Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Body Systems Interactions Chart
Uploaded by
Jacinto SanzCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Body Systems Interactions Chart
Uploaded by
Jacinto SanzCopyright:
Available Formats
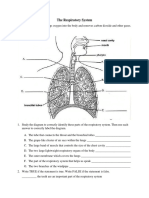
Name _________________________________ Period _______ Date _________________
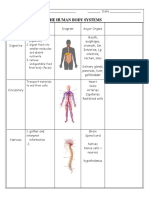
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
System
Digestive
Function
1. take in food
(ingestion)
2. digest food into
smaller molecules
and absorb
nutrients
3. remove
undigestable food
from body (feces)
Transport materials
to and from cells
Circulatory
Nervous
1. gathers and
interprets
information
2. responds to
information
3. helps maintain
homeostasis
Diagram
Major Organs
Mouth,
esophagus,
stomach, Sm.
Intestine, Lg.
intestine,
rectum, anus
Salivary glands,
pancreas, liver,
gall bladder
Heart
Veins
Arteries
Capillaries
Red blood cells
Brain
Spinal cord
Nerves
Nerve cells =
neurons
hypothalamus
InteractionsWorking with Other
Systems
1. w/circulatory absorb &
deliver the digested
nutrients to the cells
2. w/muscular control the
contractions of many of the
digestive organs to pass
food along
3.w/nervous hypothalamus
maintains homeostasis by
triggering appetite
(stomach growling), digest.
1. w/respiratory deliver O2 from
lungs to cells and drop off CO2
from cells to lungs
2. w/digestive absorb and
deliver digested nutrients to cells
3. w/excretory kidneys filter
cellular waste out of blood for
removal
4. w/lymphatic both transport
things to and from cells
5. w/immune transports WBCs
throughout body to fight disease
6. w/nervous brain controls
heartbeat
7. w/endocrine trans. hormones
Controls all other
systems
Hypothalamus maintains
homeostasis by working
with all systems
System
Excretory
Function
1. removes waste
products from
cellular
metabolism (urea,
water, CO2)
2. filters blood
Takes in oxygen
Respiratory and removes carbon
dioxide and water
Skeletal
1. protects organs
2. provides shape,
support
3. stores materials
(fats, minerals)
4. produces blood
cells
5. allows movement
Diagram
Major Organs
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
Lungs
Skin sweat
glands
Liver (produces
urea)
Nose
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
lungs
Bones
Cartilage
ligaments
InteractionsWorking with Other
Systems
1. w/circulatory filters
waste out of blood
2. w/lungs removes
excretory waste
3. w/integumentary
removes excretory waste
1. w/circulatory takes
in O2 for delivery to cells
and removes CO2 brought
from cells
2. w/excretory removes
excretory waste
3. w/nervous controls
breathing
4. w/muscular
diaphragm controls
breathing
1. w/muscular allow
movement
2. w/circulatory
produce blood cells
3. w/immune produce
white blood cells
4. w/circulatory and
respiratory protects
its organs
System
Muscular
Endocrine
Function
Diagram
Major Organs
Allows for
movement by
contracting
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
tendons
1. w/skeletal allow
movement
2. w/digestive allow
organs to contract to push
food through
3. w/respiratory
diaphragm controls
breathing
4. w/circulatory controls
pumping of blood (heart)
5. w/nervous controls all
muscle contractions
Regulates body
activities using
hormones. Slow
response, long
lasting
Glands
*Hypothalamus
*Pituitary
*Thyroid
*Thymus
*Adrenal
*Pancreas
*Ovaries
*Testes
1. w/circulatory
transports hormones to
target organs
2. w/nervous maintain
homeostasis, hormone
release
3. w/reproductive
controlled by hormones
4. w/skeletal controls
growth of bones
Glands produce
Hormones
Immune
InteractionsWorking with Other
Systems
Fights off foreign
invaders in the
body
White Blood
Cells
*T cells
*B cells
-produce
antibodies
*Macrophages
Skin
1. w/circulatory
transports WBCs to
fight invaders
2. w/lymphatic has lots
of WBCs to fight
invaders, spleen filters
bacteria/viruses out of
blood
3. w/skeletal WBCs
made in bone marrow
4. w/integumentary
prevents invaders from
getting in
System
Function
1. barrier against
IntegumenInfection (1st line
tary
of defense)
2. helps regulate
body temp.
3. removes
excretory waste
(urea, water)
4. protects against
suns UV rays
5. produces vitamin
D
1. stores and
Lymphatic
carries WBCs
that fight
disease
2. collects excess
fluid and returns
it to blood (2nd
circulatory
system-reaches
places other one
cant between
cells)
Reproductive
Allows organisms to
reproduce which
prevents their
species from
becoming extinct.
Diagram
Major Organs
SKIN
*Epidermis
*Dermis
- sweat gland
- sebaceous
gland (oil)
- hair follicle
- blood
vessels
- nerves
Lymph (liquid
part of blood
plasma, when
its in lymph
vessels)
Lymph Vessels
Lymph Nodes
Contain WBCs
InteractionsWorking with Other
Systems
1. w/excretory removes
cellular waste
2. w/nervous controls
body temperature
(sweating, goose bumps)
3. w/immune prevents
pathogens from entering
1. w/immune holds lots
of WBCs to fight
pathogens
2. w/circulatory to
transport materials to
and from cells
Ovaries
1. w/endocrine controls
*produce eggs production of sex cells
2. w/muscular uterus
Testes
contracts to give birth
*produce
controlled by hormones
sperm
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerNathaniel FerrerNo ratings yet
- Human Body System NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Body System NotesShannon BandyNo ratings yet
- A-P - Ch01 - Organ Systems Overview HandoutDocument3 pagesA-P - Ch01 - Organ Systems Overview HandoutMaggie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Biliran Province State University ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesBiliran Province State University ISO 9001: 2015 CERTIFIED: Republic of The PhilippinesRica MariaeNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System ActivityDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory System ActivityCarmelite Nazareth100% (2)
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Systems BookletDocument8 pagesSystems Bookletapi-383568582No ratings yet
- 2013 Body Systems NotesDocument5 pages2013 Body Systems Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - The VitaminsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - The VitaminsYcell LatidoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Plant and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesParts of A Plant and Their FunctionsLydia RodioNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument28 pagesRespiratory Anatomy & PhysiologyKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Digestive System-1Document3 pagesDigestive System-1elinandreaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System WorksheetDocument1 pageMuscular System Worksheetapi-238647540No ratings yet
- Chapter25 Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesChapter25 Urinary Systemkikajet23No ratings yet
- Reference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EDocument11 pagesReference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EAnnalei GagnéNo ratings yet
- CH 03 Lecture Presentation-1 PDFDocument136 pagesCH 03 Lecture Presentation-1 PDFanon_33138328No ratings yet
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Cells and TissuesClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of MedicineDocument3 pagesReview Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of Medicineeddy surielNo ratings yet
- Pollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderDocument16 pagesPollution Is The Introduction of Contaminants Into A Natural Environment That Causes Instability, DisorderJassi Layal100% (2)
- CirculatorySystem GizmoDocument4 pagesCirculatorySystem GizmoNashly Ramirez50% (2)
- Joint PainDocument8 pagesJoint Painحنين حسن عبد علي حسينNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in BloodDocument12 pagesWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Practice TestDocument5 pagesBody Systems Practice TestTINAIDANo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems ChartDocument3 pagesHuman Body Systems ChartJamie Sims100% (2)
- The Endocrine System Study GuideDocument4 pagesThe Endocrine System Study Guideapi-2776680980% (1)
- Review Sheet Chapter 2 - Language of MedicineDocument4 pagesReview Sheet Chapter 2 - Language of Medicineeddy surielNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The CellDocument132 pagesChemical Composition of The Cellazfdin100% (3)
- Genetics Unit OutineDocument2 pagesGenetics Unit Outinejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System WorksheetDocument2 pagesRespiratory System WorksheetPeter Mazowiecki-KocykNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: Hs Bio 002-General Biology 2Document2 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: Hs Bio 002-General Biology 2AndreaNicoleBanzonNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesParts of The Skeletal SystemJohn Paul Espineli FeranilNo ratings yet
- Blood: 1. Medullary Cavities of Long Bones 2. Spongiosa of Vertebral Bodies, Ribs, Sternum 3. Flat Bones of The PelvisDocument2 pagesBlood: 1. Medullary Cavities of Long Bones 2. Spongiosa of Vertebral Bodies, Ribs, Sternum 3. Flat Bones of The PelvisKrizza Mariz Bautista PolaronNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nursing ExamDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology of Nursing ExamBasava VillanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Circulatory Systemolivia majcherNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- Resume of Bijo MathewDocument6 pagesResume of Bijo MathewBijo Mathew100% (1)
- Endocrine System Study SheetDocument2 pagesEndocrine System Study SheetberracoudashNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Study GuideDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System Study Guideapi-237316144No ratings yet
- Anatomy Ch. 9 The Senses NotesDocument7 pagesAnatomy Ch. 9 The Senses Notesprincepalestine100% (1)
- Anph121lb CardiovascularDocument28 pagesAnph121lb CardiovascularDANIELA PEREZNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument15 pagesLipidsZam-zamNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 The Special SensesDocument8 pagesUnit 14 The Special SensesJess LNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundation of Nursing - Florence NightingaleDocument9 pagesTheoretical Foundation of Nursing - Florence NightingaleAshley Nicole BeltranNo ratings yet
- GENETICS Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesGENETICS Reviewer PDFMargarita RosarioNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and MetabolismDocument9 pagesNutrition and MetabolismarunatejaNo ratings yet
- 30.1 Organization of The Human BodyDocument30 pages30.1 Organization of The Human Bodymoniaguayo98No ratings yet
- Chapter1-AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODYDocument9 pagesChapter1-AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODYKie MusstisqueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab 1: Sectional Planes & TerminologyDocument9 pagesAnatomy Lab 1: Sectional Planes & TerminologyaliNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Molecules of LifeDocument20 pagesBiochemistry: Molecules of Lifeapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Bped 65 Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesBped 65 Urinary SystemDollie May Maestre-TejidorNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance and DisodersDocument86 pagesAcid-Base Balance and DisodersPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- On Biological Science of Mark Mina and Krichelle Jane LopezDocument5 pagesOn Biological Science of Mark Mina and Krichelle Jane LopezMark MinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Hormones & Endocrine Glands - Tutorial WorksheetDocument2 pagesChapter 15 Hormones & Endocrine Glands - Tutorial Worksheetapi-3728508No ratings yet
- Digestive System in HumanDocument20 pagesDigestive System in Humanapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Ch05 Answer Key-TissuesDocument10 pagesCh05 Answer Key-TissuesGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- Body Systems NotesDocument2 pagesBody Systems NotesAndrea González MercadoNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Systems: - NotesDocument2 pagesThe Human Body Systems: - NotesGil Perez VelizNo ratings yet
- ZooLec Reviewer February 24Document2 pagesZooLec Reviewer February 24Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Notes 4Document1 pageBody Systems Notes 4Andrea González MercadoNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis 2Document8 pagesSymbiosis 2api-293216402No ratings yet
- Staar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7Document39 pagesStaar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7api-293216402No ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument2 pagesBody Systemsapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Protein Enzymes PPDocument13 pagesProtein Enzymes PPapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Tips For Writing A Children's Picture Storybook: CharacterizationDocument1 pageTips For Writing A Children's Picture Storybook: CharacterizationAni LucianaNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Cell BookDocument3 pagesRubric For Cell Bookapi-234295657No ratings yet
- Cell Book ResearchDocument3 pagesCell Book Researchapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Careers in Science PBLDocument4 pagesCareers in Science PBLapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Energy FlowDocument21 pagesEnergy Flowapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument3 pagesBody Systemsapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Frog PosterDocument2 pagesFrog Posterapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Plant StructureDocument16 pagesPlant Structureapi-293216402No ratings yet
- TropismDocument2 pagesTropismapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Bound BookDocument28 pagesBound Bookapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Plant TropismDocument10 pagesPlant Tropismapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Virus 4cDocument32 pagesVirus 4capi-293216402No ratings yet
- SymbiosisDocument12 pagesSymbiosisapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Ecological LevelsDocument15 pagesEcological Levelsapi-293216402No ratings yet
- From Single Cell To Me 5c-1Document13 pagesFrom Single Cell To Me 5c-1api-293216402No ratings yet
- KingdomsDocument2 pagesKingdomsapi-293216402No ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument28 pagesTaxonomyapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Transport of MoleculesDocument7 pagesTransport of Moleculesapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument1 pageMitosis Vs Meiosisapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Evolution VocabDocument13 pagesEvolution Vocabapi-293216402No ratings yet
- Venn Diagram Comparing Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageVenn Diagram Comparing Mitosis and Meiosisapi-293216402No ratings yet
- CancerDocument1 pageCancerapi-234295657No ratings yet
- Maternal Book MCNPDocument66 pagesMaternal Book MCNPChie BelisarioNo ratings yet
- Health Lesson Plan Sample: Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesHealth Lesson Plan Sample: Communicable Diseasecmonroe25100% (1)
- CBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetISHAAN GOYAL67% (3)
- List of Empanelled Lapro Service Providers - 2020-21Document10 pagesList of Empanelled Lapro Service Providers - 2020-21AartiNo ratings yet
- Bioethical Issues On Current Reproductive Technology Artificial Insemination (Ai)Document8 pagesBioethical Issues On Current Reproductive Technology Artificial Insemination (Ai)Dred Gementiza AlidonNo ratings yet
- Antenatal & Postnatal Care: 1. General InformationDocument7 pagesAntenatal & Postnatal Care: 1. General InformationanishnithaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation PreeclampsiaDocument41 pagesCase Presentation PreeclampsiaJomari Zapanta50% (2)
- Diagnosing and Treating Ectopic Pregnancy: A Review of Current EvidenceDocument3 pagesDiagnosing and Treating Ectopic Pregnancy: A Review of Current Evidencedrajayhalder9192No ratings yet
- Abortion Essay AndyDocument4 pagesAbortion Essay Andyapi-461151244No ratings yet
- Meiosis: Teacher's GuideDocument45 pagesMeiosis: Teacher's GuideLary Bags50% (2)
- Kegel ExcerciseDocument2 pagesKegel ExcerciseKezia Ariesta BenoNo ratings yet
- Essential Intrapartum Care RecommendationsDocument12 pagesEssential Intrapartum Care RecommendationsLot RositNo ratings yet
- Minimal Stimulation and Natural Cycle in Vitro Fertilization by Gautam N. Allahbadia, Markus Nitzschke (Eds.)Document114 pagesMinimal Stimulation and Natural Cycle in Vitro Fertilization by Gautam N. Allahbadia, Markus Nitzschke (Eds.)Quản Anh DũngNo ratings yet
- AMC Batch 47Document3 pagesAMC Batch 47noha darwishNo ratings yet
- Yoga Poses For Fertility and ConceptionDocument16 pagesYoga Poses For Fertility and ConceptionsuzibenNo ratings yet
- Lower Higher Plants TaxonomyDocument36 pagesLower Higher Plants TaxonomyIvka Zemiakova100% (2)
- Epithelial Tissue - Overview PDFDocument9 pagesEpithelial Tissue - Overview PDFAslak TorgersenNo ratings yet
- 1st Year - Unit 4 TestDocument1 page1st Year - Unit 4 TestFannyNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS) Tahir Kundki 6Document22 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases (STDS) Tahir Kundki 6shahrukhziaNo ratings yet
- 1 - BGB 201aDocument81 pages1 - BGB 201aAnkush YadavNo ratings yet
- Republic of the Philippines Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health ActDocument14 pagesRepublic of the Philippines Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health ActManuel Bertulfo DerainNo ratings yet
- PM - Lab.125+ (Rev+a) SSIP95063 B01 AixplorerMach30&Mach20 ObstetricalReferencesDocument164 pagesPM - Lab.125+ (Rev+a) SSIP95063 B01 AixplorerMach30&Mach20 ObstetricalReferencesSyed Muhammad BadarNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Scheme Of WorkDocument44 pagesForm 3 Science Scheme Of WorkMona MohtarNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Care and Childbirth EducationDocument41 pagesPrenatal Care and Childbirth EducationEvan ChrissantaNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi Matritva Sahyog Yojana cash incentive scheme for pregnant womenDocument2 pagesIndira Gandhi Matritva Sahyog Yojana cash incentive scheme for pregnant womenshobanaaaradhanaNo ratings yet
- HumanReproductionLessonFinal Grade 10Document18 pagesHumanReproductionLessonFinal Grade 10Valerie TingalaNo ratings yet
- Gr. 7 Health LM (Q1 To 4)Document141 pagesGr. 7 Health LM (Q1 To 4)Om NamaNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Conditions To Treat With AuriculoTxDocument13 pagesTop 10 Conditions To Treat With AuriculoTxAngela100% (1)
- Androgen PharmacologyDocument10 pagesAndrogen PharmacologySri Nurliana BasryNo ratings yet
- Jtgga 4 2 110 165Document56 pagesJtgga 4 2 110 165drklftNo ratings yet