Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table of Thermodynamic Equations - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
Zaw Moe KhineCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table of Thermodynamic Equations - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
Zaw Moe KhineCopyright:
Available Formats
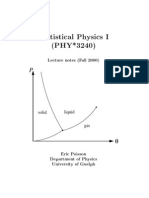
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
1 of 13
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Table of thermodynamic equations
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For list of mathematical notation used in these equations, see mathematical notation.
Main article: List of thermodynamic properties
Thermodynamics
This article is summary of common equations and quantities in thermodynamics (see
thermodynamic equations for more elaboration). SI units are used for absolute
temperature, not celsius or fahrenheit.
The classical Carnot heat engine
Contents
Branches
1 Definitions
1.1 General basic quantities
1.2 General derived quantities
1.3 Thermal properties of matter
1.4 Thermal transfer
2 Equations
2.1 Phase transitions
2.2 Kinetic theory
2.2.1 Ideal gas
2.3 Entropy
2.4 Statistical physics
2.5 Quasi-static and reversible processes
2.6 Thermodynamic potentials
2.7 Maxwell's relations
2.8 Quantum properties
3 Thermal properties of matter
3.1 Thermal transfer
3.2 Thermal efficiencies
4 See also
5 References
Definitions
Main articles: List of thermodynamic properties, Thermodynamic potential, Free entropy,
Defining equation (physical chemistry)
Many of the definitions below are also used in the thermodynamics of chemical
reactions.
General basic quantities
Classical
Statistical
Chemical
Equilibrium / Non-equilibrium
Laws
Zeroth
First
Second
Third
Systems
State
Equation of state
Ideal gas
Real gas
State of matter
Equilibrium
Control volume
Instruments
Processes
Isobaric
Isochoric
Isothermal
Adiabatic
Isentropic
Isenthalpic
Quasistatic
Polytropic
Free expansion
Reversibility
Irreversibility
Endoreversibility
Cycles
Heat engines
Heat pumps
Thermal efficiency
System properties
Note: Conjugate variables in italics
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
2 of 13
Quantity (Common
(Common)
Name/s)
Symbol/s
SI Units
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
y' '
dimensionless
dimensionless
Number of moles
mol
[N]
Temperature
[]
Heat Energy
Q, q
[M][L]2[T]2
Latent Heat
QL
[M][L]2[T]2
Number of molecules
Property diagrams
Intensive and extensive properties
Dimension
Functions of state
Temperature / Entropy (introduction)
Pressure / Volume
Chemical potential / Particle number
Vapor quality
Reduced properties
Process functions
General derived quantities
Quantity
(Common
Name/s)
(Common)
Symbol/s
Work
Heat
Defining Equation
SI Units
J1
Entropy
J K1
Negentropy
J K1
[T]2[M]1[L]2
Specific heat capacity
temperature
Partition
Function
Gibbs free
energy
[M][L]2[T]2
[]1
[M][L]2[T]2
[]1
[M][L]2[T]2
[M][L]2[T]2
dimensionless dimensionless
Internal Energy U
Enthalpy
[M][L]2[T]2
Chemical
potential (of
component i in
a mixture)
Helmholtz free
energy
(Ni, S, V must all be
[M][L]2[T]2
[M][L]2[T]2
constant)
A, F
, G
[M][L]2[T]2
Carnot's theorem
Clausius theorem
Fundamental relation
Ideal gas law
Maxwell relations
Onsager reciprocal relations
Bridgman's equations
Table of thermodynamic equations
Free energy
Free entropy
Helmholtz free energy
Gibbs free energy
potential
Massieu
J K1
entropy
Planck
potential, Gibbs
free entropy
Equations
Enthalpy
Energy, Grand
Helmholtz free
Thermal expansion
Internal energy
potential,
Potential,
Compressibility
Potentials
Landau
Landau Free
Material properties
Property databases
Thermodynamic
beta, Inverse
Dimension
J K1
[M][L]2[T]2
[]1
[M][L]2[T]2
[]1
History
Culture
History
General
Heat
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
3 of 13
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Thermal properties of matter
Entropy
Gas laws
Main Articles: Heat capacity, Thermal expansion
Quantity (common
(Common)
name/s)
symbol/s
General heat/thermal
capacity
Heat capacity
(isobaric)
Specific heat capacity
(isobaric)
Molar specific heat
capacity (isobaric)
Heat capacity
(isochoric/volumetric)
Specific heat capacity
(isochoric)
Molar specific heat
capacity (isochoric)
Specific latent heat
"Perpetual motion" machines
Defining equation
SI units
Entropy and time
Entropy and life
Brownian ratchet
Maxwell's demon
Heat death paradox
Loschmidt's paradox
Synergetics
[M][L]2[T]2
J K 1
Cp
J K 1
Cmp
J kg1 K1
Cnp
JK
Philosophy
Dimension
[]1
[M][L]2[T]2
[]1
mol1
CV
J K 1
CmV
J kg1 K1
CnV
J K 1 mol1
J kg1
[L]2[T]2
Theories
[]1
Caloric theory
Theory of heat
[M][L]2[T]2
[]1 [N]1
Vis viva ("living force")
Mechanical equivalent of heat
[M][L]2[T]2
Motive power
[]1
Key publications
[L]2[T]2
[]1
[M][L]2[T]2
"An Experimental Enquiry
Concerning ... Heat"
"Reflections on the
Motive Power of Fire"
[L]2[T]2
Ratio of isobaric to
Timelines
isochoric heat
capacity, heat
"On the Equilibrium of
[]1 [N]1 Heterogeneous Substances"
capacity ratio,
adiabatic index
Thermal transfer
Main article: Thermal conductivity
dimensionless dimensionless
Thermodynamics
Heat engines
Art
Education
Maxwell's thermodynamic surface
Entropy as energy dispersal
Scientists
Bernoulli
Carnot
Clapeyron
Clausius
Carathodory
Duhem
Gibbs
von Helmholtz
Joule
Maxwell
von Mayer
Onsager
Rankine
Smeaton
Stahl
Thompson
Thomson
Waterston
Book:Thermodynamics
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
4 of 13
Quantity
(common
(Common)
symbol/s
name/s)
Defining equation
Temperature No standard
SI units
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Dimension
K m1
[][L]1
W=J
[M] [L]2
s1
[T]3
W m2
[M] [T]3
analogue of q
W m2
[M] [T]3
gradient
symbol
v
t
e (https://en.wikipedia.org
/w/index.php?title=Template:Thermodynamics&
action=edit)
Thermal
conduction
rate, thermal
current,
thermal/heat
flux, thermal
power
transfer
Thermal
intensity
Thermal/heat
flux density
(vector
thermal
intensity
above)
Equations
The equations in this article are classified by subject.
Phase transitions
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
5 of 13
Physical
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Equations
situation
Adiabatic
transition
Isothermal
transition
Isobaric
For an ideal gas
p1 = p2, p = constant
transition
Isochoric
V1 = V2, V = constant
transition
Adiabatic
expansion
Free
expansion
Process
Work done
by an
expanding
gas
Net Work Done in Cyclic Processes
Kinetic theory
Ideal gas equations
Physical
situation
Nomenclature
Equations
p = pressure
V = volume of container
T = temperature
Ideal gas law
n = number of moles
R = Gas constant
N = number of molecules
k = Boltzmann's constant
Pressure of
m = mass of one molecule
an ideal gas
Mm = molar mass
Ideal gas
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
6 of 13
Quantity
General Equation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Isobaric
Isochoric
Isothermal
p = 0
V = 0
T = 0
(for monatomic ideal
(for monatomic
Adiabatic
Work
W
Heat
Capacity
(as for real gas)
gas);
ideal gas);
C
(for diaatomic ideal gas)
(for diatomic
ideal gas)
Internal
Energy
U
Enthalpy
H
Entropy
S
[1]
Constant
Entropy
, where kB is the Boltzmann constant, and denotes the volume of macrostate in the phase space or otherwise called
thermodynamic probability.
, for reversible processes only
Statistical physics
Below are useful results from the MaxwellBoltzmann distribution for an ideal gas, and the implications of the Entropy quantity. The distribution is
valid for atoms or molecules constituting ideal gases.
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
7 of 13
Physical
Nomenclature
situation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Equations
v = velocity of
atom/molecule,
m = mass of each molecule
(all molecules are identical in
kinetic theory),
Non-relativistic speeds
(p) = Lorentz factor as
Maxwell
function of momentum (see
Boltzmann
below)
distribution
Ratio of thermal to rest
mass-energy of each
Relativistic speeds (Maxwell-Jttner
distribution)
molecule:
</div">
K2 is the Modified Bessel function
of the second kind.
Entropy
Logarithm of
the density
of states
Pi = probability of system in
microstate i
= total number of
where:
microstates
Entropy
change
Entropic
force
Average kinetic energy per degree of
freedom
Equipartition
theorem
df = degree of freedom
Internal energy
Corollaries of the non-relativistic MaxwellBoltzmann distribution are below.
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
8 of 13
Physical
Nomenclature
situation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Equations
Mean speed
Root mean
square speed
Modal speed
= Effective cross-section
Mean free
path
n = Volume density of
number of target particles
= Mean free path
Quasi-static and reversible processes
For quasi-static and reversible processes, the first law of thermodynamics is:
where Q is the heat supplied to the system and W is the work done by the system.
Thermodynamic potentials
Main article: Thermodynamic potentials
See also: Maxwell relations
The following energies are called the thermodynamic potentials,
Name
Symbol
Formula
Natural variables
Internal energy
Helmholtz free energy
Enthalpy
Gibbs free energy
Landau Potential (Grand potential)
and the corresponding fundamental thermodynamic relations or "master equations"[2] are:
Potential
Differential
Internal energy
Enthalpy
Helmholtz free energy
Gibbs free energy
Maxwell's relations
The four most common Maxwell's relations are:
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
9 of 13
Physical
Nomenclature
situation
= Enthalpy
potentials as
their natural
variables
Equations
= Internal energy
Thermodynamic
functions of
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
= Helmholtz free
energy
= Gibbs free
energy
More relations include the following.
Other differential equations are:
Name
GibbsHelmholtz equation
Quantum properties
Indistinguishable Particles
where N is number of particles, h is Planck's constant, I is moment of inertia, and Z is the partition function, in various forms:
Degree of freedom
Partition function
Translation
Vibration
Rotation
where:
= 1 (heteronuclear molecules)
= 2 (homonuclear)
Thermal properties of matter
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Coefficients
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Equation
Joule-Thomson coefficient
Compressibility (constant temperature)
Coefficient of thermal expansion (constant pressure)
Heat capacity (constant pressure)
Heat capacity (constant volume)
Derivation of heat capacity (constant pressure)
Since
Derivation of heat capacity (constant volume)
Since
(where Wrev is the work done by the system),
Thermal transfer
10 of 13
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Physical situation
Nomenclature
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Equations
Texternal = external
temperature (outside of
Net intensity
emission/absorption
system)
Tsystem = internal
temperature (inside system)
= emmisivity
CV = isovolumetric heat
Internal energy of a
substance
capacity of substance
T = temperature change of
substance
Cp = isobaric heat capacity
Meyer's equation
CV = isovolumetric heat
capacity
n = number of moles
Series
i = thermal conductivity of
Effective thermal
conductivities
substance i
net = equivalent thermal
conductivity
Parallel
Thermal efficiencies
Physical
situation
Nomenclature
Equations
= efficiency
W = work done by engine
QH = heat energy in higher
Thermodynamic engine:
temperature reservoir
Thermodynamic
engines
QL = heat energy in lower
temperature reservoir
TH = temperature of higher
Carnot engine efficiency:
temp. reservoir
TL = temperature of lower
temp. reservoir
Refrigeration performance
Refrigeration
K = coefficient of
refrigeration performance
Carnot refrigeration performance
See also
11 of 13
Antoine equation
GibbsHelmholtz equation
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Bejan number
Gibbs' phase rule
Bowen ratio
Kopp's law
Bridgman's equations
KoppNeumann law
ClausiusClapeyron relation
NoroFrenkel law of corresponding states
Departure functions
Onsager reciprocal relations
DuhemMargules equation
Stefan number
Ehrenfest equations
Triple product rule
References
12 of 13
1. ^ Keenan, Thermodynamics, Wiley, New York, 1947
2. ^ Physical chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Oxford University Press, 1978, ISBN 0 19 855148 7
Atkins, Peter and de Paula, Julio Physical Chemistry, 7th edition,
W.H. Freeman and Company, 2002 [ISBN 0-7167-3539-3].
Chapters 1 - 10, Part 1: Equilibrium.
McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1961.
Reichl, L.E., "A Modern Course in Statistical Physics", 2nd edition,
New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1998.
Schroeder, Daniel V. Thermal Physics. San Francisco: Addison
Bridgman, P.W., Phys. Rev., 3, 273 (1914).
Landsberg, Peter T. Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics.
New York: Dover Publications, Inc., 1990. (reprinted from Oxford
University Press, 1978).
Lewis, G.N., and Randall, M., "Thermodynamics", 2nd Edition,
Wesley Longman, 2000 [ISBN 0-201-38027-7].
Silbey, Robert J., et al. Physical Chemistry. 4th ed. New Jersey:
Wiley, 2004.
Callen, Herbert B. (1985). "Thermodynamics and an Introduction
to Themostatistics", 2nd Ed., New York: John Wiley & Sons.
v
t
e (https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Template:Branches_of_physics&action=edit)
Branches of physics
Applied
Divisions
Experimental
Theoretical
Thermodynamics
Mechanics
Classical
Lagrangian
Energy
Motion
Hamiltonian
Continuum
Celestial
Statistical
Fluid
Quantum
Gravitation
Electromagnetism
Waves
Quantum field theory
Fields
Relativity
Special
General
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
Table of thermodynamic equations - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_of_thermodynamic_equations
Accelerator
Acoustics
Astrophysics
Nuclear
Stellar
Heliophysics
Solar
Space
Astroparticle
Atomicmolecularoptical (AMO)
Computational
Condensed matter
Solid-state
By speciality
Digital
Engineering
Material
Mathematical
Nuclear
Optics
Geometrical
Physical
Nonlinear
Quantum
Particle
Phenomenology
Plasma
Polymer
Statistical
Biophysics
Cardiophysics
Biomechanics
Medical
Physics with
other
sciences
Neurophysics
Agrophysics
Soil
Atmospheric physics
Chemical
Econophysics
Geophysics
Psychophysics
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Table_of_thermodynamic_equations&oldid=659267302"
Categories: Thermodynamic equations
13 of 13
This page was last modified on 26 April 2015, at 09:01.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the
Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
6/3/2015 4:09 PM
You might also like
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsFrom EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Lecture 1Document27 pagesLecture 1Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Temperature, Ideal Gas (Ch. 1) : OutlineDocument26 pagesLecture 1. Temperature, Ideal Gas (Ch. 1) : OutlinePiousNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics MergedDocument539 pagesThermodynamics MergedShivani KumariNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: A Dynamical Systems ApproachFrom EverandThermodynamics: A Dynamical Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Statistical ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesStatistical ThermodynamicsRavichandran SundaramNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument26 pagesThermodynamics: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaglh00No ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Thermodynamics of Chemical ProcessesDocument17 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Thermodynamics of Chemical Processesnetsanet alemayehuNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Two-Temperature Fractional Order Generalized Thermoelastic Diffusion Inside A Spherical ShellDocument13 pagesThe Influence of Two-Temperature Fractional Order Generalized Thermoelastic Diffusion Inside A Spherical ShellInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Classical and Statisitcal ThermodinamicsDocument111 pagesClassical and Statisitcal ThermodinamicsitotoNo ratings yet
- Du Long Petit PDFDocument3 pagesDu Long Petit PDFTahir ArshadNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- IndexDocument286 pagesIndexTuan HoangNo ratings yet
- Solid LiquidDocument97 pagesSolid LiquidMilija JovicicNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument292 pagesThermodynamicsxitta0092% (12)
- Kinetic TheoryDocument7 pagesKinetic TheoryngvanduysnNo ratings yet
- EOS Residuales Thermodynamics & Chemicals Kinetics (ChBC-34)Document292 pagesEOS Residuales Thermodynamics & Chemicals Kinetics (ChBC-34)swerty619No ratings yet
- Heat and Energy: - Summer Term 2004 - Weeks 1-6Document48 pagesHeat and Energy: - Summer Term 2004 - Weeks 1-6Abubakkar SiddiqNo ratings yet
- PCL1Document37 pagesPCL1SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Advanced Thermodynamics - Web CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Advanced Thermodynamics - Web CourseAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction ThemoDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction ThemoOctGolibib100% (1)
- Poisson StatPhys IIDocument113 pagesPoisson StatPhys IIThongkool CtpNo ratings yet
- Time's Arrow: The Origins of Thermodynamic BehaviorFrom EverandTime's Arrow: The Origins of Thermodynamic BehaviorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- H T T E: EAT Ransfer and Hermal QuilibriumDocument2 pagesH T T E: EAT Ransfer and Hermal Quilibriumsyafr.e.424No ratings yet
- High-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationFrom EverandHigh-Pressure Fluid Phase Equilibria: Phenomenology and ComputationNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Mechanics: A Supplement to Theoretical Mechanics of Particles and ContinuaFrom EverandNonlinear Mechanics: A Supplement to Theoretical Mechanics of Particles and ContinuaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesFundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicstNo ratings yet
- EME 2315 Chapter 1Document9 pagesEME 2315 Chapter 1Andy OchiengNo ratings yet
- Table of Thermodynamic EquationsDocument10 pagesTable of Thermodynamic EquationsHarris Chacko100% (1)
- 4 Intro To Thermodynamics and Ideal Gas LawDocument12 pages4 Intro To Thermodynamics and Ideal Gas Lawstuart3390No ratings yet
- SFU PHYS 344 Lecture 2Document5 pagesSFU PHYS 344 Lecture 2Donald Ng Jer YiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Cycles Lectures 1 - 2 - Chapter 1Document77 pagesThermodynamics Cycles Lectures 1 - 2 - Chapter 1nandi777100% (1)
- Finite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 2: Complex SystemsFrom EverandFinite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 2: Complex SystemsNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Final PDFDocument47 pagesThermochemistry Final PDFAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemo 101Document4 pagesChemo 101Hizkiyas TekalignNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Mastering PhysicsDocument16 pagesKinetic Mastering PhysicsKyle DonagheyNo ratings yet
- Reflection at The Free Surface of Magneto-Thermo-Microstretch Elastic SolidDocument9 pagesReflection at The Free Surface of Magneto-Thermo-Microstretch Elastic SolidMike AlexNo ratings yet
- Phys 253 Thermal PhysicsDocument1,019 pagesPhys 253 Thermal Physicsdavid_berardo6537No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesFundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicstNo ratings yet
- IB Phyiscs Final RevisionDocument2 pagesIB Phyiscs Final Revisionjungwoohan72No ratings yet
- Gases (Chapter 5) : (1.00 Mol) (0.08206 Mol K L Atm) (273 K) 22.414 LDocument11 pagesGases (Chapter 5) : (1.00 Mol) (0.08206 Mol K L Atm) (273 K) 22.414 LHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- 1302.1485 ThermoDocument18 pages1302.1485 ThermoliamfuentezNo ratings yet
- Postulational ThermoDocument27 pagesPostulational ThermoJeffrey ElliottNo ratings yet
- Week 1&2Document56 pagesWeek 1&2ISLAMIC VOICENo ratings yet
- Document 34Document5 pagesDocument 34LaibaNo ratings yet
- Francois Sears & Gerhard Salinger 'Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory of Gasses and Statistical Mechanics' PDFDocument462 pagesFrancois Sears & Gerhard Salinger 'Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory of Gasses and Statistical Mechanics' PDFanon_25384875991% (55)
- 0apzl by D Grant, Ph.D. Turriff AB53 UK: Rate K X X XDocument66 pages0apzl by D Grant, Ph.D. Turriff AB53 UK: Rate K X X Xdrdgrant6055No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument8 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesGupta GuptaNo ratings yet
- Finite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 1: FundamentalsFrom EverandFinite Physical Dimensions Optimal Thermodynamics 1: FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of The Thermal Runaway in Cylindrical 18650 Lithium-Ion BatteriesDocument7 pagesModeling and Simulation of The Thermal Runaway in Cylindrical 18650 Lithium-Ion BatteriesKamel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- HB v6 ch7Document75 pagesHB v6 ch7artukovicNo ratings yet
- Light Commercial (Non-Inverter) Catalogue PDFDocument10 pagesLight Commercial (Non-Inverter) Catalogue PDFZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Stair SSL Ventilation and Pressurization (SG ACMV HVAC)Document7 pagesStair SSL Ventilation and Pressurization (SG ACMV HVAC)Zaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Psychrometrics SI, 2nd Ed PDFDocument180 pagesFundamentals of Psychrometrics SI, 2nd Ed PDFZaw Moe Khine100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Heating and Cooling Loads IP 2017Document1 pageFundamentals of Heating and Cooling Loads IP 2017Zaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- 2014 FGI SustainableDesign HOPDocument20 pages2014 FGI SustainableDesign HOPZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Water System DesignDocument1 pageFundamentals of Water System DesignFalak KhanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Desgin Control Central Chilled Water Plant IpDocument336 pagesFundamental Desgin Control Central Chilled Water Plant IpAbou Hasiba Mohamed92% (12)
- ACMV Main Equipments ListDocument15 pagesACMV Main Equipments ListZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- 2014 FGI SustainableDesign HOPDocument21 pages2014 FGI SustainableDesign HOPeimreh100% (1)
- 13D Form Calculations PDFDocument2 pages13D Form Calculations PDFZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- 2014 FGI SustainableDesign HOPDocument20 pages2014 FGI SustainableDesign HOPZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Haad B Hospital Morgue UnitDocument7 pagesHaad B Hospital Morgue UnitZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- 8.0 Engineering Services 8.1. Engineering Services Distribution RoutesDocument8 pages8.0 Engineering Services 8.1. Engineering Services Distribution RoutesZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Staircase MV Fan SelectionDocument2 pagesStaircase MV Fan SelectionZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Bangkok: Standard Standard Perez 2000-2009 1991-2010Document5 pagesBangkok: Standard Standard Perez 2000-2009 1991-2010Zaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Wall Mounted Fire Damper RC400V-ADocument1 pageWall Mounted Fire Damper RC400V-AZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Fgi Guidelines 2014 Hop TocDocument10 pagesFgi Guidelines 2014 Hop TocZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- PHMC GuidelinesDocument58 pagesPHMC GuidelinesZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- 201511ERACS.C Air-Cooled ChillerDocument16 pages201511ERACS.C Air-Cooled ChillerZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Installing FHC PDFDocument4 pagesInstalling FHC PDFZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Chiang Mai AirpDocument5 pagesChiang Mai AirpZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Minimum Pipe SizeDocument1 pageMinimum Pipe SizeZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Checklist - Dry Riser SystemDocument2 pagesChecklist - Dry Riser SystemZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- HL ManualDocument17 pagesHL ManualZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial To Getting Started With FHC: Hydraulic Calculation Software For Water Based Fire Protection SystemsDocument7 pagesA Tutorial To Getting Started With FHC: Hydraulic Calculation Software For Water Based Fire Protection SystemsZaw Moe Khine100% (1)
- Yangon Myanmar 480970 SI UnitsDocument1 pageYangon Myanmar 480970 SI UnitsZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- RI Checklist - MV - AC SystemDocument4 pagesRI Checklist - MV - AC SystemZaw Moe Khine100% (1)
- 3.6 Longitudinal Changes in DraftDocument20 pages3.6 Longitudinal Changes in DraftZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Boquilla de Refuerzo Asme Secc. VIIIDocument1 pageBoquilla de Refuerzo Asme Secc. VIIIEmmanuel Cervantes VelázquezNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument95 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityKristine Santiago AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Cha 4Document8 pagesMicroeconomics Cha 4haile GetachewuNo ratings yet
- Probability of R Successes in N TrialsDocument33 pagesProbability of R Successes in N Trialsdevavrat.singhNo ratings yet
- ECSE 534 Project (Final Phase) A First-Order, Single-bit, Lowpass ΔΣ A/D Converter: System and Circuit Level ImplementationDocument13 pagesECSE 534 Project (Final Phase) A First-Order, Single-bit, Lowpass ΔΣ A/D Converter: System and Circuit Level ImplementationRafid KhanNo ratings yet
- Python GlossaryDocument9 pagesPython GlossaryNoNo ratings yet
- 4024 w11 QP 11Document20 pages4024 w11 QP 11Muhammad Azhar HayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document8 pagesChapter 8Aldon JimenezNo ratings yet
- Module No 8 - Manufacturing Overhead DepartmentalizationDocument3 pagesModule No 8 - Manufacturing Overhead DepartmentalizationRafols AnnabelleNo ratings yet
- Guidance Notes C&B and ENV 001: Elements of Method Validation For Chemical TestingDocument16 pagesGuidance Notes C&B and ENV 001: Elements of Method Validation For Chemical TestingBoon Ping SeeNo ratings yet
- Youssef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Auth.), Youssef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Eds.) - Autonomous Search-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2012)Document307 pagesYoussef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Auth.), Youssef Hamadi, Eric Monfroy, Frédéric Saubion (Eds.) - Autonomous Search-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2012)Alvaro Gómez RubioNo ratings yet
- Bound ChargesDocument17 pagesBound ChargesJorge GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Laminated Rubber Bridge BearingDocument10 pagesLaminated Rubber Bridge BearingSaeedreza ZahNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology & Biostatistics: DR Waqar Ahmed AwanDocument73 pagesResearch Methodology & Biostatistics: DR Waqar Ahmed AwanWaqar Ahmed AwanNo ratings yet
- SHR Out Rodgers Annual Review 2018Document28 pagesSHR Out Rodgers Annual Review 2018Francisco Gonzalez ValdebenitoNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Non-Circular Bars - Saint Venants - Prandle MethodDocument40 pagesTorsion of Non-Circular Bars - Saint Venants - Prandle MethodMathew JohnNo ratings yet
- Alan TuringDocument10 pagesAlan TuringtomNo ratings yet
- Quantifiers in English Author(s) : Ray S. Jackendoff Source: Foundations of Language, Vol. 4, No. 4 (Nov., 1968), Pp. 422-442 Published By: Springer Stable URL: Accessed: 15-07-2015 09:54 UTCDocument22 pagesQuantifiers in English Author(s) : Ray S. Jackendoff Source: Foundations of Language, Vol. 4, No. 4 (Nov., 1968), Pp. 422-442 Published By: Springer Stable URL: Accessed: 15-07-2015 09:54 UTCAnindita PalNo ratings yet
- INTRO TO ECE - HW Assignment 2:, I, I, I V, V, V, V, P P PDocument8 pagesINTRO TO ECE - HW Assignment 2:, I, I, I V, V, V, V, P P PVienNgocQuangNo ratings yet
- Fea Lab Session4Document11 pagesFea Lab Session4aaqibaminNo ratings yet
- Existence and UniquenessDocument5 pagesExistence and UniquenessAndres Orlando Lopez MorenoNo ratings yet
- Modu 18 - FaepDocument60 pagesModu 18 - FaepHAFIDY RIZKY ILHAMSYAHNo ratings yet
- Comp312 Chapter3 - BordonDocument14 pagesComp312 Chapter3 - BordonJULIUS BORDON100% (1)
- Grade 2 DLL MATH 2 Q4 Week 8Document12 pagesGrade 2 DLL MATH 2 Q4 Week 8Chad Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Two-Way ANOVA and InteractionsDocument15 pagesTwo-Way ANOVA and InteractionsBrian WebbNo ratings yet
- Book3 6Document28 pagesBook3 6Puneet GoyalNo ratings yet
- Support Vector MachineDocument45 pagesSupport Vector MachinekevalNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsvp02091988No ratings yet
- Math Winter Holidays Homework AnswerDocument8 pagesMath Winter Holidays Homework AnsweribrahimNo ratings yet
- Calculating Tank VolumeDocument12 pagesCalculating Tank VolumeJoka Joka100% (1)
- GR 4 Unit 7 Part 1 Measuring Angles Form ADocument4 pagesGR 4 Unit 7 Part 1 Measuring Angles Form Aapi-280863641No ratings yet