Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Econ Practice Exam 2
Uploaded by
MK0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views15 pagesThis document appears to be a practice economics test containing 37 multiple choice questions covering various microeconomics and international trade concepts. Some of the concepts tested include: how improvements in technology affect markets; opportunity costs and comparative advantage; market equilibrium; demand and supply shifts; production possibilities frontiers; elasticity; tariffs and quotas; and gains from trade.
Original Description:
Fink Econ 2020 Auburn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document appears to be a practice economics test containing 37 multiple choice questions covering various microeconomics and international trade concepts. Some of the concepts tested include: how improvements in technology affect markets; opportunity costs and comparative advantage; market equilibrium; demand and supply shifts; production possibilities frontiers; elasticity; tariffs and quotas; and gains from trade.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views15 pagesEcon Practice Exam 2
Uploaded by
MKThis document appears to be a practice economics test containing 37 multiple choice questions covering various microeconomics and international trade concepts. Some of the concepts tested include: how improvements in technology affect markets; opportunity costs and comparative advantage; market equilibrium; demand and supply shifts; production possibilities frontiers; elasticity; tariffs and quotas; and gains from trade.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
1. How would an improvement in technology affect the market for detergent?
A. Supply would increase, causing equilibrium price to rise and quantity to fall
B. Supply would increase, causing equilibrium price to fall and quantity to rise
C. Supply would decrease, causing equilibrium price to rise and quantity to fall
D. Supply would decrease, causing equilibrium price to fall and quantity to rise
E. Demand would increase, causing equilibrium price and quantity to both rise
Jules can cook 30 pizza bagels or 10 tiramisus in an hour.
Miroki can cook 20 pizza bagels or 4 tiramisus in an hour.
2. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. Juless opportunity cost of a pizza bagel is 3 tiramisus
B. Mirokis opportunity cost of a pizza bagel is 5 tiramisus
C. Miroki has the absolute advantage in pizza bagels
D. Jules has a comparative advantage in producing tiramisus
3. Assume that one tiramisu trades for 4 pizza bagels. If Jules and Miroki completely specialize,
and the tiramisu producer trades 3 units, which of the following quantities will be consumed?
A. Miroki will consume 8 pizza bagels and 7 tiramisus
B. Jules will consume 18 pizza bagels and 3 tiramisus
C. Miroki will consume 8 pizza bagels and 3 tiramisus
D. Jules will consume 42 pizza bagels and 7 tiramisus
4. Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A. Economists believe that price rationing is the mist efficient rationing method
B. Price rationing is the allocation of goods among consumers using prices
C. Price rationing allows every consumer that would like the good to have it
D. Price rationing allows every consumer willing to pay at least the equilibrium price to have it
5. A fall in the price of a mystery good caused a change in the market for burritos that led to a fall in
the price of burritos as well. Which of the following could possibly be the mystery good?
A. Spanish rice (a complement)
B. Chinese food (a substitute)
C. Tortillas (an import)
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
Champ can cook 30 pancakes or 15 waffles in an hour.
Brick can cook 24 pancakes or 6 waffles in an hour.
6. Bricks opportunity cost of a waffle is
A. 24 pancakes
B. 9 waffles
C. 18 pancakes
D. 0.25 pancakes
E. 4 pancakes
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
7. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. Brick has a comparative advantage in producing pancakes
B. Brick has an absolute advantage in producing pancakes
C. Brick has an absolute advantage in producing waffles
D. Champ has a comparative advantage in producing pancakes
8. Assume that one waffle trades for 3 pancakes. If Champ and Brick completely specialize, and
the waffle producer trades 4 units, which of the following quantities will be consumed?
A. Brick will consume 8 pancakes and 3 waffles
B. Champ will consume 12 pancakes and 11 waffles
C. Brick will consume 12 pancakes and 10 waffles
D. Champ will consume 18 pancakes and 4 waffles
9. If consumer income falls, how does that affect the market for an inferior good?
A. Demand decreases
B. Initially there is a surplus at the old price
C. Equilibrium price eventually rises
D. Equilibrium quantity eventually falls
10. Ron Burgandy faces the following production possibilities
Scotch drinks: 100
90
70
40
0
Jazz flutes:
0
1
2
3
4
What is the opportunity cost of producing the 2 nd jazz flute?
A. 35 scotch drinks
B. 20 scotch drinks
C. 30 scotch drinks
D. 1 scotch drink
E. 18 scotch drinks
11. Which of the following statements about Rons economy above is TRUE?
A. His opportunity cost of producing jazz flutes stays constant as he produces more flutes
B. His opportunity cost of producing jazz flutes increases as he produces more flutes
C. The PPF is a straight line
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
12. The signal that tells producers what and how much to produce is called the
A. Price
B. Cost
C. Scarce goods
D. Labor
13. Seth faces the following production possibilities:
Binions:
72
60
44
24
0
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
Goldstick:
What is the opportunity cost of producing the third unit of Goldslick?
A. 48 Binions
B. 8 Binions
C. 18 Binions
D. 24 Binions
E. 20 Binions
14. Which of the following statements about Seths economy above is TRUE?
A. The PPF is a straight line
B. His opportunity cost of producing Goldslick increases as output increases
C. The PPF is a bowed line
D. A and B only
E. B and C only
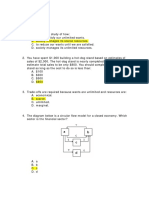
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
15. Assume the above economy is on PPF1. What would a movement from point C to point B
represent?
A. An increase in the unemployment rate
B. A decrease in the unemployment rate
C. A technological improvement
D. An increase in the quantity of resources
E. B, C, D only
16. Which of the following could cause a shift from PPF1 to PPF2?
A. A technological improvement
B. A change in regulation
C. An increase in the quantity of resources
D. Trade with another economy
E. All of the above
17. Which of the following will NOT shift the demand curve?
A. Change in the price of a compliment
B. Change in the price of a substitute
C. Change in the price of an input
D. Change in tastes and preferences
E. Changes in all of the above WILL shift demand
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
18. The above economy will import
A. 30 units of eye make-up
B. 30 comforters
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
C. 50 units of eye makeup
D. 10 comforters
19. One comforter trades for
A. 1.67 units of eye makeup
B. unit of eye make up
C. 2 units of eye make up
D. 3 units of eye makeup
E. 1 unit of eye make up
20. A recent study found that an increase in the Federal tax on beer (and thus an increase in the
price of beer) would reduce the demand for marijuana. We can conclude that:
A. beer and weed are substitute goods
B. beer and weed are complementary goods
C. beer is an inferior good
D. weed is an inferior good
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
21. What is the value of the tariff?
A. $15
B. $60
C. $9
D. $25
E. $6
22. The areas labeled c represent?
A. Deadweight loss
B. Tax revenue
C. Domestic partner revenue
D. Foreign producer revenue
E. Gained producer surplus
23. If the government uses an import quota rather than a tariff to restrict trade, then the area
labeled B would represent
A. Deadweight loss
B. Tax revenue
C. Domestic partner revenue
D. Foreign producer revenue
E. Gained producer surplus
24. At the midpoint of the firms demand curve
A. Total reveue is maximized
B. Price elasticity of demand is equal to zero
C. Price elasticity of demand is equal to one
D. A and B only
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
E. A and C only
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
25. The above economy will export
A. 20 frozen peas
B. 40 tattoos
C. 10 frozen peas
D. 20 tattoos
26. One unit of frozen peas trades for
A. 3 tattoos
B. 4 tattoos
C. 2 tattoos
D. 0.5 tattoos
E. 0.25 tattoos
27. A producer faces a price elasticity of demand of 1.2 when the price of the good is $16 and the
quantity demanded is 7500 units. Find the change in quantity demanded if the producer decreases
price by $1.50. (Round to nearest unit)
A. 703
B. 844
C. 4167
D. 260
E. 1125
28. A perfectly elastic demand curve
A. is represented on a graph by a horizontal line
B. is represented on a graph by a vertical line
C. has an elasticity coefficient equal to infinity
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
29. Given the graph above, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. D2 is more elastic than D1
B. For a given price change, the elasticity coefficient for D1 is bigger than that for D2
C. For a given price change, the change in Qd along D1 is smaller than the change in Qd
along D2
D. A and B only
E. A and C only
30. International trade arises primarily from
A. Tariffs and quotas
B. Economic growth
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
C. Comparative advantage
D. Absolute advantage
31. Helen faces the following production possibilities:
Giant cookies: 200
160
120
80
40
Chocolate ftns: 0
1
2
3
4
0
5
What is the opportunity cost of producing the 4 th chocolate fountain?
A. 160 giant cookies
B. 10 giant cookies
C. 40 giant cookies
D. 36 giant cookies
32. Which of the following statements about the economy above is TRUE?
A. Her opportunity cost of producing chocolate fountains increases as she produces more
chocolate fountains
B. Her opportunity cost of producing chocolate fountains stays constant as she produces
more chocolate fountains
C. The PPF is a straight line
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
33. Which of the following would cause a consumers demand to become relatively more elastic?
A. The consumer finds she has less time to make the purchase
B. The consumer finds an additional substitute is available
C. The good becomes a smaller proportion of the consumers budget
D. A and B only
E. B and C only
Annie
Cakes
Carrots
48
12
Rhodes 42
34. Rhodess opportunity cost of a carrot is
A. 0.167 cakes
B. 1.14 cakes
C. 0.125 cakes
D. 4 cakes
E. 6 cakes
35. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. Rhodes has a comparative advantage in producing cakes
6
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
B. Rhodes has an absolute advantage in producing cakes
C. Rhodes has an absolute advantage in producing carrots
D. Annie has a comparative advantage in producing cakes
36. Assume that one carrot trades for 5 cakes. If Annie and Rhodes completely specialize, and the
carrot producer trades 4 units, which of the following quantities will Rhodes consume?
A. 20 cakes and 8 carrots
B. 20 cakes and 3 carrots
C. 22 cakes and 4 carrots
D. 22 cakes and 11 carrots
37. A federal regulation bans cheese imports completely, requiring that all cheese consumed in the
US must be produced in the US. This quota is likely to
A. Increase cheese consumption in the US
B. Increase the demand for wine (a complement) in the US
C. Increase the price of cheese in the US
D. Increase cheese imports
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
38. Which of the following could cause a movement from point B to point A?
A. A decrease in the unemployment rate
B. An increase in the unemployment rate
C. A technological improvement
D. An increase in the quantity of resources
E. C and D only
39. Which of the following would allow the economy to reach point C?
A. An increase in the quantitiy of resources
B. A technological improvement
C. Trade with another economy
D. All of the above
E. B and C only
40. The cross elasticity coefficient between a Wilson Phillips CD and a mystery good is -0.82. The
mystery good is probably
A. Plastic (an input)
B. A CD player (a complement)
C. A Wilson Phillips concert (a substitute_
D. A puppy (a weird party favor)
41. Using the midpoint formula, find the elasticity coefficient for a producer when a price increase
from $12.00 to $13.00. causes a fall in quantity demanded from 340 units to 310 units.
A. 0.87
B. 0.80
C. 1.15
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
D. 1.0
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
42. With free trade, the above economy will
A. import 15 units
B. export 15 units
C. import 35 units
D. export 35 units
43. The gained consumer surplus is represented by area
A. ABC
B. PnACPw
C. PnABPw
44. At which point would the Dd demand curve be relatively more elastic?
A. A
B. C
C. Elasticity is constant along a demand curve
45. Cake Baby faces a price elasticity of demand of 0.95. How should management alter price if
they desire to increase total revenue?
A. Increase price
B. Decrease price
C. Cake Baby is already maximizing TR
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
46. With free trade, the above economy will
A. Import 15 units
B. Export 15 units
C. Import 35 units
D. Export 35 units
47. The gained consumer surplus is represented by are
A. ABC
B. PnABPw
C. PnACPw
48. Which point on the above demand curve would be relatively more elastic?
A. A
B. C
C. Elasticity is constant along a demand curve
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
49. Using the midpoint formula, find the elasticity coefficient for a producer when a price increases
from $7.50 to $9.50 causes a fall in quantity demanded from 117 units to 103 units.
A. 0.69
B. 1.44
C. 1.0
D. 1.85
E. 0.54
50. Which of the following would cause a consumers demand to become relatively more inelastic?
A. The consumer finds she has less time to make the purchase
B. The consumer finds an additional substitute is available
C. The good becomes a larger proportion of the consumers budget
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
51. International trade arises primarily from
A. Economic growth
B. Absolute advantage
C. Import quotas
D. Comparative advantage
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
52. The above economy will export
A. 30 footballs
B. 30 crab cakes
C. 90 footballs
D. 120 footballs
53. One crab cake trades for
A. Cowboys from Arizona
B. footballs
C. 2 footballs
D. 3 footballs
E. 1 football
54. Holy Shirts and Pants faces a price elasticity of demand of 0.88. How should management
alter price if they desire to increase total revenue?
A. Decrease price
B. Increase price
C. Holy shirts and pants is already maximizing TR
Pizza
John
Maple
Syrup
60
Jeremy
36
15
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
55. Johns opportunity cost of a maple syrup is
A. 24 pizzas
B. 1.67 pizzas
C. 45 pizzas
D. 0.25 pizzas
E. 4 pizzas
56. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. Jeremy has comparative advantage in producing pizza
B. John has comparative advantage in producing maple syrup
C. Jeremy has an absolute advantage in producing maple syrup
D. John has a comparative advantage in producing pizza
57. Assume that one pizza trades for 4 maple syrups. If John and Jeremy completely specialize,
and the pizza producer trades 5 units, which of the following quantities will John consume?
A. 40 maple syrups and 20 pizzas
B. 40 maple syrups and 5 pizzas
C. 16 maple syrups and 5 pizzas
D. 80 maple syrups and 10 pizzas
E. 20 maple syrups and 10 pizzas
58. A producer faces a price elasticity of demand of 1.4 when the price of the good is $16 and the
quantity demanded is 9000 units. Find the change in quantity demanded if the producer change
price by $2.00.
A. 804
B. 201
C. 1575
D. 276
E. 788
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
59. How many units did the economy import AFTER the tariff?
A. 110
B. 25
C. 15
D. 20
E. 60
60. The area labeled A represents
A. gained producer surplus
B. tax revenue
C. domestic partner revenue
D. foreign producer revenue
E. deadweight loss
10
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
61. If the government uses an import quota rather than a tariff to restrict trade, then the area
labeled B would represent
A. gained producer surplus
B. tax revenue
C. domestic producer revenue
D. deadweight loss
E. foreign producer revenue
62. The cross elasticity coefficient between crab cakes and mystery good is -0.82. The mystery
good is probably
A. bread crumbs (an input)
B. a glass of wine (a complement)
C. bacon-wrapped scallops (a substitute)
D. a box of fresh Wyoming air (a bad wedding gift)
63. A perfectly elastic demand curve
A. is represented on a graph by a horizontal line
B. is represented on a graph by a vertical line
C. has an elasticity coefficient equal to infinity
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
64. Given the graph above, which of the following statements is FALSE?
A. D1 is more inelastic than D2
B. For a given price change, the elasticity coefficient for D1 is bigger than that for D2
C. For a given price change, the change in Qd along D1 is smaller than the change in Qd
along D2
D. A and B only
E. A and C only
65. A federal regulation that requires that all cheese consumed in the US must be produced in the
US is likely to
A. Increase cheese imports
B. Drive up the price of cheese in the US
C. Increase cheese consumption in the US
D. Increase the demand for wine (a complement) in the US
E. C and D only
66. Total revenue is maximized when
A. Marginal revenue is equal to 1
B. Price elasticity of demand is equal to 1
C. A firm produces at the midpoint of the demand curve
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
11
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
67. Secretary Cleary faces the following production possibilities
Cigars:
175
150
120
85
45
0
Sailboats:
0
1
2
3
4
5
What is the opportunity cost of producing the 2 nd sailboat?
A. 30 cigars
B. 60 cigars
C. 35 cigars
D. 118 cigars
68. Which of the following statements about the economy above is FALSE?
A. His opportunity cost of producing sailboats stays constant as he produces more sailboats
B. His opportunity cost of producing sailboats increases as he produces more sailboats
C. The PPF is a straight line
D. A and C only
E. B and C only
(Refer to the hand drawn graph)
69. Which of the following could cause a shift from PPF1 to PPF2?
A. A decrease in the unemployment rate
B. An increase in the quantity of resources
C. A technological improvement
D. All of the above
E. B and C only
70. Which of the following could cause a movement from point B to point A?
A. An increase in the unemployment rate
B. A decrease in the unemployment rate
C. A technological improvement
D. An increase in the quantity of resources
E. C and D only
12
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
ANSWER KEY
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
13
B
D
C
C
E
E
A
B
C
B
B
A
E
E
B
E
C
B
E
B
E
A
D
E
D
C
B
D
B
C
C
E
B
E
A
C
C
B
D
B
C
C
B
A
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
A
C
C
A
E
A
D
A
E
B
D
D
E
C
C
A
E
B
D
B
B
E
A
D
E
A
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
14
FINK ECONOMICS TEST 2
15
You might also like
- Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (25 Marks) : Code: FallDocument30 pagesSection A: Multiple Choice Questions (25 Marks) : Code: FallDennys TNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Sample ExamDocument8 pagesMicroeconomics Sample ExamLeona AriesintaNo ratings yet
- econs onlineDocument14 pagesecons onlineCaleb AsharleyNo ratings yet
- Mid Term BeDocument7 pagesMid Term BeBách HuyNo ratings yet
- Concordia University Department of Economics ECON 201 Fall 2014 Instructor: Ivan Tchinkov Midterm Examination With AnswersDocument13 pagesConcordia University Department of Economics ECON 201 Fall 2014 Instructor: Ivan Tchinkov Midterm Examination With Answersfouad khouryNo ratings yet
- ECN 211 HOMEWORK #1 MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLESDocument7 pagesECN 211 HOMEWORK #1 MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLESMadds HNo ratings yet
- Use The Following To Answer Questions 5-7:: Figure: Strawberries and SubmarinesDocument16 pagesUse The Following To Answer Questions 5-7:: Figure: Strawberries and SubmarinesMahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Professor Elliott Parker Spring 2006 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument8 pagesProfessor Elliott Parker Spring 2006 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of Microeconomicshyung_jipmNo ratings yet
- Exam Code: 01: Part 1: Multiple Choice Questions: (1.6 Points Each)Document7 pagesExam Code: 01: Part 1: Multiple Choice Questions: (1.6 Points Each)Thế HùngNo ratings yet
- Economics Competition Question Book 2017 - AnswersDocument8 pagesEconomics Competition Question Book 2017 - AnswersDIVA RTHININo ratings yet
- Professor Elliott Parker Spring 2005 Midterm Exam 1 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument9 pagesProfessor Elliott Parker Spring 2005 Midterm Exam 1 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of Microeconomicshyung_jipmNo ratings yet
- Loren's TestDocument7 pagesLoren's TestMelissa KaneNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Practice Exam 2015 QuestionsDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Economics Practice Exam 2015 Questionsjess100% (1)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument12 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionthisisfordesignNo ratings yet
- Study Questions For Econ 101 Midterm Exam I - Fall 2015-2016Document11 pagesStudy Questions For Econ 101 Midterm Exam I - Fall 2015-2016Farid BabayevNo ratings yet
- MN - Economic Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesMN - Economic Practice QuestionsMartin GerardNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Final Exam MAE103 T2 2014Document28 pagesPractice Questions For Final Exam MAE103 T2 2014Jason LohNo ratings yet
- 1B03 - Midterm Review - W23 - Ch. 1-6 - StudentsDocument21 pages1B03 - Midterm Review - W23 - Ch. 1-6 - StudentsQhiraNo ratings yet
- End-of-Semester Exam for Introductory EconomicsDocument14 pagesEnd-of-Semester Exam for Introductory EconomicsM Aminuddin AnwarNo ratings yet
- Try Out Harian Day 1Document9 pagesTry Out Harian Day 1Dwi Aprina Simarmata X MIPA 1No ratings yet
- Session 3Document7 pagesSession 3omaritani2005No ratings yet
- Practice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageDocument7 pagesPractice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageGabby CustodioNo ratings yet
- ECON 101 2-3 Orazem Bteahan MT1ADocument15 pagesECON 101 2-3 Orazem Bteahan MT1ASown NhaNo ratings yet
- AP-Style Practice Test Sections 1-4Document10 pagesAP-Style Practice Test Sections 1-4Nastassja LopezNo ratings yet
- Econ 1510 1617 Sem2Document17 pagesEcon 1510 1617 Sem2nadhiraasyraNo ratings yet
- BS I 2021 Mcqs Micro EcoDocument9 pagesBS I 2021 Mcqs Micro EcoTooba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Econ 201 Past Final ExamDocument15 pagesEcon 201 Past Final ExamSooHan MoonNo ratings yet
- Test Sample (Nov2021)Document7 pagesTest Sample (Nov2021)2021492824No ratings yet
- ECON 1000 Exam Review Worksheet Sample FinalDocument5 pagesECON 1000 Exam Review Worksheet Sample FinalSlock TruNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Karlan Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Karlan Test Bank Full Chapter PDFqueeningalgatestrq0100% (12)
- Agricultural Economics and Marketing Pre TestDocument21 pagesAgricultural Economics and Marketing Pre Testkarla arellano100% (1)
- Economics Grade 10 TestDocument7 pagesEconomics Grade 10 TestThomassiniNo ratings yet
- MCQ and Conceptual QuestionsDocument14 pagesMCQ and Conceptual QuestionsAbhisek MishraNo ratings yet
- Test 1version 2Document15 pagesTest 1version 2Rashid AyubiNo ratings yet
- ECO 561 Final ExamDocument12 pagesECO 561 Final ExamAssignmentehelpNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - Utility ExplainedDocument16 pagesElasticity - Utility ExplainedreemmajzoubNo ratings yet
- IMBA Homework1 - SOLUTIONSDocument12 pagesIMBA Homework1 - SOLUTIONSTaza Ilham AssidiqhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReviewDocument14 pagesChapter 3 ReviewMateo NogueraNo ratings yet
- Econ exam+1+VADocument13 pagesEcon exam+1+VABlackBunny103No ratings yet
- Economics ReviewerDocument5 pagesEconomics ReviewerPrenzel VailocesNo ratings yet
- Consumer Surplus and Elasticity Review for Test 2Document13 pagesConsumer Surplus and Elasticity Review for Test 2caitlin1593No ratings yet
- D AND S MCQDocument14 pagesD AND S MCQSarmela DamotheranNo ratings yet
- AC 2203 Long Exam 1 TestpaperDocument12 pagesAC 2203 Long Exam 1 TestpaperIssah Marie HingabayNo ratings yet
- Test01 Worksheet AnswersDocument8 pagesTest01 Worksheet Answerst199611261126No ratings yet
- Mock Exam Economics Mid Term 2021Document13 pagesMock Exam Economics Mid Term 2021FrancinalanfermanNo ratings yet
- Filr DeTracNghiem Mau-FullDocument12 pagesFilr DeTracNghiem Mau-FullNguyễn Phương ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Exam Review: Market Equilibrium and ExternalitiesDocument24 pagesExam Review: Market Equilibrium and ExternalitiesDavid LimNo ratings yet
- MCQ Economics Revision GuideDocument11 pagesMCQ Economics Revision GuidejancyNo ratings yet
- Practice MCQs Sessions 1 To 3 - ClassDocument9 pagesPractice MCQs Sessions 1 To 3 - ClassHIMANSHU VARMANo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 1Document5 pagesPractice Problem Set 1AkshayNo ratings yet
- FPSC (Lectuer Economics)Document6 pagesFPSC (Lectuer Economics)ShAkeel AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Session 2 QuestionsDocument10 pagesSession 2 QuestionsreemmajzoubNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 1 With AnswersDocument7 pagesPractice Problem Set 1 With AnswersJoy colabNo ratings yet
- IMBA Homework1Document11 pagesIMBA Homework1Taza Ilham AssidiqhiNo ratings yet
- Econ201 Quiz 4Document10 pagesEcon201 Quiz 4arichard88215No ratings yet
- Identifying key economic concepts on a testDocument12 pagesIdentifying key economic concepts on a testNgọc Ninh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- RYERSON ECN 104 INTRODUCTORY MICROECONOMICSDocument19 pagesRYERSON ECN 104 INTRODUCTORY MICROECONOMICSzodiac1b1100% (1)
- 90,95,2000 Macro Multiple ChoiceDocument37 pages90,95,2000 Macro Multiple ChoiceAaron TagueNo ratings yet
- Answer: ADocument7 pagesAnswer: AusjaamNo ratings yet
- ECO 201 Final Project Guidelines and RubricDocument6 pagesECO 201 Final Project Guidelines and RubricSabina AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Market Study of The Construction Industry in Mauritius - CCM Preliminary ReportDocument57 pagesMarket Study of The Construction Industry in Mauritius - CCM Preliminary ReportION News100% (1)
- Gross Profit: Income Statement For The Year Ended December 31Document3 pagesGross Profit: Income Statement For The Year Ended December 31Jane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 18.price DiscriminationDocument13 pages18.price DiscriminationAgANo ratings yet
- Introduction of Cosmetic in PakistanDocument3 pagesIntroduction of Cosmetic in PakistanSyed Zeeshan Hyder Zaidi67% (3)
- ECON F211 Principles of Economics I Sem 2021-22 HODocument2 pagesECON F211 Principles of Economics I Sem 2021-22 HOUrvi ModiNo ratings yet
- Manila University corporate finance midterm exam ratiosDocument3 pagesManila University corporate finance midterm exam ratiosUnivMan LawNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Media Math RDocument104 pagesLecture 6 Media Math RZeljana Maric100% (1)
- ACM 31 FM LEC 9n10Document34 pagesACM 31 FM LEC 9n10Vishal AmbadNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Factors Affecting The Household Final Consumption Expenditure in The Philippines Using Two-Stage Least Squares (2SLS)Document8 pagesMacroeconomic Factors Affecting The Household Final Consumption Expenditure in The Philippines Using Two-Stage Least Squares (2SLS)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- MCD ProjectDocument17 pagesMCD ProjectAbhinandanMalhotraNo ratings yet
- How To Manage Inventory FIFO LIFO AVCO Small Business Guides Xero (.SRT)Document5 pagesHow To Manage Inventory FIFO LIFO AVCO Small Business Guides Xero (.SRT)Nurainin AnsarNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Probabilistic Risk Analysis - Examples - With NotesDocument6 pages11.1 Probabilistic Risk Analysis - Examples - With NotesFlora LinNo ratings yet
- Daqo New Energy CorpDocument154 pagesDaqo New Energy Corpdkdude007No ratings yet
- Books On Retail MGTDocument5 pagesBooks On Retail MGTssyashu6685No ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership Processes for Organizational ChangeDocument25 pagesTransformational Leadership Processes for Organizational ChangeRavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Econ DevDocument40 pagesEcon DevLhowella AquinoNo ratings yet
- Product PositioningDocument3 pagesProduct PositioningNizar AhamedNo ratings yet
- OLD Alternate Report by Ludwig ChincariniDocument14 pagesOLD Alternate Report by Ludwig ChincariniJonathan ChanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 Mathematical FinanceDocument3 pagesAssignment 5 Mathematical FinanceYuengNo ratings yet
- Production and Cost Analysis I: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument28 pagesProduction and Cost Analysis I: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinMayank TalesaraNo ratings yet
- Bond ValuationDocument15 pagesBond ValuationSoumili MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Solved Ten Identical Consumers All Have Individual Willingness To Pay Curves PDocument1 pageSolved Ten Identical Consumers All Have Individual Willingness To Pay Curves PM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- India's Uber Price Ceiling Hurts Riders, Drivers and EconomyDocument3 pagesIndia's Uber Price Ceiling Hurts Riders, Drivers and EconomyTamal MaitraNo ratings yet
- Mba Operations Project in Process ManagementDocument66 pagesMba Operations Project in Process ManagementVidhiya AmbigapathyNo ratings yet
- Dqs389-Interim PaymentDocument31 pagesDqs389-Interim Paymentillya amyraNo ratings yet
- Project AppraisalDocument6 pagesProject AppraisalRohan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Nods02052014 Feb 12 2014Document63 pagesNods02052014 Feb 12 2014Kasey JohnsonNo ratings yet
- PORTER AnalysisDocument7 pagesPORTER AnalysisAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management and Business Policy 15e, Global EditionDocument37 pagesStrategic Management and Business Policy 15e, Global EditionTeh Chu Leong0% (1)