Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Relay Coordion Analysis Engineering Essay 3
Uploaded by
Gary Goh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 pagerelay
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentrelay
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 pageRelay Coordion Analysis Engineering Essay 3
Uploaded by
Gary Gohrelay
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Third part is the trip circuit of a relay and there is a source that supply the power to the circuit
to trip the coil of circuit breaker to
disconnect any fault that occur [7].
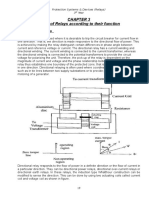
2.2.2 Circuit breaker
Circuit breaker is a mechanical switching device use to protect the electrical wiring, breaking, and carrying current under normal
situation. It is also used to disconnect the power supply in case of under specified abnormal condition such as overload and
short circuit (IEC 947-1) [8]. Circuit breaker is divided into two categories that are low voltage circuit breaker (LVCB) and high
voltage circuit breaker (HVCB). A circuit breaker will serve the following functions to the customer [9].
Motor protection
Short circuit protection
Protection of installation
Disconnecting fault
Tripping indication
Remote switching
Circuit breakers have the capability to interrupt the short circuit current. So, this capability is divided in categories depending on
the type of construction, and their capability to limit the short circuit current. Hence, the circuit breaker can be classifies under
current limiting type of circuit breaker and current-zero interrupting type of circuit breaker [9].
Figure A diagram of circuit breaker
2.2.3 Fuse
The fuse is an initial protective device. The fundamental component of a fuse is the link. The link of a fuse is a metal strip or
wire that can melt to disconnect the supply of power to activate a safety system [10]. The fuse link is constructed so that heat
produced for a normal current can be hold by the fuse's link and will melt when the current rise to a higher temperature [11]
[10]. As the voltage and power magnitude in electrical appliances increase, fuse protection become deficient. So, this leads to
the new development of more reliable protective devices such a relay and circuit breaker [12].
Figure Current and voltage during the operation of fuse [13]
In Figure 3 is the current characteristic of a fuse. So, let through current smaller than the peak current meaning there is current
clamping. The operating time of the fuse is the added up of melting fuse time and arcing fuse time [13] [14].
2.3 Principle types of relays
Protective relay is a protective device that measures the current, voltage, frequency and other electrical power quantities from
the source to detect any abnormal condition [15]. There are two type of common relay that are electromechanical relays (EMR)
which the contact of the relay opened or closed by a magnetic force and the other type is the solid state relay (SSR) which
there is no contact on the relay and switching is all done electronically [16] [17]. So, electromechanical relay has been used
wide to serve the protection to the electrical network and are based on few basic operating principles [12] . Generally,
electromechanical protective relay operates using either magnetic attraction or magnetic induction principles.
Following are the types of electromechanical relays:
Attracted-armature relays
Moving-coil relays
You might also like
- Switchgear and Industrial Protection 6 Semester, Electrical EnggDocument8 pagesSwitchgear and Industrial Protection 6 Semester, Electrical EnggKetan KishoreNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent ProtectionDocument5 pagesOvercurrent ProtectionMisael CabansagNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Circuit BreakersDocument13 pagesUnit-I Circuit Breakerspurushg62No ratings yet
- MV circuit breakers: Vacuum interrupters and arc extinguishingDocument24 pagesMV circuit breakers: Vacuum interrupters and arc extinguishingrajuanthati100% (1)
- PSGDocument13 pagesPSGya vikaNo ratings yet
- Switch Gear and Protective Devices PDFDocument132 pagesSwitch Gear and Protective Devices PDFAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Types and Revolution of Electrical RelaysDocument23 pagesTypes and Revolution of Electrical RelaysKishan DarjiNo ratings yet
- Switchgear and Transformer Maintenance: Compiled by P.Murugesan Dy - Director M.Ravichandrababu Asst - DirectorDocument104 pagesSwitchgear and Transformer Maintenance: Compiled by P.Murugesan Dy - Director M.Ravichandrababu Asst - DirectorGnanavel GNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 NoteDocument21 pagesUnit-3 NoteSankara nathNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Breakers PDFDocument21 pagesElectrical Circuit Breakers PDFRomnick PascuaNo ratings yet
- Cahier Technique by SchneiderDocument30 pagesCahier Technique by SchneiderKS CheeNo ratings yet
- Fuse MCB ELCBDocument29 pagesFuse MCB ELCBIshitaBhatt30No ratings yet
- Conventional and Non-Conventional SourcesDocument12 pagesConventional and Non-Conventional SourcesAkhtarNo ratings yet
- PSP Notes PDFDocument8 pagesPSP Notes PDFpriyank srivastavaNo ratings yet
- PSP Notes 1Document13 pagesPSP Notes 1priyank srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Fault Protection ExplainedDocument21 pagesFault Protection ExplainedСергей БойкоNo ratings yet
- Ircuit Reakers: (Theory, Classification, & Applications)Document28 pagesIrcuit Reakers: (Theory, Classification, & Applications)Syed Muhammad Munavvar Hussain100% (5)
- Installing Electrical Protective Devices For Distribution, Power, Lightning Protection and Grounding SystemsDocument23 pagesInstalling Electrical Protective Devices For Distribution, Power, Lightning Protection and Grounding SystemsYamut Si ako67% (6)
- 28 35 Talha Ali Qasmi PDocument9 pages28 35 Talha Ali Qasmi PAhmed Said GhonimyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3nassim.1979No ratings yet
- SwitchgearDocument23 pagesSwitchgearAnonymous Yq9ibs100% (1)
- Lect 1 e 1435 Power System ProtectionDocument41 pagesLect 1 e 1435 Power System ProtectionabdullahNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Project on Protective DevicesDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering Project on Protective DevicesEsai StephenNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument12 pagesMini ProjectHima Bindu PambalaNo ratings yet
- Disjuntores de Média TensãoDocument19 pagesDisjuntores de Média TensãoDiogo do Espírito SantoNo ratings yet
- Notes21 ProtectionDocument22 pagesNotes21 ProtectionJerome SantosNo ratings yet
- Double Freq TransientDocument22 pagesDouble Freq TransientMelissa Miller100% (1)
- 0600 DB 0301Document18 pages0600 DB 0301awadhesha20022033No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Switchgear and Protection: What Is Switchgear? - Features, Components and ClassificationDocument57 pagesUnit 1 Switchgear and Protection: What Is Switchgear? - Features, Components and ClassificationMadhubala DarwaiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Circuit Breakers: Difference Between An Isolator and Circuit BreakerDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Circuit Breakers: Difference Between An Isolator and Circuit BreakerdemokykNo ratings yet
- Substation Equipment and Switching DevicesDocument14 pagesSubstation Equipment and Switching DevicesOmkar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of Circuit BreakersDocument23 pagesTypes of Circuit Breakerspmankad60% (5)
- Notes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Document32 pagesNotes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Pratik SinghNo ratings yet
- Five Switching Devices You Are Likely To Spot in Most of The Low Voltage SwitchgearDocument15 pagesFive Switching Devices You Are Likely To Spot in Most of The Low Voltage SwitchgearHaris MakrigiannakisNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Overcurrent Protection Fundamentals FINALDocument54 pagesOvercurrent Protection Fundamentals FINALSaranga JayawardanaNo ratings yet
- 6th Ele SGPDDocument118 pages6th Ele SGPDAkash RawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter2 PDFshaik jaheerNo ratings yet
- Logo 9 PDFDocument6 pagesLogo 9 PDFJobin JoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document15 pagesChapter 7Khaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- Articulos EEP de Sistemas de Potencia3Document435 pagesArticulos EEP de Sistemas de Potencia3Ernesto MoraNo ratings yet
- Introduction to High Voltage Circuit BreakersDocument18 pagesIntroduction to High Voltage Circuit BreakersMeer ShakirNo ratings yet
- HRC VS MCB PDFDocument5 pagesHRC VS MCB PDFRajuNo ratings yet
- Protect loads from over and under voltagesDocument6 pagesProtect loads from over and under voltagesRika Elvan YulindaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii OvervoltagesDocument16 pagesUnit Iii Overvoltageslvb123No ratings yet
- Sinha power plant written questions solutionDocument14 pagesSinha power plant written questions solutionRaihanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Electrical Protection SystemDocument101 pagesChapter-3 Electrical Protection Systemgerrzen64No ratings yet
- Utilisation of Electrical Energy: Circuit Protection For Distribution and InstallationDocument28 pagesUtilisation of Electrical Energy: Circuit Protection For Distribution and InstallationceastlandNo ratings yet
- Electrical System Components - Switchgears DDocument38 pagesElectrical System Components - Switchgears DAbongshing MaxwellNo ratings yet
- SG 1Document6 pagesSG 1Jeeva BharathiNo ratings yet
- What Is Switchgear? - Features, Components and ClassificationDocument4 pagesWhat Is Switchgear? - Features, Components and ClassificationAsifShahzadNo ratings yet
- Protection TechnicalDocument44 pagesProtection TechnicalTarek MatarNo ratings yet
- Transfo Reviewer V V T TDocument19 pagesTransfo Reviewer V V T TcatherinejeanasNo ratings yet
- Circuit Protection PrincipleDocument44 pagesCircuit Protection PrincipleNoli OtebaNo ratings yet
- The Branch Circuit: An OverviewDocument12 pagesThe Branch Circuit: An OverviewGaming DeathNo ratings yet
- Empowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearFrom EverandEmpowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearNo ratings yet
- Gary Eye 2 CN103784573ADocument6 pagesGary Eye 2 CN103784573AGary GohNo ratings yet
- Gary Eye 1 CN1123631ADocument4 pagesGary Eye 1 CN1123631AGary GohNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNo ratings yet
- Spore Solar StatisticsDocument1 pageSpore Solar StatisticsGary GohNo ratings yet
- Test Case A With Panel - !Document1 pageTest Case A With Panel - !Gary GohNo ratings yet
- OLV1 One-Line Diagram Star SequenceDocument1 pageOLV1 One-Line Diagram Star SequenceGary GohNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNo ratings yet
- Test Case A in kVARDocument1 pageTest Case A in kVARGary GohNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 496.3 KW 11.8 KvarDocument1 pageOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 496.3 KW 11.8 KvarGary GohNo ratings yet
- Givdan Load FlowDocument1 pageGivdan Load FlowGary GohNo ratings yet
- Test Case A in KWDocument1 pageTest Case A in KWGary GohNo ratings yet
- Ggivadan Shot CircuitDocument1 pageGgivadan Shot CircuitGary GohNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 0.4 KV 0.4 KVDocument1 pageOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 0.4 KV 0.4 KVGary GohNo ratings yet
- Gen SpecDocument1 pageGen SpecGary GohNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteDocument1 pagePower Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteGary GohNo ratings yet
- Panel ScheduleDocument2 pagesPanel ScheduleGary GohNo ratings yet
- Fundamental ElectricDocument1 pageFundamental ElectricGary GohNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteDocument1 pagePower Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteGary GohNo ratings yet
- Fast Acting LimiterDocument1 pageFast Acting LimiterGary GohNo ratings yet
- Speed Math RotateDocument1 pageSpeed Math RotateGary GohNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase TransformerDocument1 page3 Phase TransformerGary GohNo ratings yet
- Drag DropDocument1 pageDrag DropGary GohNo ratings yet
- Isolator GGDocument1 pageIsolator GGGary GohNo ratings yet
- Switchgear Operation and Maintenance Fo : LibraryDocument1 pageSwitchgear Operation and Maintenance Fo : LibraryGary GohNo ratings yet
- TX Impedance Reader9382Document1 pageTX Impedance Reader9382Gary GohNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Transformer PDFDocument115 pages3 Phase Transformer PDFGary GohNo ratings yet
- 3D Generator RoomDocument1 page3D Generator RoomGary GohNo ratings yet
- GG Technical Report 028 Short-CircuitDocument1 pageGG Technical Report 028 Short-CircuitGary GohNo ratings yet
- ENGN2218 CourseDescription 2011 v1Document13 pagesENGN2218 CourseDescription 2011 v1Chuah Chian YeongNo ratings yet
- Electrocompaniet 25W PWR SCHDocument2 pagesElectrocompaniet 25W PWR SCHA Daniel LazarescuNo ratings yet
- 2-Channel Analog Input 4-20 Ma HART NAMUR NE43 Intrinsically SafeDocument2 pages2-Channel Analog Input 4-20 Ma HART NAMUR NE43 Intrinsically SafeIsaac FernándezNo ratings yet
- Lighting Controls: LCP3000EZ PanelsDocument1 pageLighting Controls: LCP3000EZ PanelsAg Oe NgNo ratings yet
- Liquid Crystal Display Module SpecificationDocument10 pagesLiquid Crystal Display Module SpecificationSohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- CMOS Translinear CellsDocument4 pagesCMOS Translinear CellsSumitChoudharyNo ratings yet
- TOTALLY ENCLOSED FAN COOLED INDUCTION MOTORSDocument24 pagesTOTALLY ENCLOSED FAN COOLED INDUCTION MOTORSfabiandimiNo ratings yet
- N4 ElectrotechnicsDocument57 pagesN4 ElectrotechnicsLogan JesseNo ratings yet
- Pioneer PDP 433PEDocument108 pagesPioneer PDP 433PEPaulo GardelNo ratings yet
- Nordac ProDocument220 pagesNordac ProMd.ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Controller Operating InstructionsDocument56 pagesReactive Power Controller Operating InstructionsMelissa Fry100% (1)
- AnswersDocument34 pagesAnswersMahmoud Elsayed MohamedNo ratings yet
- How Voltage Doublers WorkDocument2 pagesHow Voltage Doublers WorkErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerNo ratings yet
- Guide ElectricalCode SaskPower Interpretations 2018Document134 pagesGuide ElectricalCode SaskPower Interpretations 2018allanng30No ratings yet
- RadphysicsDocument143 pagesRadphysicspia toledoNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: AC/DC Dual Power Professional Balance Charger/DischargerDocument28 pagesInstruction Manual: AC/DC Dual Power Professional Balance Charger/DischargerSavaKrsticNo ratings yet
- Sharp AR-5726 AR-5731 SM PC PDFDocument201 pagesSharp AR-5726 AR-5731 SM PC PDFkostas_san100% (3)
- H2 Change Operating Pattern-1 PDFDocument6 pagesH2 Change Operating Pattern-1 PDFgibran jimenez100% (1)
- PHYSICS (9702) Rules.Document5 pagesPHYSICS (9702) Rules.Sheraz Ahmed - 65640/Laboratory Assistant/BBECNo ratings yet
- Picostrain Digital LoadCell PDFDocument48 pagesPicostrain Digital LoadCell PDFdliyaxNo ratings yet
- Gcm02 MT Ing r6bDocument57 pagesGcm02 MT Ing r6bKaiser Iqbal100% (1)
- 830 Series Silicon 25V Hyperabrupt Varactor Diodes: ZC829, ZDC833, ZMV829, ZMDC830 and ZV831 DescriptionDocument8 pages830 Series Silicon 25V Hyperabrupt Varactor Diodes: ZC829, ZDC833, ZMV829, ZMDC830 and ZV831 Descriptionjuan mateuzNo ratings yet
- 6823 Datasheet PDFDocument3 pages6823 Datasheet PDFingucvNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier ApplicationsDocument47 pagesOperational Amplifier ApplicationsMani Kandan KNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Principles: 1.1 Power in Single-Phase AC CircuitsDocument9 pages1 Basic Principles: 1.1 Power in Single-Phase AC CircuitsDharamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BJT AmplifiersDocument13 pagesChapter 6 BJT AmplifiersCamilleNo ratings yet
- SMAW 9 HTask 1Document5 pagesSMAW 9 HTask 1Michael John SegarinoNo ratings yet
- Controlled Rectifier DC Drives GuideDocument25 pagesControlled Rectifier DC Drives GuideshonmlrNo ratings yet
- System Sensor I Series: Photoelectric Smoke DetectorsDocument2 pagesSystem Sensor I Series: Photoelectric Smoke DetectorsMinhthien NguyenNo ratings yet
- OEC One Service Manual SM 6888001-1EN 5Document319 pagesOEC One Service Manual SM 6888001-1EN 5victor100% (1)