Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Movement of Substances in Living Things
Uploaded by
GabriellaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Movement of Substances in Living Things
Uploaded by
GabriellaCopyright:
Available Formats
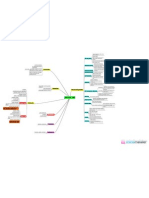
molecules are dispersed in a
random direction
spread from an area of higher
concentration to an area of lower
concentration
process dispersion continues until
molecules are evenly
distributed
homogeneous state/
matter is made up of small, discrete equilibrium
molecules/ particles in constant random
motion Molecules/ Particles the net movement of molecules moving
from a region of higher concentration to a
region of lower concentration to reach
Diffusion equillibrium (the movement is down a
concentration gradient)
substances are moved
without the use of energy
the difference in concentration between two
regions is known as the concentration
a dilute solution contains more water water potential is a measure of the gradient
molecules than a concentrated solution, tendency of water to move from one place Concentration Gradient the steeper the concentration gradient,
hence it has a higher water potential to another the faster the movement of the
the passage of water from a region of higher molecules
water potential through a particular
permeable membrane to a region of lower
water potential Movement of Substances in
Living Things
medium surrounding cell has movement of carbon dioxide
higher water potential than during photosynthesis
cell diffusion of chemical substances important
in keeping living organisms alive and transpiration
more water will enter the cell growing
than will leave Hypotonic Solution movement of oxygen and
carbon dioxide in animals
net result: water will enter --> cell
becomes turgid (plant)/ bursts
(animal)
Osmosis
medium is exactly the same
water potential as the cell allows all molecules to pass
Permeable through it
amount of water going in is
the same as the water going Isotonic Solution only allows certain
out molecules to pass through
it
net result: no movement -->
cell stays the same size plasma membrane
(surrounding the cell)
medium has lower water
potential than cell small molecules like oxygen,
Partially Permeable water, carbon dioxide,
more water will leave the cell ammonia, glucose, amino
than will enter acids, etc. can pass through
Membranes
occurs when water is drawn out of Hypertonic Solution
larger molecules like sucrose,
the cell and into the extracellular starch, protein, etc. cannot pass
fluid net result: water will leave -->
cell becomes plasmolysed through
the [plant] cell membrane Plasmolysis (plant)/ crenated (animal) separates the internal cell
shrinks away from its cell environment from the external
wall environment
controls passage of
molecules across
membranes
You might also like
- War - Original PoemDocument2 pagesWar - Original PoemGabriellaNo ratings yet
- Life & Death - Original PoemDocument1 pageLife & Death - Original PoemGabriellaNo ratings yet
- NutrientsDocument1 pageNutrientsGabriellaNo ratings yet
- Unit of Life - CellsDocument1 pageUnit of Life - CellsGabriellaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Int Esws at Y9 Workbook Answers TTPPDocument37 pagesInt Esws at Y9 Workbook Answers TTPPChrystal GraceNo ratings yet
- PACKAGING OF MEAT AND MEAT PRODUCTSDocument46 pagesPACKAGING OF MEAT AND MEAT PRODUCTSrajesh bethaNo ratings yet
- 01Document97 pages01cheery1No ratings yet
- Set 2 MSDocument7 pagesSet 2 MSsanjith4arisNo ratings yet
- Astm A1007 PDFDocument9 pagesAstm A1007 PDFSeahorseNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual Machine Shop 1 PDFDocument59 pagesLaboratory Manual Machine Shop 1 PDFVinz Bryan AlmacenNo ratings yet
- Predampening Benefits Shotcrete Quality and SafetyDocument3 pagesPredampening Benefits Shotcrete Quality and SafetySantosh UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4: Standardization of Sodium Thiosulphate Solution With A Standard Potassium Dichromate SolutionDocument20 pagesExperiment No. 4: Standardization of Sodium Thiosulphate Solution With A Standard Potassium Dichromate Solutionshiam50% (2)
- Sodium Carbonate Production from Trona OreDocument17 pagesSodium Carbonate Production from Trona OreVaanNo ratings yet
- Rohm & Haas Amberlite IRN 150 LDocument2 pagesRohm & Haas Amberlite IRN 150 LMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Project Content ChemistryDocument6 pagesProject Content ChemistryPrathmesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: by Bibhabasu MohantyDocument54 pagesAir Pollution: by Bibhabasu MohantyJaned PerwiraNo ratings yet
- Hygene EPIHANIOU Faucets INT EN-1 PDFDocument55 pagesHygene EPIHANIOU Faucets INT EN-1 PDFattikourisNo ratings yet
- UT ProcedureDocument14 pagesUT Procedurepoodook100% (3)
- Chemistry Lecture Planner - Prayas 2022 - Complete Lecture Planner - Early Dropper Batch JEE - Chemistry PlannerDocument2 pagesChemistry Lecture Planner - Prayas 2022 - Complete Lecture Planner - Early Dropper Batch JEE - Chemistry PlannerPradeep Yadav100% (1)
- Labreport 4 Biophysical Chem LowryDocument15 pagesLabreport 4 Biophysical Chem LowryJerry CaldwellNo ratings yet
- Jin Shuren: 1. The Present Situation of Chinese Modified StarchDocument13 pagesJin Shuren: 1. The Present Situation of Chinese Modified StarchTatiana AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Coaxial Cables: Section VDocument6 pagesCoaxial Cables: Section VFrancisco CamposNo ratings yet
- MSS SP-44-2016 Steel Pipeline FlangesDocument52 pagesMSS SP-44-2016 Steel Pipeline Flangesarnoldbatista55100% (2)
- My New ResumeDocument4 pagesMy New ResumeSurajNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesLearning ObjectivesALEX CLEVER ALEJO HOYOSNo ratings yet
- Biology For QLD An Aust Perp 3E Units1!2!9780190310219 Sample Chapter 3 Low Res SecureDocument38 pagesBiology For QLD An Aust Perp 3E Units1!2!9780190310219 Sample Chapter 3 Low Res SecureRocil Clyde LumbayNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant activity of phenolic pigments from cocoa hullsDocument6 pagesAntioxidant activity of phenolic pigments from cocoa hullsdjguevara1No ratings yet
- Lab Manual 11 Infrared SpectrosDocument5 pagesLab Manual 11 Infrared SpectrosLuca Selva CampobassoNo ratings yet
- Objectives Identify The Two Main Classes of Vitamins. List Seven Minerals Your Body Needs inDocument28 pagesObjectives Identify The Two Main Classes of Vitamins. List Seven Minerals Your Body Needs inyosysilalahiNo ratings yet
- Dow Carbowax PEGs PDFDocument12 pagesDow Carbowax PEGs PDFMattNo ratings yet
- Heavy Duty Slurry Pumps Specs & Performance DataDocument12 pagesHeavy Duty Slurry Pumps Specs & Performance DataMaximiliano BettarelNo ratings yet
- Group II Cation AnalysisDocument4 pagesGroup II Cation AnalysisClare CaspeNo ratings yet
- Catalog Copeland KCLDocument40 pagesCatalog Copeland KCLIsidro MendozaNo ratings yet
- Tai RaporDocument39 pagesTai RaporerdemersoyNo ratings yet