Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exam 1 Answers
Uploaded by
LawangeenzCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exam 1 Answers
Uploaded by
LawangeenzCopyright:
Available Formats
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
90 minutes
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
D
D
D
E
C
C
B
C
C
C
B
B
B
B
D
C
C
D
B
B
E
B
A
C
E
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
(B)
D
B
C
B
B
C
D
C
D
E
B
B
C
A
B
D
C
C
C
A
B
D
C
D
A
B
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
1.
90 minutes
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a yeast, would be most closely related to which of the following
species?
D.
2.
Homo sapiens
L1/S4
Yeasts, which are fungi, are closer in phylogeny to animals than to molds or plants.
Which of the following statements regarding the cytoskeleton is correct?
D.
3.
Each filament monomer interacts by noncovalent interactions.
L1/S7,10
Actin filaments are the smallest; it is dynamic; it helps cells and organelles move; it also aids in
cell division (mitosis). Each filament is compose of protein monomers bound noncovalently
to form a long polymer.
Which of the following functional groups is not represented in the molecule below?
D.
4.
Sulfhydryl
L1/S19
Dont miss these problems.
Which molecule is the heaviest, on average, and how many of its molecules exist in a typical
human cell?
E.
DNA; 46
L1/S16
DNA is the heaviest molecule at 1 1011 g mol-1 (or Da), and there are 46 molecules (46
chromosomes) in a typical diploid cell.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
5.
90 minutes
The arrangement of water molecules in ice is:
C.
6.
A tetrahedral lattice due to 4 hydrogen bonds.
L2/S4
Solids typically have lattice structures. Ice is stated to use all 4 of the possible hydrogen
bonds. Gases are the ones with no fixed arrangement. Liquid water has the flickering
structure. Sheets of molecules that can slide are actually a characteristic of graphite, not ice.
An unknown solution has a pH of 12.33 due to a compound. Given that
["# ]
[%"]
is 24.24, what
is the ' of the chemical in solution?
C.
1.12 10-11
L2/S22
Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
0
= ' +
12.33 = ' + 24.24
12.33 1.39 = 10.95 = '
' = 100;<= = 100>?.@A
' = 1.13100>>
7.
A researcher discovers a new acid, X. At pH 6.4, there is one thousand more times XH than
X-. What is the pKa of X?
B.
9.4
L2/S22
Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
= ' +
6.4 = ' +
1
1000
6.4 + 3 = 9.4 = '
Remember that its + Log, not Log. This makes sense because if you increase [A], you
increase the amount of base, so pH should increase because the Log expression increases.
8.
Which of the following statements is true?
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
C.
9.
90 minutes
Protein structure determines phenotype.
L3
DNA is transcribed into RNA, not translated. mRNA is translated into protein, not
transcribed. The minor groove is a palindrome, so to speak, in that the forward and reverse
base sequences are read in the same way, so it cant be more specific than the major groove.
Nucleosides lack the phosphate, nucleotides have the phosphate. It is true that protein
expression is what determines ones phenotype. Even if you were unsure about whether this
was true, you could eliminate the other definitely false answers to arrive here.
The molecules below are the monophosphate versions of (d)NTPs. Pyrophosphorylation of
which of these molecules forms the dominant energy currency for all living cells?
C.
L3/S8
Pyrophosphate is 2 inorganic phosphates. The molecule in question is adenylate, or
adenosine 5monophosphate, AMP. Addition of 2 inorganic phosphates to AMP forms
ATP, the main form of energy in living cells. Note that it is not the deoxy form, or else we
would call it dATP, so the 2OH is present.
10.
In the year 2013, a deceased alien life form was found in a crater. Scientists analyzed its
genetic code, and found that it was similar to Earth-based life. They discovered that the
percent of thymine was 37%, and its genetic code was 3.2 109 base pairs long, similar to
humans. Given that the GC content in humans is about 41%, how would the thermal
stability of the aliens genome compare with that of a humans?
C.
It would be less stable, because genome stability depends linearly on GC content
L3/S10
%T = 37% = %A, so %AT = 74%, and %GC = 26%. This is lower than the human %GC of
41%, so its genome would be less stable. From graph 2 on S20, Tm is seen to depend
linearly on %GC. A higher Tm inplies a greater stability.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
11.
90 minutes
Which of the following diagrams correctly indicates the pattern of hydrogen bonding in an
AT base pair?
B.
L3/S13
Just draw these bases out a bunch of times. One way to remember it might be to pair up the
numbers. Ex. N1NH3 and NH6O4. Try to see these from multiple perspectives,
because, like here, they may not be in the same arrangement as in the slides.
-mercaptoethanol is commonly used to break disulfide bonds. Which of the following
molecules would react with -mercaptoethanol?
12.
B.
13.
Cystine
L4/S20
Only cystine and methionine have sulfurs, so eliminate A and D. Recall that the pairing of
2 cysteine molecules yields cystine, which has a disulfide bond.
Which of the following sequences is not a valid sequence of amino acids?
B.
14.
ADMIRALACKBAR
L4/S29
If you know your one-letter codes, you should realize that B is not an amino acid you are
responsible for, so treat it as an invalid entry.
Which of the following amino acids can be synthesized de novo in the human body?
B.
L4/S30
If the body can synthesize it, its not an essential amino acid. Y is not an essential amino
acid. Some people like to use PVT TIM HaLL to remember the essential ones, but thats a
little confusing since those arent actually the one-letter abbreviations. I like WTF MILK
H(I)V better.
15.
What is the pI of the following amino acid, given that it has buffer points at 2.18, 8.95, and
10.53?
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
D.
16.
9.74
L4/S10
Buffer points just means those are its pKas. pI occurs when the net charge is 0, and that will
happen when the C terminus (2.18) is deprotonated, the N terminus (8.95) is protonated, and
the side chain (10.53) is neutral. So, between 8.95 and 10.53, Lys (this amino acid) will have a
neutral charge. Average 8.95 and 10.53 to obtain 9.74. If you had trouble determining which
was the N terminus and which was the R group, most N termini are around 9 and most C
termini are near 2. 8.95 is closer to 9 than 10.53 is.
What is the approximate length of a peptide bond?
C.
90 minutes
1.32
L5/S7
Peptide bonds are 1.32 long, notably shorter than the CN bond adjacent.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
17.
90 minutes
Find the isoelectric point of the following peptide:
Given this information:
Amino acid
His
Glu
Leu
Lys
Ser
C.
pKa1
1.82
2.19
2.36 (1)
2.18
2.21
pKa2
6.00 (3)
4.25 (2)
9.60
8.95
9.15
pKa3
9.17 (4)
9.67
10.53 (5)
7.59
L5/S16-17
First, work out the relevant pKas. The ones to consider are highlighted in red, and are
ranked numerically. Start at the fully protonated form, at pH = 1:
pH = 1: +3 charge
pH = 2.36: +2.5 charge
pH = 3: +2 charge
pH = 4.25: +1.5 charge
pH = 5: +1 charge
pH = 6.00: +0.5 charge
pH = 7: 0 charge
pH = 9.17: -0.5 charge
pH = 10: -1 charge
E.??F@.>G
Average the pKas on either side of the 0 charge: =
= .
H
If you werent sure which pKas to use for Lysine and got 7.48, try to remember that the N
terminus is usually around 9, and the C terminus is around 2. 8.95 is closer to 9 than 10.53
is, so 10.53 should be the R group and 8.95 the N terminus.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
18.
90 minutes
A dodecapeptide is capable of having how many possible sequences?
D.
19.
4.10 1015
L5/S19
Dodeca = 12, so a peptide with 12 amino acids. To find the number of sequences of a
dodecapeptide (12), do 2012.
A homodimerized protein weighs 213 kDa. About how many amino acids are in the
undimerized protein?
B.
968
L5/S18
H>L??? M'
213 kDa = 213,000 Da,
= 1936 in the full protein, so in a homodimer (dimer
>>? M' ""#N
= 2 units, homo = same a 2 unit protein with each unit having the same sequence), each
>@LE
subunit will have
= 968 amino acids
H
20.
The protein PMP22 is a structural protein of the myelin surrounding certain neurons.
Mutations in PMP22 can lead to CharcotMarieTooth (CMT) disease, which occurs in
several types. Type 1E CMT disease is caused by amino acid substitutions, and hearing loss is
a common symptom of type 1E CMT disease.
PMP22 consists partly of four transmembrane helices embedded within the myelin
membrane. A researcher theorizes that type 1E CMT disease may be caused by a substitution
of alanine by proline. Is this a likely assessment?
B.
Yes, because proline substitution is implicated in destruction of helices.
L6/S9
The term missense mutation may not mean much to you, but you should know that a single
changed amino acid wont always destroy a proteins structure. While C might be partially
correct, it isnt in this case because Pro is known to destroy helices.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
90 minutes
For the following arrangement of sheets, indicate the direction in which each strand runs:
21.
E.
None of these.
Without an initial condition given, this problem is a little more tricky. But you should realize
that none of the answers would have worked.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
22.
90 minutes
The structure of PMP22, described in question 20, is shown below:
N
C
Where N and C represent the respective termini of the protein.
In which of the regions of the associated Ramachandran plot would one expect a high
density of allowed conformation angles?
I.
II.
III.
IV.
B.
A
B
E
D
I and III only
L6/S26-28
PMP22 is seen to contain RH helices and antiparallel strands. Thus, one would expect
torsion plots to have greatest density in regions A and E of the Ramachandran plot above.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
90 minutes
Which of the following sequences is most likely to form sheets?
23.
A.
YRVIWYTWV
L6/S23
Know those three mnemonics. Use IVY For The Win.
This is a little on the simpler side of what could be asked.
What is the value of G for the following reaction?
24.
HO
O
H
O
H
H 2N
H
O
O
O
OH
C.
25.
H 3N
NH 3
O
H
O
OH
H 2N
H
O
OH
G = 0
L7/S12
Keq for the reaction is 1. You could use 2 solutions to this problem: Either use =
ln , plugging in 1 for K to obtain 0; or realize that hydrogen bonding does not drive
protein folding forward, and that therefore it would not effect a change in G.
Which of the following statements is true of Van der Waals interactions?
I.
II.
III.
E.
They are a type of non-covalent interaction.
They contribute to protein stability in hydrophobic molecules.
The attractive force () of Van der Waals forces follows 0E , with being the
dipole length.
I, II, and III
L8/S11
Non-covalent interactions are just that: Interactions that are not covalent bonds, which still
contribute to protein stability and structure. Clearly, VDW forces are non-covalent.
They contribute to protein structure. Individually, they are very weak, but the summation of
all these forces makes a great difference.
Attractive force is proportional to (distance)-6.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
26.
90 minutes
The GroELGroES complex is an example of a chaperonin that assists certain proteins in
folding. What is the correct sequence of steps in the chaperoninassisted folding of a protein
by GroELGroES?
D.
27.
Intermediate delivered by Hsp70ADP ATP binds GroES binds ADP dissociates
ATP is hydrolyzed
L7/S19
Amyloid is a transmembrane protein, the misfolding of which has been implicated in the
formation of plaques in Alzheimer patient brain tissue. Which of the following statements
regarding Alzheimers Disease involving amyloid would be observed?
B.
A shift in density from ( = 90, = 60) to ( = 170, = 150) on a
Ramachandran plot (refer to the plot in question 22).
This one is difficult. First, you must realize that amyloid involves the change from an
helix to a strand. Therefore, the distance between adjacent residues would increase, not
decrease (L6/S22). Selfassociation does occur in prion diseases (L7/S22,23), but this
happens in the unwinding of to . Choice D implies a shift from to helices, which is
not a characteristic of amyloid. Denaturation of helices due to Pro substitution is likewise
not applicable for this disease, although it is responsible for others. You could answer this by
process of elimination or by referring back to where the four main 2 structures are located
on the Ramachandran plot, in terms of their / angles.
28.
Which of the following statements about protein folding is false?
C.
Protein folding is driven by hydrogen bonding
L7/S12
Protein folding is not driven by hydrogen bonding. All of the other statements are true.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
29.
90 minutes
An overworked and unpaid undergraduate performs chromatography on a sample of
proteins in order to separate them. The protein she is interested in has several
helices which loop around in the cytosol, and consists of a series of repeating units with
the following sequence:
(1) LHAGSMQHLK MLKISTRKAG DKRERRGKLA (30)
Based on this sequence, which of the following chromatography types might she want
to use?
B.
Cation exchange
L7/S13
H, R, and K makes this peptide positively charged, so a cation exchanger is required.
You can eliminate gas because that is not a topic weve covered in this class. Eliminate
size-exclusion because no statement is made about the sizes of the other proteins in the
sample.
You might be tempted to default to affinity, but for one, youre not given any
information as to whether a specific antibody or coenzyme exists for the protein, and
for another, the question asks you to select a chromatography type based on this
sequence. The best answer is cation exchange, because the sequence doesnt tell you
anything with regards to affinity for specific molecules, but only its charge.
30.
A cell extract is comprised of proteins with the following molecular weights:
I.
II.
III.
IV.
Hemoglobin: 68 kDa
Myoglobin: 16.7 kDa
Bovine serum albumin: 66.4 kDa
Fibrinogen: 340 kDa
Which of these proteins would elute last in sizeexclusion chromatography?
B.
II only
L7/S15
The smaller a protein, the longer the elution time, because they get stuck in the
pores. Eluting last means that it would take the longest to fall off the column,
making myoglobin, the smallest of the batch, the last to elute.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
31.
90 minutes
In an experiment to isolate myoglobin from hemoglobin from a sample of human
blood, a researcher used a salt to precipitate the proteins sequentually from solution.
He obtained the following graph:
Where .
Based on the graph, which of the following would the researcher be able to conclude?
C.
32.
Myoglobin is more soluble than hemoglobin because a higher salt concentration is
needed to precipitate it.
L7/S10
The more salt needed, the more soluble it is, and vice versa.
Which of the following statements regarding electrophoresis is false?
D.
Proteins with a higher native charge travel farther in SDS-PAGE.
L7/20-22
The point of applying SDS-PAGE is to flood a protein with a negative charge. This makes it
so that the initial charge doesnt matter, and only its Mr does.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
33.
90 minutes
Which of the following statements about myoglobin is false?
C.
The 1 structure of myoglobin is similar to that of a single hemoglobin subunit.
L8/S13
The 3 and 2 structures are highly similar, but there are few similarities in the 1 structures
other than the positions of the His residues.
Hemoglobin A, adult hemoglobin, is a tetramer comprised of (141 AA) and (146 AA)
chains. Hemoglobin A most commonly uses Heme B. What is the estimated molecular weight
of fully oxidated hemoglobin? (Heme B = Lk LH k k )
34.
D.
35.
65,732 Da
2 -strands: 146 110 2
2 -strands: 141 110 2
Heme B = (34 12) + 32 + (14 4) + (16 4) + 56 = 616
4 Heme B per Hb = 616 4
4 O2 per Heme B = 32 4
(141 110 2) + (146 110 2) + [(616 + 32) 4] = 65,732
Arrange the affinities for oxygen of the following globins:
22, 22BPG, myoglobin, 22
E.
36.
Myoglobin > 22 > 22 > 22BPG
L8/S22,32
Myoglobin has the highest affinity for O2. The subunit (in fetuses) is higher affinity
than the subunit (adult subunit). BPG lowers the affinity of Hb for O2.
Which of the following statements is false?
B.
C.
Enzymes change the equilibrium constant.
L10/S3
Enzymes do not affect equilibria, only rate.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
37.
90 minutes
IgG is depicted in the image belo
2
3
1 to a foreign organism; and
2 to a macrophage?
At which region(s) would IgG bind:
B.
1 & 2; 5
L8/S33-35
The Y-shaped region bind the antigens (foreign organism) at both tips (1, 2), and the base
of the Y (5) binds the white blood cell.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
38.
90 minutes
The following graph shows the oxygen dissociation curves for hemoglobin and myoglobin:
Where pO2 (mmHg) is plotted on the xaxis, and mole fraction of oxygen (t H ) is plotted
on the yaxis.
In the presence of BPG, how would the curves for hemoglobin and myoglobin change?
C.
The curve for hemoglobin will shift right; the curve for myoglobin will not shift.
L8/S22
BPG lowers the affinity of Hb by binding in between -subunits. Mb has no other subunits,
so it does not bind BPG. A rightward shift on the graph indicates a lower affinity for O2
(more pO2 is needed to have the same partial pressure).
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
39.
90 minutes
A researcher wants to identify the sequence of an unknown peptide. One of the steps she
takes in doing so is to digest part of it with chymotrypsin. SDS-PAGE analysis of the original
protein shows one band, and analysis after digestion shows 4 bands. Which of the following
could be the sequence of the peptide?
A.
40.
(N) PSLY THECRRECTANSERY NAW TMPA (C)
L10/S21
3 new bands forming means there was 1 to begin with and now there are 4. The correct
peptide pieces are shown by spaces. Chymotrypsin cleaves at the C-end of the amino acids
Y, W, F, unless there is a P immediately afterwards (ruling out choice B).
A researcher is studying an enzymatic reaction scheme, and believes he has come up
with the correct pathway. A very simplified version is reproduced below:
To prevent this reaction from occurring, a competitive inhibitor can be developed,
which is an analog of the molecule for which the enzyme has the highest affinity.
Which of the labeled molecules might this analog resemble?
B.
B only
L9/S20-22
Enzymes have the highest specificity for the transition state. A good competitive
inhibitor would resemble the transition state, which is molecule B.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
90 minutes
In one particular trial, a researcher begins recording his measurements for ? after starting
an enzyme-catalyzed reaction using 10 M of enzyme and 1 M of substrate. The initial
velocity for this trial is determined to be about 3.6 M per minute, as per the graph below,
and he determines v'w to be 4.0 M per minute. From this trial, and the following graph
of his complete results, he calculates the rate-limiting step to have a rate constant of about:
41.
D.
0.396 0>
L12/S14
The Michaelis-Menten equation is ? =
yz={ |{ [}]
<~ F[}]
. The rate-limiting step is ' . Weve
been given a particular set of initial conditions which will make it easier to calculate this
value.
? = 3.6 0>
= 10
= 1
>
Leaving us to calculate v . v is the substrate concentration [ ] at which = v'w .
H
v'w is given to be 4.0 0> , so v will be found at 2.0 0> . Draw the lines
over, and youll find that [] at this point is roughly 0.1 . Therefore:
3.6
' 10 1
=
0.1 + 1
= . 0
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
42.
90 minutes
The Lineweaver-Burk plot for the enzyme (labeled E1) studied in question 41 is shown
below, with that of 2 other enzymes (which also catalyze the same reaction) also
superimposed onto the graph (E2, E3).
Which of the following assessments is valid regarding the activity of these enzymes with
regards to E1?
C.
E2 has the same affinity and a higher v'w ; E3 has a lower affinity and the same v'w .
L12/S19
If they catalyze the same reaction, they can be compared.
E1 and E2 are seen to intersect the x-axis at the same point, so they have the same v . E1
and E3 are seen to intersect the y-axis at the same point, so they have the same v'w . This
much was given to you.
E1 intersects the y-axis higher than E2 does. This means that
>
~=
is greater for E1. This
means that v'w is actually smaller for E1.
E1 intersects the x-axis more leftward than E3 does. This means that
>
<~
is greater for E1,
meaning v is actually smaller as well. Dont let that negative throw you off.
An easy way to remember this: Slower-acting enzymes have steeper lines. This is why
inhibition steepens the line. Any change that steepens this line (higher y-intercept, or more
rightward x-intercept) will result in a slower reaction, which can result from, respectively, a
lower v'w , or a higher v . (Remembering of course that a higher v means a lower
affinity!)
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
43.
90 minutes
Which of the following is not a general example of covalent modification leading to
regulation of an enzyme?
C.
44.
Allosteric interactions of molecular oxygen on hemoglobin.
L13/S11
Hemoglobin, while being regulated by the presence of oxygen, is not an enzyme, but rather
a binding protein. In addition, the binding of oxygen is allosteric. The rest of these are
examples of covalent (as opposed to allosteric) modifications as per the slide given.
The structures of Saquinavir and Indinavir are shown below:
These two molecules are capable of inhibiting HIV proteases. What type of inhibition do
both of these carry out?
C.
Competitive non-covalent
L12/S30
Even if you didnt remember this outright, it is partially answerable by elimination.
Both of these structures are fairly similar. Chances are, its competitive inhibition.
Otherwise, covalent vs. non-covalent is more straight recall.
Coupling with the hydrolysis of the phosphate of ATP is one way enzymes overcome
energy barriers to unfavorable processes. Which law of thermodynamics does this
exemplify?
45.
A.
First law
L13/S12
Energy may change form, and may be transported, but energy cannot be created or
destroyed.
Energy from ATPs hydrolysis contributing to overcoming an endergonic reactions
activation energy is a great example of the first law of thermodynamics.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
46.
90 minutes
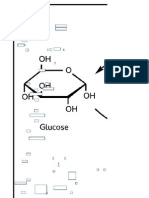
Which term best describes the relationship between glucose and galactose?
B.
47.
Epimers
L14/S7
Glucose and galactose, along with mannose and fructose, are the four carbohydrates whose
names are boxed; take this to mean you should know their structures rote.
Constitutional isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula. Surely,
glucose and galactose do so, but the question asks you to pick the best term. A more specific
term for these exists.
They are not enantiomers, because they do not differ in configuration at every carbon.
Conformational isomers differ in their conformation. Examples are: Ring flips, Fischer
projections, rotations about a single bond.
Glucose and galactose differ in orientation at just 1 carbon, C4. The best term for these two
molecules is epimers.
You discover two new sugars, Tyrannose and Tricerose, named after the organisms from
which they were found. Their structures are shown below:
Anomeric carbon
1
2
Similarly to how 5
membered cyclic ethers
Anomeric carbon
are called pyrans, 7 membered cyclic ethers are oxepanes and 4 membered ones are oxetanes.
When mixed together, tyrannose and tricerose bond together to make a disaccharide thusly:
According to standard IUPAC carbohydrate nomenclature, characterize this disaccharide.
D.
-D-tyrannooxepanosyl-(12)--D-tricerooxetanose
L14/S13
The left sugar gets osyl, the right sugar gets ose. Tyrannose is , because the anomeric OH
and the CH2OH are trans. Tricerose is , because the anomeric OH and the CH2OH are cis.
The bond is from 1 to 2. Both molecules are D, because their Fischer projections have the
next-to-last OH groups on the right.
BCH4024 SU2015 E1A
48.
90 minutes
The following molecule could be a part of what type of carbohydrate?
C.
49.
Dextran
L14/S18
This molecule has a (12) linkage. Such linkages are a characteristic of dextrans. If you see
a molecule that isnt (16) or (14) theres a good chance its a dextran.
Which of the following fatty acids would have the lowest melting point?
D.
50.
16:1(9) cis-Hexadeceneoic acid
L15/S5
Dont memorize this table. But, do realize that even one unit of unsaturation will sharply
decrease the melting point. 16:1(9) beats 18:1(9) because the latter has 2 more carbons, and
increasing carbon count increases melting point. You might be tempted to pick 12:0 because
it has 4 fewer carbons than 16:1(9), but it is important to see that the effects of adding carbon
are much less pronounced than of adding a double bond.
What is the general structure of a phospholipid?
A.
A polar head group attached to two fatty acid chains.
L15/S11
Know the general structure of each type of fatty acid complex.
Bonus1
T / F: The fatty acid below can be characterized as an omega-3 fatty acid:
7
3
B.
F
Omega-3 fatty acids have a double bond starting at the third carbon, when counting from
the opposite side.
There are no bonuses on your exam
You might also like
- Ventricular System Arslan&Wiranowska Post 1Document41 pagesVentricular System Arslan&Wiranowska Post 1LawangeenzNo ratings yet
- KovaaK Aim Workout RoutinesDocument14 pagesKovaaK Aim Workout RoutinesLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- 3.17.17 Neuroendocrine Control (Breslin)Document48 pages3.17.17 Neuroendocrine Control (Breslin)LawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Clinical Clerkship Survival Guide: USF Morsani College of Medicine Class of 2020Document56 pagesClinical Clerkship Survival Guide: USF Morsani College of Medicine Class of 2020Lawangeenz40% (5)
- E3 2014Document2 pagesE3 2014LawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Programs IDocument1 pagePrograms ILawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Kinetic vs. Thermodynamic EnolatesDocument2 pagesKinetic vs. Thermodynamic EnolatesLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Practice 3Document4 pagesPractice 3LawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism WorksheetDocument1 pageCarbohydrate Metabolism WorksheetLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 ScoresDocument2 pagesExam 1 ScoresLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Lecture Schedule 2011Document2 pagesLecture Schedule 2011LawangeenzNo ratings yet
- MDU 4004 Spring 2014 SyllabusDocument10 pagesMDU 4004 Spring 2014 SyllabusLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- BCH 6206-2011 SyllabusDocument4 pagesBCH 6206-2011 SyllabusLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- BSC 3096 Fall 2013 ScheduleDocument2 pagesBSC 3096 Fall 2013 ScheduleLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- OkamiDocument51 pagesOkamiphilbatman100% (1)
- 081 CH 14Document4 pages081 CH 14LawangeenzNo ratings yet
- TPRH CorrelationDocument2 pagesTPRH CorrelationLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 No AnswersDocument10 pagesChapter 17 No AnswersLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- TBRBiology 1Document372 pagesTBRBiology 1Fabliha Huq100% (11)
- Homework 0: LESSONS in The Course Website. It Is Very HelpfulDocument3 pagesHomework 0: LESSONS in The Course Website. It Is Very HelpfulLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- Mystic ForestDocument6 pagesMystic ForestLawangeenzNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Bhalani New Pathology 3456 - 67392Document6 pagesBhalani New Pathology 3456 - 67392shreyas mhapadiNo ratings yet
- Common Communicable DiseasesDocument213 pagesCommon Communicable Diseasesɹǝʍdןnos100% (24)
- Hydradinitis SupparativaDocument46 pagesHydradinitis SupparativaSaqib SaeedNo ratings yet
- ENT Emergency PresentationDocument135 pagesENT Emergency PresentationshahiruddinNo ratings yet
- Elective 102 Module 4 Activities:: Test Your Nursing KnowledgeDocument5 pagesElective 102 Module 4 Activities:: Test Your Nursing KnowledgeEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Mixed Radiolucent/radio-Opaque Jaw Lesions (Schematic Radiographic Approach)Document1 pageMixed Radiolucent/radio-Opaque Jaw Lesions (Schematic Radiographic Approach)Vansh Vardhan MadaharNo ratings yet
- Implantable Cardioverter DefibrillatorDocument5 pagesImplantable Cardioverter DefibrillatorvishwanathNo ratings yet
- BLOCK II LMS Quiz AnatomyDocument27 pagesBLOCK II LMS Quiz AnatomyAshley BuchananNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument41 pagesSurgical Management of Coronary Artery Diseaseapi-19916399No ratings yet
- MastitisDocument12 pagesMastitismanal at100% (1)
- Qtern 84413Document19 pagesQtern 84413Manoj KaluvakotaNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: Dr. Narendra Singh Shekhawat Assistant Professor Department of Shalya TantraDocument21 pagesIntussusception: Dr. Narendra Singh Shekhawat Assistant Professor Department of Shalya TantrakhushbuNo ratings yet
- List of Occupational DiseasesDocument20 pagesList of Occupational DiseasesAbhishek S PillaiNo ratings yet
- Os 1Document4 pagesOs 1rizwanNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaDocument59 pagesNeuro-Onkologi: Bagian/SMF Saraf FK-UGM/RS Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaNovasiska Indriyani HutajuluNo ratings yet
- Kubba 2001 (Intervention For Recurren Idiopathix Epistaksis in ChildrenDocument26 pagesKubba 2001 (Intervention For Recurren Idiopathix Epistaksis in ChildrenRaudhah SimahateNo ratings yet
- VestibulitisDocument3 pagesVestibulitisDeniNo ratings yet
- Drug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsDocument4 pagesDrug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsYusoff RamdzanNo ratings yet
- Thymosin Hormone InfographicDocument1 pageThymosin Hormone InfographicCarolina VargasNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Neuropsychiatric Effects Psychotropic Interact IonsDocument13 pagesAntibiotics: Neuropsychiatric Effects Psychotropic Interact Ionsracm89No ratings yet
- Spinal Tumors: Dr. Samuel Oluka Supervisor Dr. J KiboiDocument62 pagesSpinal Tumors: Dr. Samuel Oluka Supervisor Dr. J KiboiSam OlukaNo ratings yet
- What Is-Thrombocythemia and ThrombocytosisDocument4 pagesWhat Is-Thrombocythemia and ThrombocytosisFred C. MirandaNo ratings yet
- Need Motivates The Behaviour of A Person.: Human Needs TheoryDocument8 pagesNeed Motivates The Behaviour of A Person.: Human Needs TheoryDan Ataniel EnsaladaNo ratings yet
- Pathologyq'sDocument358 pagesPathologyq'sNick JacobNo ratings yet
- Interrelations Between Essential Metal Ions and Human Diseases (Sigel) PDFDocument603 pagesInterrelations Between Essential Metal Ions and Human Diseases (Sigel) PDFEduardo Cienfuegos100% (1)
- Internal Diseases Propedeutics Part I. Diagnostics of Pulmonary Diseases PDFDocument94 pagesInternal Diseases Propedeutics Part I. Diagnostics of Pulmonary Diseases PDFYashwanth vNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure - Components of TherapyDocument22 pagesTreatment of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure - Components of TherapyYahaira Borquez RiosNo ratings yet
- TBI QuizletDocument4 pagesTBI QuizletLoraine CometaNo ratings yet
- PChapter 12 Nerve Tissue PDFDocument3 pagesPChapter 12 Nerve Tissue PDFRuel MateoNo ratings yet
- Piron I 2016Document13 pagesPiron I 2016Yacine Tarik AizelNo ratings yet