Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uoaa Brochure Bowel en
Uploaded by
Andrei Espinal BarretoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uoaa Brochure Bowel en
Uploaded by
Andrei Espinal BarretoCopyright:
Available Formats
SURGICAL OPTIONS FOR BOWEL DIVERSION
UOAA is an association of affiliated,
nonprofit, support groups who
are committed to the improvement
of the quality of life of people who
have, or will have, an intestinal
or urinary diversion.
INTRODUCTION TO BOWEL
DIVERSION PROCEDURES
Page 1 of 2
These solutions may be appropriate:
If you need to have your colon and rectum removed
because of ulcerative colitis or familial polyposis several
operations may be available.
Proctocolectomy (removal of the colon and rectum)
and Conventional Ileostomy
Ileo-Anal Reservoir / Pelvic Pouch / J-Pouch*
Continent Ileostomy / Kock Pouch / BCIR*
Whatever operation is chosen, it must be remembered
that a major organ has been removed with permanent
(not detrimental) alteration in gastrointestinal function.
* Note: The internal pouch surgeries (J-Pouch and
Continent ileostomy) are not recommended for people
with Crohns disease.
The ultimate goal is protection from further
complications and cure of the disease, so that a normal
lifestyle may be resumed.
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Not every person is a candidate for these operations.
Most surgeons carefully screen their patients for the ileoanal reservoir and the continent ileostomy since there are
many considerations in addition to the patients
preferences.
This brochure provides information about the surgical
procedures commonly available today. Each procedure
has its own advantages and disadvantages. All offer the
potential for cure of the disease and a normal lifestyle.
There are many satisfied people who have undergone
each of these operations.
While this brochure is designed to help you make a more
effective decision, individuals who are faced with the
need to have the colon and rectum removed are advised
to seek out complete professional information on all the
possible procedures before making decisions.
It is recommended that you seek advice from qualified
healthcare professionals who have been trained and have
experience with these surgeries. It is also highly
recommended that you seek consultation before and after
surgery with a certified Wound, Ostomy and Continence
Nurse (WOCN) or ostomy nurse.
Continent ileostomy / Kock pouch
An internal reservoir for stool storage, made from ileum
and attached to the abdominal wall by a special stoma /
one-way valve, emptied by inserting a catheter through
this stoma. The BCIR is a variant of this procedure
Conventional ileostomy
The standard surgery perfected by Dr. Brooke in the
early 1950s; also called end ileostomy.
Ileo-anal reservoir / J-pouch
An internal reservoir for stool storage, made from ileum
and attached to the anus to allow more-or-less normal
evacuation. Includes J-, S- and W- variants.
Intubation
Insertion of a special tube or catheter through the
abdominal stoma to empty the reservoir of a Continent
ileostomy.
Pouchitis
Inflammation of the internal reservoir in a J-pouch or
Continent ileostomy.
If you need a colectomy (removal of the colon) for:
Proctocolectomy
Ulcerative colitis with severe disease or long-term
colitis with risk of cancer or dependency on steroids.
Removal of the colon and rectum.
Familial polyposis with high risk of colorectal cancer.
SURGICAL OPTIONS FOR BOWEL DIVERSION
UOAA is an association of affiliated,
nonprofit, support groups who
are committed to the improvement
of the quality of life of people who
have, or will have, an intestinal
or urinary diversion.
Page 2 of 2
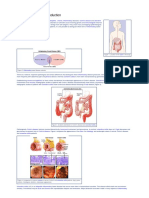
PROCTOCOLECTOMY AND
CONVENTIONAL ILEOSTOMY
ILEO-ANAL RESERVOIR /
PELVIC POUCH / PULLTHROUGH / J-POUCH
CONTINENT ILEOSTOMY /
ABDOMINAL POUCH / KOCK
POUCH / BCIR
Procedure
Procedure
Procedure
Remove the entire colon, rectum and
anus, and construct an end/Brooke
ileostomy.
The entire colon is removed. Anal
muscles are preserved. Sphincter
control is essential. A reservoir is
constructed from small intestine and
attached to the anus.
Colon, rectum and anus are removed.
An internal reservoir with a nipple
valve is constructed. The opening is
on the abdomen.
Advantages
May cure the disease.*
No pouching system required.
Normal route of stool evacuation.
May cure the disease.*
A patch to absorb moisture is the
only external equipment needed,
i.e., no pouching system needed.
Disadvantages
Disadvantages
Highest risk of complications,
operation revision is often
required.
Must intubate to empty 2-4 times
daily.
Chance of pouchitis which may
require periodic irrigations/
medication.
Long-term results are unknown.
Advantages
May cure the disease.*
Known long-term results.
Relatively simple surgery.
Fewest complications.
Disadvantages
Requires external pouching
system.
Pouching system requires periodic
changes.
Pouching system must be emptied
4-6 times daily.
Occasional problems with the
ileostomy such as prolapse,
narrowing, retraction and skin
problems.
Often requires two surgeries.
Higher risk of complications.
4-8 bowel movements daily.
Possible peri-anal skin problems.
Chance of pouchitis which may
require periodic irrigations/
medication.
Possible irregularity and/or
incontinence.
Longer period of adaptation.
Long-term results are unknown.
Advantages
* Complete removal of the colon and rectum and of the anal mucosa is considered curative for ulcerative colitis and
familial polyposis. It isnt curative if the patient actually has Crohns disease or if Crohns disease develops later. The
internal pouches (J-Pouch and Continent ileostomy) are susceptible to pouchitis, which occurs more frequently in patients
who have these surgeries for ulcerative colitis than for polyposis, and is sometimes similar to the original colitis. When
internal pouch surgeries are done for familial polyposis, polyps may develop in the internal reservoir.
You might also like
- (Medicalstudyzone - Com) Surgery Vol 1 4.0Document266 pages(Medicalstudyzone - Com) Surgery Vol 1 4.0medico designNo ratings yet
- ILEOSTOMYDocument11 pagesILEOSTOMYShine Khay100% (1)
- ILEOSTOMYDocument11 pagesILEOSTOMYShine Khay100% (1)
- Ostomias PDFDocument17 pagesOstomias PDFRicardo Uzcategui Arregui100% (1)
- Doctors Charges-Thirteenth ScheduleDocument60 pagesDoctors Charges-Thirteenth ScheduleMohd Syariefudien Mohd AriffinNo ratings yet
- Ostomy CareDocument13 pagesOstomy Carekyshb100% (1)
- General SurgeryDocument50 pagesGeneral Surgerykllo_85No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiologysushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument14 pagesUlcerative ColitisAstari Puspaningdyah100% (1)
- Basic Nursing Fundamentals EliminationDocument35 pagesBasic Nursing Fundamentals Eliminationlisa100% (1)
- Colostomy & Colostomy CareDocument56 pagesColostomy & Colostomy Careapi-3722454100% (31)
- 2015 PM Lecture 4 Barium EnemaDocument62 pages2015 PM Lecture 4 Barium EnemaObrian ReidNo ratings yet
- Uoaa Sexuality enDocument22 pagesUoaa Sexuality enAndrei Espinal BarretoNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument12 pagesUlcerative ColitisSanthu SuNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Having An Ileostomy: Surgical Opening Small Intestine Ileum Pouching System Groin AbdomenDocument7 pagesReasons For Having An Ileostomy: Surgical Opening Small Intestine Ileum Pouching System Groin AbdomenContented LinganNo ratings yet
- 8D Gastrointestinal FinalwithdxDocument27 pages8D Gastrointestinal FinalwithdxGlenn Daryll SantosNo ratings yet
- By: Emmeline M. Baltero, SNDocument54 pagesBy: Emmeline M. Baltero, SNMichelle B. AloveraNo ratings yet
- 006 Large IntestineDocument26 pages006 Large IntestineDeepthi SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Gastric Sleeve Diet: Step By Step Guide For Planning What to Do and Eat Before and After Your SurgeryFrom EverandGastric Sleeve Diet: Step By Step Guide For Planning What to Do and Eat Before and After Your SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Bowel Obstruction SurgeryDocument12 pagesBowel Obstruction SurgeryDivya JoyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Presented by Group 22 BSN 206: In-Depth View On CholecystectomyDocument46 pagesCase Study Presented by Group 22 BSN 206: In-Depth View On CholecystectomyAjiMary M. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Gastrostomy and JejunostomyDocument43 pagesGastrostomy and JejunostomyLeslie Anne Alcibar TababaNo ratings yet
- LaparotomyDocument36 pagesLaparotomydenekeNo ratings yet
- Hysterectomy, (Removal of Uterus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHysterectomy, (Removal of Uterus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CHOLECYSTECTOMYDocument9 pagesCHOLECYSTECTOMYGuenever Tesoro100% (1)
- Chole SysDocument8 pagesChole SysKas MulyadiNo ratings yet
- Metab II DiverticulosisDocument94 pagesMetab II DiverticulosisEthel Lourdes Cornejo AmodiaNo ratings yet
- COLONOSDocument5 pagesCOLONOSJyoti YadavNo ratings yet
- CholecystectomyDocument17 pagesCholecystectomyStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- ColostomyDocument60 pagesColostomymathisyncNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall Defects: Omphalocele and Gastroschisis: DR - Enono Yhoshu Department of Pediatric SurgeryDocument42 pagesAbdominal Wall Defects: Omphalocele and Gastroschisis: DR - Enono Yhoshu Department of Pediatric SurgeryYogi drNo ratings yet
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- 07-2006 Chassin Operative Strategy - Colorectal SurgeryDocument293 pages07-2006 Chassin Operative Strategy - Colorectal SurgeryConstantin DaradiciNo ratings yet
- Colostomy CareDocument35 pagesColostomy CareRashmita DahalNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument12 pagesUlcerative Colitisquidditch07No ratings yet
- Stoma Care BasicsDocument83 pagesStoma Care BasicsTeoh HsNo ratings yet
- Colostomy Wps OfficeDocument19 pagesColostomy Wps Officehealthseeker159No ratings yet
- Colostomy CareDocument35 pagesColostomy CareRoyster CabralNo ratings yet
- Learning Content: Caring For A Colostomy: Preoperative CareDocument9 pagesLearning Content: Caring For A Colostomy: Preoperative CarePrince TulauanNo ratings yet
- M Edsurg: Partial ColectomyDocument18 pagesM Edsurg: Partial ColectomyMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Colectomy - : A Colectomy Is Surgery To Remove Either All or Part of The ColonDocument9 pagesColectomy - : A Colectomy Is Surgery To Remove Either All or Part of The ColonTricia100% (1)
- PT in SrgryDocument64 pagesPT in SrgryHiral V.No ratings yet
- July 27, 2009 Exploratory Laparotomy and Transverse Loop Colostomy 1.Document8 pagesJuly 27, 2009 Exploratory Laparotomy and Transverse Loop Colostomy 1.MaRVNo ratings yet
- Colostomy by PHLLPDocument68 pagesColostomy by PHLLPkiyermsangi00No ratings yet
- Urinary DiversionDocument15 pagesUrinary Diversionpipoahmed51No ratings yet
- ColostomyDocument2 pagesColostomyFenelie AblazaNo ratings yet
- Esophagostomy in BovinesDocument23 pagesEsophagostomy in BovinesWasaq BukhariNo ratings yet
- Surgical Stoma Large Intestine Colon Incision Anterior Abdominal Wall Suturing Stoma Appliance FecesDocument10 pagesSurgical Stoma Large Intestine Colon Incision Anterior Abdominal Wall Suturing Stoma Appliance FecesTamil VillardoNo ratings yet
- Bladder Injuries: Mohammad Ihmeidan Pgy2Document22 pagesBladder Injuries: Mohammad Ihmeidan Pgy2محمد حميدانNo ratings yet
- Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop: Why Do I Need This Surgery?Document6 pagesUrinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop: Why Do I Need This Surgery?Panji SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Management of Genital ProlapseDocument39 pagesManagement of Genital Prolapsecool_ice2t6No ratings yet
- Providing Special CareDocument23 pagesProviding Special CareJan LagriaNo ratings yet
- Modul Perawatan OstomiDocument18 pagesModul Perawatan OstomiNurhanifahNo ratings yet
- Barium EnemaDocument5 pagesBarium EnemaarturogarcesjrNo ratings yet
- Anorectal MalformationsDocument24 pagesAnorectal MalformationsVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- ColonosDocument20 pagesColonosCarl miguel LoretoNo ratings yet
- Bowel SurgeryDocument92 pagesBowel Surgeryandrea.maungca.mnlNo ratings yet
- Urinary Diversion Is Any One of SeveralDocument4 pagesUrinary Diversion Is Any One of SeveralKirstele Nicole QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Colonoscopy / Page ofDocument4 pagesColonoscopy / Page offallenangelleNo ratings yet
- 1.gallblader Location: Open Cholecystectomy: With Open Surgery, Your Surgeon Operates ThroughDocument2 pages1.gallblader Location: Open Cholecystectomy: With Open Surgery, Your Surgeon Operates ThroughMarcelo CruzNo ratings yet
- Umbilical HerniaDocument15 pagesUmbilical Herniatsega tilahunNo ratings yet
- Entero Cutaneous FistulaDocument35 pagesEntero Cutaneous FistulaNikhil PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument5 pagesPeritoneal DialysisLisette TupasNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction AditiDocument67 pagesIntestinal Obstruction Aditiaditi BahugunaNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTECTOMYDocument6 pagesCHOLECYSTECTOMYRaymond Sabanal BanquirigoNo ratings yet
- IleostomyDocument7 pagesIleostomyPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Which Conditions Can Be Treated? Under Local Anesthesia: The Excision of The Foreskin (Prepuce)Document9 pagesWhich Conditions Can Be Treated? Under Local Anesthesia: The Excision of The Foreskin (Prepuce)John Jose Sy GalauranNo ratings yet
- ColonDocument7 pagesColonch3zk4No ratings yet
- Urostomy Guide - American Cancer SocietyDocument19 pagesUrostomy Guide - American Cancer SocietyDipa HandraNo ratings yet
- Alumno: Andrei Espinal BarretoDocument39 pagesAlumno: Andrei Espinal BarretoAndrei Espinal BarretoNo ratings yet
- Internet Language InformationDocument106 pagesInternet Language InformationAndrei Espinal BarretoNo ratings yet
- Ipi 121389Document15 pagesIpi 121389Sang PemantikNo ratings yet
- Nej Mo A 1404595Document11 pagesNej Mo A 1404595Astri Faluna SheylavontiaNo ratings yet
- Ibd MedicationsDocument25 pagesIbd MedicationsBassem DopamineNo ratings yet
- Ta 76 1 2013 11 22 SchwartzDocument2 pagesTa 76 1 2013 11 22 SchwartzRagabi RezaNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersDocument33 pagesManagement of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Experience of General Surgery Residents in The Creation of Small Bowel and Colon AnastomosesDocument7 pagesExperience of General Surgery Residents in The Creation of Small Bowel and Colon AnastomosesDiego Andres VasquezNo ratings yet
- IBD (Crohn's and Ulcerative Colitis) TransDocument7 pagesIBD (Crohn's and Ulcerative Colitis) TranstristineNo ratings yet
- Academy of Life Underwriting - ALU 201 - Intermediate Medical Life Insurance Underwriting (2022)Document478 pagesAcademy of Life Underwriting - ALU 201 - Intermediate Medical Life Insurance Underwriting (2022)KALPESH SHAHNo ratings yet
- Contrast Enema ExaminationDocument40 pagesContrast Enema ExaminationOscar NogueraNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Intestinal and RectaldisordersDocument16 pagesManagement of Patients With Intestinal and RectaldisordersintotheunknownNo ratings yet
- 2020 原著論文 Outcomes of Colonic Resection for Chronic Idiopathic Constipation in ChildhoodDocument4 pages2020 原著論文 Outcomes of Colonic Resection for Chronic Idiopathic Constipation in ChildhoodRyo TamuraNo ratings yet
- GastrointestinalDocument16 pagesGastrointestinalCelestial, Maybelle MarieNo ratings yet
- (2017) IBD - Spesific Health Related QoL InstrumentDocument13 pages(2017) IBD - Spesific Health Related QoL InstrumentfikriafisNo ratings yet
- Tube IleostomyDocument5 pagesTube IleostomyabhishekbmcNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Reporting of Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument12 pagesSampling and Reporting of Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDiego Fernando Ortiz TenorioNo ratings yet
- Asge Primer 2017 Pgs117 125 Single PageDocument9 pagesAsge Primer 2017 Pgs117 125 Single PageMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Disease - 2023 - Freund - Can Preoperative CT MR Enterography Preclude The Development of Crohn S Disease LikeDocument10 pagesColorectal Disease - 2023 - Freund - Can Preoperative CT MR Enterography Preclude The Development of Crohn S Disease Likedavidmarkovic032No ratings yet
- Abdominal Surgery Concept MapDocument1 pageAbdominal Surgery Concept MapMa. Therese GarganianNo ratings yet
- Slow Transit Constipation A Review of A Colonic FuDocument8 pagesSlow Transit Constipation A Review of A Colonic FuErin Bleza FaylonaNo ratings yet
- Colitis UlcerrosaDocument5 pagesColitis UlcerrosaCarlos MichasNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Ostomy: Classification, Indications, Ostomy Care and Complication ManagementDocument8 pagesIntestinal Ostomy: Classification, Indications, Ostomy Care and Complication ManagementEriekafebriayana RNo ratings yet
- Toxic Megacolon...Document10 pagesToxic Megacolon...Vikas MataiNo ratings yet