Professional Documents
Culture Documents
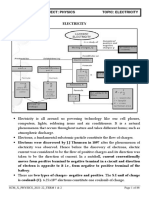
Defining Electrical Concepts and Applying Ohm's Law
Uploaded by
Temoteo L. Pupa IIIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Defining Electrical Concepts and Applying Ohm's Law
Uploaded by
Temoteo L. Pupa IIICopyright:
Available Formats
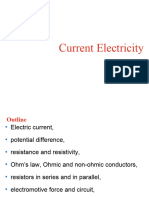
define the ff.
a.current
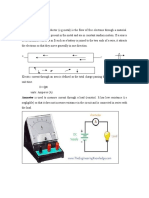
a flow of electricity which results from the ordered directional movement of
electrically charged particles.
In electrostatic situations the electric field is zero everywhere within the conductor,
and there is no current.
The motion of the electrons is random, so there is no net flow of charge in any
direction and hence no current.
conventional current-choice or convention for the direction of current flow
definition of current- I=dQ/dt
The SI unit of current is the ampere; one ampere is defined to be one coulomb per
second (1 A = 1 C/s).
This unit is named in honor of the French scientist Andr Marie Ampre (17751836).
direct current- direction of the current is always the same.
alternating current- the current continuously changes direction.
examples 25.7-25.5-25.1-25.6-
b. voltage
an electromotive force ( EMF) or potential differ
ence expressed in volts.
Potential is potential energy per unit charge ( V=U/qo or U=qoV where U=potential
energy;qo=unit charge.
The SI unit of potential, called one volt (1 V) in honor of the Italian electrical
experimenter Alessandro Volta (17451827), equals 1 joule per coulomb:
1 V = 1 volt = 1 J/C = 1 joule/coulomb
potential due to a point charge: V=U/qo= 4 o r
potential due to a collection of point charge: V=
potential due to a continuous distribution of charge: V= 4 o r
U
1
qi
=
qo 4 o i ri
1
dq
1 V/m= 1N/C
terminal voltage, source with internal resistance: Vab= -Ir, where =EMF and Ir=
internal resistance.
c.resistance
the degree to which a material or device opposes the passage of an electric current,
causing energy dissipation.
the resistance of a wire or other conductor of uniform cross section is directly
proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area.S
conductors have zero or least amount of resistance
insulators have greatest or infinite amount of resistance
Semiconductors have resistance transitional between those of conductors
and insulators.
A circuit device made to have a specific value of resistance between its ends is called
a resistor.
The SI unit of resistance is the ohm, equal to one volt per ampere ( 1= 1 V/A).
The kilohm (1k= 10^3 ) and megohm (1 M= 10^6 ) are commonly used.
relationship among voltage, current, and resistance: V=IR
The resistance of a cylindrical conductor is related to its resistivity , length L, and crosssectional area A: R=
L
A
(give at least 5 ex. with solution use univ. college physics)
define the ff.
a. power
the rate of doing work, measured in watts or horse power.
the power P equals the product of the potential difference and the current.
rate at which energy is delivered to or extracted from a circuit element:
P=VabI
Vab 2
power delivered to a resistor: P=VabI=I^2R=
R
energy
is the property of the body or system of bodies by virtue of which work
can be done. It is also defined as the ability to do work. Energy is a
scalar quantity.
A measure of this capacity, expressed as the work that it does in changing to some
specified reference state.
It is measured in joules (SI units)
Definition of energy: E=Pt
3. ohms law
the principle that the electric current passing through a conductor is directly proportional
to the potential difference across it, provided that the temperature remains constant. the
constant of proportionality is the resistance of the conductor.
It was discovered in 1826 by the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm (1787
1854).
definition of ohms law: R=V/I
(give 5 problems applying the ohms law)
You might also like
- Engineering Utilities 1 ReviewerDocument20 pagesEngineering Utilities 1 ReviewerBaby John lystier NadayaoNo ratings yet
- Ch 12 Electricity Class 10th Study Material NotesDocument5 pagesCh 12 Electricity Class 10th Study Material NotesSavita ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12: ElectricityDocument22 pagesChapter - 12: ElectricityAgrasen SinghNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 ReviewerDocument22 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Reviewercharydel.oretaNo ratings yet
- ' ElectricityDocument98 pages' Electricitya9758127118No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 ElectricityDocument6 pagesChapter 12 ElectricityShiv Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Aberdeen Electronics PrinciplesDocument8 pagesAberdeen Electronics PrinciplestettehsackeyNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity NotesCarlos KasambiraNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesCurrent ElectricityKamesh RajputNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 ElectricityDocument65 pagesBab 2 ElectricityAnonymous oW9OeJvEvNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJoyce LonzagaNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Electricity (Notes)Document10 pagesClass 10th Electricity (Notes)Kamya SyalNo ratings yet
- Name: Renzo Jan H. Amorado Date: August 30, 2022 Course-Year-Section: BSME-2-EDocument6 pagesName: Renzo Jan H. Amorado Date: August 30, 2022 Course-Year-Section: BSME-2-ELev ShouyoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Notes For CBSE Class 10 PhysicsDocument5 pagesElectricity Notes For CBSE Class 10 Physicssadiyaarchive22No ratings yet
- Modul 1-Besaran ListrikDocument32 pagesModul 1-Besaran ListrikYusup SuryadiNo ratings yet
- 5.1: Electrical DistributionDocument31 pages5.1: Electrical DistributionShuhada SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument20 pagesElectricity and MagnetismMido YoussefNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit TheoryDocument6 pagesElectric Circuit TheoryPaula ZofioNo ratings yet
- BEEE 2marks (With Ans)Document25 pagesBEEE 2marks (With Ans)Nanda SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 2Document20 pagesUnit-1 2Akhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Current and Resistance Current and Current DensityDocument20 pagesCurrent and Resistance Current and Current Densityminhajul.cse.diuNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity (AutoRecovered)Document16 pagesRadioactivity (AutoRecovered)muhamad masudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Electricity Revision NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 12 - Electricity Revision NotesAyush RajNo ratings yet
- 09 CurrentElectricity IDocument9 pages09 CurrentElectricity ILearner PointNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Made By:-Tushar Bhutani X - ADocument36 pagesElectricity: Made By:-Tushar Bhutani X - ATushar BhutaniNo ratings yet
- IB CHAPTER 5 - Electricity and MagnetismDocument67 pagesIB CHAPTER 5 - Electricity and Magnetismkostas100% (1)
- Module 7Document15 pagesModule 7Laiza GranaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument33 pagesELECTRICITYSumiNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument66 pagesElectricitybhaveshjangaleNo ratings yet
- Ib Physics HL Chapter 5 and 10 and 11 Electricity and MagnetismDocument28 pagesIb Physics HL Chapter 5 and 10 and 11 Electricity and MagnetismAnastasia VergouNo ratings yet
- CH 12 ElectricityDocument10 pagesCH 12 ElectricityMohammed SafwanNo ratings yet
- Foundation of ElectricityDocument26 pagesFoundation of ElectricityRaven TarroquinNo ratings yet
- 12 Electricity FinalsDocument33 pages12 Electricity FinalsKelly FajardoNo ratings yet
- 3.3 ELECTRICAL TerminologyDocument10 pages3.3 ELECTRICAL TerminologyPalu AritNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITY_imp_notes_Document2 pagesELECTRICITY_imp_notes_q-tipNo ratings yet
- Widya F. Rompas 19101105017Document14 pagesWidya F. Rompas 19101105017Widya RompasNo ratings yet
- Phy 103Document11 pagesPhy 103Yin KuzNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- SCM X Physics 202122 Term 1 and 2Document86 pagesSCM X Physics 202122 Term 1 and 2Evilzen GamingNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Electricity: ChargeDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Electricity: ChargeJahnavi MeharNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument14 pagesELECTRICITYTia-marie Mc AlisterNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 1Document48 pagesUnit 2 Module 17sky7harveyNo ratings yet
- Phy 061 Electrodynamics (Circuits - Series and Parallel)Document8 pagesPhy 061 Electrodynamics (Circuits - Series and Parallel)Angel Lou LiwagonNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Chapter3 Current ElectricityDocument13 pagesPhysics Formula Chapter3 Current Electricitytripathikritika2009No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Electric PotentialDocument8 pagesBasic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Electric PotentialtusharNo ratings yet
- ElectricDocument40 pagesElectricnishant kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 ElectricityDocument3 pagesChapter 12 ElectricityShashank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism ConceptsDocument29 pagesElectricity and Magnetism ConceptsNashrul HaqNo ratings yet
- A Level Electric Current Slides 001Document43 pagesA Level Electric Current Slides 001markwelly367No ratings yet
- Current Electricity. MiaDocument42 pagesCurrent Electricity. MiaVerla MfeerNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document32 pagesClass 1Bhargav LahonNo ratings yet
- Electricity at HomeDocument10 pagesElectricity at HomeWilliam HaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDocument96 pagesFundamentals of Electrical EngineeringfrankieyiiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 10th Class Notes (KPKDocument24 pagesPHYSICS 10th Class Notes (KPKamir khanNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PhysicsDocument21 pagesGroup 4 PhysicsStephenNo ratings yet
- Physics Class X For Sa I 2016 17Document94 pagesPhysics Class X For Sa I 2016 17Praveen MaramNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesClass 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanObul Reddy PolimeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 CircuitsDocument9 pagesChapter 20 CircuitsjojonNo ratings yet
- Direct Current and PowerDocument5 pagesDirect Current and PowerElizabeth AnyegaNo ratings yet
- Political History of The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesPolitical History of The PhilippinesTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- 79th ARAW NG DABAW-final EventDocument42 pages79th ARAW NG DABAW-final EventTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- 79th ARAW NG DABAW-final EventDocument42 pages79th ARAW NG DABAW-final EventTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Quiz: Identify Advertisements and Propaganda StatementsDocument20 pagesQuiz: Identify Advertisements and Propaganda StatementsTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- SsDocument3 pagesSsTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- 79th ARAW NG DABAW-final EventDocument42 pages79th ARAW NG DABAW-final EventTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- CE-520 Reinforced Concrete Design: Cor Jesu CollegeDocument15 pagesCE-520 Reinforced Concrete Design: Cor Jesu CollegeTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- English 6Document21 pagesEnglish 6Temoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Two Way Slaba DirectdesignDocument51 pagesTwo Way Slaba DirectdesignTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Intro RCDocument33 pagesIntro RCTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Araling PanlipunanDocument36 pagesAraling PanlipunanTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Essential Kitchen Utensils Every Home NeedsDocument4 pagesEssential Kitchen Utensils Every Home NeedsTemoteo L. Pupa III100% (1)
- FE SyllabusDocument26 pagesFE SyllabusClassic11No ratings yet
- Conventional Water Treatment Processes: CoagulationDocument17 pagesConventional Water Treatment Processes: CoagulationTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Song LyricsDocument12 pagesSong LyricsTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Educational Tour Journal 3Document5 pagesEducational Tour Journal 3Temoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- A B C D B B: Ground Floor Plan Second Floor PlanDocument1 pageA B C D B B: Ground Floor Plan Second Floor PlanTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- CIVIL and Construction ENGINEERING 201: Engineering Graphics and Design Syllabus Fall 2009 Credit Hours: 3Document6 pagesCIVIL and Construction ENGINEERING 201: Engineering Graphics and Design Syllabus Fall 2009 Credit Hours: 3Temoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument1 pageContentsTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- FE SyllabusDocument26 pagesFE SyllabusClassic11No ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Principle: Created By: Keith P. Murphy Winston Churchill High School Potomac, MDDocument12 pagesBernoulli's Principle: Created By: Keith P. Murphy Winston Churchill High School Potomac, MDTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- CIVIL and Construction ENGINEERING 201: Engineering Graphics and Design Syllabus Fall 2009 Credit Hours: 3Document6 pagesCIVIL and Construction ENGINEERING 201: Engineering Graphics and Design Syllabus Fall 2009 Credit Hours: 3Temoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Alumni Homecoming Program2Document1 pageAlumni Homecoming Program2Temoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Sr. Zoselie T. Escolano, O. PDocument6 pagesSr. Zoselie T. Escolano, O. PTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- A1 Kiblawan Church-ModelDocument1 pageA1 Kiblawan Church-ModelTemoteo L. Pupa III100% (1)
- Final PsychDocument46 pagesFinal PsychTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Concrete Column Schedule DetailsDocument1 pageConcrete Column Schedule DetailsTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- TowerDesign Hints PDFDocument4 pagesTowerDesign Hints PDFTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Project Study Format GuideDocument3 pagesProject Study Format GuideTemoteo L. Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- 53 PDFDocument13 pages53 PDFTemoteo L. Pupa III100% (1)
- HV Substation Overvoltage Computation Taking Into Account Frequency Dependent Transients On The Substation Grounding SystemDocument6 pagesHV Substation Overvoltage Computation Taking Into Account Frequency Dependent Transients On The Substation Grounding Systemostojic007No ratings yet
- HVDocument24 pagesHVGANGADHARA P KNo ratings yet
- HydrodynamicsDocument18 pagesHydrodynamicsPrince Israel Eboigbe100% (1)
- Introduction To ElectricityDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Electricityjayson platinoNo ratings yet
- WB-Mech 120 Ch04 StaticDocument49 pagesWB-Mech 120 Ch04 StaticmrezaianNo ratings yet
- Art Magic: by Unknown Edited by Emma Hardinge BrittenDocument270 pagesArt Magic: by Unknown Edited by Emma Hardinge BrittenCristian CmNo ratings yet
- 856 Electrical System 856 Electrical SystemDocument48 pages856 Electrical System 856 Electrical SystemSahba Kiyanoush100% (3)
- Projectile Motion Lab Report 3Document6 pagesProjectile Motion Lab Report 3DYLANIPHONSOALISTERJACOBS DYLANIPHONSOALISTERJACOBSNo ratings yet
- History of emDocument16 pagesHistory of emyunafanelNo ratings yet
- Buckingham π Theorem Dimensional Analysis ProblemsDocument1 pageBuckingham π Theorem Dimensional Analysis ProblemsVivek ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Analysis On Buildings and Structures Course Title-Finite Element Analysis Course No-CE G619 Instructor in Charge - Dr. PN RaoDocument33 pagesWind Load Analysis On Buildings and Structures Course Title-Finite Element Analysis Course No-CE G619 Instructor in Charge - Dr. PN RaoJHAVERI RONAK KIRTIKUMARNo ratings yet
- Drag CoefficientDocument7 pagesDrag CoefficientAdrian John Soe Myint100% (1)
- New Gate Driver Baser Ir2110Document4 pagesNew Gate Driver Baser Ir2110Ayoub RajawiNo ratings yet
- Types of Capacitors and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesTypes of Capacitors and Their ApplicationsRalph Justine Hernandez100% (1)
- AE 203 Fluid Dynamics Homework #5 HandoutDocument3 pagesAE 203 Fluid Dynamics Homework #5 HandoutRam VaradhanNo ratings yet
- H.W Chapter-5Document2 pagesH.W Chapter-5hwuhwuheNo ratings yet
- Manning Formula Pipe Flow CalculatorDocument14 pagesManning Formula Pipe Flow Calculatorchemkumar16No ratings yet
- Mechanical Accelerometer System AnalysisDocument4 pagesMechanical Accelerometer System AnalysisAlejandro López SaldañaNo ratings yet
- ACS800-67 Wind Turbine Converters: System Description and Start-Up GuideDocument120 pagesACS800-67 Wind Turbine Converters: System Description and Start-Up GuideEliel TrNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Test-2 For IIT JEEDocument3 pagesClass 11 Test-2 For IIT JEESanjay Kumar DokaniaNo ratings yet
- Zeeman and Paschen-Back EffectDocument12 pagesZeeman and Paschen-Back EffectKamanpreet Singh100% (1)
- Science Grade 5-Lessons 5 & 6 Light & Sound EnergyDocument48 pagesScience Grade 5-Lessons 5 & 6 Light & Sound Energyclyde domingoNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Force Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesCentripetal Force Multiple Choice QuestionsMalaika ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ch5 - Rotation SpectraDocument13 pagesCh5 - Rotation SpectraRajkumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- G60A Test Checklist SiteDocument9 pagesG60A Test Checklist SitezakariaNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Induction MotorsDocument6 pagesSpeed Control of Induction Motorsthamilmaran alwarNo ratings yet
- ms300 SeriesqDocument516 pagesms300 SeriesqHerbert Quispe RjsNo ratings yet
- Three Phase LocomotiveDocument138 pagesThree Phase LocomotiveManas Moharana67% (3)
- Question Text Question Type Option 1Document7 pagesQuestion Text Question Type Option 1kinanti sellaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Across The PN JunctionDocument2 pagesVoltage Across The PN JunctionEmil RudzainiNo ratings yet