Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrolyte Mnemonic Quizlet
Uploaded by
A.h.MuradCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrolyte Mnemonic Quizlet
Uploaded by
A.h.MuradCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrolytes: functions, levels and symptoms
Study online at quizlet.com/_euola
1.
Calcium
What is the function of
Calcium in the body?
Calcium functions to:
stabilizes cell membranes
assists in blood clotting
regulates muscle contraction and
relaxation
maintains cardiac function
2.
Calcium
What is the normal serum
level of Calcium?
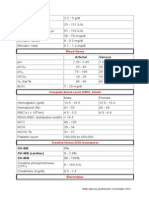
normal serum level 8.5-10.0
3.
Chloride
What is the normal serum
level?
What is the function?
normal serum level is 98-106
functions in the acid-base
balance
anion
direct relationship with sodium
and potassim
inverse relationship with
bicarbonate
4.
Chvostek and Trousseau's
Sign, causes of:
Hypocalcemia and
hypomagnesemia
8.
Hyperkalemia EKG
changes
Prolonged P R
Wide Q R S
ST segment depression
Tall-tented T-waves
9.
Hyperkalemia symptoms of:
mnemonics:
MURDER the TWAVES
serum level greater than 5.0
---MURDER--M - Muscle weakness
U - urine oliguria/anuria
R - respiratory distress
D - decreased cardiac contractility
E - EKG changes
R - reflexes hyper
---T-WAVES--T - tall tented t-waves
W - weakness in lower extremities;
A - anxiety and irritability
V - v fib and dysrhythmias
E - EKG changes
10.
Hypermagnesemia:
EKG changes
Hypotension
ECG Changes begin at Mg greater
than10
Bradycardia
Prolonged P R
Prolonged Q R S
Prolonged Q T
Complete heart block at 30 mg/dL
Asystole at 34-40 mg/dL
11.
Hypermagnesemia;
symptoms of:
mneumonic
SLOW RENAL
serum level greater than 2.6
---SLOW RENAL--S - slow, shallow respirations
L - lethargy (can lead to coma)
O - out of steam,decreased muscle and
nerve activity
W - weak pulse, decrease cardiac
function can lead to cardiac arrest
R - reflexes decreased
(weakness/paralysis)
E - EKG changes, bradycardia,
hypotension
N - nausea, vomiting
A - appearance is flushed
L - lethargy (drowsiness, can lead to
coma)
Hyperphosphatemia
5.
Hypercalcemia EKG
changes
decreases neuromuscular
irritability,
Shortened Q T
Shortened S T
Widened T wave
6.
Hypercalcemia,
symptoms of:
mneumonics
hydrate HARD or
Moans, Groans, Bones,
Stones and Overtones
serum level greater than10.0
---HARD--H - hypoactive DTR's, weakness,
lethargy
A - abdominal cramping
R - renal stones
D - dysrhythmias (can lead to
cardiac arrest)
---Groans,Moans, Bones, Stones,
and Overtones--Groans - constipation
Moans - pain in joints
Bones - loss of Calcium
Stones - renal stones
Overtones - psychiatric
overtones, depression, confusion
7.
Hyperchloremia;
symptoms of:
mneumonic
take a WALK
serum level greater than106
---WALK--W - weakness
A - active heart (tachycardia,
increased BP)
L - lethargy
K - Kussmaul respirations
12.
Hypernatremia - symptoms of:
mnemonics
TRIP; SALT
FRIED, if dehydrated
tremors, twitching,
hyperreflexia
restlessness
intense thirst
pulmonary and
peripheral edema
skin flushed
agitation
low grade fever
thirst
---if dehydrated--fever, flushed skin
restlessness, agitation
increased fluid
retention
edema
decreased urine output
13.
14.
Hyperphosphatemia - symptoms
of:
mneumonic:
can't DANCE because my
extremities are tingling
CHEMO
Hypocalcemia EKG changes
serum level greater
than 4.5
---DANCE--D - decreased CNS
A - anorexia
N - neuromuscular
irritability
C - Chvostek and
Trousseau's sign
E - extremity tingling
---CHEMO--C - cardiac irregularities
H - hyperreflexia
E - eating poorly
M - muscle weakness
O - oliguria
increases
neuromuscular
irritability
prolonged Q T
prolonged S T
15.
Hypocalcemia sypmtoms of:
mneumonics
TETANY and CATS
serum level less than <8.5
---TETANY--T - twitching in face (Chvostek)
E - EKG changes
T - Trousseau's sign
A - anxiety and confusion
N - numbness (paresthesia)
Y - lar"y"ngeal spasms
---CATS--C - convulsions
A - arrhythmias
T - tetany
S - spasms and stridor
16.
Hypochloremia symptoms of:
mnemonic
get SMART quick
---SMART--S - seizures, coma;
M - muscle cramps;
A - arrhythmias;
R - respiratory arrest;
T - twitching, tetany, hyper DTR's;
Trousseau and Chvostek signs
17.
Hypokalemia EKG
changes
Flattened or inverted T-wave
appearance of U waves
Depressed S T segment
18.
Hypokalemia sypmtoms of:
mnemonic
SUCTION the 6 L's
serum level less than 3.5
---SUCTION--S - skeletal muscle weakness, leg cramps,
lethargy
U -- U-waves
C - constipation
T - toxic effects of digoxin
I - irregular weak pulse
O - orthostatic hypotension
N - numbness (paresthesia)
---6L's--Lethargy, leg cramps, limp muscles, low,
shallow respirations, lethal cardiac
dysthymias
19.
Hypomagnesemia:
EKG changes
Widened Q R S
Prolonged Q T
Decrease T wave
Atrial / ventricular arrhythmias
especially if on digoxin
20.
21.
Hypomagnesemia:
symptoms of:
mneumonics:
STARVED and
IRRITATE
Hyponatremia,
symptoms of:
mnemonic
Tactile and Salt loss,
if dehydrated
serum level less than 1.6
---STARVED--S - seizures
T - tetany
A - anorexia, arrhythmias
R - increased heart rate
V - vomiting
E - emotional labiality
D - DTR's increased
---IRRITATE--I - irritates the CNS-confusion, seizures
R - respiratory muscles labored
R - rapid heart rate
I - irritates the myocardium
T - twitching, tremors, tetany, DTR's
increased
A - anorexia, arrhythmias
T - Trousseau and Chvostek signs
E - EKG changes
tremors, twitching, weakness
abdominal pain
cool, pale skin
skip
tachycardia
lethargy, decreased LOC, confusion
skip
Stupor/coma;
Anorexia
Lethargy, no energy
Tendon reflexes decreased
Limp muscles
Orthostatic hypotension;
Seizures/headache
Stomach cramps
22.
Hypophosphatemia;
symptoms of
mneumonic:
LOW energy and
bone strength
serum level less than 2.6
---LOW--L - lethargy, confusion
O - osteomalacia and rhabdomyolysis
W - weak muscles
23.
Magnesium:
What are the
functions of
magnesium in the
body?
Magnesium is important to
neuromuscular transmission and
cardiac function enzyme reactions,
synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids
A decrease causes neuromuscular
excitability
An increase decreases acetylcholine
release which causes a sedative effect.
Is needed for absorption of potassium
24.
Magnesium
What is the normal
serum level?
normal serum level is 1.6-2.6
25.
Phosphate What is the function of
phosphate in the
body?
phosphate functions:
** is important to the acid-base
balance**
acidosis = less free Calcium; alkalosis
= more ionized Calcium
ATP production
RBC function in O 2 delivery
Neuromuscular function
Metabolism of fats, carbs, and
proteins
26.
Phosphate What is the normal
serum level?
normal serum level is 2.6-4.5
27.
Potassium (K)
What is the normal
serum level?
normal serum level is 3.5-5.0
28.
Potassium
What is the function of
potassium in the
body?
Cardiac and neuromuscular
function
Helps to maintain resting potential
29.
Sodium (Na)
What is the function
of:
Primary regulator of volume,
osmolality and distribution of
extracellular fluid
Involved in Neuromuscular activity
30.
Sodium
What is the normal
serum level?
normal serum level is 135-145
31.
Which electrolytes
have a direct
relationship?
Potassium-Magnesium
Potassium-Calcium
Sodium and Chloride
Potassium and Chloride
32.
Which electrolytes
have an inverse
relationship?
Chloride and Bicarbonate
Sodium and Potassium
Phosphate and Calcium
Phosphate and Magnesium
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Torsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandTorsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCardiac Arrest, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAbnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- LegMusclesDocument78 pagesLegMusclesJoevet T. TadlasNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Explanation by AllnursesDocument3 pagesChest Tube Explanation by AllnursesYemaya84No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular IV and VDocument6 pagesCardiovascular IV and VJessicaNo ratings yet
- Respirotary MnemonicsDocument9 pagesRespirotary MnemonicsAymen Omer0% (1)
- Cardio TransDocument7 pagesCardio TransweissNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Test 4 ReviewDocument11 pagesMedsurg Test 4 ReviewTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Arrythmia Review TableDocument6 pagesArrythmia Review TablealobrienNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDysrhythmias Cheat SheetKandice ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination GuideDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination GuideKarl Jimenez Separa100% (2)
- Chapter 25heart Failure and Inflammatory DysfunctionDocument10 pagesChapter 25heart Failure and Inflammatory DysfunctionNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Arrhythmic Agents For Pharmacy PDFDocument41 pagesAnti-Arrhythmic Agents For Pharmacy PDFKelvinTMaikanaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology RevisedDocument59 pagesPharmacology Revisedjohnstockton12100% (1)
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Pulmonary PathoPhysiologyDocument45 pagesPulmonary PathoPhysiologySuliman Garalleh100% (1)
- Cardiac DrugsDocument8 pagesCardiac Drugsdawggj100% (2)
- Disorders of Acid Base BalanceDocument1 pageDisorders of Acid Base BalanceLyn Domingo EllaquezNo ratings yet
- Vasopressors and InotropesDocument31 pagesVasopressors and InotropesReza Prakosa SedyatamaNo ratings yet
- Medications and assessmentsDocument225 pagesMedications and assessmentsJessica 'Baker' IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Low Output HF High Output HFDocument7 pagesHeart Failure: Low Output HF High Output HFJake BurrNo ratings yet
- Medical MneumonicsDocument139 pagesMedical MneumonicsdrtpkNo ratings yet
- Patient Sticker Patient Sticker: AM LabsDocument3 pagesPatient Sticker Patient Sticker: AM LabsNurse BettyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Exam Guide: Hands to NeckDocument13 pagesCardiovascular Exam Guide: Hands to NeckBitu JaaNo ratings yet
- Gastro MnemonicsDocument8 pagesGastro MnemonicsRufina SoomroNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte DisordersDocument10 pagesElectrolyte DisordersSlavicaNo ratings yet
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument3 pagesRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Health HistoryDocument19 pagesHealth HistoryAngelene Caliva100% (1)
- CardiacDocument10 pagesCardiacMarcus Reynolds100% (1)
- Cardiac Disorders HandoutDocument14 pagesCardiac Disorders HandoutRizielle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Source NotesDocument30 pagesSource NotesChris Jardine Li100% (1)
- Medical Surgical NotesDocument18 pagesMedical Surgical NotesshalomNo ratings yet
- Cardiology MnemonicsDocument12 pagesCardiology MnemonicsEliza SparkNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Chest and LungsDocument46 pagesAssessment of The Chest and LungsSumathi GopinathNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Normal Lab ValuesDocument5 pagesNormal Lab ValuesNadiya Elfira BilqisNo ratings yet
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesFrom EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Acute Resuscitation and Crisis Management: Acute Critical Events Simulation (ACES)From EverandAcute Resuscitation and Crisis Management: Acute Critical Events Simulation (ACES)David NeilipovitzNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Hypertension, Cardiovascular Disease, Analgesics, and Endocrine DisordersFrom EverandHypertension, Cardiovascular Disease, Analgesics, and Endocrine DisordersJack Z. YetivNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewFrom EverandPediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Function: Section of Pharmacology of the International Union of Physiological SciencesFrom EverandPharmacology of Cardiac Function: Section of Pharmacology of the International Union of Physiological SciencesOtto KrayerNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For NursesDocument29 pagesMnemonics For Nursesashdmb217100% (2)
- Nursing Mnemonics 09Document41 pagesNursing Mnemonics 09bryanjd91767100% (16)
- Medical MnemonicsDocument3 pagesMedical Mnemonicsle chix100% (1)
- Parathyroid DisordersDocument19 pagesParathyroid DisordersmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Causes of Increased Serum K+ and Related ConditionsDocument6 pagesCauses of Increased Serum K+ and Related ConditionsAlyssaMarieSyNo ratings yet
- RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHYDocument4 pagesRESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHYA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Membership of the Royal Colleges of Physicians UK Exam ResultsDocument129 pagesMembership of the Royal Colleges of Physicians UK Exam ResultsA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- 81ventricular Tachy SCD ICD Melgarejov2 PDFDocument28 pages81ventricular Tachy SCD ICD Melgarejov2 PDFA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- 81ventricular Tachy SCD ICD Melgarejov2 PDFDocument28 pages81ventricular Tachy SCD ICD Melgarejov2 PDFA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Diabetes - What To Do When You Are Ill PDFDocument2 pagesDiabetes - What To Do When You Are Ill PDFA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolism Reducing Venous Thromboembolism Risk Orthopaedic SurgeryDocument16 pagesVenous Thromboembolism Reducing Venous Thromboembolism Risk Orthopaedic SurgeryA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Defining The Factors of Fitch Rankings in The European Banking SectorDocument25 pagesDefining The Factors of Fitch Rankings in The European Banking SectorA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Reference RangesDocument6 pagesReference RangesA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of sleep-related breathing disordersDocument5 pagesGuidelines on diagnosis and treatment of sleep-related breathing disordersA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Your Skincare PlanDocument1 pageYour Skincare PlanA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- IJ-ELTS Explores Translation Strategies for Introducing American Crime Fiction to Libyan ReadersDocument14 pagesIJ-ELTS Explores Translation Strategies for Introducing American Crime Fiction to Libyan ReadersFrau YahiNo ratings yet
- Q22ADocument1 pageQ22AA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- EmergencyTreatmentOfAnaphylacticReactions PDFDocument50 pagesEmergencyTreatmentOfAnaphylacticReactions PDFHerakles PantelidakisNo ratings yet
- 81ventricular Tachy SCD ICD Melgarejov2 PDFDocument28 pages81ventricular Tachy SCD ICD Melgarejov2 PDFA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Some Oncology Tips & Tricks by DR Khaled MagdyDocument8 pagesSome Oncology Tips & Tricks by DR Khaled MagdyA.h.Murad100% (1)
- Treatment and Care Towards The End of Life English 1015 PDF 48902105 PDFDocument88 pagesTreatment and Care Towards The End of Life English 1015 PDF 48902105 PDFA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- ECG Normal Sinus Rhythm GuideDocument10 pagesECG Normal Sinus Rhythm GuideNakul GaurNo ratings yet
- Care After Stroke and TIA - Information For Patients and Their Carers - 0 PDFDocument32 pagesCare After Stroke and TIA - Information For Patients and Their Carers - 0 PDFA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- 100 Important Points of Physiology..Document3 pages100 Important Points of Physiology..A.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- DVLA GuidanceDocument3 pagesDVLA GuidanceA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders - Medical GraduatesDocument1 pagePersonality Disorders - Medical GraduatesA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Changes During MenestruationDocument1 pageHormonal Changes During MenestruationA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Lateral Chest Radiograph Analysis: A Systematic ApproachDocument7 pagesLateral Chest Radiograph Analysis: A Systematic ApproachA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- InTech-Diabetic Foot and GangreneDocument25 pagesInTech-Diabetic Foot and GangrenePutu Reza Sandhya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Neuro - Clues - Top 10 Cases For Pacess From MRcp4AllDocument1 pageNeuro - Clues - Top 10 Cases For Pacess From MRcp4AllA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Fruits in MedicineDocument2 pagesFruits in MedicineA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology MnemonicDocument3 pagesRheumatology MnemonicA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- 12 Medical Tests To AvoidDocument2 pages12 Medical Tests To AvoidA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Renal SyndromesDocument1 pagePulmonary Renal SyndromesA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- MRCP Classical Diagnostics KeywordsDocument817 pagesMRCP Classical Diagnostics KeywordsMin MawNo ratings yet
- Cancer of Oral CavityDocument27 pagesCancer of Oral CavityMihai AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders CandraDocument38 pagesBleeding Disorders CandraDisya CittaNo ratings yet
- Sfbtnarr 2Document19 pagesSfbtnarr 2api-267074391No ratings yet
- Euro J of Neurology - 2021 - Van Den Bergh - European Academy of Neurology Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline On DiagnosisDocument28 pagesEuro J of Neurology - 2021 - Van Den Bergh - European Academy of Neurology Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline On DiagnosisSusana RocheNo ratings yet
- Kimberly Callis - Stoning Demons - Complex PTSD Recovery Workbook. 6Document44 pagesKimberly Callis - Stoning Demons - Complex PTSD Recovery Workbook. 6intenselight91% (11)
- Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPleural EffusionEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Who Trs 993 Web FinalDocument284 pagesWho Trs 993 Web FinalAnonymous 6OPLC9UNo ratings yet
- Congenital AnomaliesDocument94 pagesCongenital AnomaliesDeepti Kukreti100% (1)
- Pil 2425Document6 pagesPil 2425Gabriela ChiritoiuNo ratings yet
- SSP 1 Check List CHC Kukma Kutch 31st Aug 12Document2 pagesSSP 1 Check List CHC Kukma Kutch 31st Aug 12dhir.ankurNo ratings yet
- Thailand Dyspepsia Guidelines 2018Document12 pagesThailand Dyspepsia Guidelines 2018เด็กชายสมันตภัทร แฟนคลับอาจารย์กวงNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida OCCULTADocument1 pageSpina Bifida OCCULTArebelswanteddot_comNo ratings yet
- Huckstep Nail For Periimplant FractureDocument3 pagesHuckstep Nail For Periimplant FracturePurushothama Rao NalamatiNo ratings yet
- Nurs 205 Concept MapDocument1 pageNurs 205 Concept MapJami SpearsNo ratings yet
- AutocoidsDocument26 pagesAutocoidsA.R. ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MCQ ThyroidDocument6 pagesMCQ ThyroidFaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- Twins Bootcamp StudyDocument5 pagesTwins Bootcamp Studyandi dirhanNo ratings yet
- Rotator CuffDocument46 pagesRotator Cuffeuan00No ratings yet
- Rexulti PIDocument39 pagesRexulti PIbenaw187No ratings yet
- An Ayurvedic Formulation Trikatu' and Its ConstituentsDocument7 pagesAn Ayurvedic Formulation Trikatu' and Its ConstituentsSudheer JayaramNo ratings yet
- Speech & Language Therapy in Practice, Summer 2008Document32 pagesSpeech & Language Therapy in Practice, Summer 2008Speech & Language Therapy in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument9 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsKimberly Bomediano100% (1)
- M5W Wang FeedbackDocument21 pagesM5W Wang FeedbackIsaac HassanNo ratings yet
- Case Nephrotic SyndromeDocument32 pagesCase Nephrotic SyndromeTera SurbaktiNo ratings yet
- Class II Division 2 Malocclusion What The Clinician Should KnowDocument10 pagesClass II Division 2 Malocclusion What The Clinician Should KnowNawaf RuwailiNo ratings yet
- DR Arzoo Nephrology ThesesDocument35 pagesDR Arzoo Nephrology ThesesAzam ArzooNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Phosphorus Removal Study GuideDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Phosphorus Removal Study GuideBuenaventura Jose Huamani TalaveranoNo ratings yet
- Dim Mak and Acupuncture: Understanding the Medical Reasons Behind this Martial ArtDocument6 pagesDim Mak and Acupuncture: Understanding the Medical Reasons Behind this Martial ArtIoan NeacsuNo ratings yet
- Anc 0001 0009 0151Document42 pagesAnc 0001 0009 0151ManhaNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorder Lecture 10Document39 pagesEating Disorder Lecture 10Mawadh AlsbhiNo ratings yet