Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME 361 L2 - OpAmp
Uploaded by
আব্দুশশুকুরOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 361 L2 - OpAmp
Uploaded by
আব্দুশশুকুরCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp)
The operational amplifier, or op amp, is a low-cost and versatile integrated circuit
consisting of many internal transistors, resistors, and capacitors manufactured into
a single chip of silicon.
OP-Amp: Components
Used As:
The OP-Amp has Single Output and Two Inputs:
Amplifiers
1. Noninverting input [+]: output is in phase with input.
Integrators
2. Inverting input [-]: output is 180 out of phase with input.
Summers
Differentiators
Comparators
A/D and D/A converters
Active filters
Sample and hold amplifiers
Ideal characteristics:
1. Very high open-loop gain: A = 100,000+,
but unpredictable
2. Very high input resistance: Rin > 1 M
3. Low output resistance: Rout = 50-75 ohm
Fig. Op amp terminology and
schematic representation
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Op Amps: inside structure..
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Op Amps: assumptions..
1. It has infinite impedance at both inputs; hence, no current is drawn from the
input circuits. Therefore,
2. It has infinite gain. As a consequence, the difference between the input voltages
must be 0; otherwise, the output would be infinite. Therefore,
3. It has zero output impedance. Therefore, the output voltage does not depend
on the output current.
OP-Amp: Examples: Fig. shows an op-amp with an open-loop gain of 100,000. Find the output
for the following conditions:
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Voltage Follower
Very useful circuit
Can boost the current of a signal without increasing the voltage
Can transform a high-impedance signal into a robust low-impedance signal
Has a voltage gain of 1
Using a voltage follower to prevent load down
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
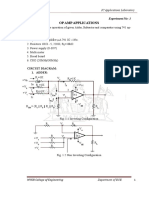
Inverting Amplifier
The most common op-amp configuration
The voltage gain is determined by the resistor values
This is an inverting amplifier because the input signal goes to the inverting
input, which means the output is out of phase with the input.
Feedback loop always goes from the output to the inverting input of the op
amp, implying negative feedback.
Fig. The inverting amplifier circuit.
H.W. An inverting amp is to have a gain of 10. The signal source is a sensor with an
output impedance of 1 k. Draw a circuit diagram of the completed amplifier.
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Non-inverting Amplifier
Positive gain
Useful in isolating one portion of a circuit from another
This circuit amplifies the input voltage without inverting the signal.
H.W. Draw the circuit diagram of a non-inverting amp with a gain of 20.
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Summing Amplifier
The summing amplifier has an output voltage that is the sum of any number of
input voltages.
It is used to add analog signals
The circuit output is the negative sum of the inputs.
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Op Amp: Vout?
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Differential Amplifier
A differential amplifier amplifies the difference between two input voltages.
The output of the amplifier (Vout) is a single voltage level referenced to ground,
sometimes called a single-ended voltage.
In analyzing this circuit, use the principle of superposition.
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Differential Amplifier
Inverting amplifier
Noninverting amplifier
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Differentiator
The relationship between voltage and current for
a capacitor:
Therefore, the output signal is an inverted, scaled
derivative of the input signal.
Caution:
One note of caution concerning using differentiation
in signal processing is that any electrical noise in the
input signal will be accentuated in the output. In
effect, the differentiator amplifies the fast-changing
noise. Integration, on the other hand, has a
smoothing effect, so noise is not a concern when
using an integrator.
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Integrator
The relationship between voltage and current for
a capacitor:
Integrating gives,
where is a dummy variable of integration
Therefore, the output signal is an inverted, scaled
integral of the input signal.
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Improving the characteristics of Integrators
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Instrumentation Amplifier
Instrumentation amplifiers are commercially available as monolithic ICs (e.g., Analog
Devices 524 and 624 and National Semiconductor LM 623). A single external resistor is
used to set the gain. This gain can be higher and is more stable than gains achievable
with a simple difference amplifier.
aminul islam khan
ME 361: Instrumentation and Measurement
Electronics : OpAmp
Instrumentation Amplifier
An instrumentation amplifier can also be constructed with inexpensive discrete op
amps and precision resistors.
Applying Ohms law to the feedback
resistors gives
and
Solving,
and
Now the rest of this amplifier is equivalent to a differential amplifier
So,
If
Then,
aminul islam khan
You might also like
- Synthesis and Properties of Bismuth Ferrite Multiferroic NanoflowersDocument8 pagesSynthesis and Properties of Bismuth Ferrite Multiferroic Nanoflowersআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Ruppur Power PlantDocument2 pagesRuppur Power Plantআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- ME 361 L1 BasicsDocument13 pagesME 361 L1 Basicsআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Thick Walled Cylinders With HolesDocument47 pagesDesign and Analysis of Thick Walled Cylinders With HolesKeryn Pelled-FeldmanNo ratings yet
- Sample Argument Response GREDocument1 pageSample Argument Response GREআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Routine FOR Section A: Date Time Course Room No. Teacher SundayDocument1 pageRoutine FOR Section A: Date Time Course Room No. Teacher Sundayআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Road to Freedom from BUETDocument2 pagesRoad to Freedom from BUETMohammad Khairul Halim Rimon50% (2)
- Asad Bin Hafiz Er KobitaDocument5 pagesAsad Bin Hafiz Er Kobitaআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Argument - A Recent Study of Eighteen Rhesus MonkeysDocument2 pagesArgument - A Recent Study of Eighteen Rhesus Monkeysআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument1 pageGas Turbineআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Look Forward Because Bygones Are Not To Come Back. They Only Way To Get Better Is Through Working HardDocument1 pageLook Forward Because Bygones Are Not To Come Back. They Only Way To Get Better Is Through Working Hardআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Quote For LifeDocument1 pageQuote For Lifeআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Do What You Love or Love What You DoDocument1 pageDo What You Love or Love What You Doআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- HSC 15 RoutineDocument3 pagesHSC 15 Routineআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- Do What You Love or Love What You DoDocument1 pageDo What You Love or Love What You Doআব্দুশশুকুরNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Current Feedback Op Amp Applications Circuit Guide: Summing AmplifierDocument9 pagesCurrent Feedback Op Amp Applications Circuit Guide: Summing Amplifiermubs73No ratings yet
- 16 - Introduction To Signal ConditioningDocument32 pages16 - Introduction To Signal ConditioningKARTHIK S SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Electronic CircuitsDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Electronic CircuitsMharlon Aladen0% (1)
- (Analog Circuits and Signal Processing) Raj Senani, D. R. Bhaskar, A. K. Singh, V. K. Singh (Auth.) - Current Feedback Operational Amplifiers and Their Applications-Springer-Verlag New York (2Document263 pages(Analog Circuits and Signal Processing) Raj Senani, D. R. Bhaskar, A. K. Singh, V. K. Singh (Auth.) - Current Feedback Operational Amplifiers and Their Applications-Springer-Verlag New York (2legarcon55100% (1)
- Given:R1 = 10 kΩR2 = 20 kΩ Vin = 2 VUsing the inverting amplifier formula:VO = -R2/R1 * VinVO = -20 kΩ/10 kΩ * 2 V VO = -4 VTherefore, the output voltage VO is -4 VDocument20 pagesGiven:R1 = 10 kΩR2 = 20 kΩ Vin = 2 VUsing the inverting amplifier formula:VO = -R2/R1 * VinVO = -20 kΩ/10 kΩ * 2 V VO = -4 VTherefore, the output voltage VO is -4 VErnesto Vergara Jr.No ratings yet
- Rin and Rout of the Inverting AmplifierDocument8 pagesRin and Rout of the Inverting Amplifierlizhi0007No ratings yet
- Opamp PesentationDocument34 pagesOpamp Pesentation2shreedNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp FundamentalsDocument50 pagesOp-Amp FundamentalsmbattmbuttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Industrial Electronic ControlDocument59 pagesChapter 2 Industrial Electronic ControlVeera KanapatyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Unit: 1 Part-A: 15 Questions (Each 1 Mark)Document37 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Unit: 1 Part-A: 15 Questions (Each 1 Mark)DINESH KUMAR DRAVIDAMANINo ratings yet
- North Maharashtra University Jalgaon (Common To All Branches of Engineering) W. E. F.2005 - 2006Document19 pagesNorth Maharashtra University Jalgaon (Common To All Branches of Engineering) W. E. F.2005 - 2006satish173No ratings yet
- PLL and MixerDocument71 pagesPLL and MixerVishwa BharathiNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier Applications - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesOperational Amplifier Applications - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaranscrib300100% (1)
- Electrical Engee&Comp SciDocument32 pagesElectrical Engee&Comp SciVishnu Kumar NadarNo ratings yet
- Acd Lab ManualDocument34 pagesAcd Lab ManualAbhishek PatelNo ratings yet
- How to Properly Bias Op-Amps for Optimal PerformanceDocument11 pagesHow to Properly Bias Op-Amps for Optimal PerformancevasiliyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 2014Document2 pagesBasic Electronics 2014Rajeswari PurushothamNo ratings yet
- DC and Ac CharcteristicsDocument17 pagesDC and Ac CharcteristicsDr A Pradeep Kumar asst.Prof(ECE)No ratings yet
- Analysis and Measurement of Intrinsic Noise in Op Amp Circuits Part IIDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Measurement of Intrinsic Noise in Op Amp Circuits Part IIleo_schenkelNo ratings yet
- ICA-UNIT-III - R19-CompleteDocument28 pagesICA-UNIT-III - R19-CompleteBhanu Kiran BKNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier ApplicationsDocument17 pagesOperational Amplifier Applicationslid20No ratings yet
- Op-Amp ApplicationsDocument64 pagesOp-Amp ApplicationsJadhav BhagavatNo ratings yet
- EveryCircuit Tutorial: Circuit Analysis Made EasyDocument31 pagesEveryCircuit Tutorial: Circuit Analysis Made EasyMika Mikic100% (1)
- II - II Linear Integrated Circuit Analysis Course Plan PDFDocument9 pagesII - II Linear Integrated Circuit Analysis Course Plan PDFshivgnitNo ratings yet
- 01 Op-Amps Student TutorialDocument12 pages01 Op-Amps Student TutorialniomariNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier EX.Document9 pagesOperational Amplifier EX.حسن صادق فرج فليحBNo ratings yet
- OP AMP APPLICATIONS LABDocument88 pagesOP AMP APPLICATIONS LABkrishna goggiNo ratings yet
- IC 741 Op Amp Specifications and ApplicationsDocument90 pagesIC 741 Op Amp Specifications and ApplicationsAhmed Al MansurNo ratings yet
- M - SC - Syllabus FinalDocument274 pagesM - SC - Syllabus FinalShyamal Sreedhar100% (1)
- DC Motor Speed Control System - ED4400BDocument14 pagesDC Motor Speed Control System - ED4400BDanang Pradika Purnomo100% (1)