Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wireless Sensor Network Application in Agriculture For Monitoring Agriculture Process.
Uploaded by
IJAFRCOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wireless Sensor Network Application in Agriculture For Monitoring Agriculture Process.
Uploaded by
IJAFRCCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Advance Foundation and Research in Computer (IJAFRC)
Volume 2, Issue 12, December - 2015. ISSN 2348 4853, Impact Factor 1.317
Wireless Sensor Network Application In Agriculture For
Monitoring Agriculture Process.
Priyanka P. Khairnar1, Deepali V. Gaikwad2, Sneha R. Kale3, Monika T. Madane4,
Prof. Manish B. Giri5
Department Of Computer Engineering, MITAOE, Pune.
1piyakhairnar999@gmail.com, 2gaikwad.deepali15@gmail.com, 3kalesneha1199@gmail.com,
4monikamadane1994@gmail.com, 5mbgiri@comp.maepune.ac.in
ABSTRACT
WSN (Wireless Sensor Network) connects the physical and computational world by monitoring
environmental phenomena through ubiquitous devices called sensor nodes or motes. India ranks
second in agriculture activities. The agriculture production process is affected by different factors
such as temperature, light, soil humidity, soil moisture. Precision agriculture is a field which
provides suitable scenarios for the deployment of wireless sensor networks (WSNs). WSNs
provide accurate information about environmental characteristics to farmers. This knowledge
represents a valuable resource because it helps in real-time decision making such as establishing
water management policies. In India there are different types of problems and one of the main
problems is the water shortage. Farmers crops are unreliable due to the variability in rainfall
amount as well as its distribution. We describe the use of wireless sensor networks (WSN) to
improve water management and for controlling other parameters such as temperature, light
humidity, moisture. Wireless sensor network(WSN) and other agricultural techniques might help
farmer to utilize and store the available water, improve their crop productivity, reduce the
production cost and instead of depending just on prediction WSN make use of real time values.
I. INTRODUCTION
Sensor networks are emerging as a great aid to improve agriculture quality, productivity and resource
optimization. Precision agriculture is a field which provides one of the most suitable scenarios for the
deployment of wireless sensor networks (WSNs)[1].To evaluate environmental parameters such as
humidity, temperature, moisture etc sensor network is used. Now a days many researchers are working
on WSN. Many new technologies in WSN have become available to improve agricultural quality. In WSN
large number of sensor node devices are spread over large geographical area. World Wide wireless
sensor network is used in many applications such as military, health care, agriculture, industrial.
Agriculture uses 85 % of available fresh water resources World Wide and this percentage will continue to
be dominant in water consumption because of population growth and increase food demand [7]. Climatic
conditions are continuously changing. So the farmer cannot depend on rainfall. Unplanned use of water
results in wastage of water. We have to utilize available water in efficient manner. Sensor network is
used to monitor environmental parameters of crop cultivation so that farmer knows when having water
or when to use certain pesticides. Precision agriculture has aim of optimizing the production. Sensor
network in agriculture is used to identify fungus, plagues infection of plant ,right harvesting time (i.e
maturity of fruit),controlled irrigation based on soil moisture. In India irrigation system is manual
controlled in which at regular interval farmers irrigates the land and sometime it is not possible to
irrigate the crop at required time due to this crop get dried. This results in less production as well as
profit to the farmer. Using Wireless Sensor Network for agriculture monitoring application human efforts
get reduced due to automated irrigation system [4].Farmer can perfectly predict environmental
conditions. The soil moisture sensor senses moisture level so that we get information about how much
53 | 2015, IJAFRC All Rights Reserved
www.ijfarc.org
International Journal of Advance Foundation and Research in Computer (IJAFRC)
Volume 2, Issue 12, December - 2015. ISSN 2348 4853, Impact Factor 1.317
water is to be sup- plied [5]. Proper irrigation management will help prevent economic losses caused by
over or under irrigation, movement of nutrients, pesticides [6]. Sensor nodes are deployed over farm.
Data sensed by different sensor nodes is given to sink node. Sink node transfer this collected data to
gateway over network. Sensor senses the information from sensor nodes transfers data to base station
.Actuator receives data from base station interpret them and generate the corresponding action [2]. A
Gateway forwards data from network to base station.
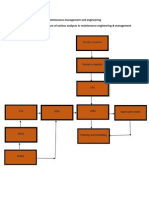
Figure 1. Architectural Functional Block Diagram
We are taking sensor values from sensor1, sensor2,...sensor n. The sensor values that we have taken are
in analog form for future computations we need digital values, so that we are using ADC to convert analog
values to digital form. ADC uses 10 bit register for computations sensor unit acquires data from ADC and
forward it to base-station through micro-controller. Micro-controller used in automatically control
products and devices such as automobile engine system, remote controls, power tools, micro-controllers,
are designed to govern operators of embedded system. Micro-controllers consist of CPU, RAM, ROM.
micro-controller works on TTL protocol and our base-station unit works on binary values, so for
communication between micro-controller and base-station we are using MAX- 232. MAX-232 works on
serial communication. Zig-Bee are flexible, they send and receive data over serial port which means they
are compatible with both computer and micro-controller.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
54 | 2015, IJAFRC All Rights Reserved
www.ijfarc.org
International Journal of Advance Foundation and Research in Computer (IJAFRC)
Volume 2, Issue 12, December - 2015. ISSN 2348 4853, Impact Factor 1.317
Sensor networks are emerging as a great aid to improve agriculture quality, productivity and resource
optimization. To evaluate environmental parameters such as humidity, temperature, moisture etc sensor
network is used. Now a days many researchers are working on WSN. Many new technologies in WSN
have become available to improve agricultural quality.
1) Young-Duk Kim et.al. On the design of beacon based wireless sensor network for agricultural
emergency
In this paper, we proposed new sensor network architecture with autonomous robots based on beacon
mode for real time agriculture monitoring system. The proposed scheme also offers a reliable association
with parent nodes and dynamically assigns network addresses. For the large scale multi-sensor
processing, the proposed system accomplished the intelligent database, which generates alert messages
to the handheld terminal by means of the fire and air-based sensor data. Thus farmers can easily check
out the current conditions of crops and farms at anytime and anywhere. Moreover, we also developed a
robot platform with network based mobility function for mobile surveillance.
2) Zhen Li et.al. Practical deployment of an in-field soil property wireless sensor network
This paper proposed two tier wireless sensor network system was for unsupervised, real-time, in-field
soil property data collection. Within the system, a local wireless sensor network was formed to acquire
real-time soil property data including volumetric water content, electrical conductivity, and temperature
at different underground depths and various locations. A long range cellular network and internet
services were used to relay the field data to a remote database on a web-server for data storage and user
querying.
3) Aqeel-ur-Rehman et.al. A review of wireless sensors and networks applications in
agriculture
A review of several solutions and efforts has been presented in this paper towards agriculture domain.
The major concerns are:
a) Solutions are too complex to implement and requires major technical support
b) Intense Cost is involved
c) Lack of generalized solution to different services and problems
4) B. Majonea* et.al. Wireless Sensor Network deployment for monitoring soil moisture
dynamics at the field scale
This paper describes deployment and testing a WSN monitoring system capable to provide spatially
distributed hydrological data relevant for eco-hydrological studies.Monitor soil moisture dynamics to
analyze interplay between soil moisture dynamics plant physiology.
5) Xin Dong et.al. Autonomous precision agriculture through integration of wireless
underground sensor networks with center pivot irrigation systems
In this work, we develop a novel system through the integration of center pivot systems with wireless
underground sensor networks, i.e., WUSA-CP, for autonomous precision agriculture (PA). The system
gathers soil information, such as soil moisture, from a WUSN in real time to automatically control the CP
for precision irrigation.
55 | 2015, IJAFRC All Rights Reserved
www.ijfarc.org
International Journal of Advance Foundation and Research in Computer (IJAFRC)
Volume 2, Issue 12, December - 2015. ISSN 2348 4853, Impact Factor 1.317
6) Xiaoqing Yu et.al. A survey on wireless sensor network infrastructure for agriculture
In this paper, we introduced a hybrid wireless sensor network architecture for agriculture. This network
reduces the intensive human involvement required in current agricultural information collection systems
and provides information that is more accurate than the existing sensor networks. This advanced sensor
network includes a terrestrial wireless sensor network and a wireless underground sensor network. The
hybrid WSN architecture combines the advantages of existing sensor techniques.
7) Robert W. Coates et.al. Wireless sensor network with irrigation valve control.
In this paper actuator hardware and firmware were designed for compatibility with a commercial
wireless network node. Wireless network range varied with radio height and type of obstructions,
reaching 1610 m under visual line-of-sight conditions and 175 m under obstructed conditions. Nodes
were updated with custom firmware that allowed commands received by the node to be passed to an
attached actuator. The actuator received commands through the node, responded with actuator data, and
operated up to 4 latching valves.
8) Joaqun Gutirrez et.al, Automated Irrigation System Using a Wireless Sensor Network and GPRS
Module.
The automated irrigation system implemented was found to be feasible and cost effective for optimizing
water resources for agricultural production. This irrigation system allows cultivation in places with
water scarcity thereby improving sustainability.
9) Zhao Liqiang et.al A Crop Monitoring System Based on Wireless Sensor Network.
This paper proposed an agricultural application of wirless sensor network. The main work is to
implement two types of nodes and building sensor network. The hardware platform is constituted by
data process unit, radio module, sensor control matrix, data storage flash, power supply unit, analog
interfaces and extended digital interfaces. The software system adopts TinyOS which is composed of
system kernel, device drivers and applications. Energy-saving algorithm is implemented in the
software system.
10) Soledad Escolar Daz et.al A novel methodology for the monitoring of the agricultural
production process based on wireless sensor networks.
This paper presents a methodology that can successfully guide the process of building monitoring
applications for agricultural production based on WSN technology. The methodology covers the complete
life cycle of applications, from requirements to maintenance. The motivation for describing a
methodology is to collect a set of best-practices and procedures that are found in the literature and
bridge the gap between how applications are built in practice and a robust, customizable approach.
III. PROJECT IDEA
Interpolation method is used to take readings in the farm where taking manual reading is not possible. If
we have two readings 30 meter away then we have to consider all the points between two readings. The
main purpose of project is to distribute water to crops if and only if there is need of water. So polynomial
interpolation technique is very useful. Objectives behind this project is to reduce human efforts, to reduce
power consumption, to utilize available water properly, to provide real time decision for water
management.
56 | 2015, IJAFRC All Rights Reserved
www.ijfarc.org
International Journal of Advance Foundation and Research in Computer (IJAFRC)
Volume 2, Issue 12, December - 2015. ISSN 2348 4853, Impact Factor 1.317
Algorithm: Polynomial Interpolation
The problem of determining a polynomial of degree one that passes through the distinct points, (x0,y0) &
(x1,y1)
f(x0)=y0 & f(x1)=y1
by means of first degree polynomial interpolating or agreeing with the value of f at given points.
Using this polynomial for approximation within the interval given by end points is called as polynomial
interpolation.
The
linear Lagrange
interpolating polynomial
P(x) =
Define the functions
through (x0,y0) & (x1,y1) is
f(x1)
P(x)=
Note that,
L0(x0)=1 L1(x0)=0 L1(x0)=0 L1(x1)=1 which implies that,
p(x0)=1.f(x0) + 0.f(x1)=f(x0)=y0 &
p(x1)=0.f(x0) + 1.f(x1)=f(x1)=y1
So P is unique polynomial of degree at most 1 that passes through (x0,y0) & (x1,y1)
Mathematical Modeling
Let S = {U,N,S,D,Sval,Sth,info,result,F}
Where ,
U = u1,u2,u3,..ui, Finite set of users.
N = Master, Slave
Where,
Master=master node.
Slave=slaves node.
Slave=slave1,slave2
S=s1,s2,s3,.,si Finite set
of sensors.
D=d1,d2,d3,.,di Finite set of devices.
Sval=sval1,sval2,,svali Finite set of ADC values of sensor[0-255].
STh=sTh1,sTh2,,sThi Finite set of Threshold set against sensor.
Info=info1,info2,,infoi Hardware status.
57 | 2015, IJAFRC All Rights Reserved
www.ijfarc.org
International Journal of Advance Foundation and Research in Computer (IJAFRC)
Volume 2, Issue 12, December - 2015. ISSN 2348 4853, Impact Factor 1.317
Functionalities:Yes/No = authenticate(uname,passwd)
Interface node(ni)
Svali = grab sensor values(Si)
Yes/No = apply threshold check(Svali,SThi)
control Device(Di,ON/OFF)
Result = apply prediction(Svali)
send data(infoi)
IV. CONCLUSION
WSN is emerging technology and it have wide range of applications. WSN plays an important role in
development of precision agriculture. Human efforts as well as electricity get reduced by making real
time decisions. Using WSN we can do proper utilization of water so that crop yield can increases to obtain
maximum profit.
V. FUTURE SCOPE
The future work is trying to improve hardware and software communication to make efficient and
reliable system which should also work in case of any type of failure. Smart monitoring system can be
design using sensor network. Most of the population in India is dependent on agriculture, so precision
agriculture help to traverse between developing country to developed country by increasing crop yield as
well as profit to farmer.
VI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We take this opportunity to express our sincere thanks to all those who have helped us and guided us to
complete this paper successfully. We would like to express our gratitude towards our project guide, Mr.
Manish Giri for his guidance during the preparation of this review paper. We would also like to thank
him for the moral support and encouragement. We would also like to thank Mrs. Uma Nagaraj, Head of
the Department for their support and their efforts in making sure that sufficient facilities were always
available to students. We are indebted to the authors whose works have been referred in completing this
seminar report. We are also thankful to all the staff members of the Computer Department of MIT
Academy Of Engineering, Alandi. We would also like to thank the institute for providing the required
facilities, Internet access and important books. Last but not list the family members and friends, We
would also like to thank them.
VII. REFERENCES
[1]
Soledad Escolar Daz , Jess Carretero Prez, Alejandro Caldern Mateos,Maria-Cristina Marinescu,
Borja Bergua Guerra A novel methodology for the monitoring of the agricultural production
process based on wireless sensor networks. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 76
(2011) 252265
58 | 2015, IJAFRC All Rights Reserved
www.ijfarc.org
International Journal of Advance Foundation and Research in Computer (IJAFRC)
Volume 2, Issue 12, December - 2015. ISSN 2348 4853, Impact Factor 1.317
[2]
Robert W. Coates a, Michael J. Delwiche a, Alan Broad b, Mark Holler b Wireless sensor network
with irrigation valve control. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture
96 (2013) 1322.
[3]
Zhao Liqiang, Yin Shouyi, Liu Leibo, Zhang Zhen, Wei Shaojun. A Crop Monitoring System Based
on Wireless Sensor Network. Procedia Environmental Sciences 11 (2011) 558 565
[4]
Aqeel-ur-Rehman a,b,, Abu Zafar Abbasi b, Noman Islam
b, Zubair Ahmed Shaikh b A review
of wireless sensors
and networks applications in agriculture. Computer Standards
& Interfaces 36 (2014) 263270
[5]
Zhen Li a, b, Ning Wang a,, Aaron Franzen a, Peyman Taher c, Chad Godsey d, Hailin Zhang d,
Xiaolin Li e Practical deployment of an in-field soil property wireless sensor network. Computer
Standards & Interfaces 36(2014) 278287
[6]
Xin Dong a,, Mehmet C. Vuran a, Suat Irmak b Autonomous precision agriculture through
integration of wireless underground sensor networks with center pivot irrigation systems . Ad
Hoc Networks 11 (2013) 19751987
[7]
Joaqun Gutirrez, Juan Francisco Villa-Medina, Alejandra Nieto-Garibay, and Miguel ngel PortaGndara Automated Irrigation System Using a Wireless Sensor Network and GPRS Module (2014)
59 | 2015, IJAFRC All Rights Reserved
www.ijfarc.org
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Detecting User Relevant ApplicationsDocument7 pagesDetecting User Relevant ApplicationsIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Detection and Defense of DDoS AttacksDocument11 pagesDetection and Defense of DDoS AttacksIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Performance Analysis and Lifetime Maximization of Wireless Sensor Network Using Efficient Clustering AlgorithmDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis and Lifetime Maximization of Wireless Sensor Network Using Efficient Clustering AlgorithmIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Data Security and Anonymization For Collaborative Data PublishingDocument7 pagesData Security and Anonymization For Collaborative Data PublishingIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Efficient Algorithm Comparison To Solve Sudoku PuzzleDocument5 pagesEfficient Algorithm Comparison To Solve Sudoku PuzzleIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Face Granulation Using Difference of Gaussian (DOG) Method For Face RecognitionDocument7 pagesFace Granulation Using Difference of Gaussian (DOG) Method For Face RecognitionIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- CFS Based Feature Subset Selection For Software Maintainance PredictionDocument11 pagesCFS Based Feature Subset Selection For Software Maintainance PredictionIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Review of BFOA Application To WSNDocument7 pagesA Review of BFOA Application To WSNIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- To Design and Algorithm Using Zero Watermarking With Stegnography For Text DocumentDocument10 pagesTo Design and Algorithm Using Zero Watermarking With Stegnography For Text DocumentIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Monitoring Applications in Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument4 pagesMonitoring Applications in Wireless Sensor NetworksIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- DDos System: A Disparagement System With Cache Based and Question Generation in Client-Server ApplicationDocument13 pagesDDos System: A Disparagement System With Cache Based and Question Generation in Client-Server ApplicationIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Pocket Barcode Application-Data Transmission Between PDA & PC Using Wireless NetworkDocument5 pagesPocket Barcode Application-Data Transmission Between PDA & PC Using Wireless NetworkIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Automated Leukemia Detection by Using Contour Signature MethodDocument8 pagesAutomated Leukemia Detection by Using Contour Signature MethodIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- A Survey On Designing of Turbo Encoder & Turbo DecoderDocument8 pagesA Survey On Designing of Turbo Encoder & Turbo DecoderIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Face Verification With Age Progression Using Discriminative Method and Gradient Orientation PyramidDocument10 pagesFace Verification With Age Progression Using Discriminative Method and Gradient Orientation PyramidIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Metamaterial Based Fractal Body Worn Antenna - A ReviewDocument6 pagesMetamaterial Based Fractal Body Worn Antenna - A ReviewIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Perceptions On Data Aggregation in Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument5 pagesPerceptions On Data Aggregation in Wireless Sensor NetworkIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Various Ways of Programming and Embedding Firmware Into An ARM Cortex-M3 Microcontroller Based HardwareDocument6 pagesThe Various Ways of Programming and Embedding Firmware Into An ARM Cortex-M3 Microcontroller Based HardwareIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- A Short Study On Effective Predictors of Academic Performance Based On Course EvaluationDocument6 pagesA Short Study On Effective Predictors of Academic Performance Based On Course EvaluationIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Application of Malicious URL Detection in Data MiningDocument6 pagesApplication of Malicious URL Detection in Data MiningIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Classification and Clustering Techniques Using Assorted Data Mining ToolsDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study On Classification and Clustering Techniques Using Assorted Data Mining ToolsIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Analytical Evolution of WIMAX Coded OFDM in Various Fading EnvironmentDocument8 pagesAnalytical Evolution of WIMAX Coded OFDM in Various Fading EnvironmentIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Reconfigurable Fixed Width Baugh-Wooley MultiplierDocument9 pagesEnergy Efficient Reconfigurable Fixed Width Baugh-Wooley MultiplierIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- A Study On Denial-Of-Service Attacks and Their Countermeasure ApproachesDocument11 pagesA Study On Denial-Of-Service Attacks and Their Countermeasure ApproachesIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Designing of Efficient FPGA Based Random Number Generators Using VHDL.Document8 pagesDesigning of Efficient FPGA Based Random Number Generators Using VHDL.IJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Effects of Social Media On The Psychology of PeopleDocument6 pagesEffects of Social Media On The Psychology of PeopleIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- A Review of Compact Asymmetric Coplanar Strip Fed Monopole Antenna For Multiband ApplicationsDocument5 pagesA Review of Compact Asymmetric Coplanar Strip Fed Monopole Antenna For Multiband ApplicationsIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Predictive Model For Blood-Brain BarrierDocument12 pagesPredictive Model For Blood-Brain BarrierIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Comparative Study of K-Means, K-Medoid and Enhanced K-Medoid AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study of K-Means, K-Medoid and Enhanced K-Medoid AlgorithmsIJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Guia Instalacion APP Huawei Fusion HmeDocument4 pagesGuia Instalacion APP Huawei Fusion Hmecalinp72No ratings yet
- The Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseDocument4 pagesThe Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseMarta HrynyovskaNo ratings yet
- ARCASIA Students Design Competition TORDocument4 pagesARCASIA Students Design Competition TORDeena McgeeNo ratings yet
- Overview of MEMDocument5 pagesOverview of MEMTudor Costin100% (1)
- 240-56062705 RTV Silicone Rubber Insulator Coating and Shed Extender Supplier StandardDocument10 pages240-56062705 RTV Silicone Rubber Insulator Coating and Shed Extender Supplier StandardJane ChatsiriphatthanaNo ratings yet
- Tree Based Machine Learning Algorithms Decision Trees Random Forests and Boosting B0756FGJCPDocument109 pagesTree Based Machine Learning Algorithms Decision Trees Random Forests and Boosting B0756FGJCPJulio Davalos Vasquez100% (1)
- Citroen CX Manual Series 2 PDFDocument646 pagesCitroen CX Manual Series 2 PDFFilipe Alberto Magalhaes0% (1)
- Climatol GuideDocument40 pagesClimatol GuideFressiaNo ratings yet
- Operations and Service ManualDocument311 pagesOperations and Service ManualELARD GUILLENNo ratings yet
- Anth 09 3 247 07 386 Yadav V S TTDocument3 pagesAnth 09 3 247 07 386 Yadav V S TTShishir NigamNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Jarir IT Flyer Qatar1Document4 pagesJarir IT Flyer Qatar1sebincherianNo ratings yet
- Social Science PedagogyDocument4 pagesSocial Science PedagogyrajendraNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2.9Document22 pagesPractical Research 2.9Michael GabertanNo ratings yet
- Validación Española ADHD-RSDocument7 pagesValidación Española ADHD-RSCristina Andreu NicuesaNo ratings yet
- Zilog Z80-SIO Technical Manual TextDocument58 pagesZilog Z80-SIO Technical Manual Textprada.rizzoplcNo ratings yet
- Electromechani Cal System: Chapter 2: Motor Control ComponentsDocument35 pagesElectromechani Cal System: Chapter 2: Motor Control ComponentsReynalene PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Package-Related Thermal Resistance of Leds: Application NoteDocument9 pagesPackage-Related Thermal Resistance of Leds: Application Notesalih dağdurNo ratings yet
- Routine (27th April)Document1 pageRoutine (27th April)SoumitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Iceberg ModelDocument5 pagesIntroduction To The Iceberg ModelAbhay Tiwari100% (1)
- 8 Lesson 13 Viking FranceDocument2 pages8 Lesson 13 Viking Franceapi-332379661No ratings yet
- AIF User Guide PDFDocument631 pagesAIF User Guide PDFÖzgün Alkın ŞensoyNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument3 pagesQuestion BankHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Zoom g2 1nu Manual Do Utilizador PDFDocument56 pagesZoom g2 1nu Manual Do Utilizador PDFEliude Gonçalves FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation FOR Rigid Pavement/RoadDocument5 pagesDesign Calculation FOR Rigid Pavement/RoadghansaNo ratings yet
- Focal Length of Convex LensDocument5 pagesFocal Length of Convex LensHey AnuragNo ratings yet
- ZH210LC 5BDocument24 pagesZH210LC 5BPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ0% (1)
- Assignment 5 WarehousingDocument4 pagesAssignment 5 WarehousingabbasNo ratings yet
- Advanced Work Packaging: A Fit For Purpose ApproachDocument17 pagesAdvanced Work Packaging: A Fit For Purpose Approachhafidz bandungNo ratings yet
- The Logic of Repetition: A Guide To Trading, Thinking, and The Cycles of LifeDocument10 pagesThe Logic of Repetition: A Guide To Trading, Thinking, and The Cycles of LifeRaghvendra kNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONAL SUPERVISORY PLAN 1st Quarter of SY 2023 2024 Quezon ISDocument7 pagesINSTRUCTIONAL SUPERVISORY PLAN 1st Quarter of SY 2023 2024 Quezon ISayongaogracelyflorNo ratings yet