Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCQs For Chapter 7-12 Key
Uploaded by
ismahijOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCQs For Chapter 7-12 Key
Uploaded by
ismahijCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr.
Ismail Hijazi
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
CHAPTER 7
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Theory
1.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
2.
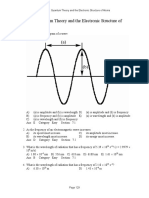
Which of the following frequencies corresponds to light with the longest wavelength?
3.00 1013 s1
4.12 105 s1
8.50 1020 s1
9.12 1012 s1
3.20 109 s1
Which form of electromagnetic radiation has the shortest wavelengths?
A) gamma rays
B)
microwaves
C)
radio waves
D) infrared radiation
E)
X rays
Use the following to answer question 10:
A photographic film needs a minimum of 80.0 kJ/mol for exposure.
3.
What is the longest wavelength of radiation with sufficient energy to expose the
film? A)
1.50 103 m
B)
1.50 106 m
C)
1.50 109 m
D) 1.50 1012 m
E)
none of these
4.
Light has a wavelength of 6.0 102 nm. What is the energy of a photon of this light?
A) 1.10 1019 J
B)
3.31 1019 J
C)
2.71 1018 J
D) 3.68 1020 J
E)
1.33 1018 J
What is the wavelength, in nanometers, of a photon of light whose frequency is 5.86 1014 Hz?
A) 1.95 102 nm
B)
5.12 102 nm
C)
3.39 102 nm
D) 2.95 102 nm
E)
1.29 10-7 nm
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
6.
Consider an atom traveling at 1% of the speed of light.The de Broglie wavelength is found to be 3.31 103
pm. Which element is this?
A) He
B)
Ca
C)
F
D) Be
E)
P
7.
From the following list of observations, choose the one that most clearly supports the conclusion that
electrons in atoms have quantized energies.
A) the emission spectrum of hydrogen
B)
the photoelectric effect
C)
the scattering of alpha particles by metal foil
D) diffraction
E)
cathode "rays"
8.
Which of the following statements is(are) true?
I.An excited atom can return to its ground state by absorbing electromagnetic radiation.
II. The energy of an atom is increased when electromagnetic radiation is emitted from it.
III. The energy of electromagnetic radiation increases as its frequency increases.
IV.An electron in the n = 4 state in the hydrogen atom can go to the n = 2 state by emitting electromagnetic
radiation at the appropriate frequency.
V. The frequency and wavelength of electromagnetic radiation are inversely proportional to each other.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
II, III, IV
III, V
I, II, III
III, IV, V
I, II, IV
9.
In an investigation of the electronic absorption spectrum of a particular element, it is found that a photon
having = 500 nm provides just enough energy to promote an electron from the second quantum level to
the third. From this information, we can deduce
A) the energy of the n = 2 level.
B)
the energy of the n = 3 level.
C)
the sum of the energies of the n = 2 and n = 3 levels.
D) the difference between the energies of the n = 2 and n = 3 levels.
E)
all of these.
10.
What is the wavelength of light that is emitted when an excited electron in the hydrogen atom falls from the
n = 5 level to the n = 2 level?
A) 5.12 10-7 m
B) 4.34 10-7 m
C)
6.50 10-7 m
D) 5.82 10-7 m
E)
none of these
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
Use the following to answer questions 20-22:
Consider the following portion of the energy-level diagram for hydrogen:
0.1361 1018 J
n=4
0.2420 1018 J
n=3
0.5445 1018 J
n=2
2.178 10 18 J
n=1
10.
For which of the following transitions does the light emitted have the longest wavelength?
A)
n = 4 to n = 3
B)
n = 4 to n = 2
C)
n = 4 to n = 1
D) n = 3 to n = 2
E)
n = 2 to n = 1
11.
In the hydrogen spectrum, what is the wavelength of light associated with the n = 2 to n = 1 electron
transition?
A) 1.097 nm
B)
364.9 nm
C)
0.1097 108 cm
D) 9.122 108 m
E)
1.216 107 m
12.
The ionization energy for a hydrogen atom is 1.31 106 J/mol. What is the ionization energy for He+?
A) 8.72 10-18 J/mol
B)
1.31 106 J/mol
C)
5.25 106 J/mol
D) 2.18 10-18 J/mol
E)
2.63 106 J/mol
13.
The wavelength of light associated with the n = 2 to n = 1 electron transition in the hydrogen spectrum is
1.216 107 m. By what coefficient should this wavelength be multiplied to obtain the wavelength
associated with the same electron transition in the Li2+ ion?
A) 1/9
B) 1/7
C) 1/4
D) 1/3
E)
1
14.
An electron in a 10.0-nm one-dimensional box is excited from the ground state into a higher energy state by
absorbing a photon with wavelength 1.374 10 -5 m. Determine the final energy level for this transition.
A)
n=2
B)
n=3
C)
n=4
D) n = 5
E)
n=6
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
15.
Which of the following is not determined by the principal quantum number, n, of the electron in a hydrogen
atom?
A) the energy of the electron
B)
the minimum wavelength of the light needed to remove the electron from the atom.
C)
the size of the corresponding atomic orbital(s)
D) the shape of the corresponding atomic orbital(s)
E)
All of the above are determined by n.
16.
Which of the following statements is true?
A) We can determine the exact location of an electron if we know its energy.
B)
An electron in a 2s orbital can have the same n, l, and ml quantum numbers as an electron in a 3s
orbital.
C) Ni has 2 unpaired electrons in its 3d orbitals.
D) In the building up of atoms, electrons occupy the 4f orbitals before the 6s orbitals.
E)
Only three quantum numbers are needed to uniquely describe an electron.
17.
How many electrons in an atom can have the quantum numbers n = 3, l = 1?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
10
2
6
18
32
18.
The number of orbitals having a given value of l is equal to
A) 2l + 1
B)
2n + 2
C)
3l
D) l + ml
E)
the number of lobes in each orbital
19.
Which of the following combinations of quantum numbers is not allowed?
(Combinations are listedas follows: n, l, m(l), m(s).)
A)
-1/2
B)
C)
D)
E)
3
3
5
3
0
1
3
2
0
1
1
0
-1/2
1/2
-1/2
1/2
20.
How many electrons can be described by the quantum numbers n = 3, l = 1?
A) 1
B)
2
C)
3
D) 5
E)
6
21.
How many f orbitals have the value n = 3?
A) 0
B)
3
C)
5
D) 7
E)
1
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
22.
What is the electron configuration for the barium atom?
A) 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s2
B)
[Xe] 6s2
C)
1s22s22p63s23p64s1
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s2
E)
none of these
23.
In which groups do all the elements have the same number of valence electrons?
A) P, O, Cl
B)
Ag, Cd, Ar
C)
Na, Ca, Ba
D) P, As, Se
E)
N, P, As
24.
What is the electron configuration of Cr3+?
A) [Ar] 4s23d1
B)
[Ar] 4s13d2
C) [Ar] 3d3
D) [Ar] 4s23d4
E)
none of these
25.
Of the following elements, which has occupied d orbitals in its ground-state neutral atoms?
A) Ba
B)
Na
C)
Al
D) P
E)
F
26.
Of the following elements, which needs 3 electrons to complete its valence shell?
A) Ba
B)
K
C)
Si
D) P
E)
Cl
27.
What is the electron configuration for Cr2+?
A) [Ar] 4s23d4
B)
[Ar] 4s13d5
C) [Ar] 3d4
D) [Ar] 4s23d2
E)
none of these
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
CHAPTER 12
Chemical Kinetics
1.
The average rate of disappearance of ozone in the reaction 2O3(g) 3O2(g) is found to be 8.9 103 atm
over a certain interval of time. What is the rate of appearance of O 2 during this interval?
A) 1.3 102 atm/time
B)
8.9 103 atm/time
C)
5.9 103 atm/time
D) 2.7 102 atm/time
E)
1.8 102 atm/time
Use the following to answer question 2:
For the reaction 2N 2O5(g) 4NO2(g) + O2(g), the following data were collected.
t (minutes)
[N2O5] (mol/L)
0
1.24 102
10.
0.92 102
20.
0.68 102
30.
0.50 102
40.
0.37 102
50.
0.28 102
70.
0.15 102
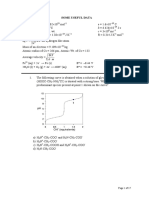
2.
The initial rate of production of NO2 for this reaction is approximately
A) 6.4 104 mol/L min
B) 3.2 104 mol/L min
C)
1.24 102 mol/L min
D) 1.6 104 mol/L min
E)
none of these
3.
The rate constant k is dependent on
A) the concentration of the reactant.
B)
the concentration of the product.
C) the temperature.
D) the order of the reaction.
E)
none of these
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
Use the following to answer questions 4-6
The oxidation of Cr 3+ to CrO42 can be accomplished using Ce 4+ in a buffered solution. The following data
were obtained:
Relative
Initial Rate
[Ce4+]0
[Ce3+]0
[Cr3+] 0
3
2
1
2.0 10
1.0 10
3.0 10 2
3
2
2
4.0 10
2.0 10
3.0 10 2
3
2
4
4.0 10
1.0 10
3.0 10 2
3
2
16
8.0 10
2.0 10
6.0 10 2
Determine the order in the rate law of the species Ce4+.
4.
A)1
B)
2
C)
3
D)1
E)
2
5.
Determine the order in the rate law of the species Ce3+.
A)1
B)
2
C)
3
D)1
E)
2
6.
Determine the order in the rate law of the species Cr3+.
A)1
B)
2
C)
3
D)1 E)
2
7.
The balanced equation for the reaction of bromate ion with bromide in acidic
solution is BrO+ 5Br + 6H+ 3Br2 + 3H2O
At a particular instant in time, the value of [Br]/t is 2.0 103 mol/L s. What is the value of [Br2]/t
in the same units?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
1.2 103
6.0 103
3.3 103
3.3 105
2.0 103
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
Use the following to answer questions 8-9:
The following questions refer to the hypothetical reaction A + B products. The kinetics data given can be
analyzed to answer the questions.
[A] 0
[B] 0
Rate of decrease
(mol/L)
(mol/L)
of [A] (M/s)
5.0
5.0
X
10.0
5.0
2X
5.0
10.0
2X
8.
Time (s)
[B] (mol/L)
10.0
20.0
30.0
100
100
100
The rate law for the reaction is Rate = k[A]x[B]y. What are the values of x and y?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
x=0
x=1
x=1
x=2
x=1
y=1
y=0
y=1
y=1
y=2
9.
What form will the pseudo-rate law have?
A) Rate = k'[A]x
B)
Rate = k'[B]y
C)
Rate = k'[A]x[B]y
D) Rate = kk'[A]x
E)
Rate = kk'[B]y
10.
The rate expression for a particular reaction is Rate = k[A][B]2. If the initial concentration of B is increased
from 0.1 M to 0.3 M, the initial rate will increase by which of the following factors?
A)
3
B)
27
C)
4
D) 6
E)
9
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
Use the following to answer questions 11-12:
The reaction
H2SeO3(aq) + 6I(aq) + 4H+(aq) 2I3(aq) + 3H2 O(l) + Se(s)
was studied at 0C by the method of initial
rates:
[H2SeO3]0
[H+] 0
[I] 0
Rate (mol/L s)
4
2
1.0 10
2.0 10
2.0 10 2
1.66 107
4
2
2
2.0 10
2.0 10
2.0 10
3.33 107
3.0 10 4
2.0 10 2
2.0 10 2
4.99 107
1.0 10 4
1.0 10 4
1.0 10 4
1.0 10 4
4.0 10 2
1.0 10 2
2.0 10 2
1.0 10 2
2.0 10 2
2.0 10 2
4.0 10 2
4.0 10 2
11.
What is the rate law?
A) Rate = k[H2SeO3][H+][I]
B)
Rate = k[H2SeO3][H+]2[I]
C)
Rate = k[H2SeO3][H+][I]2
D) Rate = k[H2SeO3]2[H+][I]
E)
Rate = k[H2SeO3][H+]2[I]3
12.
What is the numerical value of the rate constant?
A) 5.2 105
B)
2.1 102
C)
4.2
D) 1.9 106
E)
none of these
6.66
0.42
13.4
3.36
107
107
107
107
13.
For which order reaction is the half-life of the reaction independent of the initial concentration of the
reactant(s)?
A) zero order
B)
first order
C)
second order
D) all of these
E)
none of these
14.
The reaction A B + C is known to be zero order in A with a rate constant of 5.0 102 mol/L s at 25 C.
An experiment was run at 25C where [A] 0 = 1.0 103 M. What is the integrated rate law?
A) [A] = kt
B) [A] [A]0 = kt
A
= kt
C)
A 0
A = kt
A 0
D)
ln
E)
[A]0 [A] = kt
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
15.
The OH radical disproportionates according to the elementary chemical reaction OH + OH H2O + O.
This reaction is second order in OH. The rate constant for the reaction is 2.4 1012 cm3/molecule s at
room temperature. If the initial OH concentration is 1.7 1013 molecules/cm3, what is the first half-life for
the reaction?
A) 3.5 1024 s
B) 2.9 1011 s
C) 0.025 s
D) 4.9 s
E)
4.2 s
16.
The reaction A B + C is known to be zero order in A with a rate constant of 3.8 102 mol/L s at 25 C.
An experiment was run at 25C where [A] 0 = 1.8 103 M. What is the rate after 6.7 minutes?
A) 3.8 102 mol/L s
B) 1.5 1011 mol/L s
C)
6.7 104 mol/L s
D) 1.8 103 mol/L s
E)
6.8 105 mol/L s
17.
If the reaction 2HI H2 + I2 is second order, which of the following will yield a linear plot?
A) log [HI] vs. time
B)
1/[HI] vs. time
C)
[HI] vs. time
D) ln [HI] vs. time
18.
A plot of [A]2 vs. t gives a straight line.
A) zero order in A
B)
first order in A
C)
second order in A
D) all of these
E)
none of these
Use the following to answer question 19:
The following questions refer to the gas-phase decomposition of chloroethane:
C2H5Cl products
Experiment shows that the decomposition is first order.
for this reaction.
Time (s)
19.
The following data show kinetics information
ln [C2H5Cl] (M)
1.0
-1.625
2.0
-1.735
What is the rate constant for this decomposition?
A) 0.29/s
B) 0.35/s
C) 0.11/s
D) 0.02/s
E)
0.22/s
10
LIU-CHEM200: MCQ sample
Use the following to answer questions 20-21:
For a reaction aA products, [A] 0 = 4.0 M, and the first three successive half-lives are 48, 96, and 192 min.
20.
Calculate k (without units).
A) 5.2 10-3
B)
2.6 10-3
C)
4.1 10-3
D) 1.4 10-2
E)
none of these
21.
Calculate [A] at t = 81 min.
A) 1.3 M
B)
1.5 M
C)
2.6 M
D) 3.0 M
E)
none of these
22.The rate constant for a reaction increases from 10.0 s-1 to 100. s-1 when the temperature is increased from 317 K
to 427 K. What is the activation energy for the reaction in kJ/mol? (R = 8.314 J/mol K)
A) 23.6 kJ/mol
B)
10.2 kJ/mol
C)
1.74 kJ/mol
D) 21.1 kJ/mol
E)
0.0756 kJ/mol
11
You might also like
- C1100E-TDDocument27 pagesC1100E-TDghadirtaleb4No ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument26 pagesPractice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionPaolo PepsNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom - MCQsDocument4 pagesStructure of Atom - MCQsmanish561No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Practice Test AtomStrctrPeriodicTrend GOOD-KEY1Document5 pagesChapter 7 Practice Test AtomStrctrPeriodicTrend GOOD-KEY1Senthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Cairo University 3rd Year Chemistry ExamDocument3 pagesCairo University 3rd Year Chemistry ExamKhaled AbeedNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Useful ConstantsDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure: Useful ConstantsSrinjoy BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry I Exam ReviewdyrbrmNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Canadian 2Nd Edition Silberberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesChemistry Canadian 2Nd Edition Silberberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdolores.cook959100% (13)
- Atomic Structure Exercises by ResonanceDocument35 pagesAtomic Structure Exercises by Resonancechiragjn12086% (7)
- CH 7 PTDocument14 pagesCH 7 PTaaron.hartmanNo ratings yet
- Practice TestDocument0 pagesPractice TestTooba Sardar100% (1)
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Academic Session 2022-23 Worksheet-Answer KeyDocument6 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North Academic Session 2022-23 Worksheet-Answer KeyShashwatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam 1Document6 pagesChemistry Exam 1jshalda1No ratings yet
- RChE 2024 DIAG PCP 1Document4 pagesRChE 2024 DIAG PCP 1Paulo Emmanuele BetitaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Impq Ch02 Structure of Atom KvsDocument11 pages11 Chemistry Impq Ch02 Structure of Atom KvsshubhammukriNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice Week 7Document2 pagesExtra Practice Week 7ShawnNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Structure QuizDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Structure QuizKinal PatelNo ratings yet
- Nanyang Technological University Continuous Assessment Exam - I CBC111 – Principles of Modern Chemistry with Laboratory I CM1021 – Basic Inorganic Chemistry with Laboratory IDocument4 pagesNanyang Technological University Continuous Assessment Exam - I CBC111 – Principles of Modern Chemistry with Laboratory I CM1021 – Basic Inorganic Chemistry with Laboratory IJoey Tay Wei YingNo ratings yet
- One Mark QuestionsDocument4 pagesOne Mark Questionshari95No ratings yet
- Quiz Bootcamp08practicelightelectronconfigurationfa18 1Document5 pagesQuiz Bootcamp08practicelightelectronconfigurationfa18 1api-233552637No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7roxy8marie8chanNo ratings yet
- 02-Structure of AtomDocument2 pages02-Structure of AtomPriyanshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper Set 2017 SA 1Document4 pagesChemistry Paper Set 2017 SA 1Daulot SarmaNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework - Atomic Structure: o o o oDocument8 pagesHoliday Homework - Atomic Structure: o o o oRajshri PandeyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 3 Current PDFDocument9 pagesPractice Test 3 Current PDFBabeejay2No ratings yet
- Electron Configuration 2Document6 pagesElectron Configuration 2268953No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument28 pagesPhysicsSuleman KhanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of AtomDocument1 pageNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atomaadit.25520No ratings yet
- Vtu Be 1st Year Physics Question PaperDocument4 pagesVtu Be 1st Year Physics Question PapermidhunmathewNo ratings yet
- 24-10-17 - Assignment 3 Question PoolDocument1 page24-10-17 - Assignment 3 Question PoolPranavSharmaNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument16 pagesStructure of AtomMath and Science ClassesNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC STRUCTURE MCQsDocument2 pagesATOMIC STRUCTURE MCQsJeeva .sNo ratings yet
- HP Board Class XII Physics Model Question PaperDocument5 pagesHP Board Class XII Physics Model Question PaperJack DourNo ratings yet
- CH 110 Tutorial On Atomic Structure and PeriodicityDocument2 pagesCH 110 Tutorial On Atomic Structure and PeriodicityBonaventure MasekoNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet OneDocument3 pagesWork Sheet Onekaleb asegdewNo ratings yet
- Btech Model QuestionsDocument22 pagesBtech Model QuestionsAkshayKannanNo ratings yet
- Resource 20210531095551 Enrichment Work ChemistryDocument4 pagesResource 20210531095551 Enrichment Work ChemistryAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - WorkbookDocument36 pagesAtomic Structure - WorkbookJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- Within A Week of Display. Any One Problem Will Be Assigned As A Closed Book Class Test in The Following Tutorial Hour. J, Ħ 1.055 X 10Document2 pagesWithin A Week of Display. Any One Problem Will Be Assigned As A Closed Book Class Test in The Following Tutorial Hour. J, Ħ 1.055 X 10ritik12041998No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 2e (Tro)Document18 pagesChapter 7 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of The Atom: Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 2e (Tro)rulaalabadi265No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Assignment 5Document3 pagesAtomic Structure Assignment 5iamrockyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice PaperDocument7 pagesChemistry Practice PaperUmang ChapranaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Structure of AtomDocument6 pagesUNIT-2 Structure of Atomranjit sahaNo ratings yet
- Chem Wa1Document2 pagesChem Wa1Balarama RajuNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Chemistry Model ExamsDocument11 pagesGrade 12 Chemistry Model ExamsErmias100% (1)
- DPT-4 Chem & Zoo Neet 03.01.2024Document8 pagesDPT-4 Chem & Zoo Neet 03.01.2024pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- GS2011 QP ChemistryDocument17 pagesGS2011 QP ChemistryAkash AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module I-V MCQs 2 Marks 18CYB101J Virtual ExaminationDocument25 pagesModule I-V MCQs 2 Marks 18CYB101J Virtual ExaminationMAHESHWAR M R (RA2111004010136)No ratings yet
- BS109 Sem-1 Feb 2022Document4 pagesBS109 Sem-1 Feb 2022Mohammad NadirNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - Structure of AtomDocument2 pagesWork Sheet - Structure of AtomAshish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQ Module I-III ReviewDocument22 pagesChemistry MCQ Module I-III ReviewNo NameNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07tifDocument38 pagesChapter 07tifAthar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Atoms: Neutrons ProtonsDocument8 pagesAtoms: Neutrons ProtonsMelke JasinNo ratings yet
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7Document10 pagesChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7haha_le12No ratings yet
- CHEM311 191 Major2 SolvedDocument11 pagesCHEM311 191 Major2 SolvedhussainNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch36 Test BankDocument10 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch36 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom Worksheet SolutionsDocument3 pagesStructure of Atom Worksheet SolutionsMariaNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Financial Accounting Chapter 2 LECTURE - NOTESDocument14 pagesAdvanced Financial Accounting Chapter 2 LECTURE - NOTESAshenafi ZelekeNo ratings yet
- School readiness assessmentDocument10 pagesSchool readiness assessmentJave Gene De AquinoNo ratings yet
- Avanto Magnet System Error MessagesDocument21 pagesAvanto Magnet System Error MessagesMuhammad Ahmad75% (4)
- Datasheet AD549Document14 pagesDatasheet AD549Trần Hồng VănNo ratings yet
- (Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Document4 pages(Salim Ross) PUA 524 - Introduction To Law and The Legal System (Mid Term)Salim RossNo ratings yet
- Encrypt and decrypt a file using AESDocument5 pagesEncrypt and decrypt a file using AESShaunak bagadeNo ratings yet
- Geomatics Lab 6 (GPS)Document24 pagesGeomatics Lab 6 (GPS)nana100% (1)
- Mechanics of Materials: Combined StressesDocument3 pagesMechanics of Materials: Combined StressesUmut Enes SürücüNo ratings yet
- 2000 T.R. Higgins Award Paper - A Practical Look at Frame Analysis, Stability and Leaning ColumnsDocument15 pages2000 T.R. Higgins Award Paper - A Practical Look at Frame Analysis, Stability and Leaning ColumnsSamuel PintoNo ratings yet
- 4PW16741-1 B EKBT - Bufftertank - Installation Manuals - EnglishDocument6 pages4PW16741-1 B EKBT - Bufftertank - Installation Manuals - EnglishBernard GaterNo ratings yet
- Gizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsDocument5 pagesGizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsEuropaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-The Indian Contract Act, 1872, Unit 1-Nature of ContractsDocument10 pagesChapter 1-The Indian Contract Act, 1872, Unit 1-Nature of ContractsALANKRIT TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Enbrighten Scoring Rubric - Five ScoresDocument1 pageEnbrighten Scoring Rubric - Five Scoresapi-256301743No ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis MethodsDocument5 pagesSlope Stability Analysis MethodsI am AngelllNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Interview Questions and AnswersDocument34 pagesAnalog Communication Interview Questions and AnswerssarveshNo ratings yet
- CMC4 Controller Technical Support DocumentDocument148 pagesCMC4 Controller Technical Support DocumentZurab ChanturiaNo ratings yet
- Ivf Market in IndiaDocument15 pagesIvf Market in IndiaSunil Tak100% (1)
- Space 1999 Annual 1979Document62 pagesSpace 1999 Annual 1979Brin Bly100% (1)
- Strategicmanagement Finalpaper 2ndtrisem 1819Document25 pagesStrategicmanagement Finalpaper 2ndtrisem 1819Alyanna Parafina Uy100% (1)
- Fci FC CotsDocument25 pagesFci FC CotsMatthew DuNo ratings yet
- PTW QuestionareDocument63 pagesPTW QuestionareIshtiaq Ahmad100% (2)
- Causes of The Renaissance: Silk RoadDocument6 pagesCauses of The Renaissance: Silk RoadCyryhl GutlayNo ratings yet
- Edtpa Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesEdtpa Lesson Plan 1api-364684662No ratings yet
- No-Till For Micro Farms: The Deep-Mulch Method (Lean Micro Farm)Document20 pagesNo-Till For Micro Farms: The Deep-Mulch Method (Lean Micro Farm)Chelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- Rigor Mortis and Lividity in Estimating Time of DeathDocument2 pagesRigor Mortis and Lividity in Estimating Time of DeathfunnyrokstarNo ratings yet
- Tiger Tales: From Colonial MalayaDocument16 pagesTiger Tales: From Colonial MalayamatarsNo ratings yet
- Hope 03 21 22Document3 pagesHope 03 21 22Shaina AgravanteNo ratings yet
- Database Case Study Mountain View HospitalDocument6 pagesDatabase Case Study Mountain View HospitalNicole Tulagan57% (7)
- Main: Exploded ViewDocument30 pagesMain: Exploded ViewamokssantiagoNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences in NT Greek Ruben VideiraDocument62 pagesConditional Sentences in NT Greek Ruben Videiraruviso100% (1)