Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IG.27.Soil Conservation
Uploaded by
Chandra RaoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IG.27.Soil Conservation
Uploaded by
Chandra RaoCopyright:
Available Formats
www.pmfias.
com
https://www.youtube.com/c/PoorMansFriend
www.pmfias.com
Contents
Crop Rotation
Strip Cropping
Use of Early Maturing Varieties
Contour Ploughing
Checking Shifting Cultivation
Ploughing the Land in Right Direction
Mulching
Contour barriers
Rock dam
Terrace farming
Contour Bunding
Intercropping
Contour ploughing
Shelter belts or Windbreaks
Sand fences
Afforestation
Checking Overgrazing
Dams
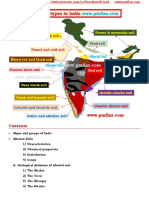
Soil Conservation
Soil conservation is the prevention of soil from erosion or reduced fertility caused by
overuse, acidification, salinization or other chemical soil contamination.
Soil erosion is the greatest single evil to Indian agriculture and animal husbandry.
Notable Quotable from Kullars Indian Geography: With soil conservation people rise and
with its destruction they fall. Neglect of soil is like killing the hen that lays the golden
egg.
Crop Rotation
Adopting sustainable agricultural practices is the most important measure to conserve
soil.
In many parts of India, a particular crop is sown in the same field year after year. This
practice leads to exhaustion of certain nutrients in the soil making it infertile.
www.pmfias.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/PoorMansFriend
www.pmfias.com
Crop rotation is a practice in which a different crop is cultivated on a piece of land each
year.
This helps to conserve soil fertility as different crops require different nutrients from the
soil. Crop rotation will provide enough time to restore lost nutrients.
For example, potatoes require much potash but wheat requires nitrate. Thus it is best to
alternate crops in the field.
Legumes such as peas, beans, and many other plants, add nitrates to the soil by
converting free nitrogen in the air into nitrogenous nodules on their roots. Thus if they
are included in the crop rotation nitrogenous fertilizers can be dispensed with.
Strip Cropping
Crops may be cultivated in alternate strips, parallel to one another. Some strips may be
allowed to lie fallow while in others different crops may be sown.
Various crops are harvested at different intervals. This ensures that at no time of the
year the entire area is left bare or exposed.
The tall growing crops act as wind breaks and the strips which are often parallel to the
contours help in increasing water absorption by the soil by slowing down run off.
Use of Early Maturing Varieties
Early maturing varieties of crops take less time to mature and thus put lesser pressure
on the soil. In this way it can help in reducing the soil erosion.
Contour Ploughing
If ploughing is done at right angles to the hill slope, the ridges and furrows break the
flow of water down the hill.
This prevents excessive soil loss as gullies are less likely to develop and also reduce runoff so that plants receive more water.
Checking Shifting Cultivation
Checking and reducing shifting cultivation by persuading the tribal people to switch over
to settled agriculture is a very effective method of soil conservation.
This can be done by making arrangements for their resettlement which involves the
provision of residential accommodation, agricultural implements, seeds, manures, cattle
and reclaimed land.
www.pmfias.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/PoorMansFriend
www.pmfias.com
Ploughing the Land in Right Direction
Ploughing the land in a direction perpendicular to wind direction also reduces wind
velocity and protects the top soil from erosion.
Mulching
The bare ground (top soil) between plants is covered with a protective layer of organic
matter like grass clippings, straw, etc.
Benefits
Protects the soil from erosion.
It helps to retain soil moisture.
Reduces compaction from the impact of heavy rains.
Conserves moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering.
Maintains a more even soil temperature.
Prevents weed growth.
Organic mulches also improve the condition of the soil. As these mulches slowly
decompose, they provide organic matter which helps keep the soil loose.
Contour barriers
Stones, grass, soil are used to build barriers along contours. Trenches are made in front
of the barriers to collect water.
They intercept downslope flowing water and soil particles. These barriers slow down the
water movement and reduce its erosive force. They also filter out and trap many of the
suspended soil particles, keeping them from being washed out of the field.
A long term advantage of barriers is that soil tends to build up behind them, creating a
terrace effect. Barriers can be classified as live (strips of living plants), dead (rocks, crop
residues), or mixed (a combination of the previous two).
Rock dam
Rocks are piled up across a channel to slow down the flow of water. This prevents gullies
and further soil loss.
Terrace farming
In terracing, a number of terraces are cut along the hill slope.
www.pmfias.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/PoorMansFriend
www.pmfias.com
These are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops.
They can reduce surface run-off and soil erosion.
Contour Bunding
Contour bunding involves the construction of banks along the contours.
Terracing and contour bunding which divide the hill slope into numerous small slopes,
check the flow of water, promote absorption of water by soil and save soil from erosion.
Retaining walls of terraces control the flow of water and help in reducing soil erosion.
Intercropping
Different crops are grown in alternate rows and are sown at different times to protect the
soil from rain wash.
Contour ploughing
Ploughing parallel to the contours of a hill slope to form a natural barrier for water to
flow down the slope
Shelter belts or Windbreaks
In the coastal and dry regions, rows of trees are planted to check the wind movement to
protect soil cover.
Sand fences
Sand fences are barriers made of small, evenly spaced wooden slats or fabric. They are
erected to reduce wind velocity and to trap blowing sand. Sand fences can be used as
perimeter controls around open construction sites to keep sediments from being blown
offsite by the wind.
www.pmfias.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/PoorMansFriend
www.pmfias.com
Afforestation
It includes the prevention of forest destruction along with growing new forests or
increase area under forests.
A minimum area 20 to 25 per cent of forest land was considered healthy for soil and
water conservation for the whole country.
It was raised to 33 per cent in the second five year plan 20 per cent for the plains and
60 per cent for hilly and mountainous regions.
Checking Overgrazing
Overgrazing accentuates erosion. During the dry period, there is shortage of fodder and
the grass is grazed to the ground and torn out to the roots by animals. Soil is pulverized
(reduce to fine particles) by the hoofs of animals. All this leads to weak top layer.
So overgrazing needs to be checked to prevent soil erosion.
This can be done by creating separate grazing grounds and producing larger quantities
of fodder.
Dams
www.pmfias.com
https://www.youtube.com/c/PoorMansFriend
www.pmfias.com
Much of the soil erosion by river floods can be avoided by constructing dams across the
rivers in proper places. This checks the speed of water and saves soil from erosion.
But indiscriminate dam construction can worsen the condition by creating floods and
landslides like it happens in the Himalayan region.
You might also like
- LR AD SurveyDocument1 pageLR AD SurveyChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Xaam - In-What Is The Difference Between GSLV and PSLV GS 3prelims 2017Document1 pageXaam - In-What Is The Difference Between GSLV and PSLV GS 3prelims 2017Chinna BabuNo ratings yet
- Stock AnalysisDocument1 pageStock AnalysisChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- LR AD SurveyDocument1 pageLR AD SurveyChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- VENUE ALLOTMENT (All Districts) NotificationNo29Document5 pagesVENUE ALLOTMENT (All Districts) NotificationNo29Chinna BabuNo ratings yet
- AP Innovation and Startup Policy 2014-2020Document9 pagesAP Innovation and Startup Policy 2014-2020hare231139No ratings yet
- Hï Ï Gïüþ (Výs &2 Ððl$Æ Œæþ Ð) L Ç (Ç Ô Æ Ç (™èlDocument1 pageHï Ï Gïüþ (Výs &2 Ððl$Æ Œæþ Ð) L Ç (Ç Ô Æ Ç (™èlChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Andhra Pradesh Current Affairs 2017Document12 pagesAndhra Pradesh Current Affairs 2017Mahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- IG 22 SoilsDocument5 pagesIG 22 SoilsChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- IG.18.Seasons SummerDocument12 pagesIG.18.Seasons SummerChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Pib - Nic.in-14th Finance Commission FFC Report Tabled in Parliament FFC Recommends by Majority Decision That TheDocument4 pagesPib - Nic.in-14th Finance Commission FFC Report Tabled in Parliament FFC Recommends by Majority Decision That TheChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Index Agri Reform Oct2016Document15 pagesIndex Agri Reform Oct2016Chandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes Standard TimeDocument8 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes Standard TimeChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes Seismic WavesDocument7 pagesEarthquakes Seismic WavesChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- IG.17.Indian Climate IntroDocument8 pagesIG.17.Indian Climate IntroChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- IG.24.Alluvial and Black SoilDocument6 pagesIG.24.Alluvial and Black SoilChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Tsunami 2004 Indian Ocean TsunamiDocument8 pagesTsunami 2004 Indian Ocean TsunamiChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- India Geographical Extent FrontiersDocument6 pagesIndia Geographical Extent FrontiersChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Tropical Cyclones Favorable Conditions FormationDocument12 pagesTropical Cyclones Favorable Conditions FormationChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- IG.11.Coastal PlainsDocument9 pagesIG.11.Coastal PlainsChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Sun Internal Structure AtmosphereDocument5 pagesSun Internal Structure AtmosphereChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- IG.21.Natural VegDocument15 pagesIG.21.Natural VegChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- IG.17.Indian Climate IntroDocument8 pagesIG.17.Indian Climate IntroChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Solar System Planets Inner PlanetsDocument4 pagesSolar System Planets Inner PlanetsChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Vital Stats - Power SectorDocument2 pagesVital Stats - Power SectorChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Sun Internal Structure AtmosphereDocument5 pagesSun Internal Structure AtmosphereChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs Polity-IIDocument28 pagesCurrent Affairs Polity-IIChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Highlights - Budget 2015-16Document6 pagesHighlights - Budget 2015-16Chandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Neethi Aayog 2015Document1 pageNeethi Aayog 2015glreddy09No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Smaw 12 Module 1Document7 pagesSmaw 12 Module 1Francis Rico Mutia RufonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 19 - Accuracy and PrecisionDocument5 pagesLecture Notes 19 - Accuracy and PrecisionSurendra RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Process Safety - Recommended Practice On KPIsDocument36 pagesProcess Safety - Recommended Practice On KPIsKB100% (2)
- 120131-Perforated Sheet Metal - IPRF - CD PDFDocument239 pages120131-Perforated Sheet Metal - IPRF - CD PDFMisagh100% (1)
- Pricelist Juli 2023 UserDocument108 pagesPricelist Juli 2023 Userfitri heriyati pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Module3notes - Answer KeyDocument31 pagesModule3notes - Answer Keymelissa.figueroamoralesNo ratings yet
- 20EN 20001 K12 PartsCatalogue QuicklubDocument112 pages20EN 20001 K12 PartsCatalogue QuicklubPakoNo ratings yet
- Busting A Cap Without Die-Ing ( With Brief Diversions in System & Hardware REDocument39 pagesBusting A Cap Without Die-Ing ( With Brief Diversions in System & Hardware REpanicopticonNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases YMS X ALJDocument9 pagesAcids and Bases YMS X ALJFaqihah Syahindah Mohammed FiroozNo ratings yet
- Unt, in Moles, of Carbon Atoms Compound A Is Completely Oxidised To Carbon Dioxide and Water. Copper Is The Only Other Product of THDocument30 pagesUnt, in Moles, of Carbon Atoms Compound A Is Completely Oxidised To Carbon Dioxide and Water. Copper Is The Only Other Product of THG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Assay of Aspirin PDFDocument9 pagesAssay of Aspirin PDFyeleidispNo ratings yet
- Honda BayDocument16 pagesHonda BayVicente Jr. BallonoNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument6 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersrajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Solid State Sintering in The of Iron Ore Pellets IndurationDocument10 pagesSolid State Sintering in The of Iron Ore Pellets IndurationCamila Barata CavalcantiNo ratings yet
- The Pneumatics Installation GuideDocument186 pagesThe Pneumatics Installation GuideHAMIT100% (1)
- Q3 Consumer Chem Mod 3 Wk5-6Document20 pagesQ3 Consumer Chem Mod 3 Wk5-6Ryan CuisonNo ratings yet
- Paper - I - General: Previous Year Paper GPAT DIDocument20 pagesPaper - I - General: Previous Year Paper GPAT DIVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Common Tea Pest and Pesticide Use in NepalDocument13 pagesCommon Tea Pest and Pesticide Use in Nepalkhadka80% (5)
- MSDS - Prominent-GlycineDocument6 pagesMSDS - Prominent-GlycineTanawat ChinchaivanichkitNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Based Safety Observation Checklist: ErgonomicsDocument2 pagesBehavioral Based Safety Observation Checklist: ErgonomicsRyan CyrillaNo ratings yet
- The Public's Love Affair With Geodes: Rock MineralDocument3 pagesThe Public's Love Affair With Geodes: Rock MineralSerkan KocapinarNo ratings yet
- CPI Group 4Document22 pagesCPI Group 4Yudhi GusmanNo ratings yet
- Essential Molecular BiologyDocument19 pagesEssential Molecular BiologySandra JelynNo ratings yet
- Emkarate RL 32H: Material Safety Data Sheet Date Revised: Feb, 2008Document6 pagesEmkarate RL 32H: Material Safety Data Sheet Date Revised: Feb, 2008angelo collaNo ratings yet
- Fisher HP and HPA Control Valves: Scope of ManualDocument64 pagesFisher HP and HPA Control Valves: Scope of ManualYogurtu NngeNo ratings yet
- Deligate ExcelFormatDocument60 pagesDeligate ExcelFormatrashidnyou0% (2)
- NASA Facts The Planet VenusDocument8 pagesNASA Facts The Planet VenusBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Hand LayupDocument3 pagesHand LayupS19M082 KRITHIK ANo ratings yet
- People VS PascuaDocument11 pagesPeople VS PascuaShiena Lou B. Amodia-RabacalNo ratings yet
- Water Hardness Case StudyDocument15 pagesWater Hardness Case StudyTaima GhNo ratings yet