: Civil Works Inside The Tank DykeDocument4 pagesPart-A: Jsa Date: 23.11.16 Work Permit No: HW-: Civil Works Inside The Tank DykevivekaramanaNo ratings yet
- Project JHA For Grading Compacting WorksDocument27 pagesProject JHA For Grading Compacting WorksBasker Balu100% (1)
- JSA Scaffolding Erection and Dismentling New 2021Document5 pagesJSA Scaffolding Erection and Dismentling New 2021Captain ChickenNo ratings yet
- JSA For The Steel Fixing and Manual Conxrete Pouring at New Flare Line Phase 2 (Brown Area)Document7 pagesJSA For The Steel Fixing and Manual Conxrete Pouring at New Flare Line Phase 2 (Brown Area)Marvin BerrensteinNo ratings yet
- JHA Blowing PressDocument5 pagesJHA Blowing PressLuqman OsmanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Cutting JsaDocument4 pagesConcrete Cutting JsaMohammad Irfan Kiki IsmailNo ratings yet
- JSA For Concrete WorkDocument6 pagesJSA For Concrete Worklê ngọc tùng0% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis (Jsa) : Title of Activity / Work: Hot Work ActivityDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (Jsa) : Title of Activity / Work: Hot Work ActivityJayendra PatelNo ratings yet
- HIRA Batching PlanDocument9 pagesHIRA Batching Plannitish tiwariNo ratings yet
- Project: Field Erection of 15000 Bbls Tank (Ik-2545) : Job Safety Analysis / Safe Work Method Statement-SWMSDocument2 pagesProject: Field Erection of 15000 Bbls Tank (Ik-2545) : Job Safety Analysis / Safe Work Method Statement-SWMSJohn100% (1)
- Demolition JhaDocument2 pagesDemolition JhaElvyn Fabellore HerreraNo ratings yet
- JSA Ladders Working at Heights 001Document2 pagesJSA Ladders Working at Heights 001Anonymous voA5Tb0No ratings yet
- 1 Scaffolding Work PDFDocument16 pages1 Scaffolding Work PDFfadliNo ratings yet
- Exacavation Job Safety AnalysisDocument1 pageExacavation Job Safety AnalysisNeelakantamNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Lifting and RiggingDocument17 pagesJob Safety Analysis Lifting and RiggingSam Seed100% (1)
- Excavation and Back Filling Works JsaDocument3 pagesExcavation and Back Filling Works JsaNazir Hussain67% (12)
- JHA - Survey WorksDocument3 pagesJHA - Survey WorksNazirul Syazwan100% (3)
- Casting ConcreteDocument9 pagesCasting ConcreteNontobeko MkhizeNo ratings yet
- 5-Risk Assessment For Excavation & Backfilling and Compaction WorksDocument15 pages5-Risk Assessment For Excavation & Backfilling and Compaction WorksAmran HossainNo ratings yet
- Rapid P20ai Jsa Box CulvertDocument8 pagesRapid P20ai Jsa Box Culvertfadli.lpgNo ratings yet
- JSA Format Erection of Column 903-C-02,03Document5 pagesJSA Format Erection of Column 903-C-02,03sakthi venkat100% (1)
- (Potential/existing) (Permits, Safety Precautions, Equipment, PPE, Recommended Actions)Document3 pages(Potential/existing) (Permits, Safety Precautions, Equipment, PPE, Recommended Actions)krisNo ratings yet
- Jha Confined SpaceDocument6 pagesJha Confined SpaceArun ArunbolluNo ratings yet
- JSA For Pipe Installation TS 3Document8 pagesJSA For Pipe Installation TS 3Shilpiengg SafetyNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDDocument4 pagesJob Hazard Analysis: Rohan Builders (I) PVT LTDsoubhagyaNo ratings yet
- JSA For RCC, Foundation & Generator Installation (R-00)Document14 pagesJSA For RCC, Foundation & Generator Installation (R-00)Suju RajanNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Worksheet: Yes NoDocument8 pagesJob Safety Analysis Worksheet: Yes NoBorislav VulićNo ratings yet
- JSA-010 Excavation Sampling PDFDocument5 pagesJSA-010 Excavation Sampling PDFArgaYurIstiawanNo ratings yet
- Crane JHA OKDocument4 pagesCrane JHA OKAbu Maaz100% (1)
- Risk Assessment Rib Erection & FabricationDocument2 pagesRisk Assessment Rib Erection & FabricationAkash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Excavations: Job Safety AnalysisDocument5 pagesExcavations: Job Safety AnalysisJICKNo ratings yet
- Tool Box Talk - MK - Emergency Response ProceduresDocument2 pagesTool Box Talk - MK - Emergency Response ProceduresPaul McGahanNo ratings yet
- JSA For Plaster WorkDocument8 pagesJSA For Plaster WorkZakeer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Sheet: Activity Potential Hazard Likely Causes Control MeasureDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis Sheet: Activity Potential Hazard Likely Causes Control MeasureM Waqas HabibNo ratings yet
- Pha ExcavationDocument13 pagesPha ExcavationirshadNo ratings yet
- Excavation of RoadDocument7 pagesExcavation of RoadCharles LambNo ratings yet
- JSA-Construction Right of WayDocument3 pagesJSA-Construction Right of Wayfrancis_e_tan100% (6)
- JSA ScaffoldingDocument2 pagesJSA ScaffoldingHrishikesh UnnikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesment For CompactionDocument12 pagesRisk Assesment For CompactionAzhar MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis SEG 6.1 - Rebar and Formwork Fabrication and Installation Carpentry Works Rev.0Document2 pagesJob Safety Analysis SEG 6.1 - Rebar and Formwork Fabrication and Installation Carpentry Works Rev.0Jayvee Baradas Valdez25% (4)
- Job Safetyanalysis: Traffic Control & FlaggingDocument2 pagesJob Safetyanalysis: Traffic Control & Flaggingnasrul draco100% (2)
- SP400 - Sumadsad-TalaveraDocument13 pagesSP400 - Sumadsad-TalaveraSharlize SumadsadNo ratings yet
- JSA ExcavationDocument6 pagesJSA Excavationkermech21607100% (1)
- Safe Work Method Statement: Fixed ScaffoldDocument11 pagesSafe Work Method Statement: Fixed ScaffoldJoe Waller100% (1)
- Scaffolding: The University of Tennessee Office of Environmental Health & SafetyDocument72 pagesScaffolding: The University of Tennessee Office of Environmental Health & SafetyEngr Faheem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- ManageDocument18 pagesManageMinesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Most Repeated Question Current Affairs - 2000 To 2015 PDFDocument20 pagesMost Repeated Question Current Affairs - 2000 To 2015 PDFEngr Faheem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- THE Senate of Pakistan Debates: T01-15APR2015 Furqan 10.10A.MDocument16 pagesTHE Senate of Pakistan Debates: T01-15APR2015 Furqan 10.10A.MEngr Faheem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Duty Cycle PDFDocument5 pagesDuty Cycle PDFEngr Faheem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- We Have To Submit The Document To Mam On Monday Sunday Till 6pmDocument2 pagesWe Have To Submit The Document To Mam On Monday Sunday Till 6pmEngr Faheem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Project ProposalDocument14 pagesEntrepreneurship: Project ProposalEngr Faheem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Oplan Tumbler ProposalDocument3 pagesOplan Tumbler ProposalKay Tuppil ManzanillaNo ratings yet
- Planetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaDocument11 pagesPlanetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaVaraha Mihira100% (11)
- 8Document3 pages8Anirban Dasgupta100% (1)
- Pnbcontr0223en (Web)Document308 pagesPnbcontr0223en (Web)James GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Exact Solution Tank DrainageDocument8 pagesExact Solution Tank DrainageFelipe CastNo ratings yet
- Edrolo ch3Document42 pagesEdrolo ch3YvonneNo ratings yet
- FUCHS LUBRITECH Product RangeDocument76 pagesFUCHS LUBRITECH Product RangeBurak GüleşNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesFourth Quarter Examjanice gumabao50% (4)
- Introduction To Second Quantization: 1.1 Single-Particle Hilbert SpaceDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Second Quantization: 1.1 Single-Particle Hilbert Space김띵No ratings yet
- Ashok Leyland Project ReportDocument40 pagesAshok Leyland Project ReportGovind kumarNo ratings yet
- Module IiDocument5 pagesModule IiFahmi PrayogiNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5Document5 pagesSoal Pat Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5Tini Bastuti Joyolaksono100% (1)
- Band Structure Engineering in Gallium Sulfde NanostructuresDocument9 pagesBand Structure Engineering in Gallium Sulfde NanostructuresucimolfettaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Global Research Trends in The Area of Food Waste D - 2020 - Food CDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Global Research Trends in The Area of Food Waste D - 2020 - Food CAliNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 DC Machines IMP QuestionsDocument30 pagesUnit-3 DC Machines IMP Questionskrishna Sai Atla VenkataNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, MixturesDocument35 pagesElements, Compounds, MixturesNorvieNo ratings yet
- IbnTaymiyyah Theological EthicsDocument361 pagesIbnTaymiyyah Theological EthicsDado Daki100% (1)
- Facility Systems, Ground Support Systems, and Ground Support EquipmentDocument97 pagesFacility Systems, Ground Support Systems, and Ground Support EquipmentSree288No ratings yet
- Unit Test 7 (PDF)Document1 pageUnit Test 7 (PDF)emirelliucNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - GIAN - 19 - ModifiedDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper - GIAN - 19 - Modifiedsayan mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- De Thi Vao 10 Chuyen Hoa Nguyen Trai Hai Duong 20212022Document2 pagesDe Thi Vao 10 Chuyen Hoa Nguyen Trai Hai Duong 20212022Trần Ngọc BíchNo ratings yet
- EPP V6 - V7 - ETS - Removal Switch - Sensor Reactivation V12Document15 pagesEPP V6 - V7 - ETS - Removal Switch - Sensor Reactivation V12Rabin TinkariNo ratings yet
- NTDCDocument8 pagesNTDCjaved_hanifNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Digital Image Fundamentals & Image TransformsDocument70 pagesUnit-I: Digital Image Fundamentals & Image TransformsNuzhath FathimaNo ratings yet
- Em - Animals A To ZDocument9 pagesEm - Animals A To ZgowriNo ratings yet
- (Q2) Electrochemistry 29th JulyDocument21 pages(Q2) Electrochemistry 29th JulySupritam KunduNo ratings yet
- Genesis of KupferschieferDocument15 pagesGenesis of KupferschieferMaricela GarciaNo ratings yet
- An Adaptive Power Oscillation Damping Controllerby STATCOM With Energy StorageDocument10 pagesAn Adaptive Power Oscillation Damping Controllerby STATCOM With Energy StorageChristian EmenikeNo ratings yet
- P eDocument22 pagesP eKiks AshNo ratings yet
- BSN Curriculum 2012Document1 pageBSN Curriculum 2012Joana Bless PereyNo ratings yet