Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sleep
Uploaded by
marice marquez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesfactors affecting sleep and its derivatives
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfactors affecting sleep and its derivatives
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesSleep
Uploaded by
marice marquezfactors affecting sleep and its derivatives
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SLEEP
Basic human need
Historically- state of unconsciousness
Recently- an altered state of
consciousness
Is a complex biological rhythms
Somnology- the study of sleep
Biological rhythms- exist in plants,
animals, and humans
Sleep disorder- irregular cycling and/or
absent sleep stages.
Sleep architecture- the basic organization
of normal sleep.
TYPES OF SLEEP
1. NREM (NON-RAPID-EYEMOVEMENT) SLEEP
Activity in the RAS is inhibited.
About 75% to 80% of sleep during a
night is NREM sleep.
Stages
Stage I- is the stage of very light
sleep and lasts only a few minutes.
Feels drowsy and relaxed, the eyes roll
from side to side, and the heart and
respiratory rates drop slightly.
Stage II- is the stage of light sleep
during which body processes continue
to slow down. The eyes are generally
still, the heart and respiratory rates
decrease slightly, and the body
temperature falls. 10 to 15 minutes;
44% to 55% of total sleep.
Stage III and IV- are the deepest
stages of sleep, differing only in the
percentage of delta waves. During
deep sleep or delta slee, the sleepers
heart and respiratory rates drop 20%
to 30% below exhibited during waking
hours.
2. REM (RAPID-EYE-MOVEMENT)
SLEEP
Usually recurs about every 90 minutes
and lasts 5 to 30 minutes.
Most dreams takes place.
Brain is slightly active.
Sometimes called PARADOXICAL
SLEEP.
NEWBORNS
Sleep 16 to 18 hours a day.
REM sleep immediately. ( active
sleep during the newborn period).
NREM sleep (quiet sleeping during
the newborn period).
Sleep cycle is about 50 minutes.
INFANTS
Awaken every 3 to 4 hours, eat,
and then sleep.
Sleep through the night from
midnight to 5 am.
Takes two naps. 14 to 15 hours of
sleep in 24 hours.
Self-soothers- falls asleep
independently.
Signallers- parental assistance to
sleep.
TODDLERS
1 to 3 yrs old= 12 to 14 hours of
sleep.
Nightmares or nighttime fears are
common.
PRESCHOOLERS
3 to 5 years old= 11 to 13 hours of
sleep/night.
Stage of dislike bedtime
Limiting TV will reduce nightmares.
SCHOOL-AGE CHILDREN
5 to 12 years old=10 to 11 hours of
sleep.
Decrease in sleep due to some
factors.
ADOLESCENT
12 to 18 years old= 9 to 10 hours
of sleep/night.
Nocturnal emissions wet dreams
(orgasm and emission of semen
during sleep).
ADULTS
7 to 9 hours of sleep.
Need sleep- drowsy & falling
asleep.
Women disrupted sleeppregnancy, menses, &
perimenopausal period.
ELDERS
65 to 75 years old.
7 to 9 hours of sleep
Dementia- sundown syndrome
( agitation, anxiety, aggression,
delusions).
FACTORS AFFECTING SLEEP
Sleep quality- is a subjective characteristic
and is often determined by whether a person
wakes up feeling energetic or not.
Quantity of sleep- is the total time the
individual sleeps.
ILLNESS
Causes pain or physical distress
Needs more sleep
Due to some illness REM sleep or
delta sleep decreases. And sleep is
affected.
ENVIRONMENT
Can promote or hinder sleep.
Noise, light and discomfort may
reduce sleep.
LIFESTYLE
Irregular morning and night time
schedule can affect sleep.
Avoid doing homework before or
after bed time.
EMOTIONAL STRESS
Number one cause of short-term
sleeping difficulties.
STIMULANTS AND ALCOHOL
Caffeine act as a stimulant of the
central nervous system.
Alcohol disrupt REM sleep.
DIET
Weight gain- reduced total sleep,
broken sleep, earlier awakening.
Weight loss- increase in sleep time,
less broken sleep.
Cheese and milk- induced sleep
SMOKING
Smokers- light sleepers
Stopped smoking improves sleep.
MOTIVATION
Can increase alertness in some
situations
MEDICATIONS
Beta blockers cause insomnia and
nightmares.
Drugs disrupts sleep or cause
excessive sleep.
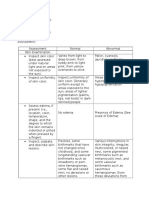
COMMON SLEEP DISORDERS
INSOMNIA
Inability to obtain a sufficient
quality or quantity of sleep.
Inability to fall asleep or remain
asleep.
Acute insomnia- last one to several
nights.
Chronic insomnia- longer than a
month.
Older age and female gender.
EXCESSIVE DAYTIME SLEEPINESS
HYPERSOMNIA
Sufficient sleep at night but still
cannot stay awake during the day.
Caused by medical condition
NARCOLEPSY
Excessive daytime sleepiness
caused by the lack of the chemical
hypocretin
Sleep paralysis
Hallucinations
SLEEP APNEA
Frequent short breathing pauses
during sleep.
May lead to Cardiac arrest & Heart
failure
Loud snoring
Men, postmenopausal women,
childhood.
Three common types of apnea:
1. Obstructive Apnea- Block the
flow of air.
2. Central Apnea- Defect in the
respiratory center of the brain.
3. Mixed Apnea
INSUFFICIENT SLEEP
Fatigue
Difficulty in work or duty
PARASOMNIAS
Behaviour that may interfere with
sleep and may even occur during
sleep.
Arousal disorders
Sleep-wake transition disorders
Nightmares
E.g.,.,.,
SLEEP HYGIENE
Interventions used to promote sleep.
END
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Sample Lab Report FormatDocument6 pagesSample Lab Report Formatmarice marquezNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Proteins and Amino Acids IDocument8 pagesProteins and Amino Acids Imarice marquezNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Marquez, Marice Abigail J. BSN 1-A April 15, 2016 7:00 Am-11:00am Nursing Skills Laboratory Ms. Floribel San Luis AssignmentDocument5 pagesMarquez, Marice Abigail J. BSN 1-A April 15, 2016 7:00 Am-11:00am Nursing Skills Laboratory Ms. Floribel San Luis AssignmentMarice Abigail MarquezNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Rle AssessDocument1 pageRle AssessMarice Abigail MarquezNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Argumentative: EssayDocument5 pagesArgumentative: EssayMarice Abigail Marquez100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Proteins and Amino Acids IDocument8 pagesProteins and Amino Acids Imarice marquezNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Argumentative: EssayDocument2 pagesArgumentative: Essaymarice marquezNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Chapter 1 Summary Notes - IGSIRDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Summary Notes - IGSIRAthul Krishna KNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Character Profile FormDocument16 pagesCharacter Profile FormPlot BUnnies100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Vu Tra Giang - 20070149 - INS3022 - 02Document7 pagesVu Tra Giang - 20070149 - INS3022 - 02Hương GiangNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument2 pagesCommunicationkiran dara100% (1)
- Apostolic Succession Ccc46568Document19 pagesApostolic Succession Ccc46568Francesca Lo Cicero100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Alvez V. Court of Appeals Case Digest - Constitutional Law Galvez V. Ca G.R. No. 114046 October 24, 1994Document10 pagesAlvez V. Court of Appeals Case Digest - Constitutional Law Galvez V. Ca G.R. No. 114046 October 24, 1994Jayson YuzonNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Eth 2Document6 pagesEth 2111111No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Michael Jackson DissertationDocument4 pagesMichael Jackson DissertationCheapestPaperWritingServiceCanada100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Crusade Prayer BookDocument59 pagesCrusade Prayer Bookmaria1grazia1mazzaNo ratings yet
- Robert Post - Legitimacy and Hate SpeechDocument11 pagesRobert Post - Legitimacy and Hate SpeechLucasNo ratings yet
- Patliputra University PatnaDocument3 pagesPatliputra University PatnaAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Storey PlanDocument6 pagesStorey Planshen LiuNo ratings yet
- List of Allotted Candidates Institute Wise For NEET UG Counseling-2019 2019 (017) Govt. Medical College, Ambedkarnagar (Govt.) Co-EducationDocument3 pagesList of Allotted Candidates Institute Wise For NEET UG Counseling-2019 2019 (017) Govt. Medical College, Ambedkarnagar (Govt.) Co-EducationDev Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Certificate of Pastor's AppreciationDocument5 pagesCertificate of Pastor's AppreciationPr. Quirino LucyaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Trade Secrets Lawsuit V ReebokDocument17 pagesTrade Secrets Lawsuit V ReebokDarren Adam HeitnerNo ratings yet
- Sps. Abejo v. Dela CruzDocument3 pagesSps. Abejo v. Dela CruzBananaNo ratings yet
- Amniocentesis Procedure OverviewDocument6 pagesAmniocentesis Procedure OverviewYenny YuliantiNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Jadavpur University 2017 Ma English Entrance Question PaperDocument6 pagesJadavpur University 2017 Ma English Entrance Question PaperZeventricNo ratings yet
- Rizal's LifeDocument19 pagesRizal's LifeLeona Patrina ArcusaNo ratings yet
- GST Certificate - Lala PipesDocument3 pagesGST Certificate - Lala PipesArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Aydin Adnan Menderes University Engineering Faculty: Internship Application FormDocument2 pagesAydin Adnan Menderes University Engineering Faculty: Internship Application FormSehidtvNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Nobel Peace Prize Winners 1908-1917Document10 pagesNobel Peace Prize Winners 1908-1917toadymamaNo ratings yet
- Chiquita in ColombiaDocument11 pagesChiquita in ColombiaMaikol Mauricio Lopez ValenciaNo ratings yet
- He Imes Eader: White House: Bin Laden UnarmedDocument44 pagesHe Imes Eader: White House: Bin Laden UnarmedThe Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Balance of Probabilities and The RuleDocument5 pagesBalance of Probabilities and The RuleGNo ratings yet
- Project Paperclip: How the US Stole Nazi ScientistsDocument18 pagesProject Paperclip: How the US Stole Nazi ScientistsAnupam0103No ratings yet
- VICTORIA MEMORIAL MUSEUM IN KOLKATADocument9 pagesVICTORIA MEMORIAL MUSEUM IN KOLKATARhugved Takalkar67% (3)
- People Vs Isleta PDFDocument9 pagesPeople Vs Isleta PDFheyoooNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 1 B PDFDocument2 pagesProgress Test 1 B PDFEva100% (1)
- Christmas Dishes From Around The WorldDocument1 pageChristmas Dishes From Around The WorldAngeles EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)