Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Non Metals Questions
Uploaded by
KelumCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Non Metals Questions
Uploaded by
KelumCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 1
The table below gives some information about the halogens:
Element
Atomic number
Molecular formula
Bond length/nm
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Astatine
17
35
53
85
C12
Br2
I2
At2
0.20
0.23
0.26
0.29
Note:
Bond length = distance between atoms in a molecule
nm = nanometres (10-9 metres)
Bond energy = energy needed to break the bond in the molecule
(a)
As the atomic number in the halogens increases, what happens to the
(i)
Bond energy/
kJ per mole
240
195
150
bond length?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) bond energy?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
What do you think is the bond energy in astatine?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Describe the relationship between bond length and bond energy as the halogen series is descended.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
The solubility of the halogens in water may be summarised as follows:
chlorine
bromine
iodine
dissolves fairly readily
dissolves slightly
almost insoluble
Chemical reactions occur when the halogens dissolve in water.
(d)
What is likely to be the reaction of astatine with water?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 1 CONTINUED
(e)
List the four elements in order of reactivity, placing the most reactive first.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(f)
Does your order of reactivity seem to fit with the bond energies?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
Give a reason for your answer.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 12
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 2
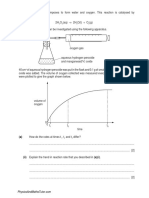
When sulphur is heated in air, a colourless, poisonous gas with an unpleasant, choking smell is formed. If this
gas is collected, dried, then cooled to below 10oC, it forms a colourless liquid. Dry pH paper dipped into this
liquid does not change colour, but damp pH paper dipped into the liquid shows a pH of less than 7.
(a)
What is the name of the colourless gas?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
What is the boiling point of the colourless liquid?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Why does the colourless liquid not affect the dry pH paper?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d)
When damp pH paper is used, the colourless liquid becomes acidic. How do you know this?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
If the colourless gas from above is reacted with oxygen at 450oC and in the presence of vanadium pentoxide,
sulphur trioxide forms as a colourless gas, which then cools to colourless crystals. If water is added to
the crystals, a fiercely exothermic reaction takes place and sulphuric acid forms.
(e)
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between the colourless gas named in part (a)
with oxygen.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(f)
The vanadium pentoxide is recovered after the above reaction.
What is its purpose in the reaction?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(g)
What is meant by an exothermic reaction?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(h)
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of sulphur trioxide with water.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(i)
In fact, this reaction is much too exothermic to carry out safely. It would spray sulphuric acid all
around the room. In practice, the sulphur trioxide is added to 98% sulphuric acid, where it reacts
with the 2% water present to form more sulphuric acid. Why is the reaction much safer when carried
out like this?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 13
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 3
The diagram below shows an apparatus that can be used to react chlorine with iron.
iron wire
excess chlorine
dry chlorine
product
HEAT
(a) (i)
Describe the appearance of the Group VII element chlorine.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) What compound is formed during the reaction that takes place?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Complete and balance the following symbol equation for the chemical change that takes place.
..... Fe (s) +
............ (g)
..... FeCl (s)
[2]
(iv) Give one reason why this reaction must be carried out in a fume cupboard.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
The element iodine is below chlorine in Group VII of the Periodic Table. If iodine was allowed to
react with iron wire, state whether you would expect this reaction to be more vigorous, less vigorous
or about the same as the reaction between chlorine and iron wire.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Group I elements also react with Group VII elements.
(i) Complete and balance the symbol equation for the reaction between sodium and bromine.
..... Na (....)
Br (....)
2
.....NaBr (s)
[2]
(ii) If the following pairs of elements were allowed to react together, choose the pair that would be
most reactive and give an explanation for your choice.
lithium and fluorine
sodium and chlorine
potassium and chlorine
potassium and fluorine
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 3 CONTINUED
The most reactive pair is: .............................................................
[1]
Give an explanation for your choice.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 11
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 4
For each of the following pairs of substances describe how you would distinguish between them by giving
one chemical test in each case.
Describe your observation on both substances.
(i)
Nitrogen and oxygen.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) Hydrogen and chlorine.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(iii) Carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(iv) Water and ammonia solution.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
TOTAL / 10
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 5
Sulphuric acid is manufactured industrially by the contact process. During the early part of the process, sulphur
is reacted with oxygen to give an oxide A. This substance is then converted into sulphur trioxide by reacting A
with the element B.
(a) (i)
Calculate the simplest formula of the oxide of sulphur A from the following information.
3.2 g of sulphur gave 6.4 g of the oxide A.
Please show how you worked out your answer.
Ar(S) = 32; Ar(O) = 16.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(ii) Name the element B.
(b)
......................................[1]
The reaction between A and B to give the gas sulphur trioxide is reversible. Explain the term reversible
and complete and balance the chemical equation.
(i) A reversible reaction is
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Complete and balance the equation;
.............. + ............
(c)
....... SO3
[2]
Both oxygen and sulphur are in the same group of the Periodic Table. One method for both to react
is to become an ion X2-. Explain in terms of their electronic structures why oxygen is more reactive
towards this change than sulphur.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 6
Plants need many substances for healthy growth and for the chemical reactions which occur within them. Most
of these substances are absorbed in solution in water through the roots. The three main essential elements which
plants need are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. These elements may be supplied naturally by the soil, but
often we need to add one or more of them in the form of fertilisers. A fertiliser is sold in a bag labelled with its
name followed by three numbers which indicate, respectively, the percentages of nitrogen, phosphorus and
potassium present. e.g. Regular 20 10 12 means that the fertiliser is called regular and contains 20%
nitrogen, 10% phosphorus and 12% potassium. Such fertilisers are known as NPK fertilisers. Here is a list of
some common fertilisers.
Universal 15 15 15
Extra grass 29 5 5
Double season PK for fertile soils 0 20 20
Maincrop potato 10 10 15 + 4.5 Mg
Concentrated maincrop potato 15 15 19
Granphos 2 40 0
Barley for high potash clay soils 29 13 0
Winter wheat 9 23 18
(a)
Why are these fertilisers known as NPK fertilisers?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)
Name the essential element which:
(i)
is already present in fertile soil and so does not need adding.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) favours green growth (e.g. grass).
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) potatoes need in extra high concentration.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Name an element, other than nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium, which potatoes need.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d)
What percentage of nitrogen would be supplied by a fertiliser of pure ammonium nitrate NH4 NO3?
(Relative atomic masses: H = 1, N = 14, O = 16).
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 6 CONTINUED
(e)
A farmer was offered a choice of potassium nitrate or urea as a fertiliser. Although much more
expensive per gram of nitrogen, he chose potassium nitrate. Give one reason which may have influenced
his choice.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 10
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 7
Phosphorus (P) is directly below nitrogen in the periodic table.
(a)
Write down the electronic configuration of phosphorus.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
Write down the formula of the compound you would expect phosphorus to form with hydrogen, and
use a dot and cross diagram to show how it is formed.
Formula .................................................................................................................................................. [3]
(c) (i)
Would you expect this compound to be a solid, a liquid or a gas at room temperature?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Explain your reasons.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d)
Give one use for phosphorus-containing compounds
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 8
(a)
Solid sulphur consists of rings of eight atoms.
Fill in the gaps in the table below to show the changes in appearance and structure of sulphur
when it is heated.
appearance
Yellow solid
Melts to form a _____ _____ liquid
structure
Rings of 8 atoms
Boils
Separated sulphur atoms and groups of atoms
[4]
(b)
Sulphur exists in two crystalline forms.
What are different crystalline forms of the same element known as?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
When molten sulphur is cooled slowly, needle-like crystals form under the surface.
Why do some rocks contain crystals when they are split open?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d)
These crystals change slowly to another form with rhombic-shaped crystals as they cool.
(i) What changes are seen as the needle-like crystals cool?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) What changes would be seen in the rhombic crystals as they cool?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 9
Medium Demand Questions
Tooth decay in the UK is a serious problem. About 7000 sets of dentures are supplied each year to school
children alone. This is a waste of healthy teeth and money.
It has been suggested that the presence of fluoride ions, F , in drinking water helps to prevent tooth decay.
The data in the following table come from six different areas of the country, where fluoride ions occur naturally
in the water supply.
DMF teeth per 100 children
430
350
240
720
250
300
Note:
(a)
fluoride concentration/ppm
0.5
0.9
2.6
0.1
1.9
1.2
DMF = decayed, missing or filled
ppm = parts per millionS
On the chart below plot a graph of DMF against ppm of fluoride concentration.
[2]
800
DMF teeth per 100
children
600
400
200
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
Fluoride concentration/ppm
(b)
Does your graph support or contradict the suggestion that fluoride ions in drinking water help to
prevent tooth decay?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 9 CONTINUED
It has been found in a much wider study from many more areas in the UK that similar results are obtained.
Also, the presence of small amounts of fluoride in the water does not appear to be at all harmful. As a result,
it has been suggested that in areas where there is no natural fluoride in the water, drinking water
should undergo fluoridation i.e. should have fluoride added.
(c)
Give a reason why fluoridation might be a good idea in areas with no natural fluoride in the
drinking water.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d)
Give one argument which might be used against fluoridation of water supplies.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(e)
Suggest two other ways, other than fluoridation of water, in which people could take small amounts
of fluoride ions
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 10
Medium Demand Questions
The table below gives some information about six different gases.
Formula of molecule
CH4
NH3
N2
O2
CO2
SO2
Mass of one mole of molecules/g
16
17
28
32
44
64
Volume occupied by 1g at rtp/dm3
1.50
1.40
0.86
0.76
0.54
0.38
rtp = room temperature and pressure
relative atomic masses: H=1, C=12, N=14, O=16, F=19, Ar=40
(a)
Give the name of the molecules listed in the first column.
CH4 = ................................................................................................................................................... [1]
NH3 = ................................................................................................................................................... [1]
N2 = ................................................................................................................................................... [1]
O2 = ................................................................................................................................................... [1]
CO2 = ................................................................................................................................................... [1]
SO2 = ................................................................................................................................................... [1]
On the chart below plot a graph of volume against mass of one mole.
[2]
1.5
1.3
Volume at rtp/dm3
(b)
1.1
0.9
0.7
0.5
0.3
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
mass of one mole/g
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 10 CONTINUED
(c)
Use your graph to find the volume at rtp occupied by:
(i)
1g of ethene, C2H4 .................................................................................................................................. [1]
(ii) 1g of argon .............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(d) (i)
What is the mass of one mole of molecules of a gas for which 1g at rtp occupies 0.52 dm3?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) If the molecule is made up of nitrogen and oxygen only, what is its formula?
Show your working.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(e)
Determine the volume at rtp occupied by 1g of hydrogen fluoride, HF.
Show your working.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [5]
TOTAL / 19
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 11
The following table contains some information about Group VII of the Periodic Table.
Element
Formula
Atomic number
Melting point (oC)
fluorine
F2
9
-223
chlorine
C12
17
-103
bromine
Br2
35
-7
iodine
I2
53
114
(a)(i)
Colour
pale yellow
yellow-green
red-brown
purple-black
Name the element with the lowest melting point.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Chlorine is a diatomic gas. Explain the meaning of diatomic.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Give the electronic structure of chlorine.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iv) Explain how chloride ions are formed from chlorine atoms.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)
Astatine, At, is another member of Group VII with an atomic number of 85.
(i)
Give the formula for astatine.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Describe the appearance of astatine.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Give the number of electrons in the outer shell of astatine.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iv) Astatine is expected to form a compound with hydrogen in a similar way to chlorine and hydrogen.
By means of a labelled diagram, show how the atoms are bonded together. Name this type of bonding.
Diagram
[2]
Type of bonding. .................................................................................................................................. [1]
TOTAL / 11
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 12
Medium Demand Questions
The table below shows some properties of elements A, B, C, D and E.
(The letters are not chemical symbols.)
Element
A
B
C
D
E
Melting point
(oC)
119
-7
98
1083
-259
Boiling point
(oC)
444
59
883
2336
-253
Conducts
heat
no
no
yes
yes
no
Brittle
Reaction with water
Shiny
yes
no
no
no
no
insoluble
slightly soluble
reacts
insoluble
slightly soluble
no
no
yes
yes
no
(a)
Give the letter of the element which is a liquid under room conditions.
(b)
Give the letters of all the elements that are non-metals giving two reasons for your answer.
(i)
The elements that are non-metals are
...................................[1]
..........................................[3]
(ii) Reasons.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Elements A and E when heated can react together to give a gas. Name the type of bonding you
would expect this compound to have. Give a reason for your answer.
Type of bonding
......................................................[1]
Reason.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d)
Gas E has no colour or smell. It burns in oxygen giving a vapour which condenses on a cold surface
as a colourless neutral liquid. The gas E has a number of important uses including the industrial
manufacture of ammonia. Name the gas E.
Gas E is
.....................................[1]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 13
Diamond and graphite are two allotropes of the element carbon.
(a)
Explain the meaning of allotropy
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
Draw the structure of both diamond and graphite.
(i) Diamond
(ii) Graphite.
[4]
(c)
Use the above structures to explain the following.
(i)
Diamond is a very hard substance often used to cut and engrave glass.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) Graphite conducts electricity and is used as electrodes in industry and as positive terminals in batteries.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 14
Medium Demand Questions
The following box contains non-metals and their atomic numbers.
hydrogen 1,
helium 2,
carbon 6,
nitrogen 7,
oxygen 8,
fluorine 9,
sulphur 16,
chlorine 17,
bromine 35.
Use only elements from these given non-metals to answer the following questions.
Each element may be used once, more than once or not at all.
(a)
Name one element which is
(i)
(b)
a liquid at room temperature,
.....................................[1]
(ii) has four electrons in its outer shell,
....................................[1]
(iii) has the electronic structure 2, 8, 7
....................................[1]
(iv) forms an ion with the formula X2-.
....................................[1]
Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to give the gas ammonia.
Give the formula and the type of bonding in ammonia.
(c)
Formula.
....................................[1]
Type of bonding.
....................................[1]
Name the element which readily burns in air with a pale blue flame giving off an
unpleasant smelling gas which is one of the main causes of acid rain.
The element is
(d)
....................................[1]
Two elements X and Y form compounds with hydrogen with the formulae H2X and YH4.
Name the elements X and Y.
Element X is
....................................[1]
Element Y is
....................................[1]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 15
(a) Give two physical properties of hydrogen.
(i) ............................................................................................................................................................. [1]
(ii) . ........................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) Some pure hydrogen was carefully burnt on a cold surface as shown in the diagram.
hydrogen
burning
Pure dry
hydrogen
cold surface
drops of liquid
A
glass
tube
(i)
Name two chemicals that could be used to make hydrogen in the laboratory.
................................................. and ....................................................
[2]
(ii) Give the precaution that must be taken before hydrogen is ignited.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii)
Name the liquid A.
......................................[1]
(iv)
Give a simple chemical test and observation to confirm the identity of the liquid.
Test. ................................................................................................................................................................. [1]
Observation. .........................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c) One of the first uses of hydrogen was in airships since it is the lightest of all gases.
Unfortunately it reacts violently with the oxygen in the air which has led to a number of disasters.
Name the safer gas which is used in present day airships.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 16
The table below contains some information about four different substances A, B, C and D.
(The letters are not chemical symbols.)
Study the table carefully and answer the given questions.
(a)
Substance
Boiling point (oC)
A
B
C
D
above 500
below 500
above 500
above 500
Conducts electricity when
solid
yes
no
no
no
Conducts electricity when
melted
yes
no
no
yes
State which substance is most likely to be:(i)
diamond,
...............................[1]
(ii) iodine,
...............................[1]
(iii) copper .
...............................[1]
(b)
The four substances are diamond, copper, iodine and sodium chloride. Which of these substances
best fits the following descriptions?
(i)
Atoms bonded by sharing electrons to form small molecules.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Atoms bonded by sharing electrons to form giant covalent structures.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Atoms bonded by electron transfer to form giant ionic structures.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
During the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride the chloride ion, Cl-, is attracted towards the
positive electrode and releases chlorine gas, Cl2.
(c)
(i)
Explain the meaning of the term electrolysis.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Complete the equation that takes place at the positive electrode.
__ Cl- C12 ________
[2]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 17
The following table gives some information about gases which are found in the air.
Gas
nitrogen
oxygen
argon
carbon dioxide
neon
helium
krypton
xenon
(a)
Boiling point/oC
-196
-183
-186
-40 (sublimes)
-246
-269
-153
-108
Soluble in water?
no
slightly
no
fairly
no
no
no
no
As well as the above, which other gas is normally found in the air?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
Which of the above gases becomes liquid at the lowest temperature?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
Carbon dioxide sublimes at 40oC. What would you observe if carbon dioxide gas was cooled
to this temperature?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d)
If a mixture of liquid nitrogen and liquid oxygen was allowed to warm up, which one would boil first?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(e)
What is the name of the process which allows nitrogen and oxygen to be separated from liquid air
by warming?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(f)
State the approximate percentages by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in the air.
[2]
Nitrogen ................................%
Oxygen .................................%
(g)
The percentages of nitrogen and oxygen in the air which has been boiled out of water are different to
those given in part (f). Why is this?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
QUESTIONSHEET 17 CONTINUED
(h)
Nitrogen and oxygen are both obtained by allowing liquid air to warm up. Why is oxygen more
expensive than nitrogen?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(i)
Green plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. How can some green plants continue to live
under water?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 11
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 18
The flow chart shows some of the reactions and changes involved in carbon compounds.
carbon
monoxide
CO
carbon dioxide
CO2
solution B
goes milky/
cloudy
calcium
carbonate
D
plants
E
solid
A
(a) Name the chemical substances labelled A and B .
A is
...............................................
[1]
B is
...............................................
[1]
(b) Name the different processes C, D and E.
C is
...............................................
[1]
D is
...............................................
[1]
E is
...............................................
[1]
(c) How can carbon dioxide be converted into carbon monoxide?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d) Give one important use of carbon dioxide.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(e) Carbon is often used as a reducing agent. When a mixture of carbon and copper oxide are heated the
copper oxide is reduced to copper. Complete and balance the equation for the reaction.
C + ..... CuO
(f)
... Cu + ..........
[2]
Carbon and silicon both belong to Group 4 of the Periodic Table of elements. They form oxides
with similar formulae CO2 and SiO2. In terms of structures explain why carbon dioxide is a gas at
room conditions but silicon dioxide has a very high melting point.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 12
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 19
Use The Periodic Table to answer this question.
(a)
Give the symbol for the element
(i)
oxygen
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii)
potassium
..............................................................................................................................................................................
(b)
Give the name of the element with the symbol
(i)
[1]
..............................................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Na
..............................................................................................................................................................................
(c)
Complete the following table.
Substance
zinc oxide
iron sulphide
sodium hydroxide
(d)
[3]
Chemical formula
ZnO
FeS
NaOH
KC1
Elements present
zinc and oxygen
potassium and chlorine
The chemical formula for carbon monoxide is CO.
(i)
How many different elements are represented in carbon monoxide?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Give the total number of atoms the formula CO represents.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(e)
The chemical formula for sulphuric acid is H2SO4.
(i)
How many different elements are present in sulphuric acid?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Give the total number of atoms present in H2SO4.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
NON-METALS
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 20
The table below gives some information about halogens.
Element
Fluorine
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Astatine
(a)
Atomic symbol
F
C1
Br
I
At
Atomic number
9
17
35
53
85
Melting point/oC
-220
-101
-7
+114
Boiling point/oC
-188
-35
+58
+183
As the atomic number increases what happens to the
(i)
melting point?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) boiling point?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
Are these elements solids, liquids or gases at room temperature (20oC)?
(b)
(i)
fluorine is a ............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(ii) chlorine is a ............................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iii) bromine is a ............................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iv) iodine is a ................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(c)
In which physical state do you think astatine exists at room temperature?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
The behaviour of the halogens with water may be summarised as follows:
fluorine
chlorine
bromine
iodine
(d)
violent reaction
dissolves fairly readily
dissolves slightly
almost insoluble
What is likely to be the behaviour of astatine with water?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(e)
List the five elements in order of reactivity, placing the most reactive first.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 10
You might also like
- Question Paper Paper 2CR June 2014 PDFDocument20 pagesQuestion Paper Paper 2CR June 2014 PDFLayonNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction PPsDocument23 pagesRate of Reaction PPstcs202231No ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 22Document19 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 22Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- 2015 Jan Chem 1Document36 pages2015 Jan Chem 1kosala naveen wijekulasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Mixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionDocument23 pagesMixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionYaakkwNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 19Document16 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 19Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Plants Questions ks3Document4 pagesPlants Questions ks3Eshal AmirNo ratings yet
- 4CH0 1C Que 20140114Document32 pages4CH0 1C Que 20140114Sahil KananiNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen & Fertilisers 4 QPDocument8 pagesNitrogen & Fertilisers 4 QPUsha PerumalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Past Paper 1C (New Syllabus)Document28 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Past Paper 1C (New Syllabus)Aneesh JatarNo ratings yet
- 4CH0 1C ChemistryDocument28 pages4CH0 1C ChemistryAbrar JahinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Jan2012 Unit-3b QPDocument16 pagesChemistry Jan2012 Unit-3b QPAkila RahmanNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Document9 pagesRate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Tomasz OstrowskiNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 2 QPDocument7 pagesIonic Bonding 2 QPHuseyn AgazadeNo ratings yet
- A-Level Paper 3 pp8Document19 pagesA-Level Paper 3 pp822S48 SUNDARAM RAMASUBBU RAKSHANo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Document20 pagesA-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Jesus ChristNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Mid Exam 2019Document12 pagesClass 10 Mid Exam 2019Khalid HassanNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Unit 6 June 2012 Question PaperDocument16 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Unit 6 June 2012 Question PaperCharlene ChiaNo ratings yet
- Chlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesChlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and Answersideal writersNo ratings yet
- Module 806Document18 pagesModule 806Hema LataNo ratings yet
- Energetics QuestionsDocument37 pagesEnergetics QuestionsG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- 4CH0 2CR Que 20160615Document20 pages4CH0 2CR Que 20160615abhayNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6Document148 pagesEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6AbdulRahman MustafaNo ratings yet
- Manufacture & Uses of Sulfur 1 QPDocument10 pagesManufacture & Uses of Sulfur 1 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Sulfur 240128 144812Document11 pagesSulfur 240128 144812omarkbkb2007suiNo ratings yet
- Energetics QuestionsDocument20 pagesEnergetics QuestionsKelum100% (1)
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter 2 QPDocument11 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter 2 QPDương TửNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Group 7Document9 pagesTopic 4 - Group 7Abirame SivakaranNo ratings yet
- Revision 3Document4 pagesRevision 3Nur HidayahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1a N C Principles of Chemistry State of Matter Atoms Atomic StructureDocument25 pagesChemistry 1a N C Principles of Chemistry State of Matter Atoms Atomic StructuresechosNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE May 2012 Chemistry Paper - 2Document16 pagesEdexcel IGCSE May 2012 Chemistry Paper - 2Coolman PoonNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument14 pagesBondingMuizzudin AzaliNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Practice Paper 4Document22 pagesPaper 3 Practice Paper 4EmoryNo ratings yet
- Amount of Substance 1 QPDocument10 pagesAmount of Substance 1 QPHajhoj CellNo ratings yet
- O4 AlkenesDocument58 pagesO4 Alkenes/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Acid-Base Exam Questions 3Document18 pagesAcid-Base Exam Questions 3Jake RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Q1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument34 pagesQ1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisChee Beng Yeap100% (1)
- 4CH0 2C Que 20150609 PDFDocument20 pages4CH0 2C Que 20150609 PDFrana0% (1)
- Photosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsEva SugarNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-05Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-05lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Topic 3Document11 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Topic 3locopocpNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Unit 3 June 2012 Question PaperDocument16 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Unit 3 June 2012 Question PaperCharlene ChiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsAmanda AnushaNo ratings yet
- 2 HoursDocument17 pages2 HoursOTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- 1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byDocument9 pages1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byKelvin DenhereNo ratings yet
- O14 Organic SynthesisDocument17 pagesO14 Organic Synthesis/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 4CH0 2C Que 20140116Document20 pages4CH0 2C Que 20140116Lalith77No ratings yet
- 10 Homework PackDocument10 pages10 Homework PackatasayNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Chapter 12 A LevelDocument6 pagesUnit Test Chapter 12 A LevelastriNo ratings yet
- Water and HydrogenDocument7 pagesWater and HydrogenOkumu KevinsNo ratings yet
- ChemicalanalysisDocument90 pagesChemicalanalysismuhammadshadid4No ratings yet
- Redox Questions Igcse ChemDocument7 pagesRedox Questions Igcse ChemCaylinNo ratings yet
- Redox 2 QPDocument7 pagesRedox 2 QPPramitaNo ratings yet
- Mytest 1Document8 pagesMytest 1Aditi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Balanced Equations & Associated Calc's 05 QPDocument8 pagesBalanced Equations & Associated Calc's 05 QPlmao lmaoNo ratings yet
- Halogenoalkanes Alcohol and Spectra Unit 2Document8 pagesHalogenoalkanes Alcohol and Spectra Unit 2Barminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- Advanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationFrom EverandAdvanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationNo ratings yet
- Ligand Coupling Reactions with Heteroatomic CompoundsFrom EverandLigand Coupling Reactions with Heteroatomic CompoundsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Bulletproof Wireless Security: GSM, UMTS, 802.11, and Ad Hoc SecurityFrom EverandBulletproof Wireless Security: GSM, UMTS, 802.11, and Ad Hoc SecurityNo ratings yet
- Front Page (Mathematics B P-1)Document1 pageFront Page (Mathematics B P-1)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Front Page (Chemistry P-2)Document1 pageFront Page (Chemistry P-2)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Front Page (English Language B)Document1 pageFront Page (English Language B)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Front Page (Mathematics B P-1)Document1 pageFront Page (Mathematics B P-1)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Front Page (Chemistry P-2)Document1 pageFront Page (Chemistry P-2)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Front Page (English Language B)Document1 pageFront Page (English Language B)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Front Page (Mathematics B P-2)Document1 pageFront Page (Mathematics B P-2)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Reversible ReactionDocument3 pagesWorksheet Reversible ReactionG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2011: GCE O Level English Language (7161/01)Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2011: GCE O Level English Language (7161/01)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Mock 1 Mock 2 Assignment O Predicte Name of Students Level Grade D Grade ASDocument4 pagesMock 1 Mock 2 Assignment O Predicte Name of Students Level Grade D Grade ASG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Serial Name of Students TimeDocument1 pageSerial Name of Students TimeG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Grade Xii Chemistry: Teacher Kawsar SabrinaDocument1 pageGrade Xii Chemistry: Teacher Kawsar SabrinaG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Front Page (English Language B)Document1 pageFront Page (English Language B)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Paper: Academic Session: 2019-2020Document7 pagesAssignment Paper: Academic Session: 2019-2020G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Serial Name of Students TimeDocument1 pageSerial Name of Students TimeG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Name: Subject: Chemistry Paper 1 Class: XI Roll: Teacher: G.M. Ali Kawsar & Sabrina Mahbub Sec: Full Marks: 40 Marks Obtained: Date: Duration: 1 HourDocument1 pageName: Subject: Chemistry Paper 1 Class: XI Roll: Teacher: G.M. Ali Kawsar & Sabrina Mahbub Sec: Full Marks: 40 Marks Obtained: Date: Duration: 1 HourG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Reversible ReactionDocument3 pagesWorksheet Reversible ReactionG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Class Test 2 (Bonding) : Academic Session: 2018-2019Document4 pagesClass Test 2 (Bonding) : Academic Session: 2018-2019G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Name: Subject: Chemistry Paper 1 Class: XI Roll: Teacher: G.M. Ali Kawsar & Sabrina Mahbub Sec: Full Marks: 40 Marks Obtained: Date: Duration: 1 HourDocument1 pageName: Subject: Chemistry Paper 1 Class: XI Roll: Teacher: G.M. Ali Kawsar & Sabrina Mahbub Sec: Full Marks: 40 Marks Obtained: Date: Duration: 1 HourG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2011: GCE O Level English Language (7161/01)Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2011: GCE O Level English Language (7161/01)G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Final Q Class 8 2016Document5 pagesFinal Q Class 8 2016G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- COVID19Document1 pageCOVID19G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- 7161 01 Que 20110107 PDFDocument16 pages7161 01 Que 20110107 PDFAbdulrahmaan NazardeenNo ratings yet
- Mastermind Science Fair FormDocument2 pagesMastermind Science Fair FormG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Class Test - Class X Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument9 pagesClass Test - Class X Magnetism and ElectromagnetismG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- The 4.5 Billion UK Confectionary Industry Is Dominated by Three Big FirmsDocument1 pageThe 4.5 Billion UK Confectionary Industry Is Dominated by Three Big FirmsG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan EnglishDocument4 pagesLesson Plan EnglishG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Neven El Shater E-TicketDocument1 pageNeven El Shater E-TicketG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2014Document14 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2014Lalith77No ratings yet
- Class X Test QuestionDocument9 pagesClass X Test QuestionG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet