Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Winter 13
Uploaded by
Yogesh BadheOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Winter 13
Uploaded by
Yogesh BadheCopyright:
Available Formats
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Important Instructions to examiners:
1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
model answer scheme.
2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may vary but the examiner may try
to assess the understanding level of the candidate.
3) The language errors such as grammatical, spelling errors should not be given more
Importance (Not applicable for subject English and Communication Skills.
4) While assessing figures, examiner may give credit for principal components indicated in the
figure. The figures drawn by candidate and model answer may vary. The examiner may give credit for any
equivalent figure drawn.
5) Credits may be given step wise for numerical problems. In some cases, the assumed constant
values may vary and there may be some difference in the candidates answers and model answer.
6) In case of some questions credit may be given by judgement on part of examiner of relevant answer based
on candidates understanding.
7) For programming language papers, credit may be given to any other program based on equivalent concept.
Q1. Attempt any TEN of the following.
a) List out two active components and two passive components.
Ans:
Active components: Diodes, transistor, FET
Passive components: resistors, capacitor, inductors
20M
2M
1M
1M
Active components
Electronic Tube
Semiconductor Device
Diode
transistor
FET
Passive components
Resistors
b) Draw symbol of JFET (n-channel)
Ans: symbol of JFET (n-channel)
capacitor
inductors
2M
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
c) What is zener breakdown?
2M
Ans:
Zener breakdown:
When the applied reverse bias voltage across the zener diode crosses the specified limit of breakdown
voltage (VZ) then suddenly the reverse current increases to higher level but the voltage across the
diode remain constant. The reverse voltage at which the current flowing through the zener diode
increases massively is called as the zener breakdown voltage and this phenomenon called zener
breakdown
d) Draw circuit diagram of single state CE amplifier.
Ans: circuit diagram of single state CE amplifier
2M
e) Draw V-I characteristics of an ideal P-N junction diode.
Ans: V-I characteristics of an ideal P-N junction diode:
2M
f) Write any four advantages of ICs.
2M
Ans:
(Any four points, M for each)
Advantages of ICs:
i. Small size and weight
ii. Low cost
iii. High reliability
iv.
It is possible to fabricate complex circuit in a small space with higher reliability.
v. Low power consumption.
vi.
High operating speed.
vii.
It is easy to replace a faulty IC.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
Subject Code: 17213
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
g) What is filter? State its need.
2M
Ans:
Filter:
1M
Filters are the electronics circuit used along with rectifier in order to get a pure ripple free dc voltage.
Its need:
1M
We want pure dc to obtain it we use filter.
OR
A filter is a device which removes the ac components of rectifier output but allows the dc components
to reach the load.
h) State the types of field effect transistor.
Ans:
Field effect transistor
Junction FET
n-channel FET
2M
MOSFET
P-channel FET
i) Draw symbol of
1) Zener diode
2) LED
Ans:
Zener diode:
depletion MOSFET enhancement MOSFET
2M
(1M each)
LED:
j) State the classification of ICs
Ans:
2M
Integrated circuit
Classification based on
active devise
Bipolar Ics
Unipolar Ics
Classification based on
application devise
Linear or
Analog Ics
OP - AMP
Comparator
Digital or
nonlinear Ics
Logic gate
counter
Flip flop
Classification based on
technology
Hybrid
Technology
Monolithic
technology
Bipolar
Unipolar
JFET
MOSFET
3
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
Subject Code: 17213
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
k) What is knee voltage?
2M
Ans: (Note: Diagram is optional)
Knee voltage:
The voltage at which the current start to increase rapidly is called cut- in or knee voltage of the diode
for silicon diode it is 0.7V, whereas for germanium diode it is about 0.3V
l) Give classification of resistors.
Ans:
2M
Resistors
Linear register
Fixed
Register
Carbon
Wire
Metal
Composition wound film
nonlinear register
variable
Register
potentiometer trimmers
thermistor
LDR
varistor
rheostats
Q2) Attempt any four of the following :
16M
a) State any four applications of electronics.
4M
Ans:
(4 marks for 4 applications)
Communication and entertainment
Defense applications
Industrial applications
Industrial applications
Medical Science.
Instrumentation
b) Describe operating principle of Tunnel Diode.
4M
Ans:
(4 marks for correct working principle)
Principle :
An ordinary PN junction diode has an impurity concentration of about 1 part in 108 and its depletion
region width is of the order 5 microns. If the concentration of impurity is increased to about 1 part in
103, the device characteristics are completely changed. Due to the thin potential energy barrier, the
electrons penetrate through the junction rather than surmounting them. This quantum mechanical
behavior is referred to as tunneling and these high impurity density PN junction devices are called
tunnel diodes.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
c) Explain the experimental set up for obtaining the input and output characteristics of NPN
transistor in CE configuration.
4M
ans:
(2 marks for diagram & 1 marks for input and 1 mark for output)
1) Input: Keep the input voltage VCE as constant at 2V by varying VCC
2) Vary the input voltage VBB in steps 1V upto 10V.
3) Measure the voltage VBE using voltmeter and current IB using ammeter for different values of input
voltage.
4) Repeat the steps 3 & 4 For different values of VCE
5) Draw the input characteristics and calculate the input resistance.
6) Output : Fix input base current IB at constant value say 10 micro-amp
7) Vary VCC in steps of 1V from 0V to 10V.
8) Measure VCE using voltmeter and current Ic using ammeter.
9) Repeat for different values of IB
10 Draw graph and find output resistance.
d) Draw the circuit diagram of transformer coupled 2 stage amplifier and state function of each
component.
4M
Ans:
(2 marks for diagram, 2 marks for explanation)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
R1, R2, RE and capacitor CE form the DC biasing and stabilization. VCC is the dc power supply.
primary winding induces the AC signal in the secondary winding which couples this AC output signal
directly to the base of next stage. Hence it is given the name transformer coupled.
e) Draw symbol of varactor diode and describe its operating principle.
Ans:
(2 marks for symbol, 2 marks for working principle)
4M
OR
Working principle:
The varactor , or varicap is a diode that exhibits the characteristics of a variable capacitor. The depletion
region at the p-n junction acts as the dielectric and plates of a common capacitor and is caused to expand
and contract by the voltage applied to the diode. This action increases and decreases the capacitance. The
schematic symbol for the varactor is shown beside. Varactors are used in tuning circuits and can be used
as high-frequency amplifiers.
f) Explain operating principle of crystal oscillator with neat diagram.
ans:
4M
Some crystals found in nature exhibit the piezoelectric effect. When an alternating voltage is applied
across them, vibrate at the frequency of the applied voltage so that conversely if they are forced to
mechanically vibrate, generating an alternating voltage of the same frequency. The main substances that
cause the piezoelectric effect are quartz, rochelle salts and tourmaline.
The crystal is connected here in the circuit as a series element in the feedback path from the collector to
the base. R1 R2 RE provides the necessary dc bias.
The frequencies of oscillations are set by
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
Subject Code: 17213
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Q3. Attempt any four of the following:
16M
a) Give classification of electronics components. Hence define Active & Passive components. 4M
Ans: Classification:
2M
Electronics components
Active components
Electronic tubes
Diodes
Passive components
Semiconductor device
transistor
Resistor
capacitor
inductor
JFET
Active components: An active components is one which introduce gain.
1M
Passive components: the Passive components is one which does not introduce any gain
1M
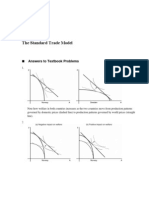
b) Draw VI characteristics of zener diode & mark portion used for obtaining constant voltage. 4M
Ans: VI characteristics of zener diode:
c) State advantages, disadvantages and applications of JFET (02 Each)
4M
Ans:
Advantages:
2M
i. It is a unipolar device so its operation depends on the flow of majority carries only.
ii. FET has better thermal stability
iii. FET is less noisy
iv.
It is relatively immune to radiation.
v. FET has a very high input resistance
Disadvantages:
1M
i. FET has small gain bandwidth product.
ii. It has main drawback of being very susceptible to overload voltage, thus requiring special
handling during installation.
Applications:
1M
i. It is use in integrated circuit.
ii. Buffer amplifies
iii. Phase-shift oscillator
iv.
Integrator
v. Amplifier
7
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
d) Draw and explain output characteristics of NPN transistor in CE configuration.
4M
Ans:
Output characteristics:
2M
1. The output characteristics may be divided into three important regions namely saturation region,
active region and cut-off region. The saturation and cut-off regions are shown by the shaded areas,
while the active region is the region between the saturation and cut-off region.
2. As the collector-to-emitter voltage (VCE) is increased above zero, the collector current (IC)
increases rapidly to a saturation value, depending upon the value of base current. It may be noted
that collector current (IC) reaches to a saturated value when VCE is above 1V.
3. When collector-to-emitter voltage (VCE) is increased further, the collector current slightly
increases. This increase in collector current is due to the fact that increased value of collector-toemitter voltage (VCE) reduces the base current and hence the collector current increases. This
phenomenon is called as energy effect.
4. When the base current is zero, a small collector exists. This is called leakage current. However, for
all practical purpose, the collector current (Ic) is zero, when the base current (IB) is zero. Under the
condition the transmitter is said to be cut-off.
Diagram:
e) Find IB, for a transistor, if dc = 0.99 IC = 6mA and ICBO = 15A.
Ans:
dc = 0.99
IC = 6mA
ICBO = 15A
IB =?
2M
4M
IC = dc IE + ICBO
2M
IB = IE - IC = 6.045 6 = 0.045mA = 45A
2M
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
f) Define oscillator. State necessary conditions required for sustained oscillations.
4M
Ans:
Oscillator:
2M
An oscillator is a device which produces an output signal without any input signal of any desired
frequency.
OR
Oscillator is a device which gets energy from the DC source and converts it into AC energy at the
same frequency as that of the input signal.
The necessary conditions required for sustained oscillations are:
2M
1. Loop gain (.Av) 1
2. Phase shift between the input and output signal must be equal to 3600 or 00.
Q4) Attempt any four of the following
16M
a) Compare conventional PN junction diode and LED depending on the following parameters:
i. Symbol
ii. Material used
iii. On state voltage drop
iv.
Applications
Ans:
(1 marks for 1 point each)
Parameters
Symbol
PN junction diode
LED
Material used
Silicon , Germanium
On state voltage drop
Applications
0.6 V for Si, 0.3V for Ge
Switch, rectifiers
Gallium Arsenide, Gallium
Arsenide phosphide,
Gallium nitride
1.2V to 2V
display
b) Explain the working of bridge rectifier with circuit diagram and waveforms.
Ans:
(1m for waveform, 1m for working, 2m for ckt)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
1)
2)
3)
4)
In this circuit four diodes are used which form a bridge, an ordinary transformer is used.
In the +ve half cycle D1, D4 hence current flows through D1, RL and D4 .
In the ve half cycle D2, D3 hence current flows through D1, RL and D4 .
In both the cases current passes through the load resistor in the same direction.
c) What is a transistor. Explain the working of PNP transistor in CE mode.
Ans:
(1m for def of transistor, 1m for explanation, 2m for ckt)
4M
Transistor = Transfer + Resistor
Transistor is a device which amplifies a weak signal and it transfers the weak signal from a
low resistance region (BE ) to a high resistance region(BC)
Hence it is given the name transistor.
1)
2)
3)
4)
Base emitter junction is forward biased and base collector is reverse biased.
The emitter is common and base is the input terminal, collector is the output terminal.
IE = IB + IC basic equation of transistor.
The holes from emitter are repelled and they move towards the base. Base is lightly doped and
they get attracted by collector which is reverse biased.
5) The current gain for CE mode is = Ic/Ib
d) Draw two stage RC coupled amplifier and explain its working.
Ans:
4M
(2m for ckt, 2m for working)
10
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
1) In this method the AC voltage signal developed across the collector load of each stage is coupled
through the capacitor to the base of next stage.
2) The second stage further amplifies this signal.
3) In this way the cascaded stages amplify the signal and overall gain is increased.
4) R1, R2, R1`, R2`, RE, RE` and capacitor CE CE` form the DC biasing and stabilization. VCC is
the dc power supply.
e) Draw the circuit diagram of CLC filter and explain function of each block
4M
Ans:
(2m for ckt, 2m for working)
1)
2)
3)
4)
The pulsating output from the rectifier is applied at the input of CLC filter.
It consists of two parts: shunt capacitor filler C1 and LC filter C2.
The rectifier output first charges the capacitor C1 to the peak value of the rectifier output.
The capacitor tends to hold the charge between successive peaks discharging slowly through L and
RL.
5) The remaining output fluctuations are opposed by the series choke and bypassed to ground through
C2.
f) Draw circuit diagram of direct coupled amplifier and explain its working
4M
Ans:
(2 marks for ckt, 2 marks for working)
1)
2)
3)
4)
It is specially used for amplifying low frequency signals.
Amplifiers are connected without any coupling devices.
The output of first stage is directly connected to the base of the next stage.
The input to be amplified is applied directly to the input of the first stage, it is amplified by the
transistor and directly applied to the next stage. The amplified is obtained at the collector of the
last stage.
11
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
Subject Code: 17213
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.
Attempt any FOUR of the following:
16 Marks
a) Draw experimental set up to study V-I characteristics of P-N junction diode in forward and
reverse biased condition.
Ans:
(2 marks for forward and 2 marks for reverse charc. Diagram)
b) Differentiate between HWR and FWR depending on any four points of the following:
Ans:
(marks as given in table below)
Sr. No.
Parameters
Half Wave
Full Wave Rectifier
Rectifier
Centre tapped
Bridge
DC Load Current
(i)- mark
or (0.138 Im)
or (0.636 Im)
or
(Idc)
(0.636
Im)
RMS Load Current
(ii)- mark
(iii)- mark
DC Load Power
Im2/
(iv)- mark
(v)- 1 mark
Ripple Factor
Ripple Frequency
1.21
Fin or 50Hz
0.482
2Fin or 100Hz
(vi)- 1 mark
PIV
Vm
2Vm
*RL
4Im2/
*RL
4Im2/ 2
*RL
0.482
2Fin
or
100 Hz
Vm
12
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
c) Explain with the help of waveforms operation of Astable Multivibrator using NPN transistor.
Ans:
(Diagram- 2 marks, waveforms-1 mark, Explantion-1 mark)
13
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Circuit Operation:
It is also called as free running relaxation oscillator and is commonly used to generate square
wave.
When DC power supply VCC is switched ON (say at t=0) one of the transistor will start conducting
more than other due to some imbalance in the circuit.
Assume Q1 starts conducting more than that of Q2. Then because of positive feedback transistor
Q1 will be driven in to saturation and transistor Q2 to cut-off.
At t>0, VB1=VBE (sat) and VC1=VCE (sat), VB1 is negative and VC2=VCC.
During time t>0 the capacitor C1 charges towards Vcc through R1. Since the base of Q2 is directly
connected to capacitor C1 as shown in Fig. (a) Therefore Vb1 also increases exponentially towards
Vcc.
As soon as Vb2 increases above cut in voltage Q2 starts conducting. It occurs at t=t1. As the Q2
goes in to saturation, its collector voltage VC2 falls to VCE (sat). The fall in voltage VC2 causes an
equal fall in voltage VB1 and cut-off Q1 and hence voltage Vc1 rises towards Vcc.
At t>t1, VB2=VBE (sat) and VC1=VCC, VB1 is negative and VC2=VCE (sat).
During time t>t1 when Q1 is OFF and Q2 is ON the voltage VB1 rises exponentially.
d) Explain formation of Depletion layer in P-N junction of a diode with neat sketch
Ans:
(2 marks for diagram and 2 marks for Explanation)
At the instant P-N junction formation, the free electrons near the junction in the N- region begin to
diffuse across the junction in to P- region where they combine with holes near the junction.
The result is that N-region loses free electrons this creates a layer of positive charges (pantavalent
ions) near the junction.
The P-region loses holes and the result that there is a negative charges (trivalent ions near the
junction.
The shaded region on both sides of the junction in Fig. below contains only immobile ions and no
free charge carriers such as electrons or holes.
In other words this region is depleted of free charge carriers. Therefore region is called as
depletion region.
Once P-N junction is formed and depletion layer is created the diffusion of free electrons stops.
The positive and negative charges set an electric field
14
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
e) Draw neat circuit diagram of transformer coupled amplifier and give its two applications.
Ans:
(2 marks for circuit diagram, 2 marks for any two applications)
Applications:
Transformer coupling is mostly employed for impedance matching.
It is used as final stage. It is used to transfer power to the low impedance lad such as loudspeaker.
For amplification of radio frequency (RF) signal.
In power amplifiers.
f) Explain operating principle of Schottky diode and state its two applications.
Ans:
(1 mark for diagram, 1 mark for principle, 2 marks for any two applications).
When the metal and semiconductor are joined together to form the junction, the electrons in the Ntype material will immediately flow into adjoining metal.
Since injected carriers have very high kinetic energy compared to the electrons of the metal they
are called as hot carriers.
Electrons are injected in to a region (metal) where electrons only are the majority carriers.
The heavy flow of electrons in to metal creates region near the junction surface which is depleted
of carriers.
This is similar to depletion region.
15
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
When forward bias voltage is applied the strength of the negative barriers (depletion region) will
reduce.
Due to this, a heavy flow of electrons across the junction will begin.
Applications:
To rectify very high frequency (above 300 MHz) signal.
As a switching device in digital computer.
In clipping and clamping circuit.
In mixing and detecting circuits used in communication systems.
In low power schottky Transistor-Transistor Logic (schottky TTL) circuits.
In low voltage power supply circuits.
6.
Attempt any FOUR of the following:
16 Marks
a) Explain operation of P-N junction under reverse bias condition.
Ans:
(2 marks for diagram and 2 marks for explanation)
When negative terminal of battery is applied to P-type and positive terminal to N-type as shown is Fig.
below then P-N junction is said to be reverse biased.
When a diode is reverse biased, holes in the P- region are attracted towards the negative terminal of
the supply.
On the other side electrons on the N-side are attracted towards positive terminal of the supply as
shown.
Widening of depletion region: due to movement of electrons and holes away from the junction width
of depletion region increases.
Increase in barrier potential: due to more number of ions present opposite side the barrier potential
will increase.
The increased potential barrier prevents the flow of charge carriers across the junction and hence
current does not flows.
16
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
b) Draw the block diagram of regulated power supply and explain function of each block.
Ans:
(2 marks for diagram and 2 marks for function of each block)
A D.C. regulated power supply which maintains the output voltage constant irrespective of a.c. mains
fluctuations or load variations is known as regulated D.C. power supply.
Input Step down transformer: Step down transformer decreases the input voltage of 230 V A.C. in to
suitable voltage handled by the next stages of rectifier, filter and voltage regulators.
Rectifier: The bridge rectifier converts the transformer secondary A.C. voltage in to pulsating D.C.
voltage.
Filter: The shunt capacitor filter reduced the pulsation in the rectifier D.C. voltage. Filter converts
pulsating D.C. in to pure D.C.
Voltage regulator: It reduces the variations in the filtered output voltages. It keeps output voltage
nearly constant weather the load current changes or there is change in input A.C. voltage.
c) Explain thermal runaway phenomenon in a BJT.
Ans:
(2 marks for diagram and 2 marks for explanation)
+1)
The collector leakage current ICBO is dependent on temperature. The flow of collector current
produces heat in transistor.
This raises transistor temperature and if no stabilization is done, the collector leakage current ICBO
also increases.
It is clear from the above equation the if ICBO increases, the collector current Ic increases.
The increased Ic will raise the temperature of transistor which in turn will cause ICBO to increase.
This effect is cumulative and in a matter of seconds the Ic may become very large causing transistor to
burn out.
The self-destruction of unsterilized transistor is known as thermal runaway.
17
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
d) Explain working of Bi-stable multivibrator with the help of a neat sketch.
Ans:
(2 marks for diagram and 2 marks for explanation)
This multivibrator has two states and can stay in any one of these two states, indefinitely as long as the
power is supplied. It changes to other state only when it receives a trigger from outside.
Operation:
When Vcc supply is switched ON one of the transistor will start conducting more than the other then
because of feedback action, this transistor will be driven into saturation and the other to cut-off.
Assume that Q1 is ON and Q2 is OFF. It is a stable state of circuit.
A negative pulse applied to set input will turn OFF the transistor Q1 and Q2 switches ON.
Suppose positive pulse is applied at the reset input. It will cause Q2 to conduct. As Q2 conducts its
collector voltage falls and it cut-offs Q1. This Q1 is OFF and Q2 is ON.
Now if positive pulse is applied at the set input, it will switch the circuit back to its original stable state
i.e. Q1 is ON and Q2 is OFF.
e) Explain working of N-channel JFET.
Ans:
(2 marks for diagram and 2 marks for explanation)
When a voltage is applied between the drain and source with a dc supply voltage (VDD) the electrons
flows from source to drain through the narrow channel existing between the depletion regions.
This constitutes ID and direction is from drain to source.
The value of drain current is maximum, when no external voltage is applied between gate and source
and is designated by IDSS.
18
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
(Autonomous)
(ISO/IEC - 27001 - 2005 Certified)
Subject Code: 17213
WINTER 13 EXAMINATION
Model Answer
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
When VGS is applied as shown in Fig. (a), the reverse biased at gate-source junction is increased.
As a result of this, the depletion regions are widened. This reduces effective width of the channel and
hence reduces ID.
When VGS is increased further, a stage is reached at which two depletion regions touch each other as
shown in Fig. (b).
At this VGS the channel is completely blocked or pinched off and ID is reduced to zero.
The gate-source voltage (VGS) at which the drain current is zero is called pinch off voltage.
f) Calculate VDC and current IDC flowing through 100 resistor connected to 240v supply through
HWR.
Ans:
(Marks distribution as given below)
Given Data:
1)
(1 mark)
2)
(1 mark)
3)
(1 mark)
4)
(1 mark)
19
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Duke Energy Coal AllocationDocument4 pagesDuke Energy Coal AllocationSatish Kumar100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Emhart GlassDocument17 pagesEmhart GlassYogesh Badhe50% (2)
- LWN Operating Manual of FanDocument20 pagesLWN Operating Manual of FanYogesh Badhe100% (1)
- 06 GDP and Economic GrowthDocument3 pages06 GDP and Economic GrowthAkash Chandak0% (2)
- Batch MischerDocument5 pagesBatch MischerYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Tpi106 de UsDocument10 pagesTpi106 de UsYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Portable Fire Extinguisher Plan PolicyDocument2 pagesPortable Fire Extinguisher Plan PolicyYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Argos ManualDocument212 pagesArgos ManualYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Iwater Ion ExchangeDocument9 pagesIwater Ion ExchangeYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- PM Master List For TestingDocument17 pagesPM Master List For TestingYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- ARKEMA-Operation Manual Updated Version 8 April 2013Document10 pagesARKEMA-Operation Manual Updated Version 8 April 2013Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- MTBF - MTTRDocument11 pagesMTBF - MTTRYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- 601-10-14-V3.7.38 (Ware Handling)Document81 pages601-10-14-V3.7.38 (Ware Handling)Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Final Schedule of Rates-R6Document2 pagesFinal Schedule of Rates-R6Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- LCM Brochure MinDocument12 pagesLCM Brochure MinYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- 11 SubstationDocument13 pages11 SubstationYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Wooden RackDocument4 pagesWooden RackYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MtechDocument8 pagesSyllabus MtechYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- SKF Electronic Stethoscope TMST 3: Easily Pinpoints Bearing and Machine NoiseDocument2 pagesSKF Electronic Stethoscope TMST 3: Easily Pinpoints Bearing and Machine NoiseYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Gas DetectorDocument6 pagesGas DetectorYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- IIT Delhi - EPPM - 4 JulyDocument12 pagesIIT Delhi - EPPM - 4 JulyYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Q. What Is Reverse Osmosis (RO) ?Document6 pagesQ. What Is Reverse Osmosis (RO) ?Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: "Studies On Radial Tipped Centrifugal Fan"Document21 pagesChapter - 1: "Studies On Radial Tipped Centrifugal Fan"Yogesh Badhe100% (1)
- Electronic Automation 1Document56 pagesElectronic Automation 1Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- From Machine Operator To Bottle Maker V2.0Document36 pagesFrom Machine Operator To Bottle Maker V2.0Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Overview Glass Furnace1Document34 pagesOverview Glass Furnace1Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- MixerDocument8 pagesMixerYogesh Badhe100% (1)
- Oxyuel Glass FurnacequestionaireDocument5 pagesOxyuel Glass FurnacequestionaireYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- DoD Energy Manager Handbook Jan 2005Document249 pagesDoD Energy Manager Handbook Jan 2005Yogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Batch MakerDocument2 pagesBatch MakerYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- Esa Manual PDFDocument125 pagesEsa Manual PDFYogesh BadheNo ratings yet
- AP Micro Ch. 5 Study GuideDocument14 pagesAP Micro Ch. 5 Study GuidecrazybowseatNo ratings yet
- Air Transport Beyond The Crisis - Pascal Huet - WTFL 2009Document18 pagesAir Transport Beyond The Crisis - Pascal Huet - WTFL 2009World Tourism Forum LucerneNo ratings yet
- IRR and NPV Conflict - IllustartionDocument27 pagesIRR and NPV Conflict - IllustartionVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Table of ContensDocument17 pagesTable of ContensEcha SkeskeneweiiNo ratings yet
- PL Nov OktDocument2 pagesPL Nov OktKahfiNo ratings yet
- CadburyDocument11 pagesCadburyAnkita RajNo ratings yet
- Superior Commercial Vs Kunnan Enterprises - DigestDocument3 pagesSuperior Commercial Vs Kunnan Enterprises - DigestGayeGabrielNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3032Document4 pagesQuiz 3032PG93No ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of VAT and GSTDocument39 pagesComparative Analysis of VAT and GSTsaahilp_10% (5)
- Partnership SBCDocument10 pagesPartnership SBChyosunglover100% (1)
- Cost CurveDocument8 pagesCost CurvearunNo ratings yet
- Insurance Company Final AccountsDocument17 pagesInsurance Company Final AccountsKirti_Bhatia_5739No ratings yet
- 3.1 - Why Businesses Seek International Markets - SHORT NOTESDocument4 pages3.1 - Why Businesses Seek International Markets - SHORT NOTESEmperor SaladinNo ratings yet
- Part B - GR/PP Procedure Disposal of Copies of Export Declaration Forms 6B.1Document3 pagesPart B - GR/PP Procedure Disposal of Copies of Export Declaration Forms 6B.1Vimala Selvaraj VimalaNo ratings yet
- 2016 HSC Maths General 2Document40 pages2016 HSC Maths General 2HIMMZERLANDNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Hotel IndustryDocument3 pagesOverview of The Hotel IndustryBrandon WaltersNo ratings yet
- Terex LiftaceDocument2 pagesTerex LiftaceEduardo SaaNo ratings yet
- Economic Cycles: Historical Evidence, Classification and ExplicationDocument29 pagesEconomic Cycles: Historical Evidence, Classification and ExplicationkyffusNo ratings yet
- Kiat Penulisan Proposal PKM Unand - CahyadiDocument43 pagesKiat Penulisan Proposal PKM Unand - CahyadinugrahaNo ratings yet
- P.7 - Cost AccumulationDocument8 pagesP.7 - Cost AccumulationSaeed RahamanNo ratings yet
- Elements of SCMDocument6 pagesElements of SCMPraveen ShuklaNo ratings yet
- IE CH 05-AnsDocument4 pagesIE CH 05-AnsHuo ZenNo ratings yet
- The Shift Towards Umbrella Branding Is Inescapable': Anandakuttan B UnnithanDocument1 pageThe Shift Towards Umbrella Branding Is Inescapable': Anandakuttan B UnnithanSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- New Ra April 2023Document279 pagesNew Ra April 2023Jagdamba OverseasNo ratings yet
- Hilado v. CIRDocument5 pagesHilado v. CIRclandestine2684No ratings yet
- CIFDocument2 pagesCIFSaikumar SelaNo ratings yet
- Casino Regulatory Manual For Entertainment City Licensees Version 4Document366 pagesCasino Regulatory Manual For Entertainment City Licensees Version 4Paige Lim100% (2)
- Stitch Classes and Stitch DefectsDocument59 pagesStitch Classes and Stitch DefectsMaanvizhi Moorthi100% (1)