Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Install and Use Eclipse CDT For C - C++ Programming PDF
Uploaded by
Anonymous 0xx2fOG1yOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How To Install and Use Eclipse CDT For C - C++ Programming PDF
Uploaded by
Anonymous 0xx2fOG1yCopyright:
Available Formats
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
yet another insignificant programming notes... | HOME
TABLE OF CONTENTS HIDE
Eclipse 4.3
(Kepler) for
C/C++
Programming
1.How to Install Eclipse C/C++ Development T
2.Writing your First C/C++ Program in Eclipse
2.1C++ Program
2.2C Program
2.3C++ Program with Makefile
3.Read the Documentation
4.Debugging C/C++ Programs in Eclipse CDT
5.Tips & Tricks
5.1C/C++ Software Development Using GCC
6. File I/O in Eclipse
How To Install
Eclipse CDT 8.2 and Get Started
Eclipse is an opensource Integrated Development Environment IDE supported by IBM. The
mother site is @ www.eclipse.org. Eclipse is popular for Java project development. It also
supports C/C++, PHP, Python, Perl, and other web project developments via extensible plugins.
Eclipse is crossplatform and runs under Windows, Linux and Mac OS.
1.How to Install Eclipse C/C++ Development Tool
(CDT) 8.1.2 for Eclipse 4.2.2 (Juno)
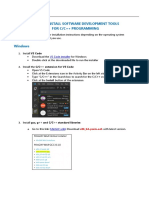
Step 0: Install MinGW GCC or Cygwin GCC
To use Eclipse for C/C++ programming, you need a C/C++ compiler. On Windows, you could
install either MinGW GCC or Cygwin GCC. Choose MinGW if you are not sure, because MinGW is
lighter and easier to install, but having less features.
1. MinGW GCC: Read "How to Install MinGW".
2. Cygwin GCC: Read "How to Install Cygwin". Make sure that you select "gcc", "g++", "gdb",
and "make" packages under the "Devel" Development category these packages are not
part of the default installation.
Step 1: Install Eclipse C/C++ Development Tool CDT
Two ways to install CDT, depending on whether you have previously installed an Eclipse:
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
1/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
1. If you have already installed "Eclipse for Java Developers" or other Eclipse packages, you
could install the CDT plugin as follows:
Launch Eclipse Help Install New Software In "Work with" field, pull down the drop
down menu and select "Kepler http://download.eclipse.org/releases/kepler" or juno for
Eclipse 4.2; or helios for Eclipse 3.7.
In "Name" box, expand "Programming Language" node Check "C/C++ Development
Tools" "Next" ... "Finish".
2. If you have not install any Eclipse package, you could download "Eclipse IDE for C/C++
Developers" from http://www.eclipse.org/downloads, and unzip the downloaded file into a
directory of your choice.
Step 2: Configuration
You do NOT need to do any configuration, as long as the Cygwin or MinGW binaries are included
in the PATH environment variable. CDT searches the PATH to discover the C/C++ compilers.
2.Writing your First C/C++ Program in Eclipse
2.1C++ Program
Step 0: Launch Eclipse
1. Start Eclipse by running "eclipse.exe" in the Eclipse installed directory.
2. Choose an appropriate directory for your workspace i.e., where you would like to save your
works.
3. If the "welcome" screen shows up, close it by clicking the "close" button.
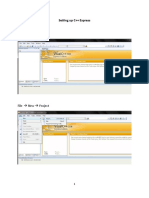
Step 1: Create a new C++ Project
For each C++ application, you need to create a project to keep all the source codes, object files,
executable files, and relevant resources.
To create a new C++ project:
1. Choose "File" menu "New" Project... C/C++ C++ project.
2. The "C++ Project" dialog pops up.
a. In "Project name" field, enter "FirstProject".
b. In "Project Types" box, select "Executable" "Empty Project".
c. In "Toolchains" box, choose your compiler, e.g., "Cygwin GCC" or "MinGW GCC"
Next.
3. The "Select Configurations" dialog appears. Select both "Debug" and "Release" Finish.
Step 2: Write a Helloworld C++ Program
1. In the "Project Explorer" leftmost panel Rightclick on "FirstProject" or use the "File"
menu New Source File.
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
2/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
2. The "New Source File" dialog pops up.
a. In "Source file" field, enter "Hello.cpp".
b. Click "Finish".
3. The source file "Hello.cpp" opens on the editor panel doubleclick on "test.cpp" to
open if necessary. Enter the following codes:
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
intmain(){
cout<<"Hello,world!"<<endl;
return0;
}
If "Unresolved Inclusion Error"
If error "unresolved inclusion" appears next to #include statement, the "include paths for
headers" are not set properly. Select "Project" menu Properties C/C++ General Paths and
Symbols In "Includes" tab:
For Cygwin GCC:
1. "Add" the following directories to "GNU C", where $CYGWIN_HOME is your Cygwin installed
directory:
$CYGWIN_HOME\lib\gcc\i686pccygwin\4.5.x\include
$CYGWIN_HOME\lib\gcc\i686pccygwin\4.5.x\includefixed
$CYGWIN_HOME\usr\include
$CYGWIN_HOME\usr\include\w32api
2. "Add" the following directories to "GNU C++", where $CYGWIN_HOME is your Cygwin
installed directory:
$CYGWIN_HOME\lib\gcc\i686pccygwin\4.5.x\include\c++
$CYGWIN_HOME\lib\gcc\i686pccygwin\4.5.x\include\c++\i686pccygwin
$CYGWIN_HOME\lib\gcc\i686pccygwin\4.5.x\include\c++\backward
$CYGWIN_HOME\lib\gcc\i686pccygwin\4.5.x\include
$CYGWIN_HOME\lib\gcc\i686pccygwin\4.5.x\includefixed
$CYGWIN_HOME\usr\include
$CYGWIN_HOME\usr\include\w32api
For MinGW GCC:
1. "Add" the following directories to "GNU C", where $MINGW_HOME is your MinGW installed
directory:
$MINGW_HOME\lib\gcc\mingw32\4.6.x\include
$MINGW_HOME\include
$MINGW_HOME\lib\gcc\mingw32\4.6.x\includefixed
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
3/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
2. "Add" the following directories to "GNU C++", where $MINGW_HOME is your Cygwin installed
directory:
$MINGW_HOME\lib\gcc\mingw32\4.6.x\include\c++
$MINGW_HOME\lib\gcc\mingw32\4.6.x\include\c++\mingw32
$MINGW_HOME\lib\gcc\mingw32\4.6.x\include\c++\backward
$MINGW_HOME\lib\gcc\mingw32\4.6.x\include
$MINGW_HOME\include
$MINGW_HOME\lib\gcc\mingw32\4.6.x\includefixed
NOTE: To find the header paths, you can do a search on headers such as "stdio.h" for C and
"iostream" for C++ under the Cygwin or MinGW installed directory.
Note : If you encounter "error while loading shared libraries" during link. Install
"libmpfr4" in cygwin.
Step 3: Compile/Build
Rightclick on the "FirstProject" or use the "Project" menu choose "Build Project" to
compile and link the program.
Step 4: Run
To run the program, rightclick on the "FirstProject" or anywhere on the source "test.cpp",
or select the "Run" menu Run As Local C/C++ Application If ask, choose Cygwin's gdb
debugger The output "Hello, world!" appears on the "Console" panel.
NOTE: You need to create a new C++ project for EACH of your programming problems. This is
messy for writing toy programs!
2.2C Program
Follow the same steps as above. Create a "C Project" instead of "C++ Project". Try the following
Helloworld program called "Hello.c".
#include<stdio.h>
intmain(){
printf("Hello,world!\n");
return0;
}
2.3C++ Program with Makefile
In the previous examples, we use socalled managedmake where Eclipse automatically
generated a makefile to build the program. We can also choose to write our own makefile for
complete control of the building process.
Step 1: Create a C++ Makefile Project
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
4/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
From "File" menu New Project... C/C++ C++ project In "Project name", enter
"HelloCppMakefile" In "Project type", choose "Makefile Project ", "Empty Project" In
"Toolchains", choose "Cygwin GCC" or "MinGW GCC". Ignore the warning message.
Step 2: Write a C++ Program
Rightclick on the project New Source File In "Source file", enter "Hello.cpp" Enter the
following source codes:
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
intmain(){
cout<<"Hello,world!"<<endl;
return0;
}
Step 3: Write a Makefile
Rightclick on the project New File In "File name", enter "makefile" Enter the
following codes. Take note that you need to use a Tab NOT Spaces for the indent.
all:Hello.exe
clean:
rmHello.oHello.exe
Hello.exe:Hello.o
g++goHello.exeHello.o
Hello.o:Hello.cpp
g++cgHello.cpp
Step 4: Build the Project
Rightclick on the project Build Project.
Step 5: Run the Program
Rightclick on the project Run As Local C/C++ Application.
[TODO] Write a makefile to compile toyprograms under one project.
3.Read the Documentation
At a minimum, you SHOULD browse through Eclipse's "Workbench User Guide" and "C/C++
Development User Guide" accessible via the Eclipse's "Welcome" page or "Help" menu. This
will save you many agonizing hours trying to figure out how to do some things later.
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
5/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
4.Debugging C/C++ Programs in Eclipse CDT
Able to use a graphics debugger to debug program is crucial in programming. It could save you
countless of hours guessing on what went wrong.
Step 0: Write a C++ Program The following program computes and prints the factorial
of n =1*2*3*...*n. The program, however, has a logical error and produce a wrong answer for
n=20 "TheFactorialof20is2102132736" a negative number?!.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
intmain(){
intn=20;
intfactorial=1;
//n!=1*2*3...*n
for(inti=1;i<=n;i++){
factorial*=i;
}
cout<<"TheFactorialof"<<n<<"is"<<factorial<<endl;
return0;
}
TheFactorialof20is2102132736
Let us use the graphic debugger to debug the program.
Step 1: Set an Initial Breakpoint A breakpoint suspends program execution for you to
examine the internal states e.g., value of variables of the program. Before starting the debugger,
you need to set at least one breakpoint to suspend the execution inside the program. Set a
breakpoint at main() function by doubleclicking on the leftmargin of the line containing
main(). A blue circle appears in the leftmargin indicating a breakpoint is set at that line.
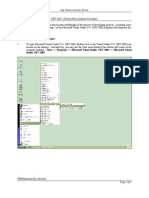
Step 2: Start Debugger Right click on the project or use the "Run" menu "Debug As"
"Local C/C++ Application" choose "Yes" to switch into "Debug" perspective A perspective is
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
6/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
a particular arrangement of
panels to suits a certain
development task such as
editing or debugging. The
program begins execution
but suspends its operation at
the breakpoint, i.e., the
main() function.
As illustrated in the following
diagram, the highlighted line
also pointed to by a blue
arrow
indicates
the
statement to be executed in the next step.
Step 3: StepOver and Watch
the Variables and Outputs
Click the "Step Over" button or select
"Step Over" from "Run" menu to
singlestep thru your program. At each
of the step, examine the value of the
variables in the "Variable" panel and
the outputs produced by your program
in the "Console" Panel, if any.
You can also place your cursor
at any variable to inspect the
content of the variable.
Singlestepping
thru
the
program and watching the
values of internal variables and
the outputs produced is the
ultimate mean in debugging programs because it is exactly how the computer runs your
program!
Step 4: Breakpoint, RunToLine, Resume and Terminate As mentioned, a
breakpoint suspends program execution and let you examine the internal states of the program.
To set a breakpoint on a particular statement, doubleclick the leftmargin of that line or select
"Toggle Breakpoint" from "Run" menu.
"Resume" continues the program execution, up to the next breakpoint, or till the end of the
program.
"Singlestep" thru a loop with a large count is timeconsuming. You could set a breakpoint at the
statement immediately outside the loop e.g., Line 12 of the above program, and issue "Resume"
to complete the loop.
Alternatively, you can place the cursor on a particular statement, and issue "RunToLine" from
the "Run" menu to continue execution up to the line.
"Terminate" ends the debugging session. Always terminate your current debugging session using
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
7/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
"Terminate" or "Resume" till the end of the program.
Step 5: Switching Back to C/C++ perspective Click the "C/C++" perspective icon
on the upperright corner to switch back to the "C/C++" perspective for further programming or
"Window" menu Open Perspective C/C++.
I can's stress more that mastering the use of debugger is crucial in programming. Explore the
features provided by the debuggers.
Other Debugger's Features
Modify the Value of a Variable: You can modify the value of a variable by entering a
new value in the "Variable" panel. This is handy for temporarily modifying the behavior of a
program, without changing the source code.
StepInto and StepReturn: To debug a function, you need to use "StepInto" to step into
the first statement of the method. You could use "StepReturn" to return back to the caller,
anywhere within the method. Alternatively, you could set a breakpoint inside a method.
NOTE: If you receive error message "Can't find a source file at /cygdrive/c..." during
debugging, you need to configure a mapping between "/cygdrive/c" and "c:/" assuming that
your program in kept in drive c. From "Window" "Preferences" "C/C++" "Debug"
"Common Source Lookup Path", select "Add" "Path Mapping".
5.Tips & Tricks
Read Eclipse for Java's Tips & Tricks for general tips in using Eclipse.
5.1C/C++ Software Development Using GCC
1. You can find the commands used in Eclipse CDT for build the project at "
<workspace>\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.cdt.ui\globalbuild.log".
2. Setting includepaths, librarypaths, and libraries: When building the
program, the compiler needs the header files to compile the source codes; the linker needs
the libraries to resolve external references. The compiler searches the "includepaths" for
the headers specified in #include directives. The linker searches the "librarypaths" for
"libraries" needed to link the program. In GCC, includepath is specified via Idir option or
environment variable CPATH. The librarypath is specified via Ldir option, or environment
variable LIBRARY_PATH. The library libxxx.a is specified via lxxx option lowercase
letter 'l', without the prefix lib and .a extension.
In Eclipse CDT, you can set the include paths, library paths and libraries by rightclick on the
project Properties C/C++ General Paths and Symbols Under tabs "Includes",
"Library Paths" and "Libraries". The settings are applicable to the selected project only.
To set the include paths and library paths for all the projects, set the environment variables
CPATH and LIBRARY_PATH. In Eclipse, choose "Window" Preferences C/C++ Build
Environment.
Alternatively, copy the headers and libraries into system directories, and you can omit the
includepaths and librarypaths.
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
OpenGL with GLUT:
8/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
3. OpenGL with GLUT: For Cygwin, you need to install gcc, g++, gdb, make under Devel
category and opengl, freeglut under graphics category. The headers gl.h, glu.h, glut.h
are kept in $cygwin\usr\include\w32api\GL. Use #include <GL/gl__.h> to include
the headers. The libraries libopengl32.a libglu32.a and libglut32.a are kept in
$cygwin\lib\w32api. To specify these libraries in linking, use lopengl32 lglu32
lglut32 options without the lib prefix and .a extension.
4. OpenGL with SDL: Download SDL from http://www.libsdl.org. Choose Development
Libraries win32 mingw32 Unzip. Copy the headers directory SDLunder include
to
copy
$cygwin\usr\include\w32api;
$cygwin\lib\w32api;
copy
the
all
runtime
the
library
library
SDL.dll
files
in
lib
into
under
bin
into
Windows/System32. In your program, include these two headers: #include<SDL/sdl.h>
and #include<SDL/sdl_opengl.h>. For linking, add these libraries: lSDL lSDLmain.
5. #pragma
Comment
Directive:
pragma
comment
directive,
e.g.,
#pragma
comment(lib,"opengl32.lib"), is often used to include a particular library same as l
option. This systemdependent directive works on Windows's compiler, but NOT in GCC.
6. Error "multiple target patterns": There is a problem with GNU make at
$Cygwin\bin\make.exe.
Replaced
by
this
copy
@
http://www.cmake.org/files/cygwin/make.exe.
7. fflush(stdout): The gcc library uses buffered I/O in accordance with the C
Specification. Output is only written out to the output stream after a newline character.
You can flush the output with a fflush().
8. Project name shall not include the word "setup": If you name your C/C++
project with a name including the word "setup", then the resultant "*setup*.exe" will
trigger UAC User Authorization Control and require administrator right to run. This took
me a few hours to figure out! Try renaming a "hello.exe" to "mysetup.exe".
6. File I/O in Eclipse
Refer to Eclipse for Java's File IO.
REFERENCES & RESOURCES
1. Eclipse's "C/C++ Development Tool User Guide", accessible via Eclipse's Help menu.
2. GCC GNU compilers mother
http://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs.
site
http://gcc.gnu.org;
GCC
manual
3. An Introduction to GCC @ http://www.networktheory.co.uk/docs/gccintro/index.html.
Latest version tested: Eclipse 4.2.2 Juno, Eclipse CDT 8.1.2
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
9/10
12/30/2015
HowtoinstallanduseEclipseCDTforC/C++programming
Last modified: April, 2013
Feedback, comments, corrections, and errata can be sent to Chua HockChuan ehchua@ntu.edu.sg |
HOME
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/howto/EclipseCpp_HowTo.html
10/10
You might also like
- Totem Pole InformationDocument18 pagesTotem Pole InformationLorrin BundesenNo ratings yet
- Cyber Deception PDFDocument318 pagesCyber Deception PDFnaeem firdous100% (1)
- Telos City - A D&D SettingDocument29 pagesTelos City - A D&D SettingMWDBookingNo ratings yet
- Academy Architecture and Architectural Review Vol 34 1908Document179 pagesAcademy Architecture and Architectural Review Vol 34 1908q3rNo ratings yet
- History of Egypt Under The PharaohsDocument238 pagesHistory of Egypt Under The Pharaohshadil7997100% (4)
- Ansys SherlockDocument11 pagesAnsys SherlockDhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- NCBI HandbookDocument492 pagesNCBI HandbookDaniela GuardiaNo ratings yet
- C# Programming Illustrated Guide For Beginners & Intermediates: The Future Is Here! Learning By Doing ApproachFrom EverandC# Programming Illustrated Guide For Beginners & Intermediates: The Future Is Here! Learning By Doing ApproachRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Tutorial Borland C++ BuilderDocument8 pagesTutorial Borland C++ BuilderHari KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Michael F. Suarez S.J., H. R. Woudhuysen-The Book - A Global History-Oxford University Press (2014)Document769 pagesMichael F. Suarez S.J., H. R. Woudhuysen-The Book - A Global History-Oxford University Press (2014)Diana Paola Guzmán Méndez100% (6)
- Vector OfficeDocument12 pagesVector OfficeWalid Haddad100% (1)
- How To Work With Code Blocks - TutorialDocument17 pagesHow To Work With Code Blocks - TutorialSuraz Verma100% (1)
- Codeblock StepsDocument6 pagesCodeblock StepsDakshitaNo ratings yet
- How To Install CodeBlocks and Get Started With C - C++ ProgrammingDocument8 pagesHow To Install CodeBlocks and Get Started With C - C++ ProgrammingrajababhuNo ratings yet
- CodeBlocks C C++Document5 pagesCodeBlocks C C++semabayNo ratings yet
- Opengl With EclipseDocument5 pagesOpengl With EclipseLee Chan PeterNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Dev C++Document4 pagesTutorial Dev C++Wasdodi Al-AssaNo ratings yet
- C Programming Essentials HandoutDocument3 pagesC Programming Essentials HandoutCharlie420No ratings yet
- Experiment: Lab No 01 Understanding The Codeblocks For C/C++ ProgrammingDocument4 pagesExperiment: Lab No 01 Understanding The Codeblocks For C/C++ ProgrammingWaqas QayyumNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Installation of C Programming EnvironmentDocument9 pagesLab 1 Installation of C Programming EnvironmentRAMEYANo ratings yet
- Dev C++ TutorialDocument8 pagesDev C++ Tutorialfaiz68No ratings yet
- C++ Env Setting and Write A ProgramDocument16 pagesC++ Env Setting and Write A ProgramZabih keraamNo ratings yet
- Programming in C++ With Eclipse: CSC121 TutorialDocument4 pagesProgramming in C++ With Eclipse: CSC121 TutorialSreenivasulu Reddy IndelaNo ratings yet
- Install OpenGL GLUT1Document15 pagesInstall OpenGL GLUT1rksNo ratings yet
- C++ NotesDocument3 pagesC++ Notesali409909758No ratings yet
- Eclipse For CDocument6 pagesEclipse For CKeijo SalonenNo ratings yet
- Vikilabs: Installing and Setting-Up Eclipse Ide To Run Your First Freertos Project (On A Windows PC)Document13 pagesVikilabs: Installing and Setting-Up Eclipse Ide To Run Your First Freertos Project (On A Windows PC)amritpati14No ratings yet
- How To Install Dev-C++ and GLUTDocument15 pagesHow To Install Dev-C++ and GLUTMelquior PaniniNo ratings yet
- Setting Up SDL & MinGW On VS Code (Windows and Ubuntu)Document20 pagesSetting Up SDL & MinGW On VS Code (Windows and Ubuntu)Abdul Majid TanwirNo ratings yet
- Setting Up C++ ExpressDocument12 pagesSetting Up C++ Express5ch1um2urgNo ratings yet
- Using Online IDE: IDE Stands For Integrated Development: Filter - None Edit Play - Arrow Brightness - 4Document107 pagesUsing Online IDE: IDE Stands For Integrated Development: Filter - None Edit Play - Arrow Brightness - 4RajiniNo ratings yet
- How To Install Dev-C++ and The Glut Libraries For Compiling Opengl Programs With Ansi CDocument21 pagesHow To Install Dev-C++ and The Glut Libraries For Compiling Opengl Programs With Ansi CIAGPLSNo ratings yet
- COMP2002 Using MS Visual Studio 2008 PDFDocument6 pagesCOMP2002 Using MS Visual Studio 2008 PDFAbdul Aziz TurdiNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2010Document4 pagesMicrosoft Visual C++ 2010jcastillo3No ratings yet
- Visual Studio Code and GCC - Installation Guide PDFDocument12 pagesVisual Studio Code and GCC - Installation Guide PDFDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Eclipse Installation On Ubuntu 14.04Document14 pagesEclipse Installation On Ubuntu 14.04melvinvitNo ratings yet
- Programming Cloud Services For Android: Setup Guide: Running Gradle Projects From EclipseDocument24 pagesProgramming Cloud Services For Android: Setup Guide: Running Gradle Projects From Eclipseadmin sdcNo ratings yet
- TUT - Introduction To MS Visual C++ For MSVS2008Document16 pagesTUT - Introduction To MS Visual C++ For MSVS2008Nguyen Huu QuangNo ratings yet
- Visual Studio IDE 2019: Bootcamp ParallelsDocument20 pagesVisual Studio IDE 2019: Bootcamp ParallelsNazrin RashidovaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual PF 12oct23Document73 pagesLab Manual PF 12oct23Muhammad TayyabNo ratings yet
- SetupCG Open GLDocument42 pagesSetupCG Open GLsoc11559No ratings yet
- Opengl Configuring GLFW and GlewDocument18 pagesOpengl Configuring GLFW and Glewxolar2002No ratings yet
- Setting Up GLUT: CS 148 Autumn 2011-2012 September 24, 2012Document3 pagesSetting Up GLUT: CS 148 Autumn 2011-2012 September 24, 2012dewddudeNo ratings yet
- In This Chapter, We Are Going To Learn How To Setup C Development Environment UsingDocument5 pagesIn This Chapter, We Are Going To Learn How To Setup C Development Environment UsingPravitha SomasekharanNo ratings yet
- Using Glut and Opengl With Visual StudioDocument5 pagesUsing Glut and Opengl With Visual StudioDaniel Conde LinaresNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 LabsheetDocument11 pagesLab 2 LabsheetPRITAM BASUNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 - Creating A Blank SolutionDocument14 pagesFigure 1 - Creating A Blank SolutionBernadus PranataNo ratings yet
- Installing SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinDocument9 pagesInstalling SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinOmotoyosi TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Installing SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinDocument9 pagesInstalling SiLabs SDCC Drivers WinOmotoyosi TaiwoNo ratings yet
- CL-1002 Programming Fundamentals: Introduction To IDE and Basic Programming ConstructsDocument19 pagesCL-1002 Programming Fundamentals: Introduction To IDE and Basic Programming Constructsjatin kesnaniNo ratings yet
- EEE554 Lab Exercise1Document2 pagesEEE554 Lab Exercise1Rohs PrasadNo ratings yet
- Install Guide WindowsDocument3 pagesInstall Guide WindowsboolxxNo ratings yet
- How To Compile and Run CDocument2 pagesHow To Compile and Run CHappa1No ratings yet
- Lab Session 01Document6 pagesLab Session 01silverfish2000No ratings yet
- Com 127 Org Practical 1Document4 pagesCom 127 Org Practical 1janeNo ratings yet
- Eclipse Installation StepsDocument6 pagesEclipse Installation StepsGurram SaiTejaNo ratings yet
- Ms Visual TutorialDocument9 pagesMs Visual TutorialMuzamilNo ratings yet
- HOWTO - Install and Configure FreeWPC OnDocument45 pagesHOWTO - Install and Configure FreeWPC OnzokiNo ratings yet
- Using Opencv in Microsoft Visual C++: Setting Up Path Environment VariableDocument6 pagesUsing Opencv in Microsoft Visual C++: Setting Up Path Environment VariableAshutosh_Mukhe_6590No ratings yet
- ENERGY 211 / CME 211: September 24, 2008Document47 pagesENERGY 211 / CME 211: September 24, 2008dantyNo ratings yet
- Lab1Document4 pagesLab1Athifa RufaidaNo ratings yet
- C Programming FAQ PDFDocument23 pagesC Programming FAQ PDFxtito2No ratings yet
- Laporan Hasil Program Sederhana C++ Jihan Salsabila 23366032Document7 pagesLaporan Hasil Program Sederhana C++ Jihan Salsabila 23366032Gebi SugaraNo ratings yet
- CG Lab Manual PDFDocument71 pagesCG Lab Manual PDFsn.bharathNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document8 pagesLab 1api-259436196No ratings yet
- C Programming Wizardry: From Zero to Hero in 10 Days: Programming Prodigy: From Novice to Virtuoso in 10 DaysFrom EverandC Programming Wizardry: From Zero to Hero in 10 Days: Programming Prodigy: From Novice to Virtuoso in 10 DaysNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Android Emulators and Installation of Android OS on Virtualbox and VMwareFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Android Emulators and Installation of Android OS on Virtualbox and VMwareNo ratings yet
- Santiago Sierra, The Black Cone, Monument To Civil DisobedienceDocument69 pagesSantiago Sierra, The Black Cone, Monument To Civil DisobedienceSantiago Sierra100% (2)
- Kuliah 1 - Konservasi GeologiDocument5 pagesKuliah 1 - Konservasi GeologiFerdianNo ratings yet
- Orientation Guide 2012 FinalDocument44 pagesOrientation Guide 2012 FinalLuqmaan FNo ratings yet
- ETpedia Grammar 500 Ideas and Activities For Teaching GrammarDocument242 pagesETpedia Grammar 500 Ideas and Activities For Teaching GrammarashilamakNo ratings yet
- Alin Hent, Gabriela Gheorghiu PDFDocument12 pagesAlin Hent, Gabriela Gheorghiu PDFAlin HențNo ratings yet
- Extending MATLAB With Numerical RecipesDocument13 pagesExtending MATLAB With Numerical Recipesparamtap4257No ratings yet
- Wix - How To Run Exe Files After Installation From Installed Directory - Stack OverflowDocument2 pagesWix - How To Run Exe Files After Installation From Installed Directory - Stack Overflowmoisés_bordalloNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu COBOL Debugging Guide: Microsoft Windows Microsoft Windows 95 Microsoft Windows NTDocument154 pagesFujitsu COBOL Debugging Guide: Microsoft Windows Microsoft Windows 95 Microsoft Windows NTLuis CamposNo ratings yet
- Munkácsy MihályDocument16 pagesMunkácsy MihályAlexandra BognarNo ratings yet
- Qasr Mshatta قصرمشتٰیDocument13 pagesQasr Mshatta قصرمشتٰیMuhammad Sher Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Notice: Culturally Significant Objects Imported For Exhibition: Impressed by Light: British Photographs From Paper Negatives, 1840-1860Document2 pagesNotice: Culturally Significant Objects Imported For Exhibition: Impressed by Light: British Photographs From Paper Negatives, 1840-1860Justia.comNo ratings yet
- C1 WPF Datagrid IonDocument90 pagesC1 WPF Datagrid IonHarry FuentesNo ratings yet
- The MVVM Design PatternDocument7 pagesThe MVVM Design PatternPaolo_RNo ratings yet
- Michael C. Andrade, LLB - , MpaDocument1 pageMichael C. Andrade, LLB - , MpaMichael C. AndradeNo ratings yet
- MomaDocument441 pagesMomaNathalie Salazar Zúñiga100% (1)
- Simio Reference GuideDocument521 pagesSimio Reference GuideVishal Tamraparni100% (1)
- 2011 Christenhusz Et Al Phytotaxa19p7 54 FernsDocument48 pages2011 Christenhusz Et Al Phytotaxa19p7 54 FernsLyta Efria RiaratriNo ratings yet
- Lbantam ClassiciteratureDocument31 pagesLbantam Classiciteraturesaha1988No ratings yet
- London KarinaLDocument2 pagesLondon KarinaLclcziprokNo ratings yet
- A Generation of Vipers by Sarah Yarwood LovettDocument254 pagesA Generation of Vipers by Sarah Yarwood Lovettk.rajeshwariNo ratings yet
- C Question BankDocument46 pagesC Question BankRanjith KumarNo ratings yet